Impact of Antibiotic and Steroid Therapy on Leptospirosis Outcomes: A Retrospective Cohort Study in Transcarpathia, Ukraine
Abstract
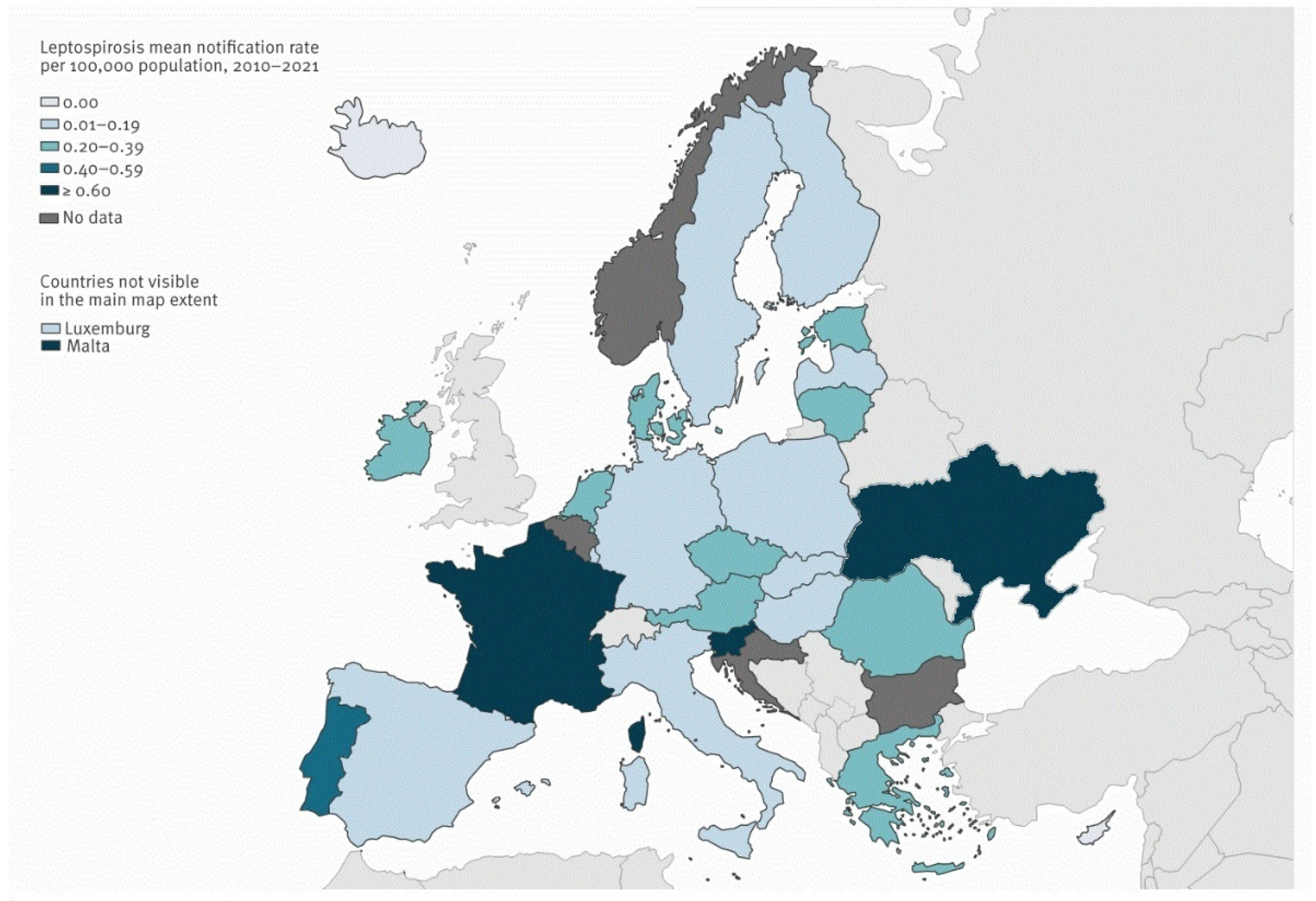
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Diagnostic Criteria
2.2. Patient Stratification and Grouping
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
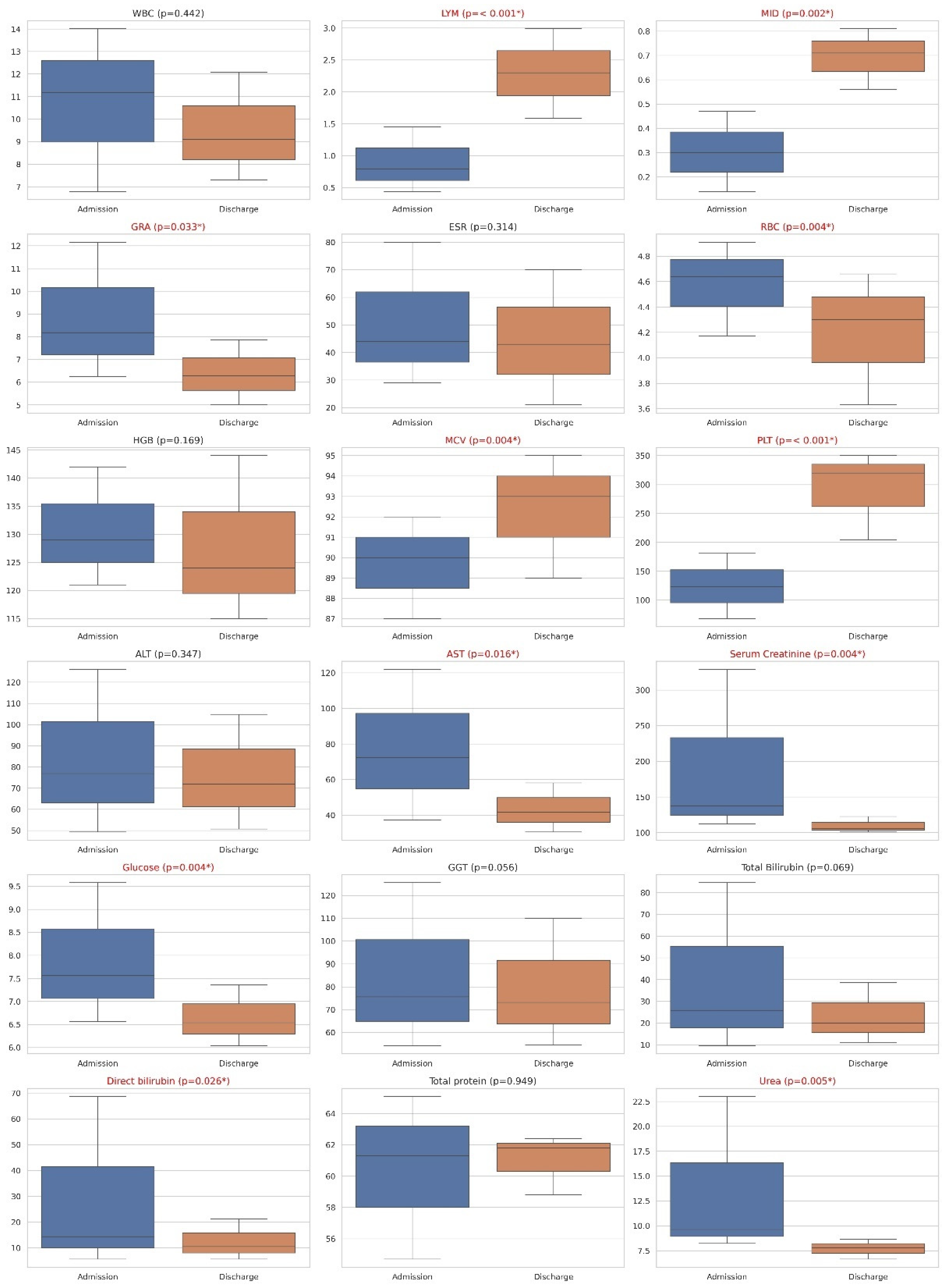
3.1. Descriptive Analysis and Sex-Dependent Changes in Variables
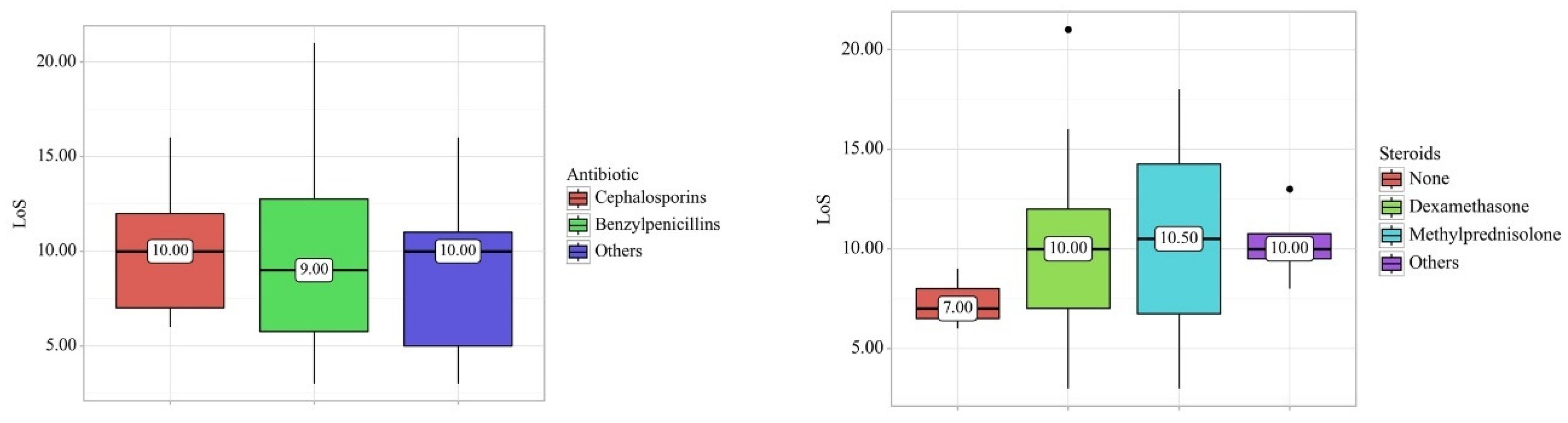
3.2. Effect of Steroid Type on Clinical and Laboratory Findings
3.3. Effect of Antibiotic Treatment on Clinical and Laboratory Findings
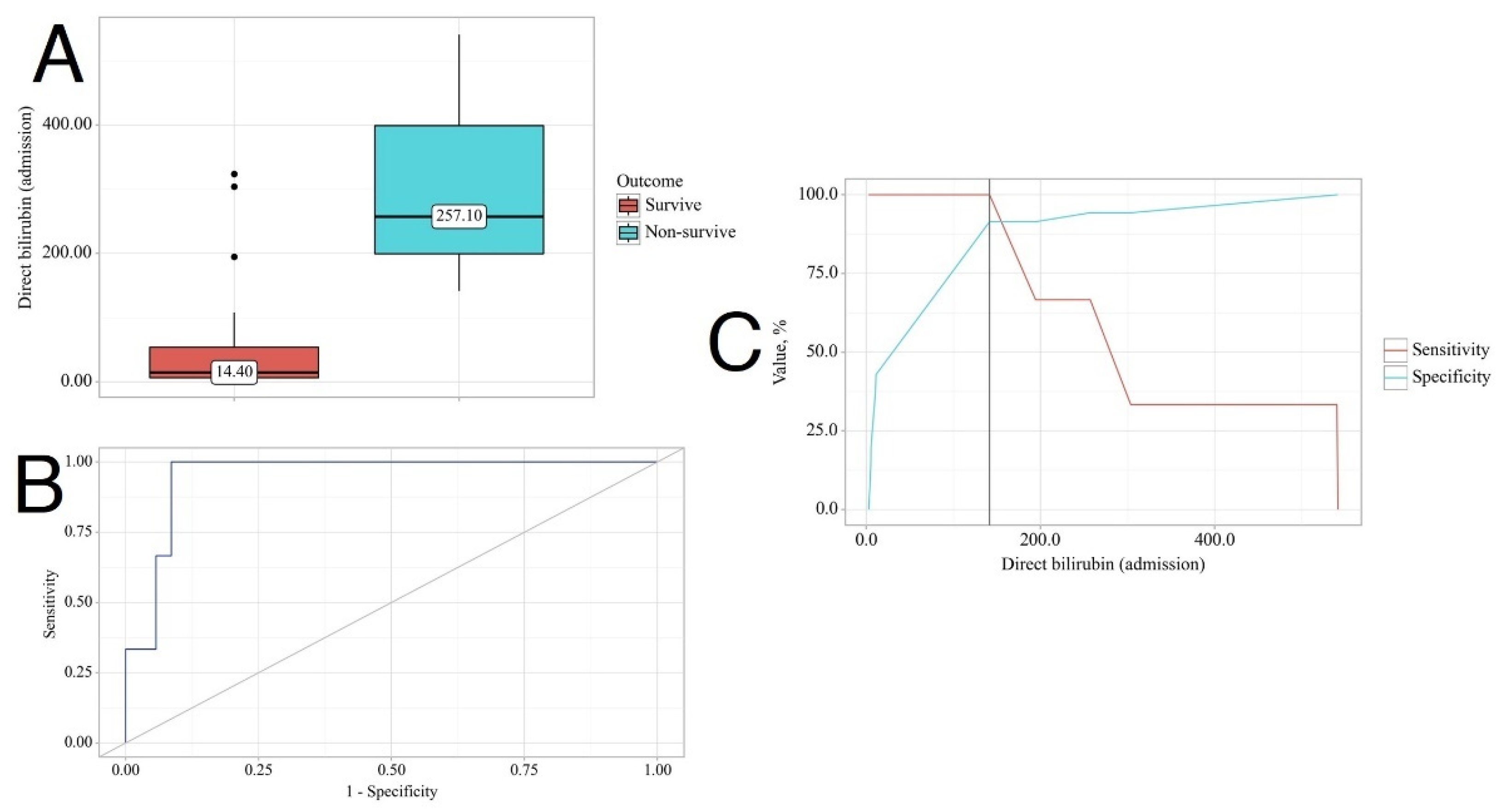
3.4. Effect of Laboratory Variables on Outcome
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haake, D.A.; Levett, P.N. Leptospirosis in humans. J. Leptospira Leptospirosis 2015, 387, 65–97. [Google Scholar]
- Philip, N.; Lung Than, L.T.; Shah, A.M.; Yuhana, M.Y.; Sekawi, Z.; Neela, V.K. Predictors of severe leptospirosis: A multicentre observational study from Central Malaysia. J. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spichler, A.S.; Vilaça, P.J.; Athanazio, D.A.; Albuquerque, J.O.; Buzzar, M.; Castro, B.; Seguro, A.; Vinetz, J.M. Predictors of lethality in severe leptospirosis in urban Brazil. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 79, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panaphut, T.; Domrongkitchaiporn, S.; Thinkamrop, B. Prognostic factors of death in leptospirosis: A prospective cohort study in Khon Kaen, Thailand. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 6, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doudier, B.; Garcia, S.; Quennee, V.; Jarno, P.; Brouqui, P. Prognostic factors associated with severe leptospirosis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2006, 12, 299–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petakh, P.; Isevych, V.; Mohammed, I.B.; Nykyforuk, A.; Rostoka, L. Leptospirosis: Prognostic Model for Patient Mortality in the Transcarpathian Region, Ukraine. