Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches for Heart Failure in Long-Term Survivors of Childhood Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Prevalence of Heart Failure in Long Survivors of Childhood Cancer
2.1. Prevalence of Symptomatic Heart Failure in Long Survivors of Childhood Cancer
2.2. Prevalence of Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction in Long Survivors of Childhood Cancer
3. New Tools for the Diagnosis of Cardiovascular Disease
3.1. Global Longitudinal Strain
3.2. Cardiac Magnetic Resonance
3.3. Blood Biomarkers
4. Cellular Senescence and Cardiotoxicity
5. Treatment of Heart Failure in Cancer Survivors
6. Future Research Direction
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Armstrong, G.T.; Liu, Q.; Yasui, Y.; Neglia, J.P.; Leisenring, W.; Robison, L.L.; Mertens, A.C. Late Mortality Among 5-Year Survivors of Childhood Cancer: A Summary From the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, A.C. Cause of mortality in 5-year survivors of childhood cancer. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2007, 48, 723–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, E.T.H.; Chang, H.M. Oncocardiology—Past, Present, and Future: A Review. JAMA Cardiol. 2016, 1, 1066–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.H.C.; Poppe, M.M.; Hua, C.H.; Marcus, K.J.; Esiashvili, N. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2021, 68, e28371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazǎr, D.R.; Farcaş, A.D.; Blag, C.; Neaga, A.; Zdrenghea, M.T.; Căinap, C.; Lazăr, F.L.; Stef, A.; Căinap, S.S. Cardiotoxicity: A Major Setback in Childhood Leukemia Treatment. Dis. Markers 2021, 2021, 8828410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanier, G.M.; Garg, J.; Shah, N. Cardiotoxicity of Chemotherapeutic Agents; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 22, pp. 1–214. [Google Scholar]
- Lieke Feijen, E.A.M.; Font-Gonzalez, A.; van der Pal, H.J.H.; Kok, W.E.M.; Geskus, R.B.; Ronckers, C.M.; Bresters, D.; van Dalen, E.C.; Broeder, E.v.D.; Berg, M.H.v.D.; et al. Risk and Temporal Changes of Heart Failure Among 5-Year Childhood Cancer Survivors: A DCOG-LATER Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e009122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, G.T.; Oeffinger, K.C.; Chen, Y.; Kawashima, T.; Yasui, Y.; Leisenring, W.; Stovall, M.; Chow, E.J.; Sklar, C.A.; Mulrooney, D.A.; et al. Modifiable risk factors and major cardiac events among adult survivors of childhood cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3673–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidler, M.M.; Reulen, R.C.; Henson, K.; Kelly, J.; Cutter, D.; Levitt, G.A.; Frobisher, C.; Winter, D.L.; Hawkins, M.M. Population-based long-Term cardiac-specific mortality among 34 489 five-year survivors of childhood cancer in Great Britain. Circulation 2017, 135, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmundsdottir, T.; Winther, J.F.; De Fine Licht, S.; Bonnesen, T.G.; Asdahl, P.H.; Tryggvadottir, L.; Anderson, H.; Wesenberg, F.; Malila, N.; Hasle, H.; et al. Cardiovascular disease in Adult Life after Childhood Cancer in Scandinavia: A population-based cohort study of 32,308 one-year survivors. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 1176–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, J.; Wingerter, A.; Neu, M.A.; Henninger, N.; Eckerle, S.; Münzel, T.; Lackner, K.J.; Beutel, M.E.; Blettner, M.; Rathmann, W.; et al. Burden of cardiovascular risk factors and cardiovascular disease in childhood cancer survivors: Data from the German CVSS-study. