A Triple Mystery of Insidious Organ Failure: Are the Lung, Kidney and Brain All Damaged by the Ageing Pulse?
Abstract
1. Introduction
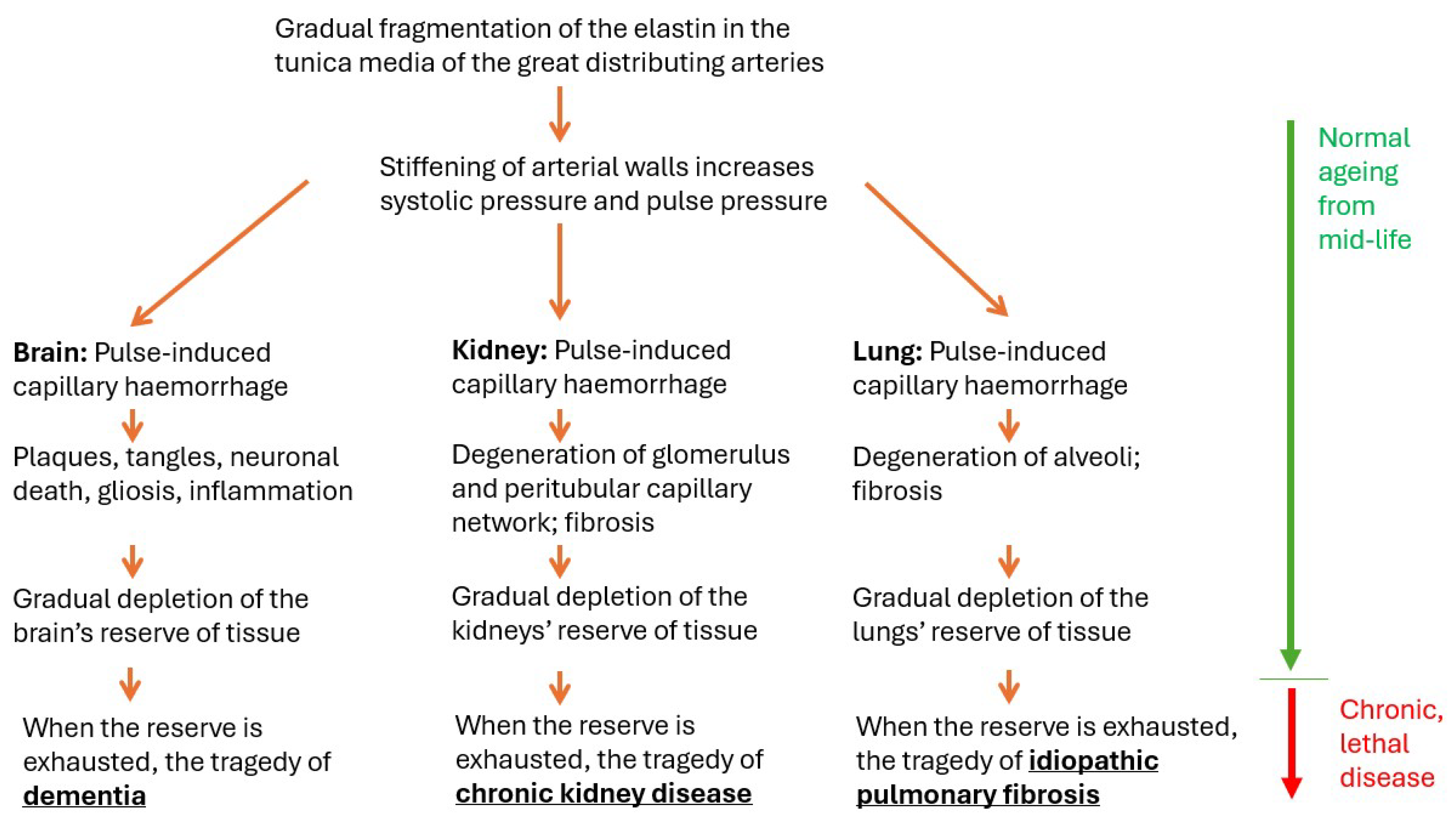
1.1. Starting Point #1: Common Features of the Pathogenesis of Dementia, CKD, and IPF
1.1.1. Common Clinical Features
1.1.2. Pathology: Shrinkage and Fibrosis/Gliosis
1.1.3. All Three Are Highly Vascular
1.1.4. Low Resistance, High Pulsatility
1.1.5. Relation to Age: The Reassuring Normality of Lethal Disease
1.1.6. Hypertension Is a Risk Factor for All Three
1.1.7. Reserve Tissue, Clinical Threshold
1.1.8. Relentless Progression
1.1.9. The Pathology of Normal Ageing Is Also the Pathology of the Lethal Condition
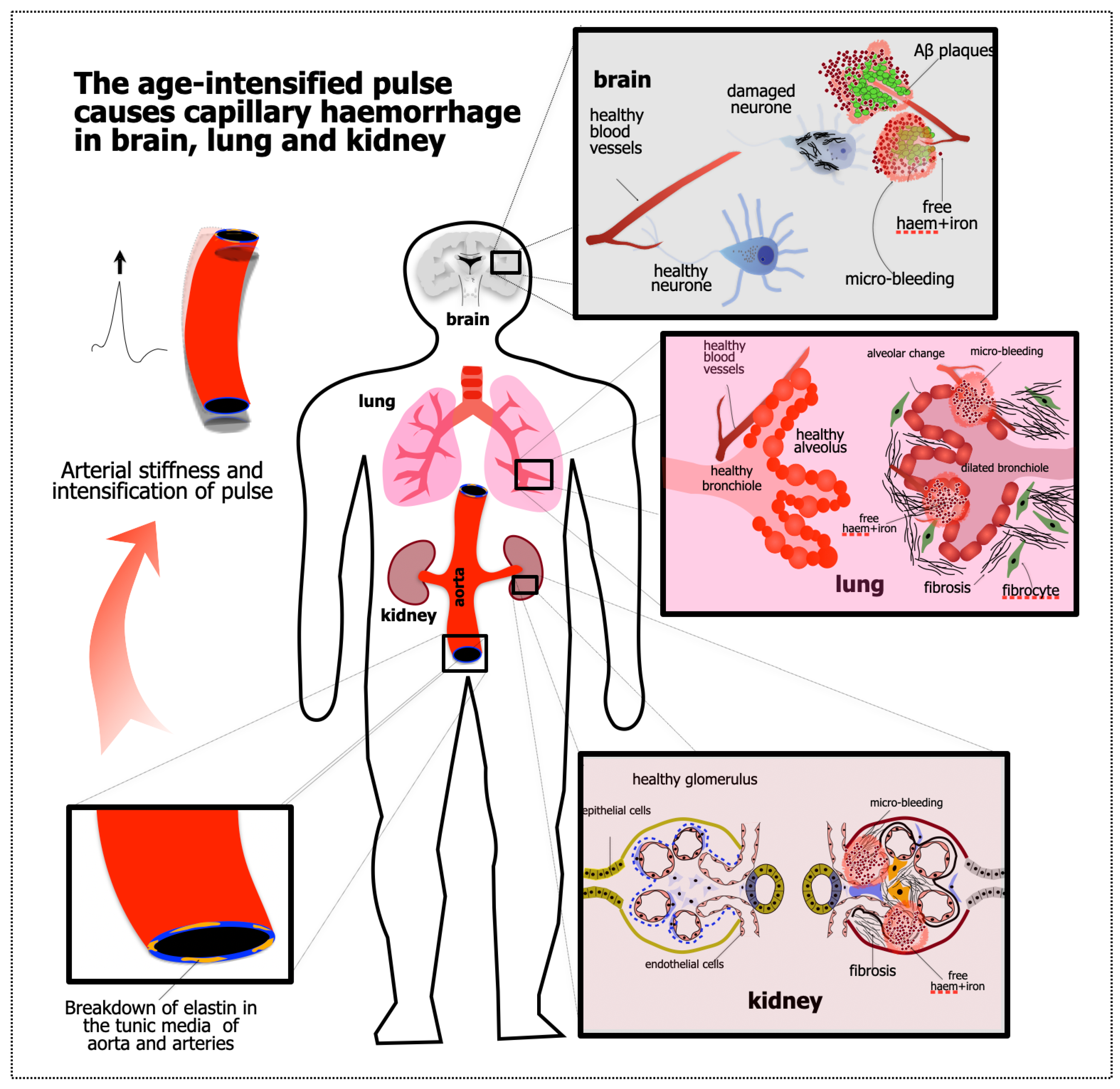
1.2. Starting Point #2: Evidence of APICH in the Ageing Brain
2. Evidence That the Kidney and Lung Are Also Damaged by APICH
2.1. Kidney
2.2. Lung
3. What About the Liver? The Spleen? The Retina?
4. Summary and Implications; Therapeutic Opportunity
4.1. Implications
4.2. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andersson, M.J.; Stone, J. Best Medicine for Dementia: The Life-Long Defense of the Brain. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2023, 94, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullen, K.M.; Kocsi, Z.; Stone, J. Microvascular Pathology in the Aging Human Brain: Evidence That Senile Plaques Are Sites of Microhaemorrhages. Neurobiol. Aging 2006, 27, 1786–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bateman, G.A. Pulse Wave Encephalopathy: A Spectrum Hypothesis Incorporating Alzheimer’s Disease, Vascular Dementia and Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. Med. Hypotheses 2004, 62, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry-Feugeas, M.C. Alzheimer’s Disease in Late-Life Dementia: A Minor Toxic Consequence of Devastating Cerebrovascular Dysfunction. Med. Hypotheses 2008, 70, 866–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, M.F. Brain Microbleeds, Amyloid Plaques, Intellectual Deterioration, and Arterial Stiffness. Hypertension 2008, 51, e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, M.F.; Safar, M.E. Relationship between Aortic Stiffening and Microvascular Disease in Brain and Kidney: Cause and Logic of Therapy. Hypertension 2005, 46, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, J.; Trollor, J.N.; Crawford, J.; O’Rourke, M.F.; Baune, B.T.; Brodaty, H.; Samaras, K.; Kochan, N.A.; Campbell, L.; Sachdev, P.S.; et al. The Association between Pulse Wave Velocity and Cognitive Function: The Sydney Memory and Ageing Study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.; Allsop, D. Amyloid Deposition as the Central Event in the Aetiology of Alzheimer’s Disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1991, 12, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karran, E.; Mercken, M.; De Strooper, B. The Amyloid Cascade Hypothesis for Alzheimer’s Disease: An Appraisal for the Development of Therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 698–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masters, C.L.; Bateman, R.; Blennow, K.; Rowe, C.C.; Sperling, R.A.; Cummings, J.L. Alzheimer’s Disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, K.M.; Kocsi, Z.; Stone, J. Pericapillary Haem-Rich Deposits: Evidence for Microhaemorrhages in Aging Human Cerebral Cortex. