A General Method to Screen Nanobodies for Cytochrome P450 Enzymes from a Yeast Surface Display Library
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
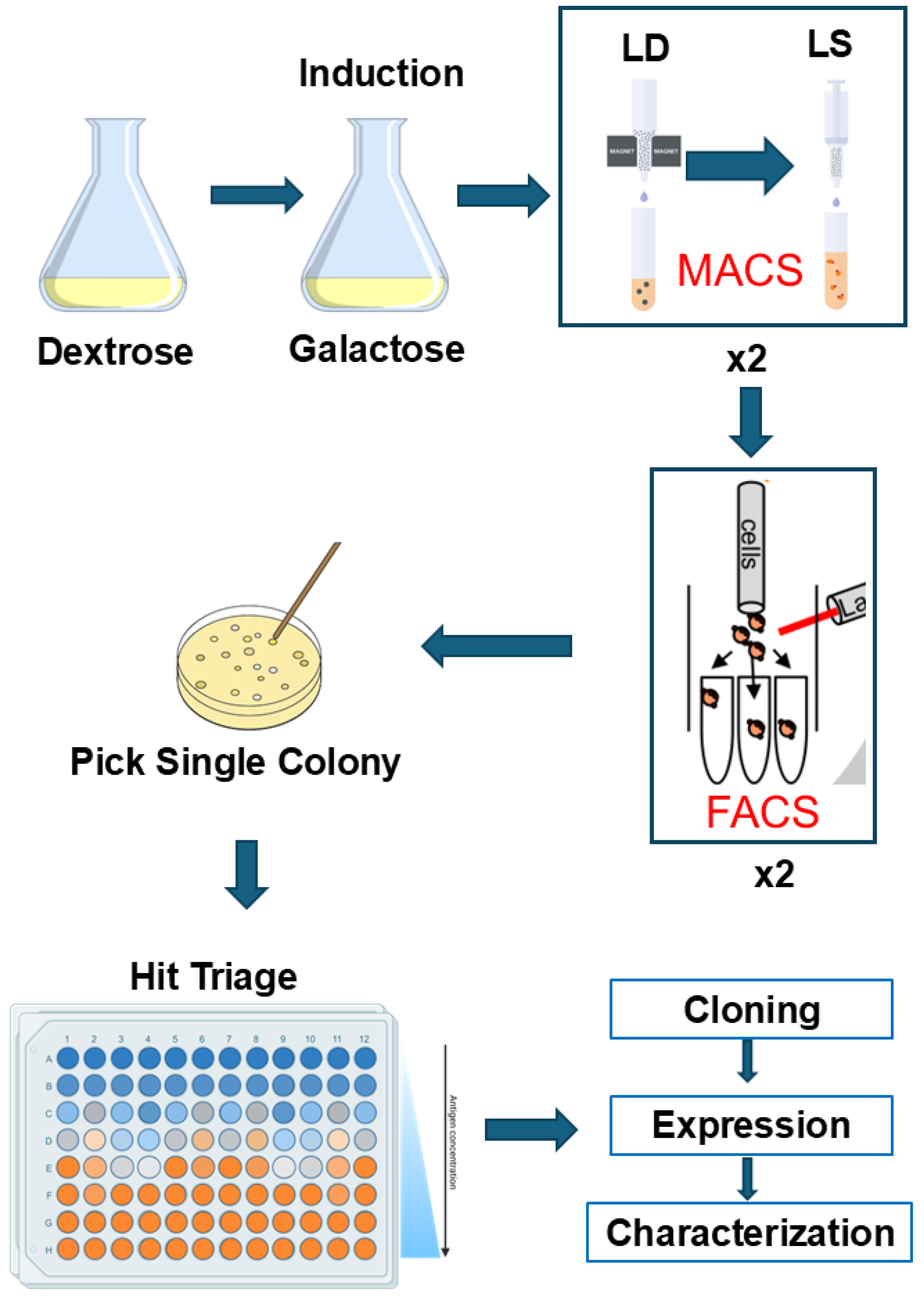
2.2. Culture Yeast Cell
2.3. Labeling CYP102A1, nNOS, 2B4:POR, and StvC
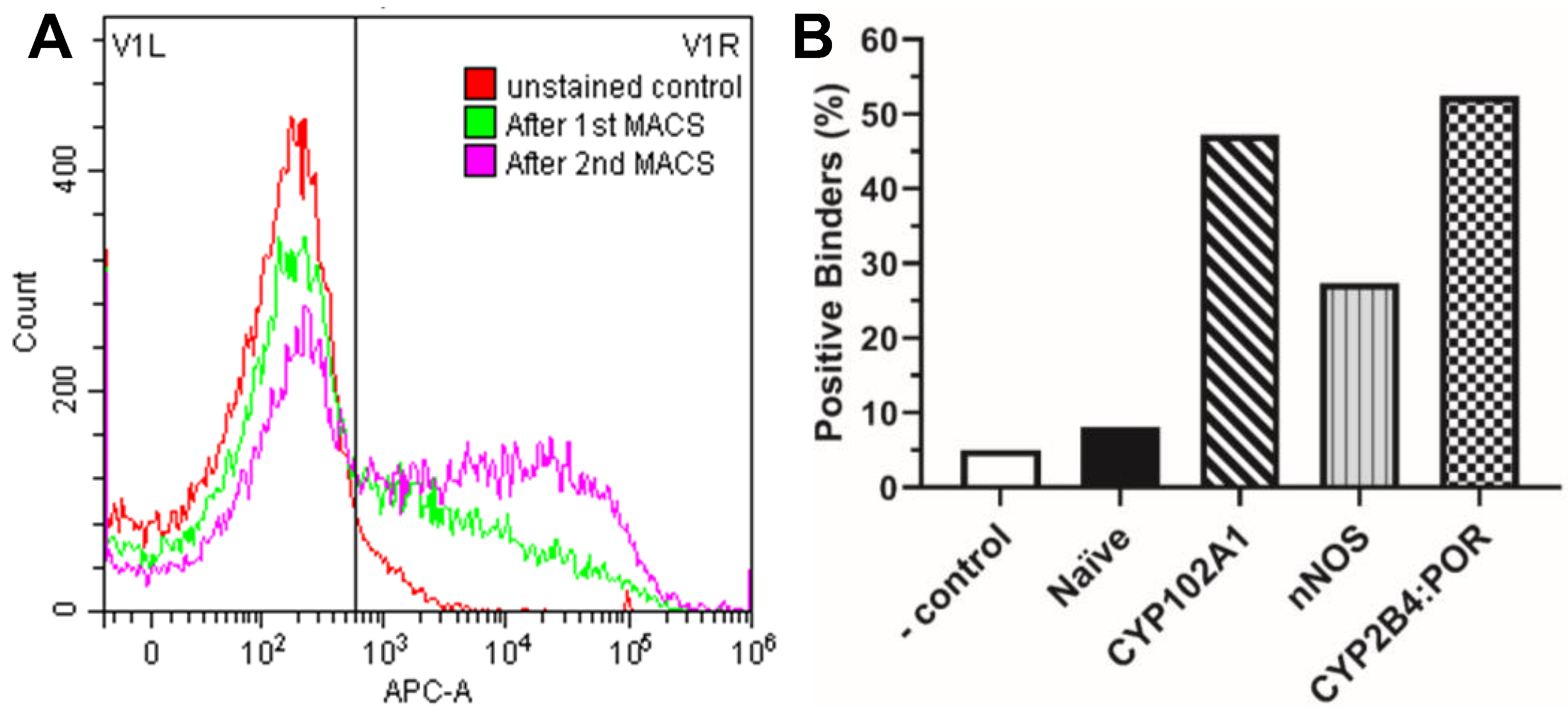
2.4. Selection of P450-Specific Nanobodies by MACS
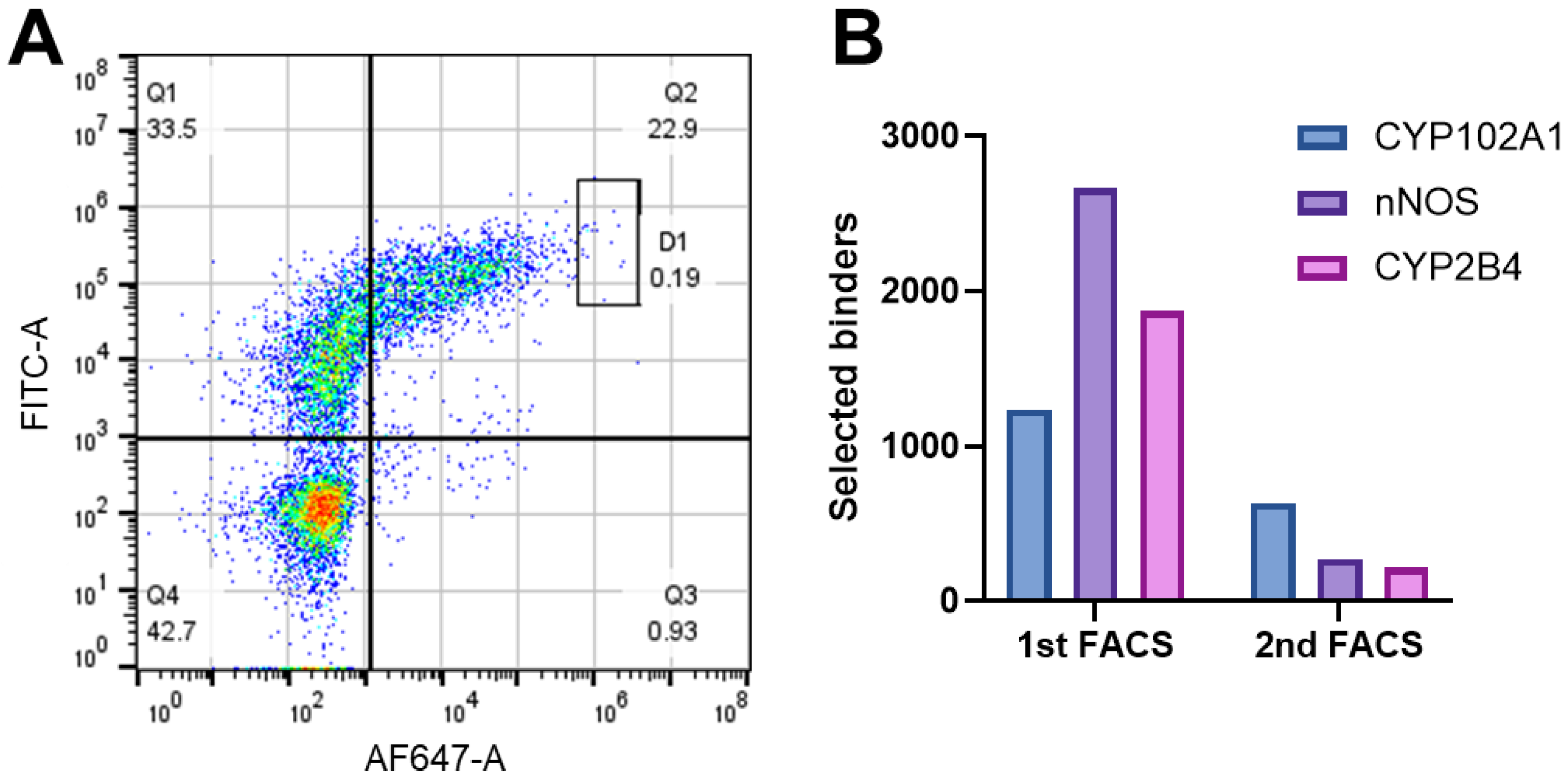
2.5. Selection of P450-Specific Nanobodies by FACS
2.6. Triage Nb-CYP102A1 Binders in Yeast Cells
2.7. Identification and Cloning of Unique Nb Clones of CYP102A1
2.8. Over-Expression and Purification of Selected Nanobodies of CYP102A1
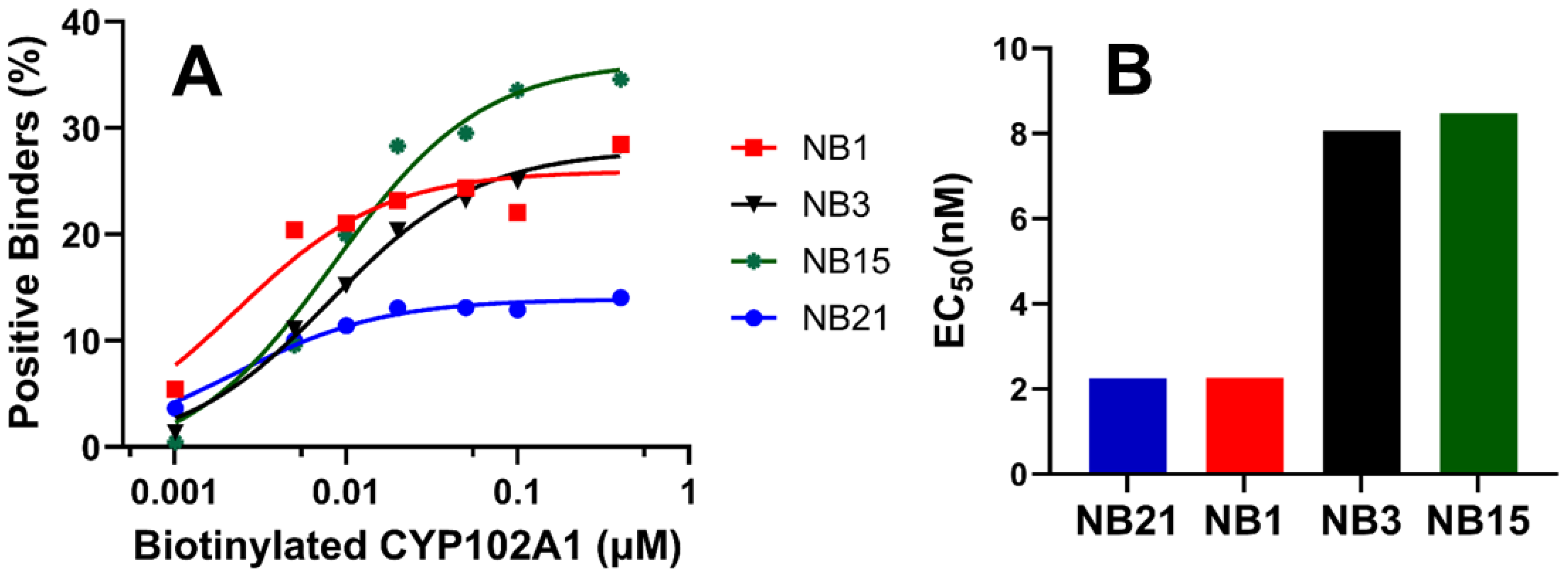
2.9. Characterization of CYP102A1-Specific Nanobodies
2.10. Over-Expression and Purification of P450s, POR, and StvC in E coli
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Screening Workflow and Strategy
3.2. MACS and FACS Selection of Nb–Antigen Binders
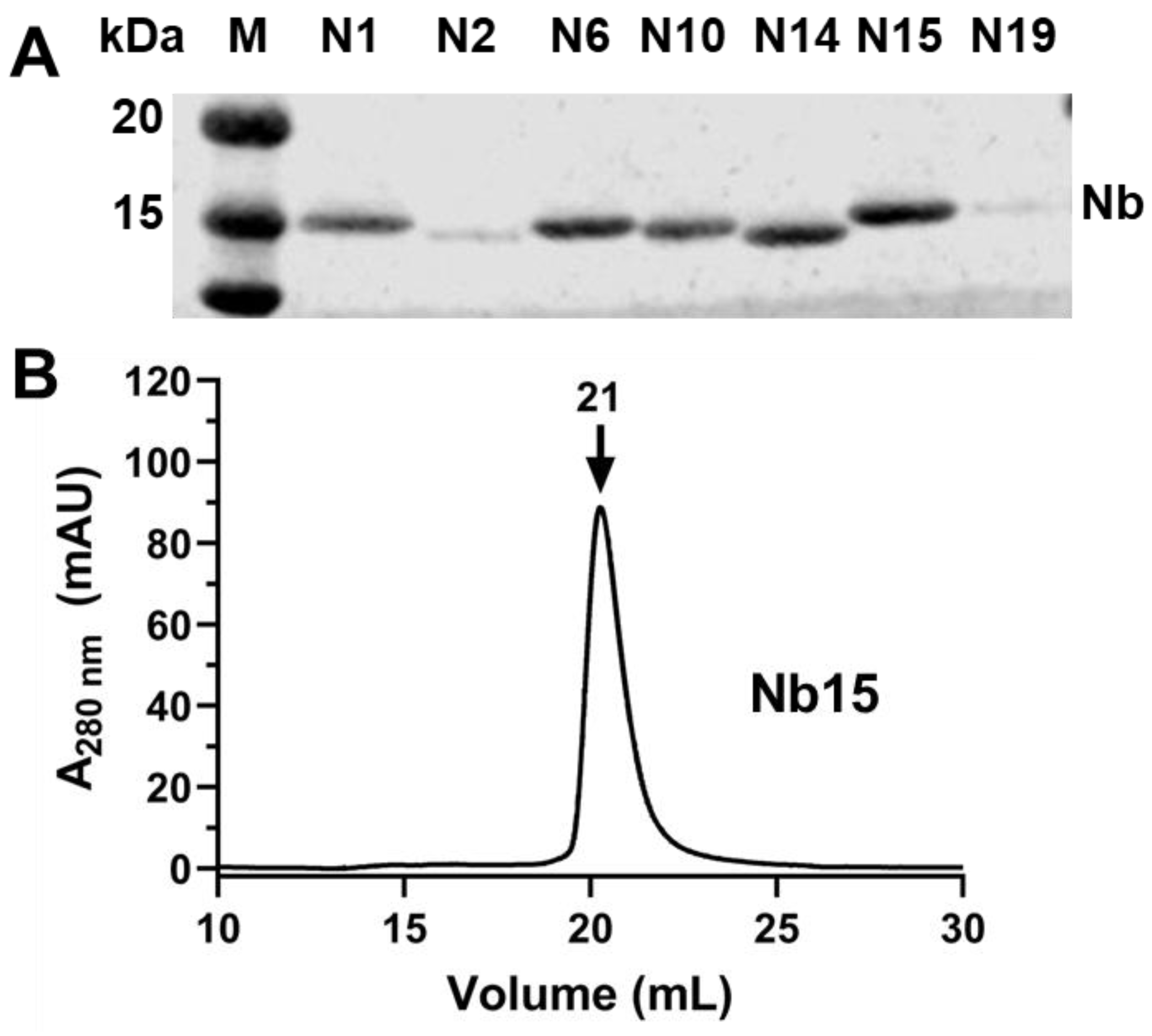
3.3. Triage Top Binders of CYP102A1
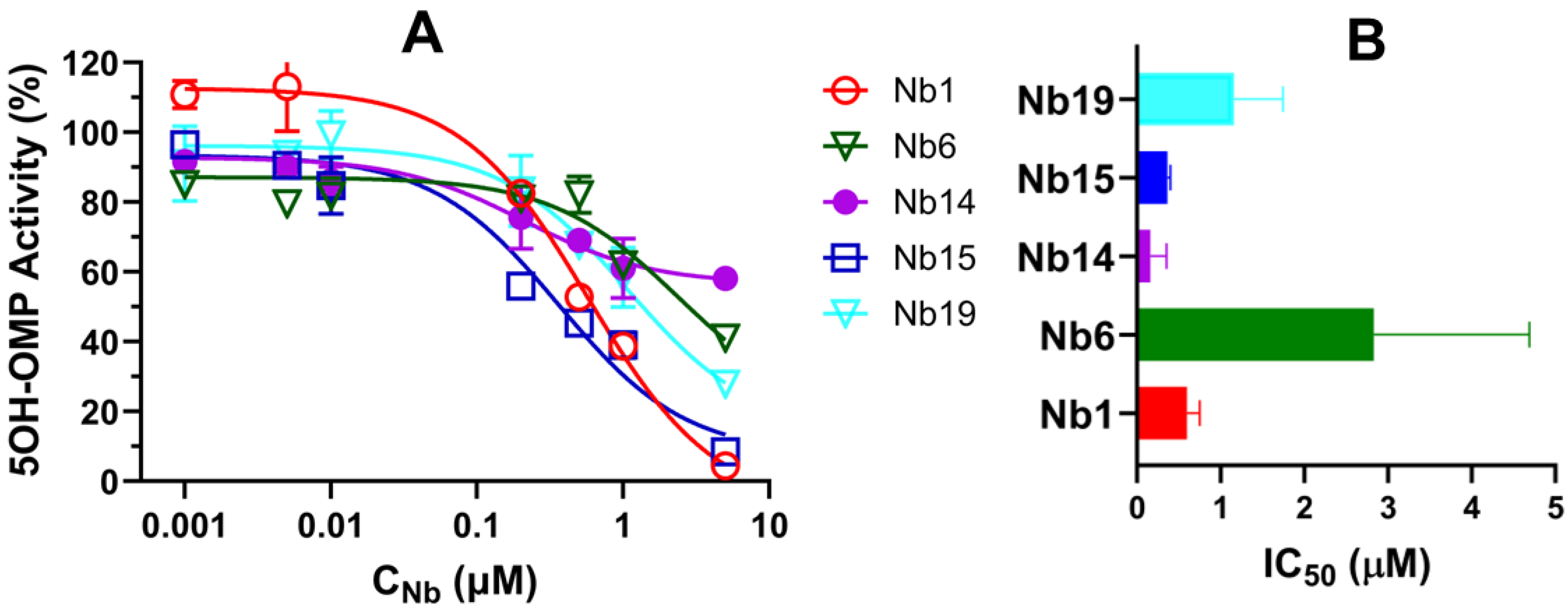
3.4. Characterization of CYP102A1-Specific Nanobodies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jovcevska, I.; Muyldermans, S. The Therapeutic Potential of Nanobodies. BioDrugs 2020, 34, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannas, P.; Hambach, J.; Koch-Nolte, F. Nanobodies and Nanobody-Based Human Heavy Chain Antibodies as Antitumor Therapeutics. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, S.G.; Choi, H.-J.; Fung, J.J.; Pardon, E.; Casarosa, P.; Chae, P.S.; DeVree, B.T.; Rosenbaum, D.M.; Thian, F.S.; Kobilka, T.S.; et al. Structure of a nanobody-stabilized active state of the β2 adrenoceptor. Nature 2011, 469, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prevost, M.S.; Barilone, N.; de la Bâtie, G.D.; Pons, S.; Ayme, G.; England, P.; Gielen, M.; Bontems, F.; Pehau-Arnaudet, G.; Maskos, U.; et al. An original potentiating mechanism revealed by the cryo-EM structures of the human α7 nicotinic receptor in complex with nanobodies. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Martinez, D.; Kong, T.; Goussard, S.; Zavala, A.; Gastineau, P.; Rey, M.; Ayme, G.; Chamot-Rooke, R.; Lafaye, P.; Vos, M.; et al. Cryo-EM structures of type IV pili complexed with nanobodies reveal immune escape mecha-nisms. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Custódio, T.F.; Das, H.; Sheward, D.J.; Hanke, L.; Pazicky, S.; Pieprzyk, J.; Sorgenfrei, M.; Schroer, M.A.; Gruzinov, A.Y.; Jeffries, C.M.; et al. Selection, biophysical and structural analysis of