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 1555–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, G.T.; Joshi, V.M.; Ness, K.K.; Marwick, T.H.; Zhang, N.; Srivastava, D.; Griffin, B.P.; Grimm, R.A.; Thomas, J.; Phelan, D.; et al. Comprehensive echocardiographic detection of treatment-related cardiac dysfunction in adult survivors of childhood cancer: Results from the St. Jude Lifetime Cohort Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 65, 2511–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massey, R.J.; Diep, P.P.; Ruud, E.; Burman, M.M.; Kvaslerud, A.B.; Brinch, L.; Aakhus, S.; Gullestad, L.L.; Beitnes, J.O. Left Ventricular Systolic Function in Long-Term Survivors of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. JACC CardioOncol. 2020, 2, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Manzanares, R.; Castillo, J.C.; Molina, J.R.; Ruiz-Ortiz, M.; Mesa, D.; Ojeda, S.; Anguita, M.; Pan, M. Automated Global Longitudinal Strain Assessment in Long-Term Survivors of Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancers 2022, 14, 1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christiansen, J.R.; Hamre, H.; Massey, R.; Dalen, H.; Beitnes, J.O.; Fosså, S.D.; Kiserud, C.E.; Aakhus, S. Left ventricular function in long-term survivors of childhood lymphoma. Am. J. Cardiol. 2014, 114, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christiansen, J.R.; Massey, R.; Dalen, H.; Kanellopoulos, A.; Hamre, H.; Fosså, S.D.; Ruud, E.; Kiserud, C.E.; Aakhus, S. Utility of Global Longitudinal Strain by Echocardiography to Detect Left Ventricular Dysfunction in Long-Term Adult Survivors of Childhood Lymphoma and Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Am. J. Cardiol. 2016, 118, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemelä, J.; Ylänen, K.; Suominen, A.; Pushparajah, K.; Mathur, S.; Sarkola, T.; Jahnukainen, K.; Eerola, A.; Poutanen, T.; Vettenranta, K.; et al. Cardiac Function After Cardiotoxic Treatments for Childhood Cancer-Left Ventricular Longitudinal Strain in Screening. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 715953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathe, M.; Carlsen, N.L.T.; Oxhøj, H.; Nielsen, G. Long-term cardiac follow-up of children treated with anthracycline doses of 300 mg/m2 or less for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2010, 54, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipshultz, S.E.; Lipsitz, S.R.; Sallan, S.E.; Dalton, V.M.; Mone, S.M.; Gelber, R.D.; Colan, S.D. Chronic Progressive Cardiac Dysfunction Years After Doxorubicin Therapy for Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 23, 2629–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thavendiranathan, P.; Grant, A.D.; Negishi, T.; Plana, J.C.; Popović, Z.B.; Marwick, T.H. Reproducibility of echocardiographic techniques for sequential assessment of left ventricular ejection fraction and volumes: Application to patients undergoing cancer chemotherapy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 61, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunderson, C.E.D.; Plein, S.; Manisty, C.H. Role of cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging in cardio-oncology. