A Comparative Analysis of Enamel Surface Roughness Following Various Interproximal Reduction Techniques: An Examination Using Scanning Electron Microscopy and Atomic Force Microscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
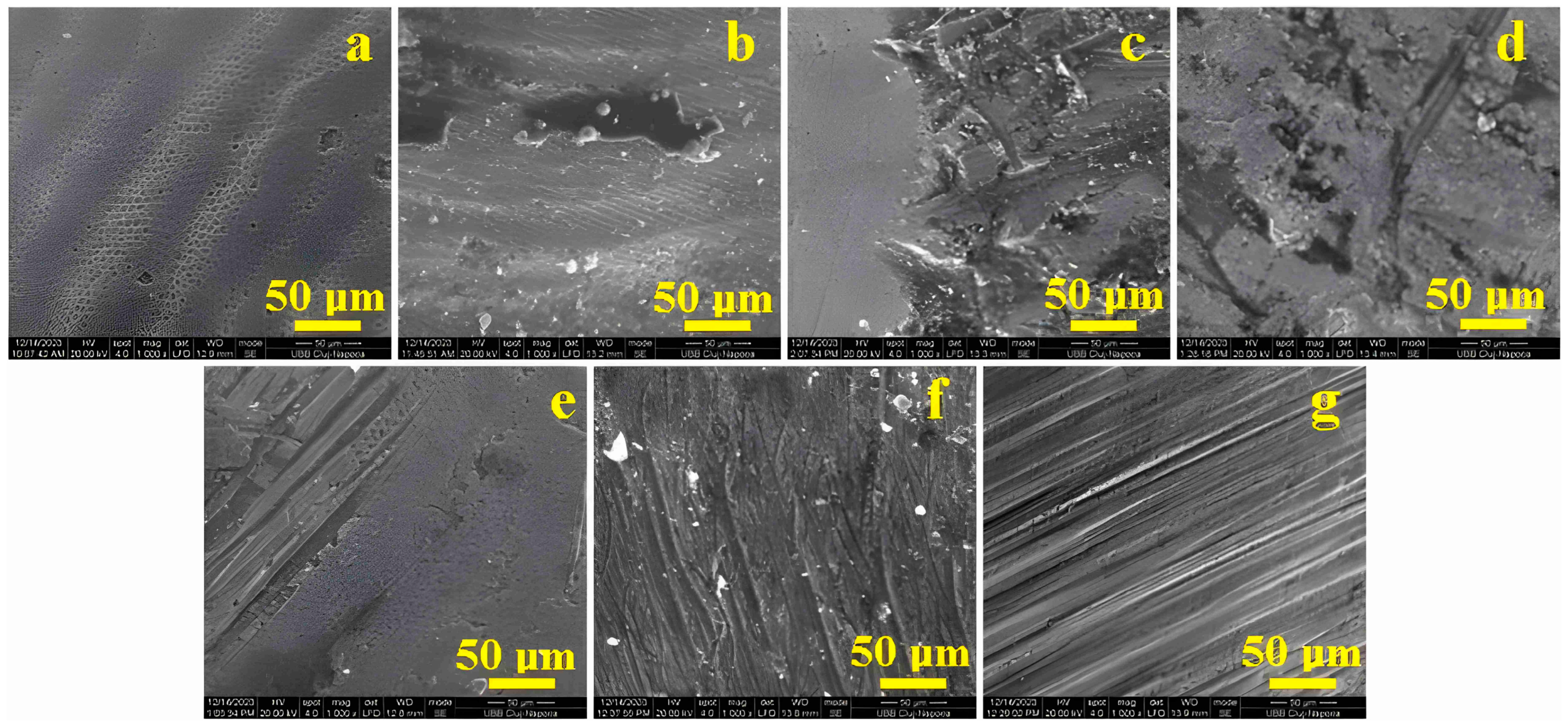
3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
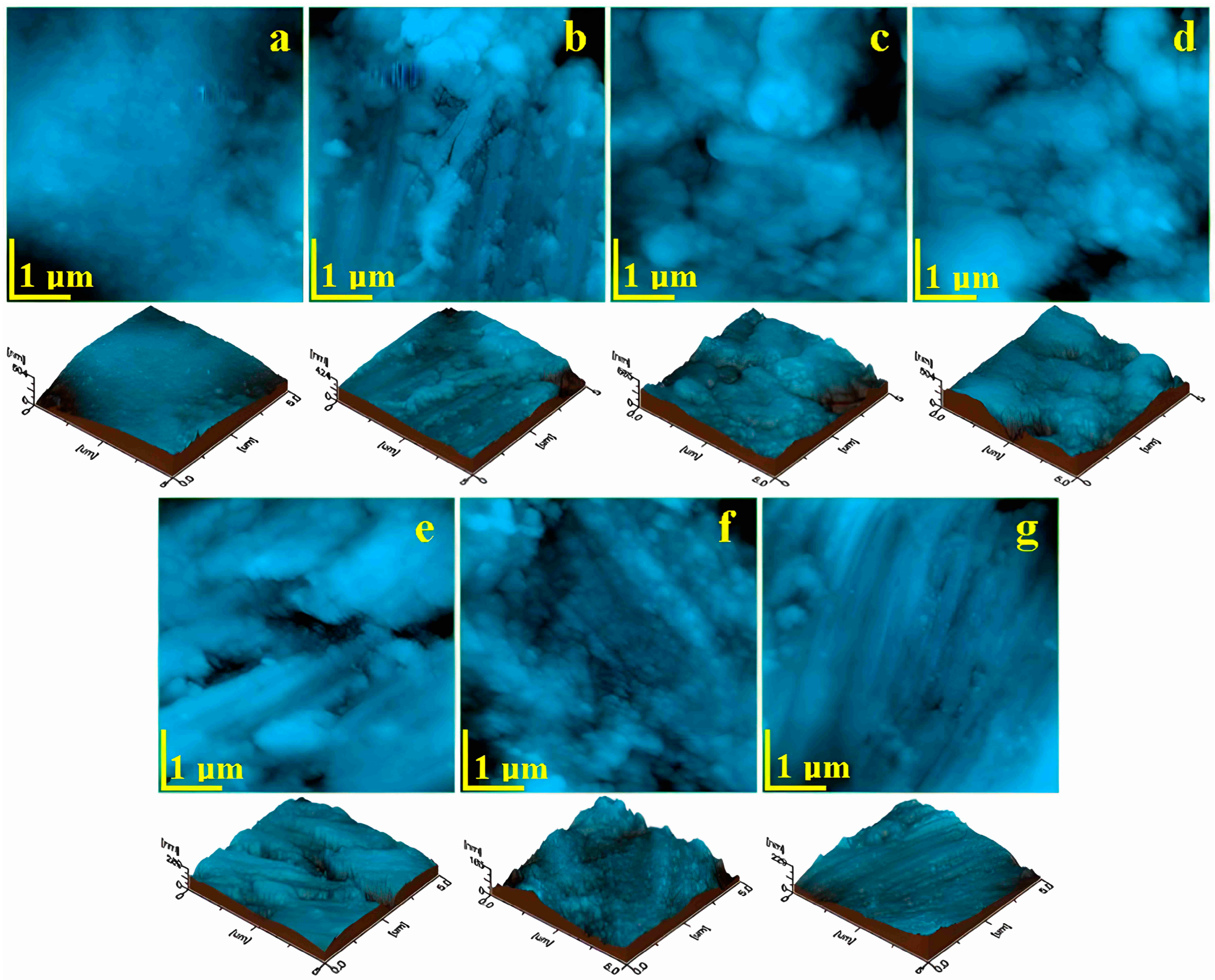
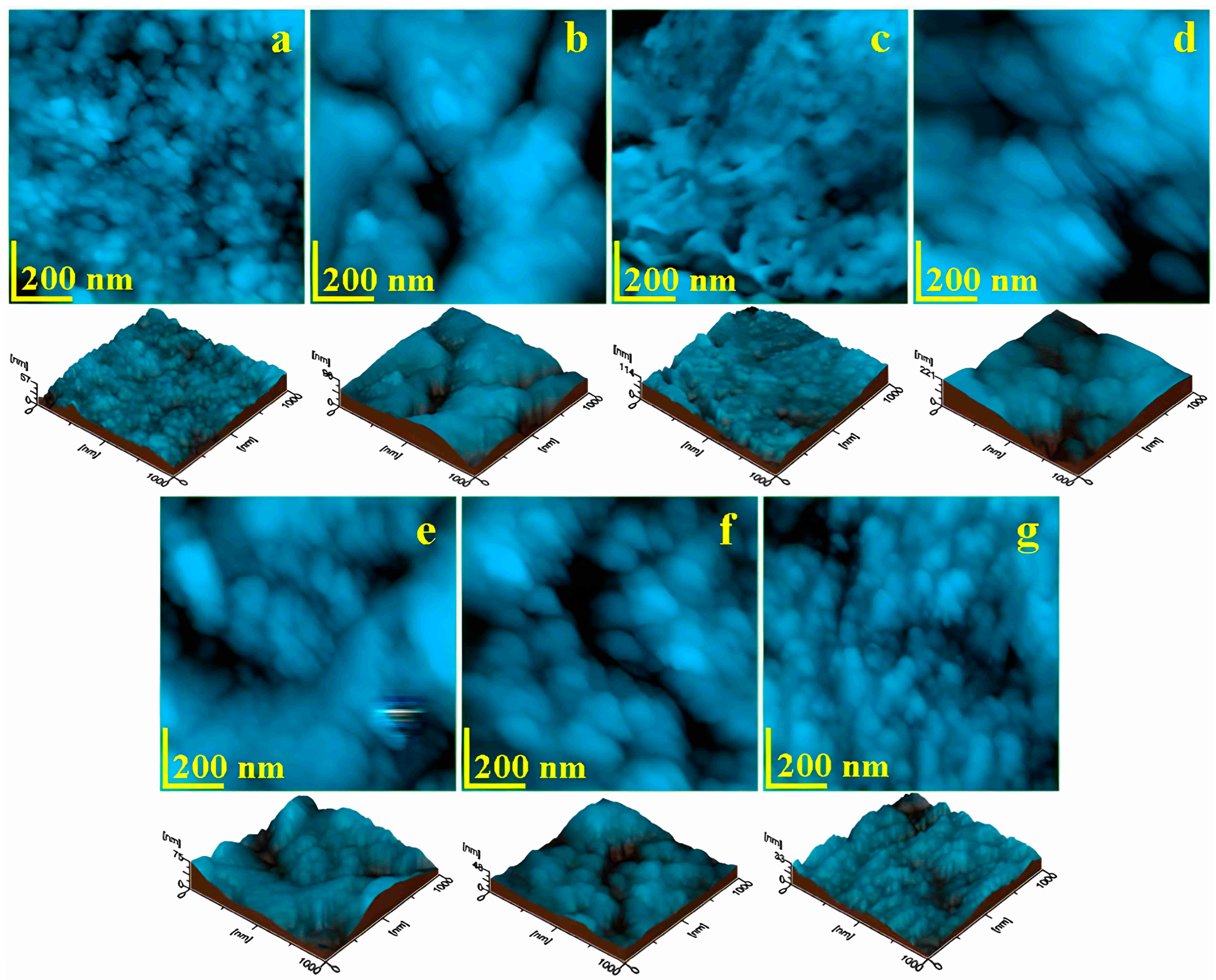
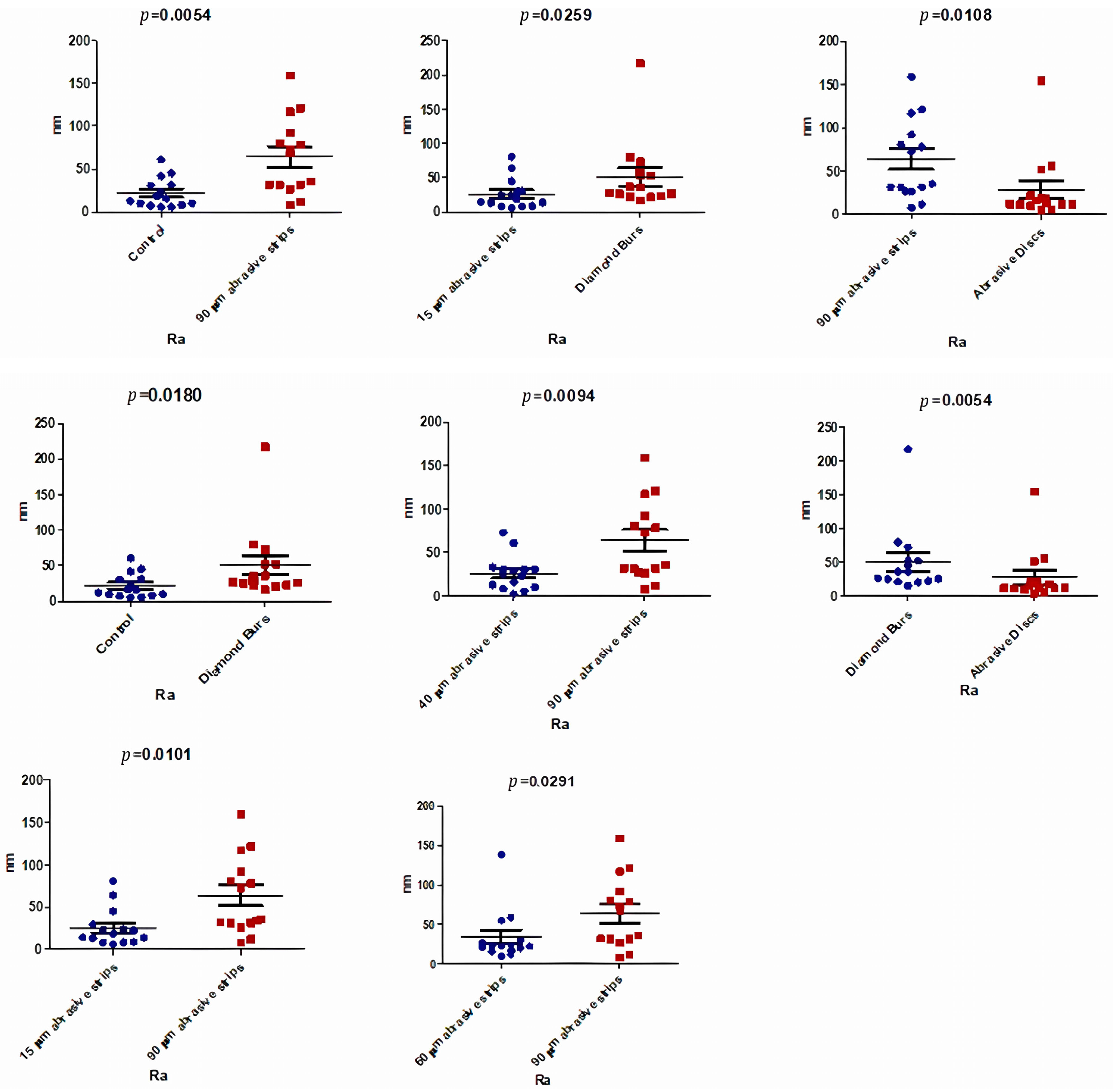
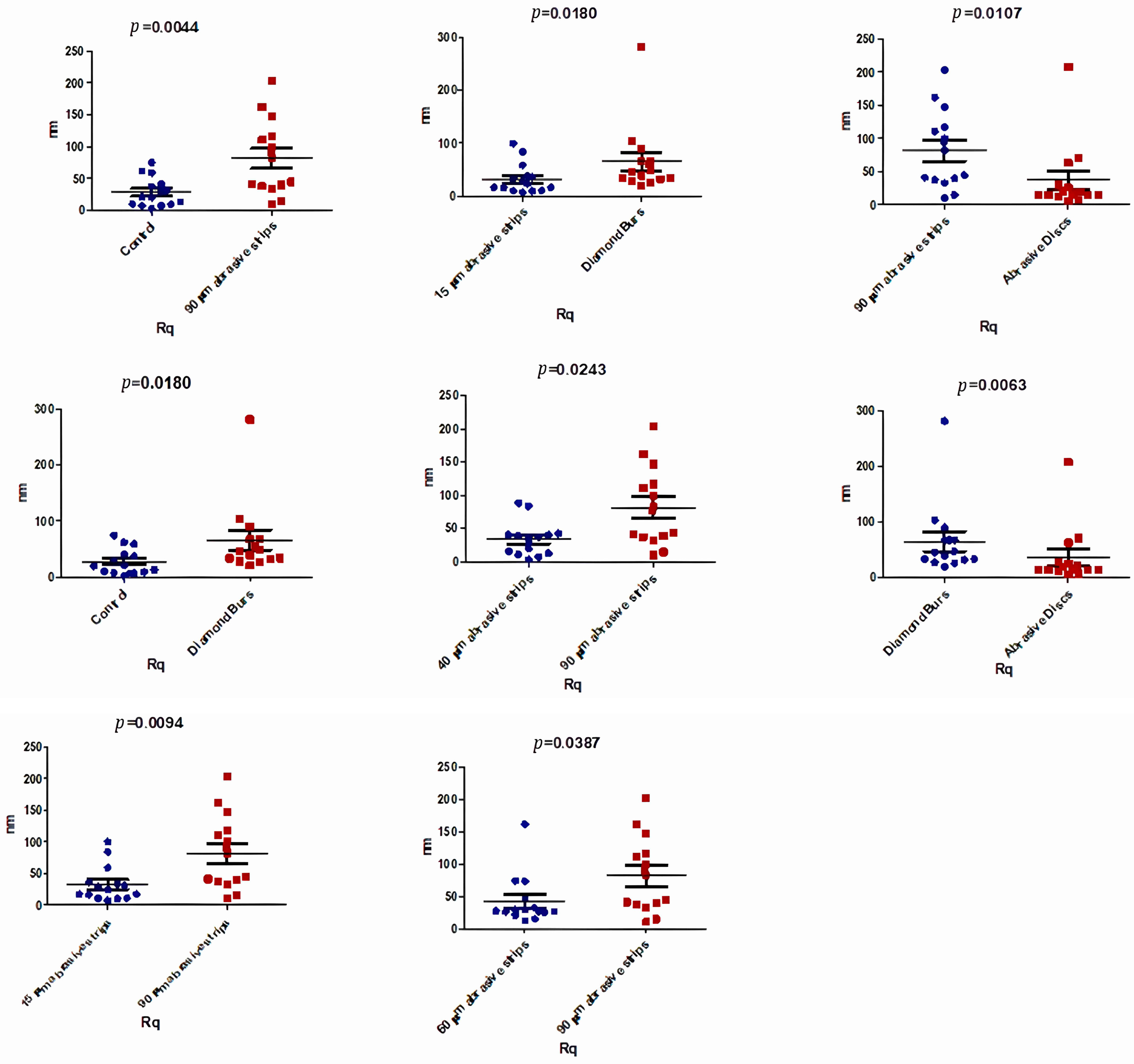
3.2. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meredith, L.; Farella, M.; Lowrey, S.; Cannon, R.D.; Mei, L. Atomic force microscopy analysis of enamel nanotopography after interproximal reduction. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2017, 151, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorobat, V.; Stanciu, D. Ortodontie si ortopedie dento-faciala. Bucur. Ed. Medicala 2014, 471–475. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, R.J.M. The primary and mixed dentition, post-eruptive enamel maturation and dental caries: A review. Int. Dent. J. 2013, 63, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, V.P.; Rossouw, P.E.; Basson, N.J. Orthodontic microabrasive reproximation. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1992, 102, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapenaite, E.; Lopatiene, K. Interproximal enamel reduction as a part of orthodontic treatment. Stomatologija 2014, 16, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Laganà, G.; Malara, A.; Lione, R.; Danesi, C.; Meuli, S.; Cozza, P. Enamel interproximal reduction during treatment with clear aligners: Digital planning versus OrthoCAD analysis. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossouw, P.E.; Tortorella, A. Enamel reduction procedures in orthodontic treatment. J Can Dent Assoc. 2003, 69, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frindel, C. Clear thinking about interproximal stripping. J. Dentofac. Anomalies Orthod. 2010, 13, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachrisson, B.U. Interdental papilla reconstruction in adult orthodontics. World J. Orthod. 