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2022, 22, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petakh, P.; Isevych, V.; Kamyshnyi, A.; Oksenych, V. Weil’s Disease-Immunopathogenesis, Multiple Organ Failure, and Potential Role of Gut Microbiota. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markovych, O.; Tymchyk, V.; Kolesnikova, I. Leptospirosis in Zakarpattia Oblast (2005–2015). Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2019, 19, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petakh, P.; Rostoka, L.; Isevych, V.; Kamyshnyi, A. Identifying risk factors and disease severity in leptospirosis: A meta-analysis of clinical predictors. Trop. Dr. 2023, 53, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petakh, P.; Kamyshnyi, A.; Tymchyk, V.; Armitage, R. Infectious diseases during the Russian-Ukrainian war—Morbidity in the Transcarpathian region as a marker of epidemic danger on the EU border. Public Health Pract. 2023, 6, 100397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petakh, P.; Tymchyk, V.; Kamyshnyi, O. Surveillance of human leptospirosis infections in Ukraine between 2018 and 2023. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1394781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beauté, J.; Innocenti, F.; Aristodimou, A.; Špačková, M.; Eves, C.; Kerbo, N.; Rimhanen-Finne, R.; Picardeau, M.; Faber, M.; Dougas, G.; et al. Epidemiology of reported cases of leptospirosis in the EU/EEA, 2010 to 2021. Eurosurveillance 2024, 29, 2300266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xavier, V.; Baby, B.; George, J.M.; Ittyachen, A.M. COVID-19 and leptospirosis, pulmonary involvement and response to steroids: A comparative observational study from a rural Tertiary care center in Kerala. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2022, 11, 294–298. [Google Scholar]