synthetic nanobodies that effectively neutralize SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esparza, T.J.; Martin, N.P.; Anderson, G.P.; Goldman, E.R.; Brody, D.L. High affinity nanobodies block SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor binding domain interaction with human angi-otensin converting enzyme. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, C.; Baier, A.S.; Pascolutti, R.; Wegrecki, M.; Zheng, S.; Ong, J.X.; Erlandson, S.C.; Hilger, D.; Rasmussen, S.G.F.; Ring, A.M.; et al. Yeast surface display platform for rapid discovery of conformationally selective nanobodies. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2018, 25, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misson Mindrebo, L.; Liu, H.; Ozorowski, G.; Tran, Q.; Woehl, J.; Khalek, I.; Smith, J.M.; Barman, S.; Zhao, F.; Keating, C.; et al. Fully synthetic platform to rapidly generate tetravalent bispecific nanobody-based immunoglobu-lins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2216612120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchański, T.; Zögg, T.; Yin, J.; Yuan, D.; Wohlkönig, A.; Fischer, B.; Rosenbaum, D.M.; Kobilka, B.K.; Pardon, E.; Steyaert, J. An improved yeast surface display platform for the screening of nanobody immune libraries. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, Y.R.; Liu, Y.; Kumbhar, R.; Zhao, P.; Gadhave, K.; Wang, N.; Li, Y.; Mao, X.; Wang, W. α-Synuclein fibril-specific nanobody reduces prion-like α-synuclein spreading in mice. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guengerich, F.P. Human Cytochrome P450 Enzymes. In Cytochrome P450: Structure, Mechanism, and Biochemistry, 3rd ed.; de Montellano, P.R.O., Ed.; Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, C.; Hamdane, D.; Shen, A.L.; Choi, V.; Kasper, C.B.; Pearl, N.M.; Zhang, H.; Im, S.-C.; Waskell, L.; Kim, J.-J.P. Conformational Changes of NADPH-Cytochrome P450 Oxidoreductase Are Essential for Catalysis and Cofactor Binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 16246–16260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, M.; Chakraborty, S.; Osawa, Y.; Zhang, H. Cryo-EM reveals the architecture of the dimeric cytochrome P450 CYP102A1 enzyme and conformational changes required for redox partner recognition. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 1637–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilderman, P.R.; Halpert, J.R. Plasticity of CYP2B Enzymes: Structural and Solution Biophysical Methods. Curr. Drug Metab. 