2004, 5, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Skinner, H.C.W. Biominerals. Miner. Mag. 2005, 69, 621–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Menezes Oliveira, M.A.H.D.M.; Torres, C.P.; Gomes-Silva, J.M.; Chinelatti, M.A.; De Menezes, F.C.H.; Palma-Dibb, R.G.; Borsatto, M.C. Microstructure and mineral composition of dental enamel of permanent and deciduous teeth. Microsc. Res. Technol. 2010, 73, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorozini, M.; dos Reis Perez, C.; Rocha, G.M. Enamel sample preparation for AFM: Influence on roughness and morphology. Microsc. Res. Technol. 2018, 81, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, F.-Z.; Ge, J. New observations of the hierarchical structure of human enamel, from nanoscale to microscale. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2007, 1, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, S.; Luo, W.; Paine, M.; Fong, H.; Sarikaya, M.; Snead, M. Biological Organization of Hydroxyapatite Crystallites into a Fibrous Continuum Toughens and Controls Anisotropy in Human Enamel. J. Dent. Res. 2001, 80, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poggio, C.; Lombardini, M.; Colombo, M.; Bianchi, S. Impact of two toothpastes on repairing enamel erosion produced by a soft drink: An AFM in vitro study. J. Dent. 2010, 38, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Świetlicka, I.; Arczewska, M.; Muszyński, S.; Tomaszewska, E.; Świetlicki, M.; Kuc, D.; Mielnik-Błaszczak, M.; Gołacki, K.; Cieślak, K. Surface analysis of etched enamel modified during the prenatal period. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 222, 117271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitehead, K.; Verran, J. The Effect of Surface Topography on the Retention of Microorganisms. Food Bioprod. Process. 2006, 84, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teutle-Coyotecatl, B.; Contreras-Bulnes, R.; Rodríguez-Vilchis, L.E.; Scougall-Vilchis, R.J.; Velazquez-Enriquez, U.; Almaguer-Flores, A.; Arenas-Alatorre, J.A. Effect of Surface Roughness of Deciduous and Permanent Tooth Enamel on Bacterial Adhesion. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerci, B.B.; Roman, L.S.; Guariza-Filho, O.; Camargo, E.S.; Tanaka, O.M. Dental enamel roughness with different acid etching times: Atomic force microscopy study. Eur. J. Gen. Dent. 2012, 1, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugsompian, K.; Tansalarak, R.; Piyapattamin, T. Comparison of the Enamel Surface Roughness from Different Polishing Methods: Scanning Electron Microscopy and Atomic Force Microscopy Investigation. Eur. J. Dent. 2020, 14, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radlanski, R.J.; Jäger, A.; Schwestka, R.; Bertzbach, F. Plaque accumulations caused by interdental stripping. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1988, 94, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundgren, T.; Milleding, P.; Mohlin, B.; Nannmark, U. Restitution of enamel after interdental stripping. Swed. Dent J. 1993, 17, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Piacentini, C.; Sfondrini, G. A scanning electron microscopy comparison of enamel polishing methods after air-rotor stripping. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1996, 109, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danesh, G.; Hellak, A.; Lippold, C.; Ziebura, T.; Schafer, E. Enamel Surfaces Following Interproximal Reduction with Different Methods. Angle Orthod. 2007, 77, 1004–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zachrisson, B.U.; Minster, L.; Øgaard, B.; Birkhed, D. Dental health assessed after interproximal enamel reduction: Caries risk in posterior teeth. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2011, 139, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quirynen, M.; Bollen, C.M.L. The influence of surface roughness and surface-free energy on supra- and subgingival plaque formation in man: A review of the literature. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1995, 22, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quirynen, M.; Bollen, C.M.; Papaioannou, W.; Van Eldere, J.; Van Steenberghe, D. The influence of titanium abutment surface roughness on plaque accumulation and gingivitis: Short-term observations. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 1996, 11, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karan, S.; Kircelli, B.H.; Tasdelen, B. Enamel surface roughness after debonding: Comparison of two different burs. Angle Orthod. 2010, 80, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollenl, C.M.; Lambrechts, P.; Quirynen, M. Comparison of surface roughness of oral hard materials to the threshold surface roughness for bacterial plaque retention: A review of the literature. Dent. Mater. 