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2005, 25, 1656–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, J. What Initiates the Formation of Senile Plaques? The Origin of Alzheimer-Like Dementias in Capillary Haemorrhages. Med. Hypotheses 2008, 71, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, J.; Mitrofanis, J.; Johnstone, D.M.; Falsini, B.; Bisti, S.; Adam, P.; Nuevo, A.B.; George-Weinstein, M.; Mason, R.; Eells, J. Acquired Resilience: An Evolved System of Tissue Protection in Mammals. Dose Response 2018, 16, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, J.; Johnstone, D.M.; Mitrofanis, J.; O’Rourke, M. The Mechanical Cause of Age-Related Dementia (Alzheimer’s Disease): The Brain Is Destroyed by the Pulse. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2015, 44, 355–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, D.M.; Mitrofanis, J.; Stone, J. The Brain’s Weakness in the Face of Trauma: How Head Trauma Causes the Destruction of the Brain. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1141568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, J.; Mitrofanis, J.; Johnstone, D.M.; Robinson, S.R. The Catastrophe of Intracerebral Hemorrhage Drives the Capillary-Hemorrhage Dementias, Including Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2024, 97, 1069–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Han, Y.P.; Chai, Y.H.; Gong, H.J.; Xu, H.; Patel, I.; Qiao, Y.S.; Zhang, J.Y.; Cardoso, M.A.; Zhou, J.B. Association of Kidney Function and Brain Health: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 82, 101762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Nagasawa, T.; Abe, M.; Mori, T. Strain Vessel Hypothesis: A Viewpoint for Linkage of Albuminuria and Cerebro-Cardiovascular Risk. Hypertens. Res. 2009, 32, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, D.; Rothwell, P.M. Disentangling the Multiple Links between Renal Dysfunction and Cerebrovascular Disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 91, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gewin, L.; Zent, R.; Pozzi, A. Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease: Too Much Cellular Talk Causes Damage. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutsey, P.L.; Chen, N.; Mirabelli, M.C.; Lakshminarayan, K.; Knopman, D.S.; Vossel, K.A.; Gottesman, R.F.; Mosley, T.H.; Alonso, A. Impaired Lung Function, Lung Disease, and Risk of Incident Dementia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, 1385–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, X.; Lei, S.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Li, J. Risk of Dementia or Cognitive Impairment in COPD Patients: A Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 962562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bors, M.; Tomic, R.; Perlman, D.M.; Kim, H.J.; Whelan, T.P. Cognitive Function in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Chron. Respir. Dis. 2015, 12, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bethlehem, R.A.I.; Seidlitz, J.; White, S.R.; Vogel, J.W.; Anderson, K.M.; Adamson, C.; Adler, S.; Alexopoulos, G.S.; Anagnostou, E.; Areces-Gonzalez, A.; et al. Brain Charts for the Human Lifespan. Nature 2022, 604, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fjell, A.M.; Walhovd, K.B. Structural Brain Changes in Aging: Courses, Causes and Cognitive Consequences. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 21, 187–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piras, D.; Masala, M.; Delitala, A.; Urru, S.A.M.; Curreli, N.; Balaci, L.; Ferreli, L.P.; Loi, F.; Atzeni, A.; Cabiddu, G.; et al. Kidney Size in Relation to Ageing, Gender, Renal Function, Birthweight and Chronic Kidney Disease Risk Factors in A General Population. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercado, N.; Ito, K.; Barnes, P.J. Accelerated Ageing of the Lung in COPD: New Concepts. Thorax 2015, 70, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Goodwin, J. Effect of Aging on Respiratory System Physiology and Immunology. Clin. Interv. Aging 2006, 1, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzheimer, A. Über eigenartige Krankheitsfälle Des Späteren Alters. Zbl. Ges. Neurol. Psychiatr. 1911, 4, 356–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheibel, A.B.; Duong, T.H.; Jacobs, R. Alzheimer’s Disease as a Capillary Dementia. Ann. Med. 1989, 21, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Torre, J.C. Alzheimer’s Disease Is a Vasocognopathy: A New Term to Describe Its Nature. Neurol. Res. 2004, 26, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, S.; Nolde, J.M.; Chan, J.; Joyson, A.; Gregory, C.; Carnagarin, R.; Herat, L.Y.; Matthews, V.B.; Robinson, L.; Vignarajan, J.; et al. Retinal Capillary Rarefaction Is Associated with Arterial and Kidney Damage in Hypertension. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puxeddu, E.; Cavalli, F.; Pezzuto, G.; Teodori, E.; Rogliani, P. Impact of Pulmonary Vascular Volume on Mortality in IPF: Is It Time to Reconsider the Role of Vasculature in Disease Pathogenesis and Progression? Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1602345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, J.; Nicholson, A.G.; Wells, A.U.; Hansell, D.M. Impact of Pulmonary Vascular Volume on Mortality in IPF: Is It Time to Reconsider the Role of Vasculature in Disease Pathogenesis and Progression? Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1602524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, G.; Collard, H.R.; Egan, J.J.; Martinez, F.J.; Behr, J.; Brown, K.K.; Colby, T.V.; Cordier, J.F.; Flaherty, K.R.; Lasky, J.A.; et al. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Statement: Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Evidence-Based Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 788–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipolla, M. Chapter 2, Anatomy and Ultrastructure. In The Cerebral Circulation; Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences: San Rafael, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Suresh, K.; Shimoda, L.A. Lung Circulation. Compr. Physiol. 2016, 6, 897–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlstrom, M.; Wilcox, C.S.; Arendshorst, W.J. Renal Autoregulation in Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 405–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driver, I.D.; Traat, M.; Fasano, F.; Wise, R.G. Most Small Cerebral Cortical Veins Demonstrate Significant Flow Pulsatility: A Human Phase Contrast MRI Study at 7T. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellevik, L.R.; Segers, P.; Stergiopulos, N.; Irgens, F.; Verdonck, P.; Thompson, C.R.; Lo, K.; Miyagishima, R.T.; Smiseth, O.A. Mechanism of Pulmonary Venous Pressure and Flow Waves. Heart Vessels 1999, 14, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagshul, M.E.; Eide, P.K.; Madsen, J.R. The Pulsating Brain: A Review of Experimental and Clinical Studies of Intracranial Pulsatility. Fluids Barriers CNS 2011, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenstein, D.A.; Lascols, N.; Prin, S.; Meziere, G. The “lung pulse”: An Early Ultrasound Sign of Complete Atelectasis. Intensive Care Med. 2003, 29, 2187–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cepeda, N.J.; Kramer, A.F.; Gonzalez de Sather, J.C. Changes in Executive Control across the Life Span: Examination of Task-Switching Performance. Dev. Psychol. 