- Gulati, S.; Gulati, A. Pulmonary manifestations of leptospirosis. Lung India Off. Organ Indian Chest Soc. 2012, 29, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolhnikoff, M.; Mauad, T.; Bethlem, E.P.; Carvalho, C.R.R. Pathology and pathophysiology of pulmonary manifestations in leptospirosis. J Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 11, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, S.R.; Brauner, J.S. Leptospirosis as a cause of acute respiratory failure: Clinical features and outcome in 35 critical care patients. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Braz. Soc. Infect. Dis. 2002, 6, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limothai, U.; Lumlertgul, N.; Sirivongrangson, P.; Kulvichit, W.; Tachaboon, S.; Dinhuzen, J.; Chaisuriyong, W.; Peerapornratana, S.; Chirathaworn, C.; Praditpornsilpa, K.; et al. The role of leptospiremia and specific immune response in severe leptospirosis. J. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petakh, P.; Nykyforuk, A. Predictors of lethality in severe leptospirosis in Transcarpathian region of Ukraine. Le Infez. Med. 2022, 30, 272–276. [Google Scholar]
- Zubach, O.; Semenyshyn, O.; Vasiuynets, L.; Velychko, O.; Zinchuk, A. Application of PCR for Specific Diagnosis of Leptospirosis in Humans in Ukraine. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2020, 69, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasiński, B.; Dutkiewicz, J. Leptospirosis-current risk factors connected with human activity and the environment. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. AAEM 2013, 20, 239–244. [Google Scholar]
- Brinker, A.J.; Blazes, D.L. An outbreak of Leptospirosis among United States military personnel in Guam. Trop. Dis. Travel Med. Vaccines 2017, 3, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkenfeld, M.; Berenji, M. Poisoned Waters of War: Ukraine’s Invisible Victims. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2024, 66, 9–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubach, O.; Pestushko, I.; Dliaboha, Y.; Semenyshyn, O.; Zinchuk, A. A Single Clinical Case of Leptospirosis in a 70-Year-Old Man During the Military Conflict in Ukraine. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2023, 23, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubach, O.; Telegina, T.; Semenyshyn, O.; Vasiunets, L.; Zinchuk, A. Leptospirosis in Ukraine (Lviv Oblast): Clinical and Epidemiological Features. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2019, 19, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenderlein, J.; Zitzl, T.; Dufay-Simon, N.; Cachet, N.; Pantchev, N.; Le Guyader, M.; Fontana, C.; Bomchil, N.; Tronel, J.-P.; Cupillard, L.; et al. Detection and Identification of Pathogenic Leptospira spp. Serogroups in Europe between 2017 and 2020 Applying a Novel Gene-Based Molecular Approach. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2024, 2024, 1101841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, A.; Stark, K.; Schneider, T.; Schöneberg, I. Sex differences in clinical leptospirosis in Germany: 1997–2005. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2007, 44, e69–e72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ittyachen, M.A.; Vk, L.; Ck, E.; Joseph, M. Methylprednisolone as adjuvant in treatment of acute respiratory distress syndrome owing to leptospirosis—A pilot study. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kularatne, S.A.; Budagoda, B.D.; de Alwis, V.K.; Wickramasinghe, W.M.; Bandara, J.M.; Pathirage, L.P.; Gamlath, G.R.R.; Wijethunga, T.J.; Jayalath, W.A.; Jayasinghe, C.; et al. High efficacy of bolus methylprednisolone in severe leptospirosis: A descriptive study in Sri Lanka. Postgrad. Med. J. 2011, 87, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenoy, V.V.; Nagar, V.S.; Chowdhury, A.A.; Bhalgat, P.S.; Juvale, N.I. Pulmonary leptospirosis: An excellent response to bolus methylprednisolone. Postgrad. Med. J. 2006, 82, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwattayakul, K.; Kaewtasi, S.; Chueasuwanchai, S.; Hoontrakul, S.; Chareonwat, S.; Suttinont, C.; Phimda, K.; Chierakul, W.; Silpasakorn, S.; Suputtamongkol, Y. An open randomized controlled trial of desmopressin and pulse dexamethasone as adjunct therapy in patients with pulmonary involvement associated with severe leptospirosis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Off. Publ. Eur. Soc. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1207–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Jian, M.; Su, X.; Pan, Y.; Duan, Y.; Ma, W.; Zhong, L.; Yang, J.; Song, J.; Wu, X.; et al. Efficacy and safety of antibiotics for treatment of leptospirosis: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Syst. Rev. 2024, 13, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Abs. | % | |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||
| Male | 27 | 71.1 |
| Female | 11 | 28.9 |
| Serogroups | ||
| Hebdomadis | 10 | 26.3 |
| Canicola | 4 | 10.5 |
| Clinical | 3 | 7.9 |
| Others | 2 | 5.3 |
| Pomona | 3 | 7.9 |
| Sejroe | 5 | 13.2 |
| Icterrohaemorrhagiae | 3 | 7.9 |
| Cynopteri | 7 | 18.4 |
| Australis | 1 | 2.6 |
| Outcome | ||
| Survive | 35 | 92.1 |
| Non-survive | 3 | 7.9 |
| Antibiotic | ||
| Cephalosporins | 17 | 44.7 |
| Benzylpenicillins | 8 | 21.1 |
| Others | 13 | 34.2 |
| Steroids | ||
| None | 3 | 7.9 |
| Dexamethasone | 29 | 76.3 |
| Methylprednisolone | 2 | 5.3 |
| Others | 4 | 10.5 |
| Variables | Median (Me) | Q₁–Q₃ (Interquartile Range) |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 50.00 | 44.25–63.75 |
| Length of Stay (LoS) (days) | 10.00 | 7.00–11.75 |
| WBC (×109/L) | 10.73 | 6.87–14.81 |
| LYM (×109/L) | 0.71 | 0.43–1.45 |
| MID (×109/L) | 0.31 | 0.14–0.63 |
| GRA (×109/L) | 8.18 | 6.25–13.38 |
| ESR (mm/h) | 46.50 | 30.00–75.25 |
| RBC (×1012/L) | 4.38 | 4.08–4.91 |
| HGB (g/L) | 128.00 | 113.50–140.75 |
| MCV (fL) | 89.50 | 87.00–92.00 |
| PLT (×109/L) | 116.50 | 68.00–181.25 |