1997, 13, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, N.; Shashikiran, N.; Singla, S.; Ravi, K.; Kulkarni, V. Atomic force microscopic comparison of remineralization with casein-phosphopeptide amorphous calcium phosphate paste, acidulated phosphate fluoride gel and iron supplement in primary and permanent teeth: An in-vitro study. Contemp. Clin. Dent. 2014, 5, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batina, N.; Renugopalakrishnan, V.; Lavín, P.C.; Guerrero, J.C.H.; Morales, M.; Garduño-Juárez, R. An atomic force microscopic study of the ultrastructure of dental enamel afflicted with amelogenesis imperfecta. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2002, 13, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cheng, Z.-J.; Wang, X.-M.; Cui, F.-Z.; Ge, J.; Yan, J.-X. The enamel softening and loss during early erosion studied by AFM, SEM and nanoindentation. Biomed. Mater. 2009, 4, 015020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SO/TS 11405; Dentistry—Testing of Adhesion to Tooth Structure. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. Available online: https://cdn.standards.iteh.ai/samples/62898/c8afc682cda547d797cf339c726837ce/ISO-TS-11405-2015.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Vartolomei, A.-C.; Serbanoiu, D.-C.; Ghiga, D.-V.; Moldovan, M.; Cuc, S.; Pollmann, M.C.F.; Pacurar, M. Comparative Evaluation of Two Bracket Systems’ Kinetic Friction: Conventional and Self-Ligating. Materials 2022, 15, 4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pytko-Polonczyk, J.J.; Jakubik, A.; Przeklasa-Bierowiec, A.; Muszynska, B. Artificial saliva and its use in biological experiments. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 68, 807–813. [Google Scholar]
- Serbanoiu, D.-C.; Vartolomei, A.-C.; Ghiga, D.-V.; Pop, S.I.; Panainte, I.; Moldovan, M.; Sarosi, C.; Petean, I.; Boileau, M.-J.; Pacurar, M. Comparative Evaluation of Dental Enamel Microhardness Following Various Methods of Interproximal Reduction: A Vickers Hardness Tester Investigation. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tisler, C.E.; Moldovan, M.; Petean, I.; Buduru, S.D.; Prodan, D.; Sarosi, C.; Leucuţa, D.-C.; Chifor, R.; Badea, M.E.; Ene, R. Human Enamel Fluorination Enhancement by Photodynamic Laser Treatment. Polymers 2022, 14, 2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, L.; Zheng, L.; Xiao, H.