Eugenol: A Potential Modulator of Human Platelet Activation and Mouse Mesenteric Vascular Thrombosis via an Innovative cPLA2-NF-κB Signaling Axis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Preparation of Human Washed Platelets and Analysis of the Changes of [Ca2+]i Level
2.3. Immunoblotting
2.4. Exploring Confocal Laser Fluorescence Microscopy: Unveiling Cellular Insights
2.5. Evaluating Sodium Fluorescein-Induced Vascular Thrombosis in Mouse Mesenteric Microvessels
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
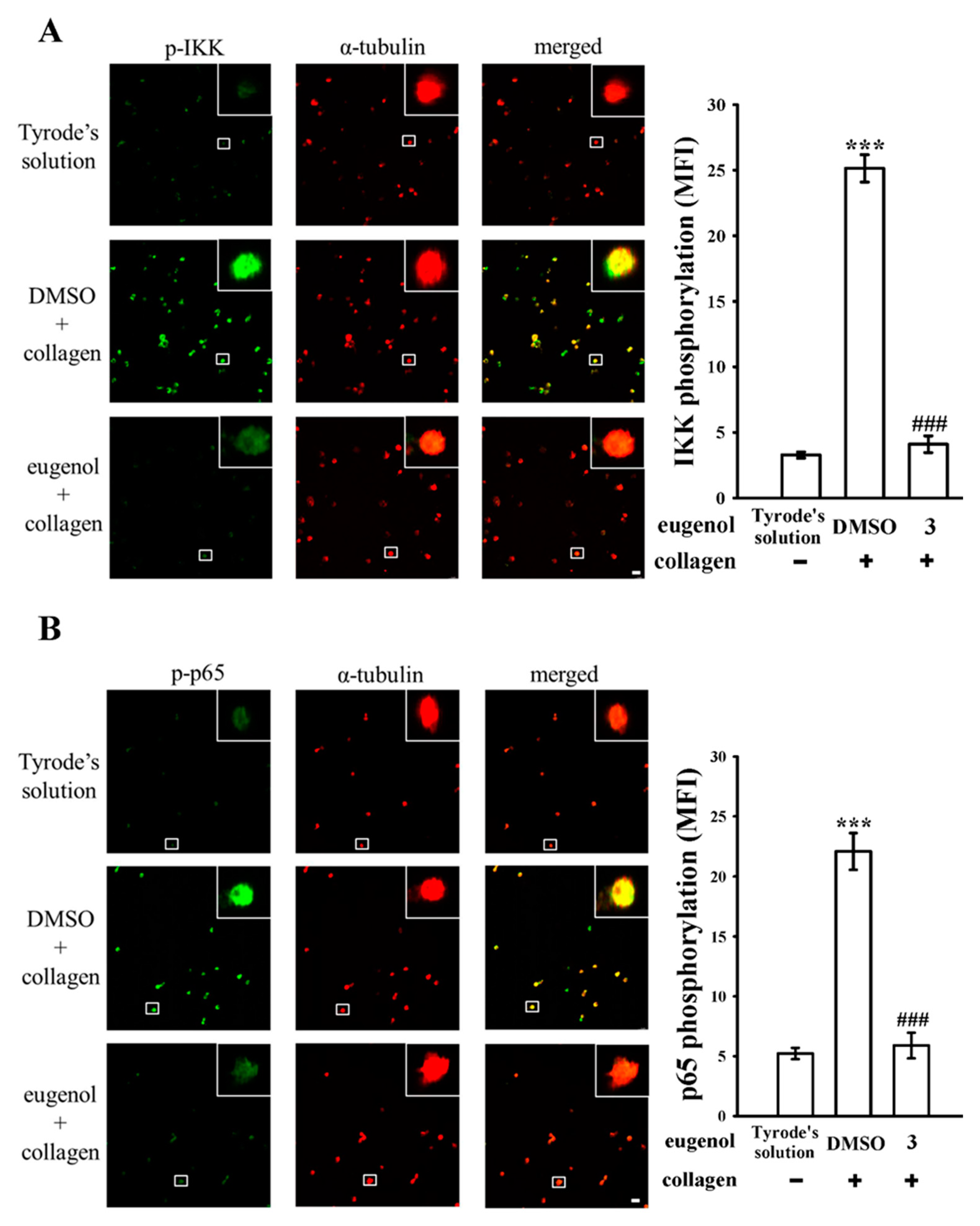
3.1. Assessing the Effects of Eugenol on Platelet NF-κB Activation Stimulated by Collagen
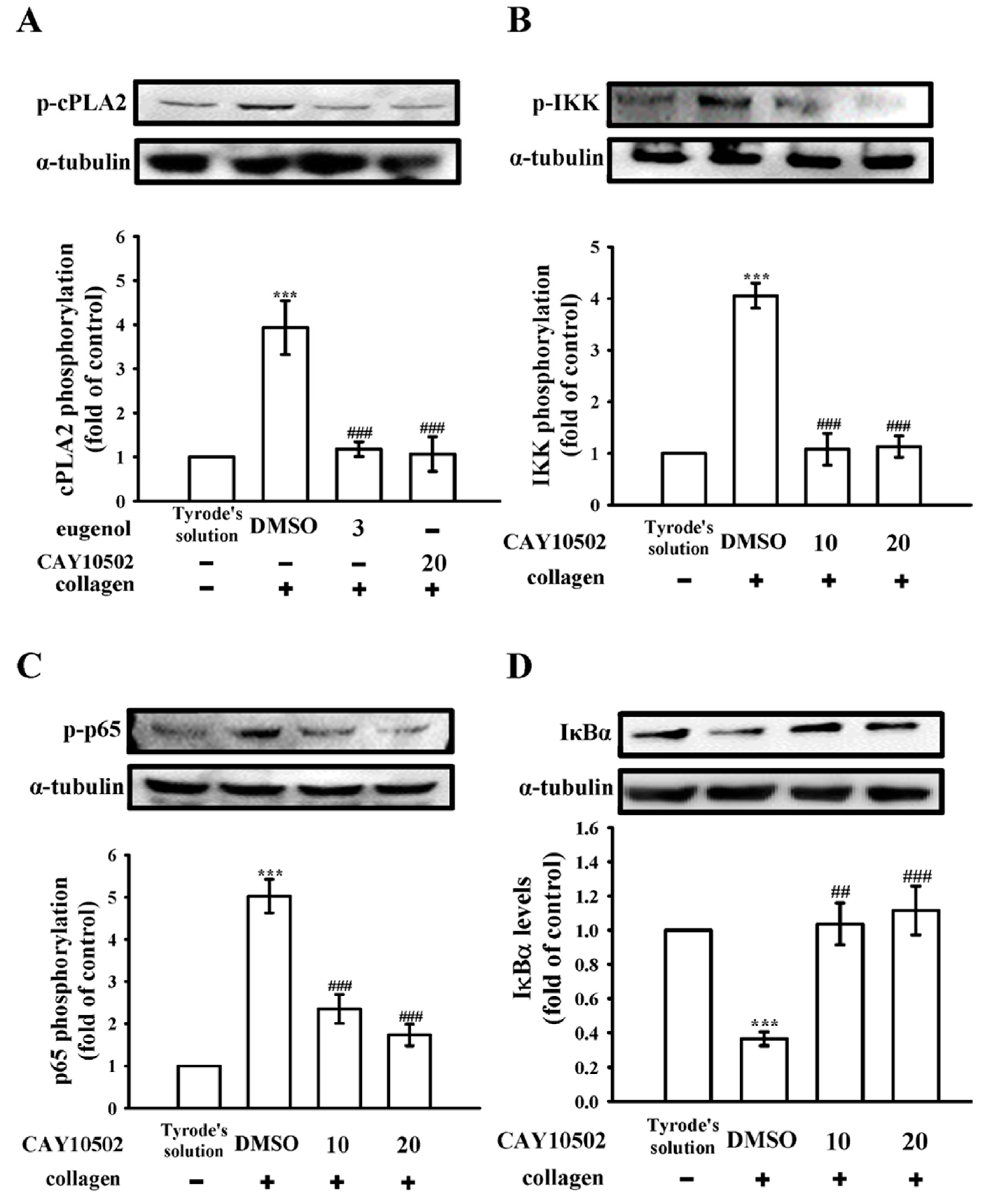
3.2. Exploring the Interplay between cPLA2 and NF-κB Signaling in Human Platelets
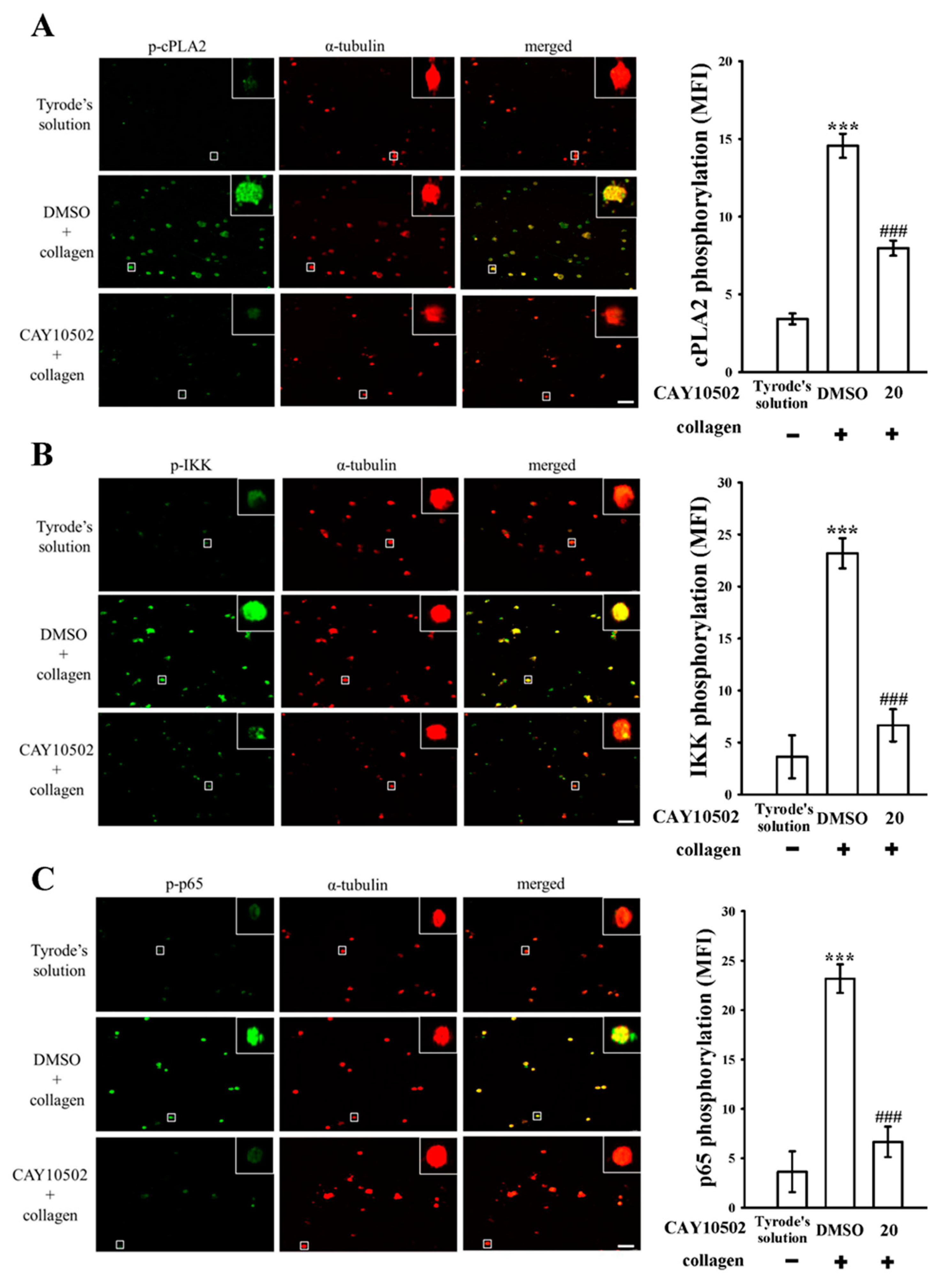
3.3. Evaluating the Impact of NF-κB on cPLA2 Activation and the Cytosolic Ca2+ Mobilization in Platelets
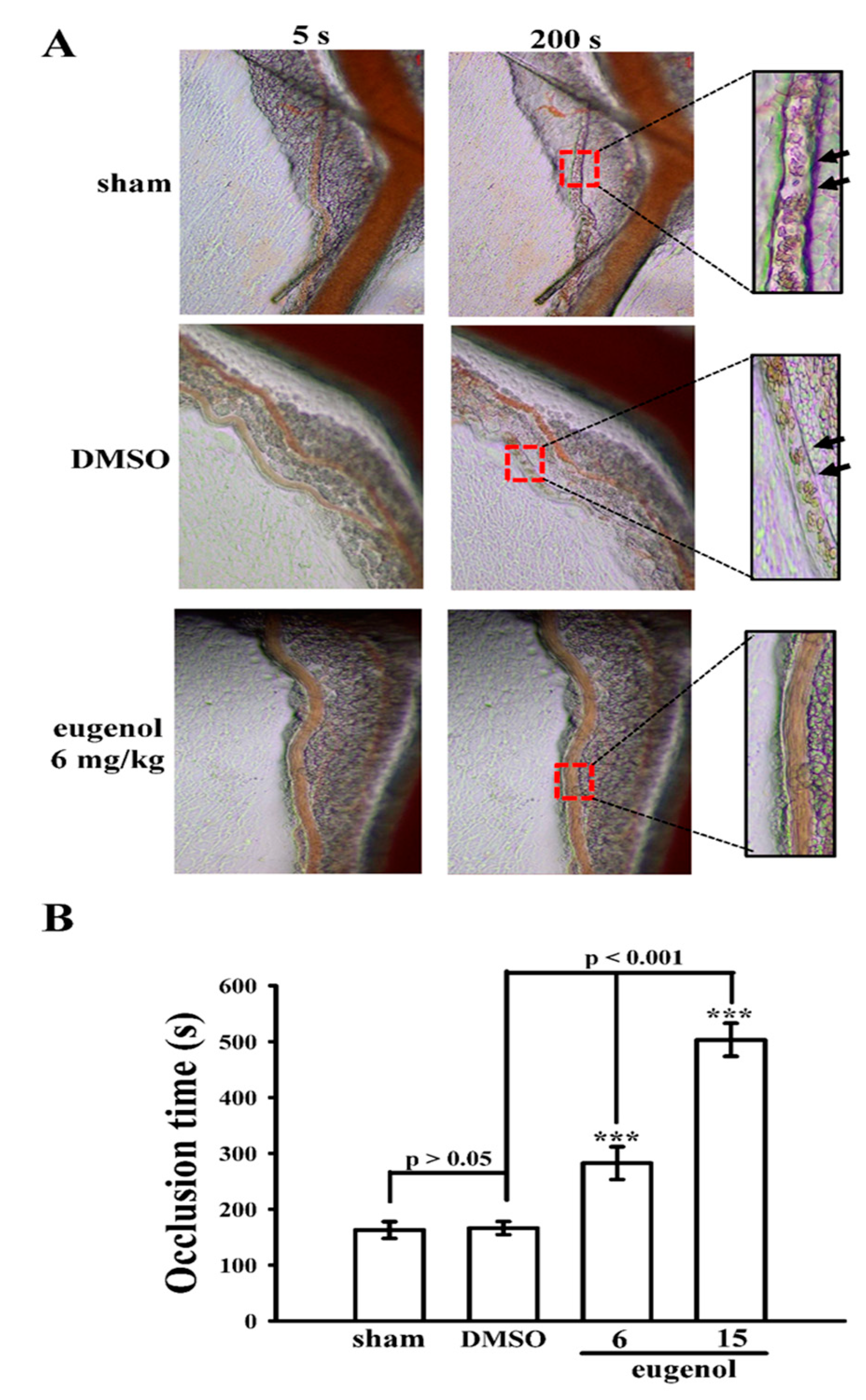
3.4. Evaluating the Anti-Thrombotic Potential of Eugenol in Sodium Fluorescein-Irradiated Mouse Mesenteric Microvessels
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AA | arachidonic acid |
| BSA | bovine serum albumin |
| cPLA2 | cytosolic phospholipase A2 |
| CVDs | cardiovascular diseases |
| DAG | diacylglycerol |
| DMSO | dimethyl sulfoxide |
| EDTA | ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| IKK | inhibitor of κB kinase |
| IP3 | inositol trisphosphate |
| IκB | inhibitor of κB |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| NaF | sodium fluoride |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor-κB |