2001, 37, 715–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedard, A.C.; Nichols, S.; Barbosa, J.A.; Schachar, R.; Logan, G.D.; Tannock, R. The Development of Selective Inhibitory Control across the Life Span. Dev. Neuropsychol. 2002, 21, 93–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scuteri, A.; Brancati, A.M.; Gianni, W.; Assisi, A.; Volpe, M. Arterial Stiffness Is an Independent Risk Factor for Cognitive Impairment in the Elderly: A pilot study. J. Hypertens. 2005, 23, 1211–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, R.A.; Carnegie, M.H.; Celermajer, D.S. Pulse Pressure: An Emerging Therapeutic Target for Dementia. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorin-Trescases, N.; Thorin, E. Lifelong Cyclic Mechanical Strain Promotes Large Elastic Artery Stiffening: Increased Pulse Pressure and Old Age-Related Organ Failure. Can. J. Cardiol. 2016, 32, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, S.; Agabiti-Rosei, C.; Bruno, R.M.; Rizzoni, D. Microcirculation and Macrocirculation in Hypertension: A Dangerous Cross-Link? Hypertension 2022, 79, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, K.; Bryant, A.J.; Sahay, S.; Wareing, N.; Zhou, Y.; Pandit, L.M.; Karmouty-Quintana, H. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Pulmonary Hypertension: Heracles Meets the Hydra. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochi, N.; Tabara, Y.; Igase, M.; Nagai, T.; Kido, T.; Miki, T.; Kohara, K. Silent Cerebral Microbleeds Associated with Arterial Stiffness in an Apparently Healthy Subject. Hypertens. Res. 2009, 32, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, L.; Shen, J.; Zeng, C.; Ji, J.; Hu, W.; Wei, T.; Mao, W. Cerebral Microbleeds Are Associated with Blood Pressure Levels in Individuals with Hypertension. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2020, 42, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugh, D.; Gallacher, P.J.; Dhaun, N. Management of Hypertension in Chronic Kidney Disease. Drugs 2019, 79, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.H.; Slusser, J.P.; Hodge, D.O.; Chen, H.H. The Vascular-Renal Connection in Patients Hospitalized with Hypertensive Crisis: A Population-Based Study. Mayo Clin. Proc. Innov. Qual. Outcomes 2018, 2, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Andrade, D.; Silva, F.; Canelas, A.; Curvo-Semedo, L.; Caseiro-Alves, F. Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage Due to Malignant Arterial Hypertension—An Unusual Manifestation of a Common Disease. J. Belg. Soc. Radiol. 2016, 100, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, J.; Leal, R.; Escada, L.; Alfaro, T. Systemic Hypertension and the Pathogenesis of Diffuse Alveolar Haemorrhage. Pulmonology 2017, 23, 47–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basrak, M.T.; Alhammad, M.F.; Anjum, S.; Altermanini, M.; Ahmed, Y.E. Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage: A Rare Complication of Severe Hypertension. Cureus 2023, 15, e33933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scahill, R.I.; Frost, C.; Jenkins, R.; Whitwell, J.L.; Rossor, M.N.; Fox, N.C. A Longitudinal Study of Brain Volume Changes in Normal Aging Using Serial Registered Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Arch. Neurol. 