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, Z. Wear mechanism of human tooth enamel: The role of interfacial protein bonding between HA crystals. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 110, 103845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iosif, C.; Cuc, S.; Prodan, D.; Moldovan, M.; Petean, I.; Badea, M.E.; Sava, S.; Tonea, A.; Chifor, R. Effects of Acidic Environments on Dental Structures after Bracket Debonding. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beniash, E.; Stifler, C.A.; Sun, C.-Y.; Jung, G.S.; Qin, Z.; Buehler, M.J.; Gilbert, P.U.P.A. The hidden structure of human enamel. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippert, F.; Parker, D.M.; Jandt, K.D. In vitro demineralization/remineralization cycles at human tooth enamel surfaces investigated by AFM and nanoindentation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 280, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habelitz, S.; Marshall, S.; Marshall, G.; Balooch, M. Mechanical properties of human dental enamel on the nanometre scale. Arch. Oral Biol. 2001, 46, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkea, M.; Jandt, K.D.; Parker, D.M. The Early Stages of Native Enamel Dissolution Studied with Atomic Force Microscopy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 232, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mester, A.; Moldovan, M.; Cuc, S.; Petean, I.; Tomuleasa, C.; Piciu, A.; Dinu, C.; Bran, S.; Onisor, F. Structural Changes in Resin-Based Composites in Saliva of Patients with Leukemia before Starting Chemotherapeutic Regimen. Polymers 2022, 14, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mester, A.; Moldovan, M.; Taulescu, M.; Sarosi, C.; Petean, I.; Vulpoi, A.; Piciu, A.; Voina-Tonea, A.; Moisescu-Goia, C.; Barbus, E.; et al. The Side Effects of Therapeutic Radioiodine-131 on the Structure of Enamel and Dentin in Permanent Human Teeth. Biology 2021, 10, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kravitz, N.D.; Kusnoto, B.; Agran, B.; Viana, G. Influence of Attachments and Interproximal Reduction on the Accuracy of Canine Rotation with Invisalign: A Prospective Clinical Study. Angle Orthod. 