| PI3K | phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| PKC | protein kinase C |
| PLCγ2 | phospholipase Cγ2 |
| PMSF | phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride |
| PRP | platelet-rich plasma |
| TxA2 | thromboxane A2 |
| U46619 | (5Z)-7-[(1R,4S,5S,6R)-6-[(1E,3S)-3-hydroxy-1-octen-1-yl]-2-oxabicyclo [2.2.1]hept-5-yl]-5-heptenoic acid |
References
- Marchese, A.; Barbieri, R.; Coppo, E.; Orhan, I.E.; Daglia, M.; Nabavi, S.F.; Izadi, M.; Abdollahi, M.; Nabavi, S.M.; Ajami, M. Antimicrobial activity of eugenol and essential oils containing eugenol: A mechanistic viewpoint. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 43, 668–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, S.; Chauhan, S.; Mannan, A.; Singh, T.G. Targeting cardiovascular risk factors with eugenol: An anti-inflammatory perspective. Inflammopharmacology 2024, 32, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, R.K.; Berndt, M.C. Platelet physiology and thrombosis. Thromb. Res. 2004, 114, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrowska, M.; Adamski, P.; Koziński, M.; Navarese, E.P.; Fabiszak, T.; Grześk, G.; Paciorek, P.; Kubica, J. Off-target effects of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor inhibitors. Cardiol. J. 2014, 21, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasparovic, H.; Petricevic, M.; Kopjar, T.; Djuric, Z.; Svetina, L.; Biocina, B. Impact of dual antiplatelet therapy on outcomes among aspirin-resistant patients following coronary artery bypass grafting. Am. J. Cardiol. 