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2021, 22, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, A.R.; López-Fernández, T.; Couch, L.S.; Asteggiano, R.; Aznar, M.C.; Bergler-Klein, J.; Boriani, G.; Cardinale, D.; Cordoba, R.; Cosyns, B.; et al. 2022 ESC Guidelines on cardio-oncology developed in collaboration with the European Hematology Association (EHA), the European Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology (ESTRO) and the International Cardio-Oncology Society (IC-OS). Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 4229–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, E.K.; Kokkinidis, D.G.; Kampaktsis, P.N.; Amir, E.A.; Marwick, T.H.; Gupta, D.; Thavendiranathan, P. Assessment of Prognostic Value of Left Ventricular Global Longitudinal Strain for Early Prediction of Chemotherapy-Induced Cardiotoxicity: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Cardiol. 2019, 4, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Avilés, C.; González-Manzanares, R.; Ojeda, S.; Molina, J.R.; Heredia, G.; Resúa, A.; Hidalgo, F.; López-Aguilera, J.; Mesa, D.; Anguita, M.; et al. Diastolic function assessment with left atrial strain in long-term survivors of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2024, 77, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameli, M.; Mandoli, G.E.; Lisi, E.; Ibrahim, A.; Incampo, E.; Buccoliero, G.; Rizzo, C.; Devito, F.; Ciccone, M.M.; Mondillo, S. Left atrial, ventricular and atrio-ventricular strain in patients with subclinical heart dysfunction. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 35, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolarek, D.; Gruchała, M.; Sobiczewski, W. Echocardiographic evaluation of right ventricular systolic function: The traditional and innovative approach. Cardiol. J. 2017, 24, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heredia, G.; Gonzalez-Manzanares, R.; Ojeda, S.; Molina, J.R.; Fernandez-Aviles, C.; Hidalgo, F.; Lopez-Aguilera, J.; Crespin, M.; Mesa, D.; Anguita, M.; et al. Right Ventricular Function in Long-Term Survivors of Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: From the CTOXALL Study. Cancers 2023, 15, 5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, J.R.; Massey, R.; Dalen, H.; Kanellopoulos, A.; Hamre, H.; Ruud, E.; Kiserud, C.E.; Fosså, S.D.; Aakhus, S. Right ventricular function in long-term adult survivors of childhood lymphoma and acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 17, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Mao, W.; Ding, B.; Liang, C.S. ERKs/p53 signal transduction pathway is involved in doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in H9c2 cells and cardiomyocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2008, 295, H1956–H1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galán-Arriola, C.; Lobo, M.; Vílchez-Tschischke, J.P.; López, G.J.; de Molina-Iracheta, A.; Pérez-Martínez, C.; Agüero, J.; Fernández-Jiménez, R.; Martín-García, A.; Oliver, E.; et al. Serial Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Identify Early Stages of Anthracycline-Induced Cardiotoxicity. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 779–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thavendiranathan, P.; Shalmon, T.; Fan, C.P.S.; Houbois, C.; Amir, E.; Thevakumaran, Y.; Somerset, E.; Malowany, J.M.; Urzua-Fresno, C.; Yip, P.; et al. Comprehensive Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Tissue Characterization and Cardiotoxicity in Women with Breast Cancer. JAMA Cardiol. 2023, 8, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, J.H.; Vasu, S.; Morgan, T.M.; D’agostino, R.B.; Meléndez, G.C.; Hamilton, C.A.; Arai, A.E.; Liu, S.; Liu, C.