2008, 78, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arman, A.; Cehreli, S.B.; Ozel, E.; Arhun, N.; Çetinşahin, A.; Soyman, M. Qualitative and quantitative evaluation of enamel after various stripping methods. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2006, 130, 131.e7–131.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twesme, D.A.; Firestone, A.R.; Heaven, T.J.; Feagin, F.F.; Jacobson, A. Air-rotor stripping and enamel demineralization in vitro. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1994, 105, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dummer, P.M.H.; Harrison, K.A. In vitro plaque formation on commonly used dental materials. J. Oral Rehabil. 1982, 9, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, L.; Busscher, H.J.; van der Mei, H.C.; Ren, Y. Influence of surface roughness on streptococcal adhesion forces to composite resins. Dent. Mater. 2011, 27, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crain, G.; Sheridan, J.J. Susceptibility to caries and periodontal disease after posterior air-rotor stripping. J. Clin. Orthod. 1990, 24, 84–85. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- El-Mangoury, N.H.; Moussa, M.M.; A Mostafa, Y.; Girgis, A.S. In-vivo remineralization after air-rotor stripping. J. Clin. Orthod. 1991, 25, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grocholewicz, K.; Janiszewska-Olszowska, J.; Szatkiewicz, T.; Tomkowski, R.; Tandecka, K. Effect of Orthodontic Debonding and Adhesive Removal on the Enamel—Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives—A Systematic Review. Med. Sci. Monit. 2014, 20, 1991–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, P.; Sharma, P.; Goje, S.K.; Kanzariya, N.; Parikh, M. Comparative evaluation of enamel surface roughness after debonding using four finishing and polishing systems for residual resin removal—An in vitro study. Prog. Orthod. 2019, 20, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, M.; Jost-Brinkmann, P.G.; Zellmann, M.; Zellmann, S.; Radlanski, R.J. Clinical Evaluation of a New Technique for Interdental Enamel Reduction. J. Orofac. Orthop./Fortschritte Der Kieferorthopädie 2000, 61, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, M.; Jost-Brinkmann, P.G.; Radlanski, R.J.; Miethke, R.R. SEM evaluation of a new technique for interdental stripping. J Clin. Orthod. 1999, 33, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