| ALT (U/L) | 92.15 | 55.00–128.85 |
| AST (U/L) | 76.15 | 44.52–123.35 |
| Serum Creatinine (µmol/L) | 138.90 | 112.67–421.27 |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 7.28 | 6.55–9.04 |
| GGT (U/L) | 85.75 | 52.62–157.88 |
| Total Bilirubin (µmol/L) | 34.00 | 12.47–121.80 |
| Direct Bilirubin (µmol/L) | 19.35 | 6.22–91.58 |
| Total Protein (g/L) | 61.20 | 55.25–63.27 |
| Urea (mmol/L) | 10.82 | 8.26–23.08 |
| Variables | Group | On Admission (Median [Q1–Q3]) | On Discharge (Median [Q1–Q3]) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WBC (×109/L) | Cephalosporins | 8.39 (6.59–14.01) | 9.25 (7.86–12.86) | 0.747 |
| Benzylpenicillins | 9.87 (7.49–12.73) | 8.96 (6.77–11.04) | 0.844 | |
| Others | 11.68 (7.12–18.00) | 9.62 (7.31–12.08) | 0.414 | |
| LYM (×109/L) | Cephalosporins | 0.62 (0.39–1.20) | 2.50 (1.68–3.02) | 0.002 * |
| Benzylpenicillins | 0.60 (0.43–0.86) | 1.73 (1.25–1.91) | 0.039 * | |
| Others | 1.18 (0.53–2.14) | 2.05 (1.58–2.81) | 0.033 * | |
| MID (×109/L) | Cephalosporins | 0.24 (0.14–0.39) | 0.68 (0.43–0.81) | 0.027 * |
| Benzylpenicillins | 0.34 (0.29–0.51) | 0.84 (0.54–1.09) | 0.028 * | |
| Others | 0.36 (0.13–0.99) | 0.71 (0.62–0.75) | 0.497 | |
| GRA (×109/L) | Cephalosporins | 7.39 (6.15–12.16) | 6.73 (5.08–8.71) | 0.109 |
| Benzylpenicillins | 8.46 (6.70–11.77) | 6.03 (5.00–7.95) | 0.250 | |
| Others | 8.54 (6.25–15.20) | 6.94 (4.70–7.87) | 0.094 | |
| ESR (mm/hr) | Cephalosporins | 40.00 (27.00–63.00) | 33.00 (20.00–60.00) | 0.378 |
| Benzylpenicillins | 63.50 (31.50–79.25) | 51.50 (34.50–75.25) | 0.641 | |
| Others | 59.00 (41.00–82.00) | 49.00 (41.00–70.00) | 0.127 | |
| RBC (×1012/L) | Cephalosporins | 4.48 (4.24–5.01) | 4.33 (3.89–4.93) | 0.207 |
| Benzylpenicillins | 4.01 (3.80–4.80) | 3.67 (3.56–4.07) | 0.039 * | |
| Others | 4.38 (4.16–4.80) | 4.37 (3.46–4.50) | 0.008 * | |
| HGB (g/L) | Cephalosporins | 130.00 (123.00–140.00) | 125.00 (116.00–144.00) | 0.782 |