-Y.; Lima, J.A.; et al. Anthracycline-Associated T1 Mapping Characteristics Are Elevated Independent of the Presence of Cardiovascular Comorbidities in Cancer Survivors. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 9, e004325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, A.A.; Elmancy, L.Y.; Abulola, S.M.; Al-Qattan, S.A.; Ibrahim, M.I.M.; Maayah, Z.H. Assessment of Native Myocardial T1 Mapping for Early Detection of Anthracycline-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Patients with Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2012, 24, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- aus dem Siepen, F.; Buss, S.J.; Messroghli, D.; Andre, F.; Lossnitzer, D.; Seitz, S.; Keller, M.; Schnabel, P.A.; Giannitsis, E.; Korosoglou, G.; et al. T1 mapping in dilated cardiomyopathy with cardiac magnetic resonance: Quantification of diffuse myocardial fibrosis and comparison with endomyocardial biopsy. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2015, 16, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Quinn, R.; Ferrari, V.A.; Daly, R.; Hundley, G.; Baldassarre, L.A.; Han, Y.; Barac, A.; Arnold, A. Cardiac Magnetic Resonance in Cardio-Oncology: Advantages, Importance of Expediency, and Considerations to Navigate Pre-Authorization. JACC CardioOncology 2021, 3, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, E.; Gómez, M.; González, J.R.; Comín, J.; Alvarez-Larrán, A.; Sánchez-González, B.; Molina, L.; Domingo-Domenech, E.; Garcia-Pallarols, F.; Pedro, C.; et al. NT-proBNP: A cardiac biomarker to assess prognosis in non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Leuk. Res. 2011, 35, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Iuliis, F.; Salerno, G.; Taglieri, L.; De Biase, L.; Lanza, R.; Cardelli, P.; Scarpa, S. Serum biomarkers evaluation to predict chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity in breast cancer patients. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 3379–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, L.; Mincu, R.I.; Mahabadi, A.A.; Settelmeier, S.; Al-Rashid, F.; Rassaf, T.; Totzeck, M. Troponins and brain natriuretic peptides for the prediction of cardiotoxicity in cancer patients: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2020, 22, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zidan, A.; Sherief, L.M.; El-Sheikh, A.; Saleh, S.H.; Shahbah, D.A.; Kamal, N.M.; Sherbiny, H.S.; Ahmad, H. NT-proBNP as early marker of subclinical late cardiotoxicity after doxorubicin therapy and mediastinal irradiation in childhood cancer survivors. Dis. Markers 2015, 2015, 513219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mladosievicova, B.; Urbanova, D.; Radvanska, E.; Slavkovsky, P.; Simkova, I. Role of NT-proBNP in detection of myocardial damage in childhood leukemia survivors treated with and without anthracyclines. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 31, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leerink, J.M.; Feijen, E.A.M.; de Baat, E.C.; Merkx, R.; van der Pal, H.J.; Tissing, W.J.; Louwerens, M.; Heuvel-Eibrink, M.M.v.D.; Versluys, A.B.; van Dalen, E.C.; et al. A Biomarker-Based Diagnostic Model for Cardiac Dysfunction in Childhood Cancer Survivors. JACC CardioOncology 2024, 6, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leger, K.J.; Leonard, D.; Nielson, D.; de Lemos, J.A.; Mammen, P.P.A.; Winick, N.J. Circulating microRNAs: Potential Markers of Cardiotoxicity in Children and Young Adults Treated With Anthracycline Chemotherapy. J. Am. Heart Assoc. Cardiovasc. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2017, 6, e004653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gareev, I.; Beylerli, O.; Yang, G.; Sun, J.; Pavlov, V.; Izmailov, A.; Shi, H.; Zhao, S. The current state of miRNAs as biomarkers and therapeutic tools. Clin. Exp. Med. 2020, 20, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggeri, C.; Gioffré, S.; Chiesa, M.; Buzzetti, M.; Milano, G.; Scopece, A.; Castiglioni, L.; Pontremoli, M.; Sironi, L.; Pompilio, G.; et al. A Specific Circulating MicroRNA Cluster Is Associated to Late Differential Cardiac Response to Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity In Vivo. Dis. Markers 2018, 2018, 8395651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaumier, A.; Robinson, S.R.; Robinson, N.; Lopez, K.E.; Meola, D.M.; Barber, L.G.; Bulmer, B.J.; Calvalido, J.; Rush, J.E.; Yeri, A.; et al. Extracellular vesicular microRNAs as potential biomarker for early detection of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2020, 34, 1260–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyabal, P.; Bhagat, A.; Wang, F.; Roth, M.; Livingston, J.A.; Gilchrist, S.C.; Banchs, J.; Hildebrandt, M.A.; Chandra, J.; Deswal, A.; et al. Circulating microRNAs and Cytokines as Prognostic Biomarkers for Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiac Injury and for Evaluating the Effectiveness of an Exercise Intervention. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 4430–4440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvano, J.; Achanzar, W.; Murphy, B.; DiPiero, J.; Hixson, C.; Parrula, C.; Burr, H.; Mangipudy, R.; Tirmenstein, M. Evaluation of microRNAs—208 and 133a/b as differential biomarkers of acute cardiac and skeletal muscle toxicity in rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2016, 312, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsten, M.F.; Dennert, R.; Jochems, S.; Kuznetsova, T.; Devaux, Y.; Hofstra, L.; Wagner, D.R.; Staessen, J.A.; Heymans, S.; Schroen, B. Circulating MicroRNA-208b and MicroRNA-499 reflect myocardial damage in cardiovascular disease. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2010, 3, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goren, Y.; Kushnir, M.; Zafrir, B.; Tabak, S.; Lewis, B.S.; Amir, O. Serum levels of microRNAs in patients with heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2012, 14, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xing, Q.; Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Tang, B. Circulating miRNA-21 is a promising biomarker for heart failure. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 7766–7774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakhani, H.V.; Pillai, S.S.; Zehra, M.; Dao, B.; Tirona, M.T.; Thompson, E.; Sodhi, K. Detecting early onset of anthracyclines-induced cardiotoxicity using a novel panel of biomarkers in West-Virginian population with breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Ren, Y.; Hou, A.; Guo, J.; Mao, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, B.; Bai, Z.; Hou, X. MicroRNA-130a Increases and Predicts Cardiotoxicity during Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-2-Positive Breast Cancer. J. Breast Cancer 2021, 24, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frères, P.; Bouznad, N.; Servais, L.; Josse, C.; Wenric, S.; Poncin, A.; Thiry, J.; Moonen, M.; Oury, C.; Lancellotti, P.; et al. Variations of circulating cardiac biomarkers during and after anthracycline-containing chemotherapy in breast cancer patients. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaib, S.; Tchkonia, T.; Kirkland, J.L. Cellular senescence and senolytics: The path to the clinic. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1556–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maejima, Y.; Adachi, S.; Ito, H.; Hirao, K.; Isobe, M. Induction of premature senescence in cardiomyocytes by doxorubicin as a novel mechanism of myocardial damage. Aging Cell 2008, 7, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelou, K.; Vasileiou, P.V.S.; Papaspyropoulos, A.; Hazapis, O.; Petty, R.; Demaria, M.; Gorgoulis, V.G. Cellular senescence and cardiovascular diseases: Moving to the “heart” of the problem. Physiol. Rev. 2023, 103, 609–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demaria, M.; O’Leary, M.N.; Chang, J.; Shao, L.; Liu, S.; Alimirah, F.; Koenig, K.; Le, C.; Mitin, N.; Deal, A.M.; et al. Cellular senescence promotes adverse effects of chemotherapy and cancer relapse. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linders, A.N.; Dias, I.B.; Ovchinnikova, E.S.; Vermeer, M.C.; Hoes, M.F.; Mavrogenis, G.M.; Deiman, F.E.; Gomez, K.F.A.; Bliley, J.M.; Nehme, J.; et al. Evaluation of Senescence and Its Prevention in Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity Using Dynamic Engineered Heart Tissues. JACC CardioOncology 2023, 5, 298–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.; Richardson, G.D.; Passos, J.F. Mechanisms driving the ageing heart. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 109, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visseren, F.; Mach, F.; Smulders, Y.M.; Carballo, D.; Koskinas, K.C.; Bäck, M.; Benetos, A.; Biffi, A.; Boavida, J.-M.; Capodanno, D.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice: Developed by the Task Force for cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice with representatives of the European Society of Cardiology and 12 medical societies With the special contribution of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology (EAPC). Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3227–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, G.; Heck, S.L.; Ree, A.H.; Hoffmann, P.; Schulz-Menger, J.; Fagerland, M.W.; Gravdehaug, B.; von Knobelsdorff-Brenkenhoff, F.; Bratland, Å.; Storås, T.H.; et al. Prevention of cardiac dysfunction during adjuvant breast cancer therapy (PRADA): A 2 × 2 factorial, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial of candesartan and metoprolol. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 1671–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seicean, S.; Seicean, A.; Alan, N.; Plana, J.C.; Budd, G.T.; Marwick, T.H. Cardioprotective effect of β-adrenoceptor blockade in patients with breast cancer undergoing chemotherapy: Follow-up study of heart failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2013, 6, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Henriksen, P.A. Anthracycline cardiotoxicity: An update on mechanisms, monitoring and prevention. Heart 2018, 104, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suntheralingam, S.; Osataphan, N.; Power, C.; Fan, C.-P.S.; Abdel-Qadir, H.; Amir, E.; Thavendiranathan, P. Safety of Continuing Trastuzumab for Mild Cardiotoxicity: A Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study. CJC Open 2024, 6, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speyer, J.L.; Green, M.D.; Dubin, N.; Blum, R.; Wernz, J.; Roses, D.; Sanger, J.; Muggia, F. Prospective evaluation of cardiotoxicity during a six-hour doxorubicin infusion regimen in women with adenocarcinoma of the breast. Am. J. Med. 1985, 78, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vejpongsa, P.; Yeh, E.T.H. Prevention of Anthracycline-Induced Cardiotoxicity: Challenges and Opportunities. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 64, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armenian, S.H.; Hudson, M.M.; Lindenfeld, L.; Chen, S.; Chow, E.J.; Colan, S.; Collier, W.; Su, X.; Marcus, E.; Echevarria, M.; et al. Effect of carvedilol versus placebo on cardiac function in anthracycline-exposed survivors of childhood cancer (PREVENT-HF): A randomised, controlled, phase 2b trial. Lancet Oncol. 2024, 25, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, G.A.; Dodd, S.; Naish, J.H.; Selvanayagam, J.B.; Dweck, M.R.; Miller, C.A. Considerations for Clinical Trials Targeting the Myocardial Interstitium. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12 Pt 2, 2319–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmakis, D.; Parissis, J.; Filippatos, G. Insights Into Onco-Cardiology: Atrial Fibrillation in Cancer. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.F.; Liu, C.J.; Chang, P.M.H.; Tsao, H.-M.; Lin, Y.-J.; Chang, S.-L.; Lo, L.-W.; Tuan, T.-C.; Li, C.-H.; Chao, T.-F.; et al. Incident thromboembolism and heart failure associated with new-onset atrial fibrillation in cancer patients. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 165, 355–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Castella, M.; Dan, J.-A.; Dilaveris, P.E.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 373–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosef, R.; Pilpel, N.; Tokarsky-Amiel, R.; Biran, A.; Ovadya, Y.; Cohen, S.; Vadai, E.; Dassa, L.; Shahar, E.; Condiotti, R.; et al. Directed elimination of senescent cells by inhibition of BCL-W and BCL-XL. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lérida-Viso, A.; Estepa-Fernández, A.; Morellá-Aucejo, Á.; Lozano-Torres, B.; Alfonso, M.; Blandez, J.F.; Bisbal, V.; Sepúlveda, P.; García-Fernández, A.; Orzáez, M.; et al. Pharmacological senolysis reduces doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity and improves cardiac function in mice. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 183, 106356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arunachalam, G.; Samuel, S.M.; Marei, I.; Ding, H.; Triggle, C.R. Metformin modulates hyperglycaemia-induced endothelial senescence and apoptosis through SIRT1. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moiseeva, O.; Deschênes-Simard, X.; St-Germain, E.; Igelmann, S.; Huot, G.; Cadar, A.E.; Bourdeau, V.; Pollak, M.N.; Ferbeyre, G. Metformin inhibits the senescence-associated secretory phenotype by interfering with IKK/NF-κB activation. Aging Cell 2013, 12, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilinyi, R.; Czompa, A.; Czegledi, A.; Gajtko, A.; Pituk, D.; Lekli, I.; Tosaki, A. The Cardioprotective Effect of Metformin in Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity: The Role of Autophagy. Molecules 2018, 23, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

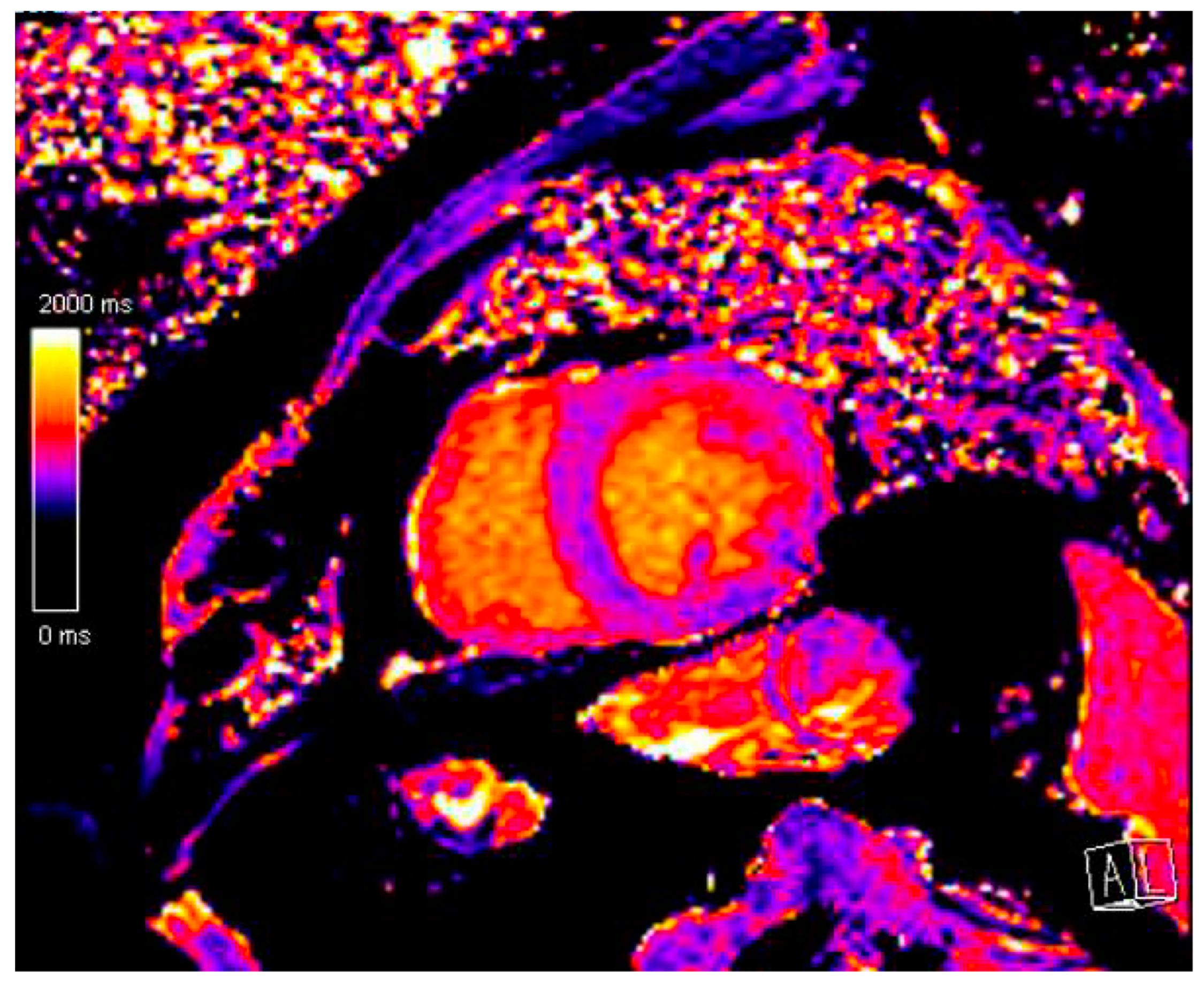
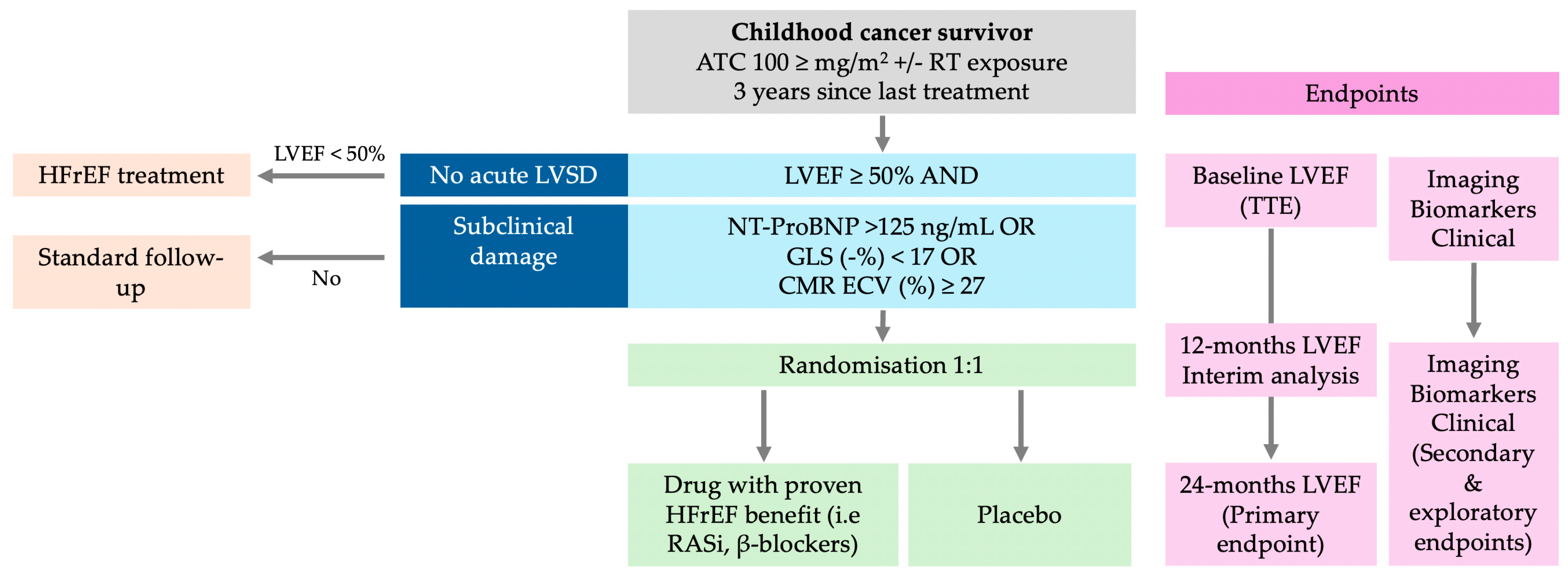
| Study | n | Follow-Up (Years) | Symptomatic HF | LVSD (EF < 50%) | Subclinical LVSD (GLS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feijen, 2019 [7] | 5845 | 19.9 (5–50) | 2% a | - | - |
| Armstrong, 2013 [8] | 10,724 | 25.6 (7–39) | 4.8% | - | - |