2014, 113, 1660–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivier, C.B.; Diehl, P.; Schnabel, K.; Weik, P.; Zhou, Q.; Bode, C.; Moser, M. Third generation P2Y12 antagonists inhibit platelet aggregation more effectively than clopidogrel in a myocardial infarction registry. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 111, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, N.E.; Holbrook, L.; Jones, S.; Kaiser, W.J.; Moraes, L.A.; Rana, R.; Sage, T.; Stanley, R.G.; Tucker, K.L.; Wright, B.; et al. Future innovations in anti-platelet therapies. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 154, 918–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackman, N. Triggers, targets and treatments for thrombosis. Nature 2008, 451, 914–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.N. Platelets. Lancet 2000, 355, 1531–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.C.; Shu, L.H.; Kuo, Y.J.; Lai, K.S.; Hsia, C.W.; Yen, T.L.; Hsia, C.H.; Jayakumar, T.; Yang, C.H.; Sheu, J.R. Eugenol suppresses platelet activation and mitigates pulmonary thromboembolism in humans and murine models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, G.; Lin, K.H.; Chang, Y.; Chen, T.L.; Tzu, N.H.; Chou, D.S.; Sheu, J.R. Protective mechanisms of inosine in platelet activation and cerebral ischemic damage. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 1998–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojok, K.; El-Kadiry, A.E.H.; Merhi, Y. Role of NF-κB in platelet function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Bai, L.; Chen, W.; Xu, S. The NF-kappaB activation pathways, emerging molecular targets for cancer prevention and therapy. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2010, 14, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsia, C.W.; Wu, M.P.; Shen, M.Y.; Hsia, C.H.; Chung, C.L.; Sheu, J.R. Regulation of human platelet activation and prevention of arterial thrombosis in mice by auraptene through inhibition of NF-κB pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Börsch-Haubold, A.G.; Ghomashchi, F.; Pasquet, S.; Goedert, M.; Cohen, P.; Gelb, M.H.; Watson, S.P. Phosphorylation of cytosolic phospholipase A2 in platelets is mediated by multiple stress-activated protein kinase pathways. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 265, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnett, J.M.; McCollum, G.W.; Penn, J.S. Role of cytosolic phospholipase A(2) in retinal neovascularization. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 1136–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Hayden, M.S. New regulators of NF-kappaB in inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Jin, Y.; Chen, X.; Ye, X.; Shen, X.; Lin, M.; Zeng, C.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, J. NF-κB in biology and targeted therapy: New insights and translational implications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, F.Y.; Davidson, S.J.; Moraes, L.A.; Traves, S.L.; Paul-Clark, M.; Bishop-Bailey, D.; Warner, T.D.; Mitchell, J.A. Role of nuclear receptor signaling in platelets: Antithrombotic effects of PPARbeta. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 326–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, L.A.; Paul-Clark, M.J.; Rickman, A.; Flower, R.J.; Goulding, N.J.; Perretti, M. Ligand-specific glucocorticoid receptor activation in human platelets. Blood 2005, 106, 4167–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, C.; Andreakos, E.; Kiriakidis, S.; Mauri, C.; Bicknell, C.; Foxwell, B.; Cheshire, N.; Paleolog, E.; Feldmann, M. Canonical pathway of nuclear factor kappa B activation selectively regulates proinflammatory and prothrombotic responses in human atherosclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 5634–5639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malaver, E.; Romaniuk, M.A.; D’Atri, L.P.; Pozner, R.G.; Negrotto, S.; Benzadón, R.; Schattner, M. NF-kappaB inhibitors impair platelet activation responses. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 7, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Börsch-Haubold, A.G.; Kramer, R.M.; Watson, S.P. Cytosolic phospholipase A2 is phosphorylated in collagen- and thrombin-stimulated human platelets independent of protein kinase C and mitogen-activated protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 25885–25892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arauna, D.; Araya-Maturana, R.; Urra, F.A.; García, Á.; Palomo, I.; Fuentes, E. Altered dynamics of calcium fluxes and mitochondrial metabolism in platelet activation-related disease and aging. Life Sci. 2024, 351, 122846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, D.I.; Kuijpers, M.J.E.; Heemskerk, J.W.M. Platelet calcium signaling by G-protein coupled and ITAM-linked receptors regulating anoctamin-6 and procoagulant activity. Platelets 2021, 32, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, J.R.; Lee, C.R.; Lin, C.H.; Hsiao, G.; Ko, W.