Can We Go beyond Pathology? The Prognostic Role of Risk Scoring Tools for Cancer-Specific Survival of Patients with Bladder Cancer Undergoing Radical Cystectomy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
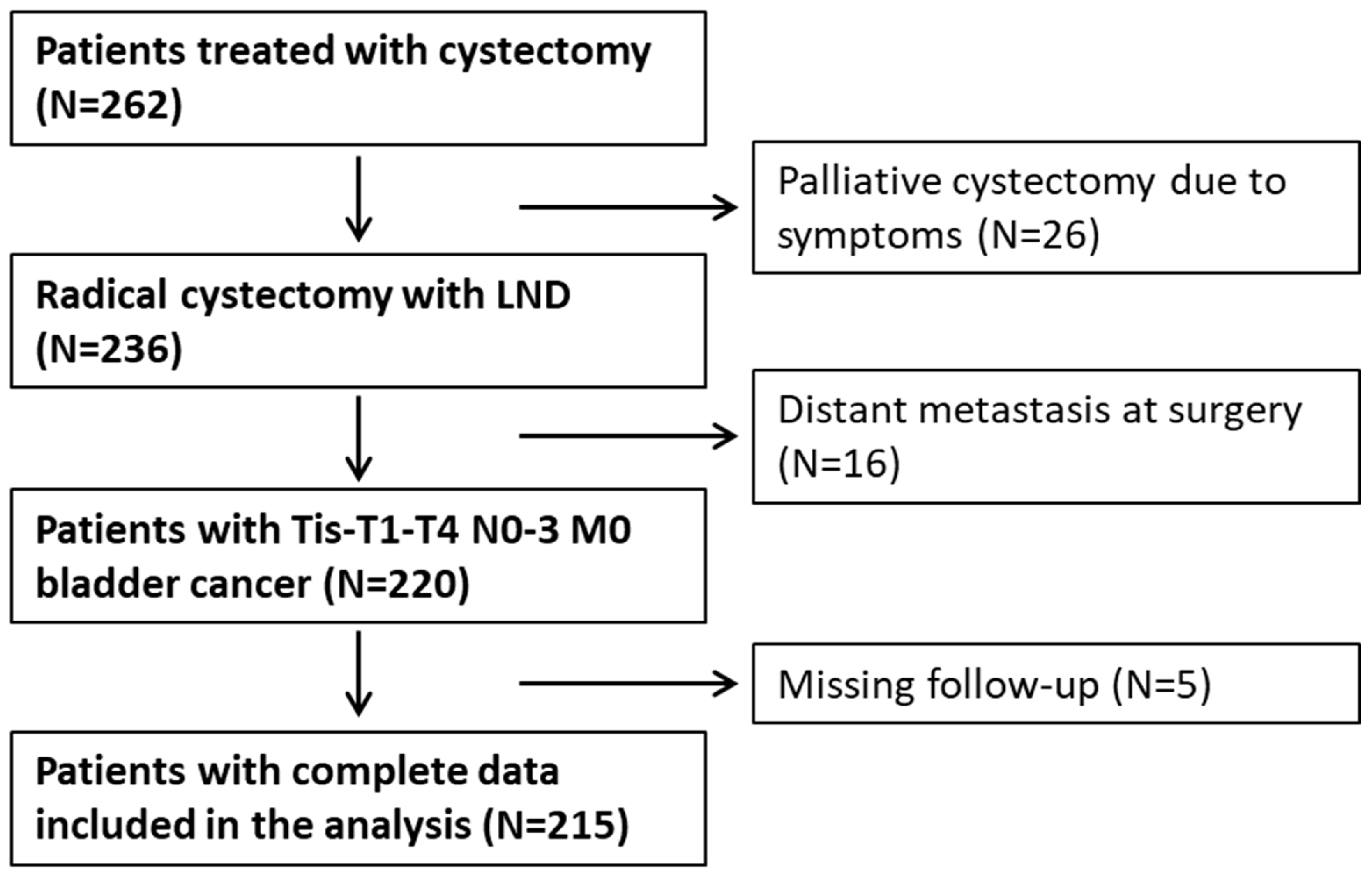
2.2. Data Acquisition
2.3. Ethics Statement
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Validation of Risk Models
3.2. Univariable Analyses for Cancer-Specific Mortality
3.3. Multivariable Analysis for Cancer-Specific Mortality
3.4. Multivariable Analysis for Overall Mortality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alfred Witjes, J.; Max Bruins, H.; Carrión, A.; Cathomas, R.; Compérat, E.; Efstathiou, J.A.; Fietkau, R.; Gakis, G.; Lorch, A.; Martini, A.; et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Muscle-Invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer: Summary of the 2023 Guidelines. Eur. Urol. 2024, 85, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretschmer, A.; Grimm, T.; Buchner, A.; Jokisch, F.; Ziegelmüller, B.; Casuscelli, J.; Schulz, G.; Stief, C.G.; Karl, A. Midterm Health-Related Quality of Life After Radical Cystectomy: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis. Eur. Urol. Focus 2020, 6, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zapała, Ł.; Ślusarczyk, A.; Korczak, B.; Kurzyna, P.; Leki, M.; Lipiński, P.; Miłow, J.; Niemczyk, M.; Pocheć, K.; Późniak, M.; et al. The View Outside of the Box: Reporting Outcomes Following Radical Cystectomy Using Pentafecta From a Multicenter Retrospective Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 841852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, E.; Djaladat, H. Long-Term Complications of Urinary Diversion. Curr. Opin. Urol. 2015, 25, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ślusarczyk, A.; Zapała, P.; Piecha, T.; Zapała, Ł.; Borkowski, T.; Radziszewski, P. Upper Urinary Tract Urothelial Cancer After Radical Cystectomy for Bladder Cancer: Survival Outcomes After Radical Nephroureterectomy. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2024, 31, 2144–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlson, M.E.; Pompei, P.; Ales, K.L.; MacKenzie, C.R. A New Method of Classifying Prognostic Comorbidity in Longitudinal Studies: Development and Validation. J. Chronic Dis. 1987, 40, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welty, C.J.; Sanford, T.H.; Wright, J.L.; Carroll, P.R.; Cooperberg, M.R.; Meng, M.V.; Porten, S.P. The Cancer of the Bladder Risk Assessment (COBRA) Score: Estimating Mortality after Radical Cystectomy. Cancer 2017, 123, 4574–4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprini, J.A.; Arcelus, J.I.; Hasty, J.H.; Tamhane, A.C.; Fabrega, F. Clinical Assessment of Venous Thromboembolic Risk in Surgical Patients. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 1991, 17 (Suppl. S3), 304–312. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aziz, A.; Gierth, M.; Rink, M.; Schmid, M.; Chun, F.K.; Dahlem, R.; Roghmann, F.; Palisaar, R.