| Faber, 2018 [11] | 951 | 28.4 (23–36) | 1.2% | - | - |
| Armstrong, 2015 [12] | 1820 | 23 (10–48) | - | 5.8% | 28.0% |
| Massey, 2020 [13] | 104 b | 17.2 ± 5.6 | - | 16.3% | 32.7% |
| Gonzalez-Manzanares, 2022 [14] | 90 | 18 (11–26) | 1.1% | 12.2% | 26.6% |
| Christiansen, 2014 [15] | 125 | 20.4 ± 8.6 | - | 4% | - |
| Christiansen, 2016 [16] | 191 | 21.6 ± 7.9 | - | - | 28% |
| Niemelä, 2021 [17] | 90 | 8.1 (6–13) | - | - | 11.1% |
| Study | Sample Size | miRNA | Context | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corsten, 2010 [48] | In total, 33 patients admitted with acute HF and 34 healthy controls | miR-499 | Acute HF | miR-499 was significantly elevated (2-fold) as compared with control subjects |
| Goren Y., 2012 [49] | In total, 30 stable chronic HFrEF patients and 30 controls | miR-423-5p, miR-320a, miR-22, and miR-92b | Chronic HFrEF | A score based on the serum levels of these four miRNAs predicted HF and was correlated to prognostic parameters such as elevated NPs or QRS width. |
| Zhang J., 2017 [50] | Hospitalized patients undergoing coronary angiogram, radiofrequency ablation, or cardiac resynchronization therapy: 80 patients with LVEF < 50% were compared to 40 with LVEF ≥ 50% | miR-21 | HFrEF | miR-21 levels in patients with LVEF < 50% were higher than in control subjects and were correlated with NPs and prognosis |
| Lakhani H.V., 2021 [51] | A total of 17 women with breast cancer | miR-34a | Acute cardiotoxicity | miR-34a increased after the completion of anthracycline treatment and was correlated with a rise in troponin I but not with LVEF |
| Feng Q., 2021 [52] | A total of 72 breast cancer patients | miR-130a | Acute cardiotoxicity | miR-130a increment during treatment was more pronounced in patients with cardiotoxicity |
| Frères P., 2018 [53] | A total of 45 breast cancer patients | miR-423 | Acute cardiotoxicity | miR-423 rise after the initiation of therapy was correlated with the decline in LVEF at follow-up |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernandez-Aviles, C.; Gonzalez-Manzanares, R.; Ojeda, S.; Castillo, J.C.; Robles-Mezcua, A.; Anguita, M.; Mesa, D.; Pan, M. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches for Heart Failure in Long-Term Survivors of Childhood Cancer. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1875. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12081875
Fernandez-Aviles C, Gonzalez-Manzanares R, Ojeda S, Castillo JC, Robles-Mezcua A, Anguita M, Mesa D, Pan M. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches for Heart Failure in Long-Term Survivors of Childhood Cancer. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(8):1875. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12081875
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernandez-Aviles, Consuelo, Rafael Gonzalez-Manzanares, Soledad Ojeda, Juan C. Castillo, Ainhoa Robles-Mezcua, Manuel Anguita, Dolores Mesa, and Manuel Pan. 2024. "Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches for Heart Failure in Long-Term Survivors of Childhood Cancer" Biomedicines 12, no. 8: 1875. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12081875
APA StyleFernandez-Aviles, C., Gonzalez-Manzanares, R., Ojeda, S., Castillo, J. C., Robles-Mezcua, A., Anguita, M., Mesa, D., & Pan, M. (2024). Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches for Heart Failure in Long-Term Survivors of Childhood Cancer. Biomedicines, 12(8), 1875. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12081875