2003, 60, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takao, H.; Hayashi, N.; Ohtomo, K. A Longitudinal Study of Brain Volume Changes in Normal Aging. Eur. J. Radiol. 2012, 81, 2801–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorin, E.; Thorin-Trescases, N. Vascular Endothelial Ageing, Heartbeat after Heartbeat. Cardiovasc. Res. 2009, 84, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.S.; Leurgans, S.E.; Boyle, P.A.; Bennett, D.A. Cognitive Decline in Prodromal Alzheimer Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment. Arch. Neurol. 2011, 68, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, J.; Mitrofanis, J.; Johnstone, D.M.; Robinson, S.R. Twelve Protections Evolved for the Brain, and Their Roles in Extending Its Functional Life. Front. Neuroanat. 2023, 17, 1280275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzheimer, A. Über eine eigenartige Erkrankung der Hirnrinde. Allg. Z. Psychiatr. Psych. Gerichtl. Med. 1907, 146–148. [Google Scholar]
- Kraepelin, E. Senile and Pre-Senile Dementias. In Psychiatrie: Ein Lehrbuch für Studierende und Ärzte; Johann Ambrosius Barth: Leipzig, Germany, 1910; pp. 553–632. [Google Scholar]
- Miyakawa, T. Vascular Pathology in Alzheimer’s Disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2002, 977, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyakawa, T.; Katsuragi, S.; Higuchi, Y.; Yamashita, K.; Kimura, T.; Teraoka, K.; Ono, T.; Ishizuka, K. Changes of Microvessels in the Brain with Alzheimer’s Disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1997, 826, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyakawa, T.; Kimura, T.; Hirata, S.; Fujise, N.; Ono, T.; Ishizuka, K.; Nakabayashi, J. Role of Blood Vessels in Producing Pathological Changes in the Brain with Alzheimer’s Disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 903, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Torre, J.; Hachinski, V. (Eds.) Cerebrovascular Pathology in Alzheimer’s Disease; New York Academy of Sciences: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Volume 826, pp. 1–519. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar-Singh, S.; Cras, P.; Wang, R.; Kros, J.M.; van Swieten, J.; Lubke, U.; Ceuterick, C.; Serneels, S.; Vennekens, K.; Timmermans, J.P.; et al. Dense-Core Senile Plaques in the Flemish Variant of Alzheimer’s Disease Are Vasocentric. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 161, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar-Singh, S.; Pirici, D.; McGowan, E.; Serneels, S.; Ceuterick, C.; Hardy, J.; Duff, K.; Dickson, D.; Van Broeckhoven, C. Dense-Core Plaques in Tg2576 and PSAPP Mouse Models of Alzheimer’s Disease Are Centered on Vessel Walls. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 167, 527–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baggeroer, C.E.; Cambronero, F.E.; Savan, N.A.; Jefferson, A.L.; Santisteban, M.M. Basic Mechanisms of Brain Injury and Cognitive Decline in Hypertension. Hypertension 2024, 81, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purushothuman, S.; Marotte, L.; Stowe, S.; Johnstone, D.; Stone, J. The Response of Cerebral Cortex to Haemorrhagic Damage: Experimental Evidence from a Penetrating Injury Model. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry-Feugeas, M.C. Intracranial MR Dynamics in Clinically Diagnosed Alzheimer’s Disease: The Emerging Concept of “Pulse Wave Encephalopathy”. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2009, 6, 488–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry-Feugeas, M.C.; Koskas, P. Cerebral Vascular Aging: Extending the Concept of Pulse Wave Encephalopathy through Capillaries to the Cerebral Veins. Curr. Aging Sci. 2012, 5, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, P.A.; Sirisriro, R.; Villemagne, V.L.; Farquharson, S.; Masters, C.L.; Rowe, C.C.; Group, A.R. Cerebral Microhemorrhage and Brain Beta-Amyloid in Aging and Alzheimer Disease. Neurology 2011, 77, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viengkhou, B.; Hayashida, E.; McGlasson, S.; Emelianova, K.; Forbes, D.; Wiseman, S.; Wardlaw, J.; Verdillo, R.; Irani, S.R.; Duffy, D.; et al. The Brain Microvasculature Is a Primary Mediator of Interferon-Alpha Neurotoxicity in Human Cerebral Interferonopathies. Immunity 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffernan, K.S.; Wilmoth, J.M.; London, A.S. Estimated Pulse Wave Velocity Is Associated with a Higher Risk of Dementia in the Health and Retirement Study. Am. J. Hypertens. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabkin, S.W. Is It Time to Utilize Measurement of Arterial Stiffness to Identify and Reduce the Risk of Cognitive Impairment? J. Clin. Hypertens. 2018, 20, 31–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmeri, A.; Ricciarelli, R.; Gulisano, W.; Rivera, D.; Rebosio, C.; Calcagno, E.; Tropea, M.R.; Conti, S.; Das, U.; Roy, S.; et al. Amyloid-beta Peptide Is Needed for cGMP-Induced Long-Term Potentiation and Memory. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 6926–6937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzzo, D.; Privitera, L.; Leznik, E.; Fa, M.; Staniszewski, A.; Palmeri, A.; Arancio, O. Picomolar Amyloid-Beta Positively Modulates Synaptic Plasticity and Memory in Hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 14537–14545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puzzo, D.; Privitera, L.; Fa, M.; Staniszewski, A.; Hashimoto, G.; Aziz, F.; Sakurai, M.; Ribe, E.M.; Troy, C.M.; Mercken, M.; et al. Endogenous Amyloid-Beta Is Necessary for Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity and Memory. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 69, 819–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, J.Y.; Lee, C.W.; Shih, Y.H.; Yang, T.; Yu, L.; Kuo, Y.M. Interactions between Amyloid-Beta and Hemoglobin: Implications for Amyloid Plaque Formation in Alzheimer’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, S.R.; Bishop, G.M. Abeta as a Bioflocculant: Implications for the Amyloid Hypothesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2002, 23, 1051–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, G.M.; Robinson, S.R. Physiological Roles of Amyloid-Beta and Implications for Its Removal in Alzheimer’s Disease. Drugs Aging 2004, 21, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwood, C.S.; Robinson, S.R.; Smith, M.A. Amyloid-Beta: Redox-Metal Chelator and Antioxidant. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2002, 4, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balin, B.J.; Little, C.S.; Hammond, C.J.; Appelt, D.M.; Whittum-Hudson, J.A.; Gerard, H.C.; Hudson, A.P. Chlamydophila Pneumoniae and the Etiology of Late-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2008, 13, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulop, T.; Witkowski, J.M.; Bourgade, K.; Khalil, A.; Zerif, E.; Larbi, A.; Hirokawa, K.; Pawelec, G.; Bocti, C.; Lacombe, G.; et al. Can an Infection Hypothesis Explain the Beta Amyloid Hypothesis of Alzheimer’s Disease? Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourgade, K.; Garneau, H.; Giroux, G.; Le Page, A.Y.; Bocti, C.; Dupuis, G.; Frost, E.H.; Fulop, T., Jr. beta-Amyloid Peptides Display Protective Activity against the Human Alzheimer’s Disease-Associated Herpes Simplex Virus-1. Biogerontology 2015, 16, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.; Joseph, J.; Perry, G. Arson. Tracking the Culprit in Alzheimer’s Disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 924, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balow, J.E. Renal Vasculitis. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 1993, 2, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.E.; Lee, S.B.; Pyo, J.Y.; Ahn, S.S.; Song, J.J.; Park, Y.B.; Lim, B.J.; Lee, S.W. Renal histopathological predictors of end-stage kidney disease in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis with Glomerulonephritis: A Single-Centre Study in Korea. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 14850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kida, Y.; Tchao, B.N.; Yamaguchi, I. Peritubular Capillary Rarefaction: A New Therapeutic Target in Chronic Kidney Disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2014, 29, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rheault, M.N. Targeting Fibrosis Pathways in Alport Syndrome-Is it Too Late? Kidney360 2023, 4, 580–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwabe, T.; Ubara, Y.; Oba, Y.; Mizuno, H.; Ikuma, D.; Yamanouchi, M.; Sekine, A.; Tanaka, K.; Hasegawa, E.; Hoshino, J.; et al. Acute Renal Intracystic Hemorrhage in Patients with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease. J. Nephrol. 2023, 36, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lishnevsky, M.; Young, L.C.; Woods, S.J.; Groshong, S.D.; Basaraba, R.J.; Gilchrist, J.M.; Higgins, D.M.; Gonzalez-Juarrero, M.; Bass, T.A.; Muller, W.A.; et al. Microhemorrhage Is an Early Event in the Pulmonary Fibrotic Disease of PECAM-1 Deficient FVB/n Mice. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2014, 97, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puxeddu, E.; Comandini, A.; Cavalli, F.; Pezzuto, G.; D’Ambrosio, C.; Senis, L.; Paci, M.; Curradi, G.; Sergiacomi, G.L.; Saltini, C. Iron Laden Macrophages in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: The Telltale of Occult Alveolar Hemorrhage? Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 28, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.K.; Kim, R.Y.; Brown, A.C.; Donovan, C.; Vanka, K.S.; Mayall, J.R.; Liu, G.; Pillar, A.L.; Jones-Freeman, B.; Xenaki, D.; et al. Critical Role for Iron Accumulation in the Pathogenesis of Fibrotic Lung Disease. J. Pathol. 2020, 251, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.C.; Horvat, J.C. Casting Iron in the Pathogenesis of Fibrotic Lung Disease. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2021, 65, 130–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, J.; Mitchell, J.A.; Jenkins, R.G. Beyond Epithelial Damage: Vascular and Endothelial Contributions to Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e172058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.S.; Patel, K.; Sari, E.; Shankar, S.; Gastanadui, M.G.; Moncada-Giraldo, D.; Soto-Vazquez, Y.; Stacks, D.; Hecker, L.; Dsouza, K.; et al. Active Transcription in the Vascular Bed Characterizes Rapid Progression in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelbrecht, E.; Kooistra, T.; Knipe, R.S. The Vasculature in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Curr. Tissue Microenviron. Rep. 2022, 3, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fliesser, E.; Lins, T.; Berg, J.L.; Kolb, M.; Kwapiszewska, G. The Endothelium in Lung Fibrosis: A Core Signaling Hub in Disease Pathogenesis? Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2023, 325, C2–C16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Pan, X.; Wang, L.; Yu, G. Alveolar Cells under Mechanical Stressed Niche: Critical Contributors to Pulmonary Fibrosis. Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonaglioni, A.; Caminati, A.; Nicolosi, G.L.; Lombardo, M.; Harari, S. Incremental Prognostic Value of Arterial Elastance in Mild-to-Moderate Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 38, 1473–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollander, H.; Makarov, F.; Stefani, F.; Stone, J. Evidence of Constriction of Optic Nerve Axons at the Lamina Cribrosa in the Normotensive Eye In Humans and Other Mammals. Ophthal Res. 1995, 27, 296–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Li, L.; Shao, C.; Cai, H.; Wang, Z. The Impact of Diabetes on Vascular Disease: Progress from the Perspective of Epidemics and Treatments. J. Diabetes Res. 2022, 2022, 1531289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Koronyo, Y.; Rentsendorj, A.; Fuchs, D.T.; Sheyn, J.; Black, K.L.; Mirzaei, N.; Koronyo-Hamaoui, M. Retinal Vasculopathy in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 731614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaire, B.P.; Koronyo, Y.; Fuchs, D.T.; Shi, H.; Rentsendorj, A.; Danziger, R.; Vit, J.P.; Mirzaei, N.; Doustar, J.; Sheyn, J.; et al. Alzheimer’s Disease Pathophysiology in the Retina. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2024, 101, 101273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, S.; Di Iorio, E.; Barbaro, V.; Ponzin, D.; Sorrentino, F.S.; Parmeggiani, F. Retinitis Pigmentosa: Genes and Disease Mechanisms. Curr. Genom. 2011, 12, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachinski, V. Preventable Senility: A Call for Action against the Vascular Dementias. Lancet 1992, 340, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stone, J.; Robinson, S.R.; Mitrofanis, J.; Johnstone, D.M. A Triple Mystery of Insidious Organ Failure: Are the Lung, Kidney and Brain All Damaged by the Ageing Pulse? Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1969. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12091969
Stone J, Robinson SR, Mitrofanis J, Johnstone DM. A Triple Mystery of Insidious Organ Failure: Are the Lung, Kidney and Brain All Damaged by the Ageing Pulse? Biomedicines. 2024; 12(9):1969. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12091969
Chicago/Turabian StyleStone, Jonathan, Stephen R. Robinson, John Mitrofanis, and Daniel M. Johnstone. 2024. "A Triple Mystery of Insidious Organ Failure: Are the Lung, Kidney and Brain All Damaged by the Ageing Pulse?" Biomedicines 12, no. 9: 1969. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12091969
APA StyleStone, J., Robinson, S. R., Mitrofanis, J., & Johnstone, D. M. (2024). A Triple Mystery of Insidious Organ Failure: Are the Lung, Kidney and Brain All Damaged by the Ageing Pulse? Biomedicines, 12(9), 1969. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12091969