| Benzylpenicillins | 121.50 (112.75–127.25) | 115.50 (112.00–117.75) | 0.028 * | |
| Others | 127.00 (110.00–142.00) | 127.00 (102.00–138.00) | 0.340 | |
| MCV (fL) | Cephalosporins | 90.00 (87.00–92.00) | 92.00 (89.00–94.00) | 0.006 * |
| Benzylpenicillins | 90.00 (86.75–93.00) | 91.50 (88.50–95.25) | 0.250 | |
| Others | 89.00 (87.00–95.00) | 90.00 (88.00–97.00) | 0.033 * | |
| PLT (×109/L) | Cephalosporins | 136.00 (73.00–229.00) | 346.00 (293.00–398.00) | 0.003 * |
| Benzylpenicillins | 85.00 (49.75–150.50) | 174.50 (132.25–338.50) | 0.039 * | |
| Others | 107.00 (68.00–139.00) | 278.00 (228.00–339.00) | <0.001 * | |
| ALT (U/L) | Cephalosporins | 93.00 (41.60–169.30) | 85.40 (64.40–106.80) | 0.159 |
| Benzylpenicillins | 85.65 (68.72–247.22) | 68.50 (62.27–132.75) | 0.250 | |
| Others | 85.30 (53.80–120.60) | 55.90 (41.10–98.50) | 0.839 | |
| AST (U/L) | Cephalosporins | 81.30 (39.10–135.80) | 49.30 (34.50–58.10) | 0.015 * |
| Benzylpenicillins | 69.80 (48.12–156.90) | 49.15 (27.60–93.25) | 0.109 | |
| Others | 76.20 (44.10–103.00) | 37.50 (27.60–53.90) | 0.168 | |
| Serum Creatinine (µmol/L) | Cephalosporins | 119.70 (107.10–243.80) | 105.90 (102.90–126.40) | 0.109 |
| Benzylpenicillins | 264.80 (124.55–524.65) | 117.75 (103.17–262.07) | 0.461 | |
| Others | 144.10 (115.30–437.20) | 109.90 (101.20–132.50) | <0.001 * | |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | Cephalosporins | 6.59 (6.45–7.77) | 6.40 (6.00–6.76) | 0.045* |
| Benzylpenicillins | 8.47 (6.75–9.48) | 6.37 (5.88–7.86) | 0.109 | |
| Others | 7.80 (6.77–9.10) | 6.78 (6.53–8.91) | 0.376 | |
| GGT (U/L) | Cephalosporins | 120.00 (57.80–172.70) | 79.90 (49.10–157.60) | 0.064 |
| Benzylpenicillins | 77.25 (50.67–123.05) | 76.70 (45.30–110.97) | 0.148 | |
| Others | 74.80 (47.60–125.60) | 74.80 (61.70–110.00) | 0.735 | |
| Total Bilirubin (µmol/L) | Cephalosporins | 25.90 (10.80–56.60) | 12.40 (11.10–29.20) | 0.009 * |
| Benzylpenicillins | 108.66 (44.82–261.20) | 43.35 (31.35–176.55) | 0.612 | |