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Yen, M.H. Mechanisms involved in the antiplatelet activity of staphylococcus aureus lipoteichoic acid in human platelets. Thromb. Haemost. 2000, 83, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, Y.; Hsia, C.-W.; Chiou, K.-R.; Yen, T.-L.; Jayakumar, T.; Sheu, J.-R.; Huang, W.-C. Eugenol: A Potential Modulator of Human Platelet Activation and Mouse Mesenteric Vascular Thrombosis via an Innovative cPLA2-NF-κB Signaling Axis. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12081689
Chang Y, Hsia C-W, Chiou K-R, Yen T-L, Jayakumar T, Sheu J-R, Huang W-C. Eugenol: A Potential Modulator of Human Platelet Activation and Mouse Mesenteric Vascular Thrombosis via an Innovative cPLA2-NF-κB Signaling Axis. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(8):1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12081689
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Yi, Chih-Wei Hsia, Kuan-Rau Chiou, Ting-Lin Yen, Thanasekaran Jayakumar, Joen-Rong Sheu, and Wei-Chieh Huang. 2024. "Eugenol: A Potential Modulator of Human Platelet Activation and Mouse Mesenteric Vascular Thrombosis via an Innovative cPLA2-NF-κB Signaling Axis" Biomedicines 12, no. 8: 1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12081689
APA StyleChang, Y., Hsia, C.-W., Chiou, K.-R., Yen, T.-L., Jayakumar, T., Sheu, J.-R., & Huang, W.-C. (2024). Eugenol: A Potential Modulator of Human Platelet Activation and Mouse Mesenteric Vascular Thrombosis via an Innovative cPLA2-NF-κB Signaling Axis. Biomedicines, 12(8), 1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12081689