| Composition | Percentage % |
|---|---|
| Na2HPO4 NaHCO3 CaCl2 | 0.3 |
| HCl-1M | 0.3 |
| H2O | 99.4 |
| IPR Instrument | Model | Manufacturer | Grit | Handpiece |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abrasive strips 15 microns | EVA active on both sides | Task Inc., Tokyo, Japan | 15 μm | Slow speed (5000 rpm) |
| Abrasive strips 40 microns | EVA active on both sides | Task Inc., Tokyo, Japan | 40 μm | Slow speed (5000 rpm) |
| Abrasive strips 60 microns | EVA active on both sides | Task Inc., Tokyo, Japan | 60 μm | Slow speed (5000 rpm) |
| Abrasive strips 90 microns | EVA active on both sides | Task Inc., Tokyo, Japan | 90 μm | Slow speed (5000 rpm) |
| Burs | 8392 “mosquito” bur | Komet, Rock Hill, SC, USA | Red Fine grit | High speed (400,000 rpm) with water cooling |
| Discs | Sof Lex System Kit | 3M, Neuss, Germany | Orange Fine 20 μm | Slow speed (5000 rpm) |
| Peak Height (nm) | Control | 15 μm Abrasive Strips | 40 μm Abrasive Strips | 60 μm Abrasive Strips | 90 μm Abrasive Strips | Diamond Burs | Abrasive Discs | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of values | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | |
| Minimum | 51.00 | 48.00 | 21.00 | 79.00 | 110.0 | 115.0 | 33.00 | |
| Median | 153.5 | 147.0 | 216.0 | 179.5 | 415.0 | 309.0 | 123.0 | 0.0120 * |
| Maximum | 594.0 | 661.0 | 691.0 | 958.0 | 1600 | 2800 | 1800 | |
| Mean | 231.1 | 232.5 | 254.1 | 289.6 | 602.2 | 540.0 | 284.5 | |
| Std. Deviation | 185.8 | 206.9 | 204.8 | 249.1 | 501.5 | 681.0 | 455.0 |
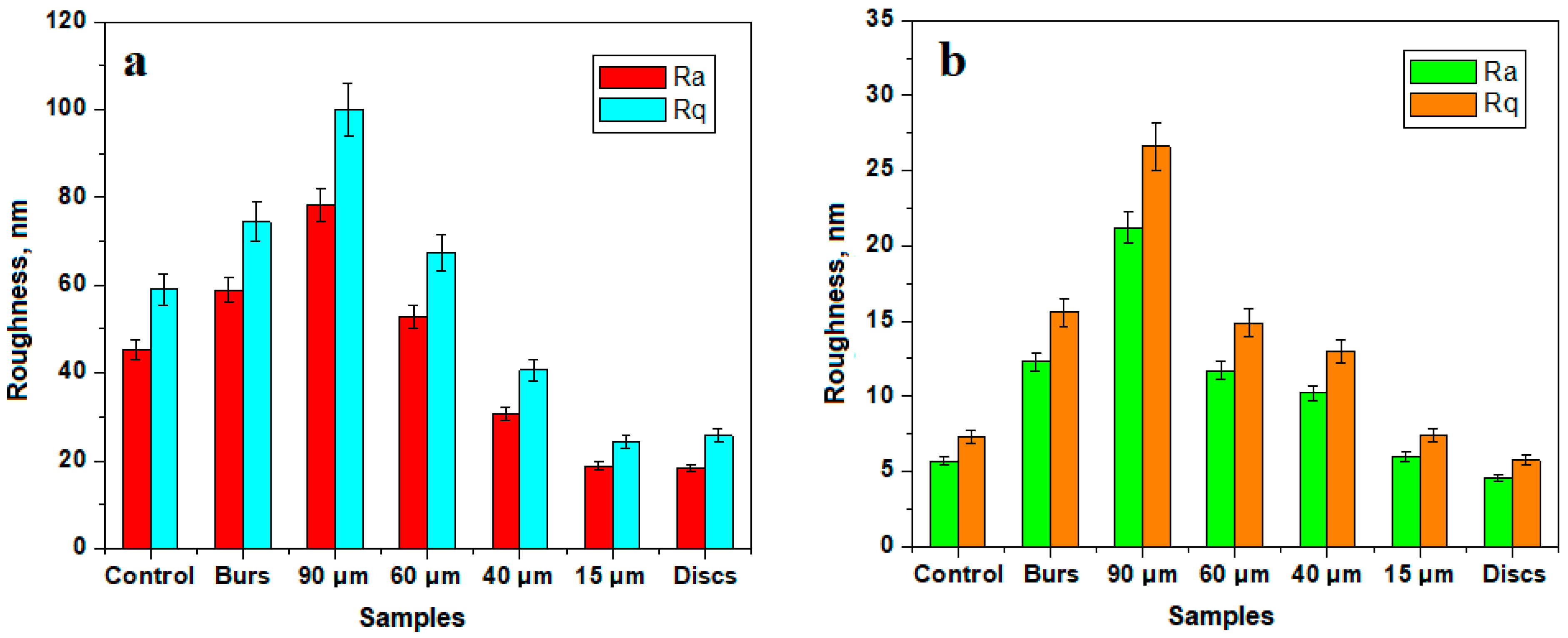
| Ra (nm) | Control | 15 μm Abrasive Strips | 40 μm Abrasive Strips | 60 μm Abrasive Strips | 90 μm Abrasive Strips | Diamond Burs | Abrasive Discs | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of values | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | |
| Minimum | 5.610 | 5.970 | 2.490 | 10.20 | 7.940 | 16.20 | 4.610 | |
| Median | 14.15 | 16.45 | 26.70 | 23.05 | 54.10 | 31.75 | 12.45 | 0.0042 * |
| Maximum | 60.90 | 80.40 | 73.10 | 138.0 | 159.0 | 217.0 | 155.0 | |
| Mean | 22.01 | 25.57 | 26.29 | 34.34 | 64.04 | 50.74 | 28.58 | |
| Std. Deviation | 17.49 | 22.60 | 20.31 | 33.02 | 46.15 | 51.75 | 39.60 |