2012, 13, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Kenaan, C.; Hamdane, D.; Hoa, G.H.B.; Hollenberg, P.F. Effect of Conformational Dynamics on Substrate Recognition and Specificity as Probed by the Introduction of a de Novo Disulfide Bond into Cytochrome P450 2B1. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 25678–25686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Bo, Z.; Hollenberg, P.; Osawa, Y.; Zhang, H. Amphipol-facilitated elucidation of the functional tetrameric complex of full-length cytochrome P450 CYP2B4 and NADPH-cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Sun, Y.; Osawa, Y.; Chen, Y.E.; Zhang, H. Computational redesign of cytochrome P450 CYP102A1 for highly stereoselective omeprazole hydroxylation by UniDesign. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 105050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, C.F.; Peet, C.; McLean, K.J.; Baynham, M.T.; Blankley, R.T.; Fisher, K.; Rigby, S.E.J.; Leys, D.; Voice, M.W.; Munro, A.W. Human P450-like oxidation of diverse proton pump inhibitor drugs by ‘gatekeeper’ mutants of flavocyto-chrome P450 BM3. Biochem. J. 2014, 460, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felker, D.; Lee, K.; Pospiech, T.H.; Morishima, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lau, M.; Southworth, D.R.; Osawa, Y. Mapping