| Others | 20.50 (14.70–159.30) | 20.10 (12.70–38.80) | 0.080 | |
| Direct bilirubin (µmol/L) | Cephalosporins | 14.40 (5.68–37.10) | 7.80 (5.40–19.40) | 0.015 * |
| Benzylpenicillins | 72.81 (31.20–170.40) | 24.30 (17.12–99.60) | 0.461 | |
| Others | 11.10 (6.90–99.20) | 9.80 (6.90–20.50) | 0.048 * | |
| Total protein (g/L) | Cephalosporins | 58.53 (54.70–63.30) | 60.50 (58.60–62.30) | 0.469 |
| Benzylpenicillins | 59.75 (56.23–63.06) | 59.53 (54.25–61.73) | 0.641 | |
| Others | 62.30 (59.60–63.20) | 61.80 (58.80–63.00) | 0.244 | |
| Urea (mmol/L) | Cephalosporins | 9.63 (8.22–20.39) | 7.35 (6.52–8.18) | 0.013 * |
| Benzylpenicillins | 20.52 (8.12–30.87) | 9.45 (7.56–18.40) | 0.945 | |
| Others | 17.45 (8.72–23.02) | 7.92 (6.65–8.63) | 0.010 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petakh, P.; Poliak, M.; Kohutych, A.; Oksenych, V.; Kamyshnyi, O. Impact of Antibiotic and Steroid Therapy on Leptospirosis Outcomes: A Retrospective Cohort Study in Transcarpathia, Ukraine. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12081685
Petakh P, Poliak M, Kohutych A, Oksenych V, Kamyshnyi O. Impact of Antibiotic and Steroid Therapy on Leptospirosis Outcomes: A Retrospective Cohort Study in Transcarpathia, Ukraine. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(8):1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12081685
Chicago/Turabian StylePetakh, Pavlo, Mykhailo Poliak, Anton Kohutych, Valentyn Oksenych, and Oleksandr Kamyshnyi. 2024. "Impact of Antibiotic and Steroid Therapy on Leptospirosis Outcomes: A Retrospective Cohort Study in Transcarpathia, Ukraine" Biomedicines 12, no. 8: 1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12081685
APA StylePetakh, P., Poliak, M., Kohutych, A., Oksenych, V., & Kamyshnyi, O. (2024). Impact of Antibiotic and Steroid Therapy on Leptospirosis Outcomes: A Retrospective Cohort Study in Transcarpathia, Ukraine. Biomedicines, 12(8), 1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12081685