| Rq (nm) | Control | 15 μm Abrasive Strips | 40 μm Abrasive Strips | 60 μm Abrasive Strips | 90 μm Abrasive Strips | Diamond Burs | Abrasive Discs | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of values | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | |
| Minimum | 2.600 | 7.450 | 3.140 | 12.60 | 10.50 | 20.30 | 5.730 | |
| Median | 20.45 | 20.70 | 36.90 | 28.45 | 63.45 | 42.70 | 15.40 | 0.0045 * |
| Maximum | 74.90 | 99.80 | 88.50 | 162.0 | 203.0 | 282.0 | 208.0 | |
| Mean | 28.11 | 32.55 | 34.29 | 43.09 | 81.69 | 65.80 | 37.04 | |
| Std. Deviation | 23.37 | 28.82 | 26.00 | 39.03 | 59.82 | 67.01 | 52.93 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Serbanoiu, D.-C.; Vartolomei, A.-C.; Ghiga, D.-V.; Moldovan, M.; Sarosi, C.; Petean, I.; Boileau, M.-J.; Pacurar, M. A Comparative Analysis of Enamel Surface Roughness Following Various Interproximal Reduction Techniques: An Examination Using Scanning Electron Microscopy and Atomic Force Microscopy. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1629. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12081629
Serbanoiu D-C, Vartolomei A-C, Ghiga D-V, Moldovan M, Sarosi C, Petean I, Boileau M-J, Pacurar M. A Comparative Analysis of Enamel Surface Roughness Following Various Interproximal Reduction Techniques: An Examination Using Scanning Electron Microscopy and Atomic Force Microscopy. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(8):1629. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12081629
Chicago/Turabian StyleSerbanoiu, Dan-Cosmin, Aurel-Claudiu Vartolomei, Dana-Valentina Ghiga, Marioara Moldovan, Codruta Sarosi, Ioan Petean, Marie-Jose Boileau, and Mariana Pacurar. 2024. "A Comparative Analysis of Enamel Surface Roughness Following Various Interproximal Reduction Techniques: An Examination Using Scanning Electron Microscopy and Atomic Force Microscopy" Biomedicines 12, no. 8: 1629. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12081629
APA StyleSerbanoiu, D.-C., Vartolomei, A.-C., Ghiga, D.-V., Moldovan, M., Sarosi, C., Petean, I., Boileau, M.-J., & Pacurar, M. (2024). A Comparative Analysis of Enamel Surface Roughness Following Various Interproximal Reduction Techniques: An Examination Using Scanning Electron Microscopy and Atomic Force Microscopy. Biomedicines, 12(8), 1629. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12081629