interactions of calmodulin and neuronal NO synthase by crosslinking and mass spectrometry. J. Biol. Chem. 2024, 300, 105464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Gruenke, L.; Saribas, A.S.; Im, S.-C.; Shen, A.L.; Kasper, C.B.; Waskell, L. Preparation and Characterization of a 5‘-DeazaFAD T491V NADPH−Cytochrome P450 Reductase. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 6804–6813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reznik, G.O.; Vajda, S.; Cantor, C.R.; Sano, T. A Streptavidin Mutant Useful for Directed Immobilization on Solid Surfaces. Bioconjugate Chem. 2001, 12, 1000–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charvolin, D.; Perez, J.-B.; Rouvière, F.; Giusti, F.; Bazzacco, P.; Abdine, A.; Rappaport, F.; Martinez, K.L.; Popot, J.-L. The use of amphipols as universal molecular adapters to immobilize membrane proteins onto solid supports. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| MACS | CYP102A1 | nNOS | 2B4:POR | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Round 1 | Round 2 | Round 1 | Round 2 | Round 1 | Round 2 | |
| Before | 4.1 × 109 | 3.0 × 109 | 3.0 × 109 | 1.8 × 109 | 3.4 × 109 | 2.5 × 109 |
| After | 2.7 × 107 | 3.0 × 108 | 1.0 × 107 | 3.2 × 107 | 1.6 × 107 | 2.1 × 108 |
| Diversity | 0.66% | 10% | 0.33% | 17% | 0.47% | 8.4% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Martinez-Ramos, C.; Chen, E.; Osawa, Y.; Zhang, H. A General Method to Screen Nanobodies for Cytochrome P450 Enzymes from a Yeast Surface Display Library. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1863. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12081863
Sun Y, Martinez-Ramos C, Chen E, Osawa Y, Zhang H. A General Method to Screen Nanobodies for Cytochrome P450 Enzymes from a Yeast Surface Display Library. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(8):1863. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12081863
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Yudong, Cristian Martinez-Ramos, Eugene Chen, Yoichi Osawa, and Haoming Zhang. 2024. "A General Method to Screen Nanobodies for Cytochrome P450 Enzymes from a Yeast Surface Display Library" Biomedicines 12, no. 8: 1863. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12081863
APA StyleSun, Y., Martinez-Ramos, C., Chen, E., Osawa, Y., & Zhang, H. (2024). A General Method to Screen Nanobodies for Cytochrome P450 Enzymes from a Yeast Surface Display Library. Biomedicines, 12(8), 1863. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12081863