-J.; Noldus, J.; Ellinger, J.; et al. Optimizing Outcome Reporting after Radical Cystectomy for Organ-Confined Urothelial Carcinoma of the Bladder Using Oncological Trifecta and Pentafecta. World J. Urol. 2015, 33, 1945–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfister, C.; Gravis, G.; Fléchon, A.; Soulié, M.; Guy, L.; Laguerre, B.; Mottet, N.; Joly, F.; Allory, Y.; Harter, V.; et al. Randomized Phase III Trial of Dose-Dense Methotrexate, Vinblastine, Doxorubicin, and Cisplatin, or Gemcitabine and Cisplatin as Perioperative Chemotherapy for Patients with Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer. Analysis of the GETUG/AFU V05 VESPER Trial Secondary Endpoints: Chemotherapy Toxicity and Pathological Responses. Eur. Urol. 2021, 79, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powles, T.; Rosenberg, J.E.; Sonpavde, G.P.; Loriot, Y.; Durán, I.; Lee, J.-L.; Matsubara, N.; Vulsteke, C.; Castellano, D.; Wu, C.; et al. Enfortumab Vedotin in Previously Treated Advanced Urothelial Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1125–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Heijden, M.S.; Sonpavde, G.; Powles, T.; Necchi, A.; Burotto, M.; Schenker, M.; Sade, J.P.; Bamias, A.; Beuzeboc, P.; Bedke, J.; et al. Nivolumab plus Gemcitabine-Cisplatin in Advanced Urothelial Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 1778–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaig, T.W.; Spiess, P.E.; Abern, M.; Agarwal, N.; Bangs, R.; Boorjian, S.A.; Buyyounouski, M.K.; Chan, K.; Chang, S.; Friedlander, T.; et al. NCCN Guidelines® Insights: Bladder Cancer, Version 2.2022: Featured Updates to the NCCN Guidelines. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2022, 20, 866–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muilwijk, T.; Akand, M.; Soria, F.; Giordano, A.; Milenkovic, U.; Moris, L.; Gevaert, T.; Van Poppel, H.; Albersen, M.; Gontero, P.; et al. The Cancer of the Bladder Risk Assessment (COBRA) Score for Estimating Cancer-Specific Survival after Radical Cystectomy: External Validation in a Large Bi-Institutional Cohort. BJU Int. 2020, 126, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zapała, Ł.; Ślusarczyk, A.; Garbas, K.; Mielczarek, Ł.; Ślusarczyk, C.; Zapała, P.; Wróbel, A.; Radziszewski, P. Complete Blood Count-Derived Inflammatory Markers and Survival in Patients with Localized Renal Cell Cancer Treated with Partial or Radical Nephrectomy: A Retrospective Single-Tertiary-Center Study. Front. Biosci. Sch. Ed. 2022, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzbeierlein, J.M.; Bixler, B.R.; Buckley, D.I.; Chang, S.S.; Holmes, R.; James, A.C.; Kirkby, E.; McKiernan, J.M.; Schuckman, A.K. Diagnosis and Treatment of Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: AUA/SUO Guideline: 2024 Amendment. J. Urol. 2024, 211, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, B.; Liedberg, F.; Khan, M.S.; Nair, R.; Thurairaja, R.; Malde, S.; Kumar, P.; Bryan, R.T.; Van Hemelrijck, M. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Delay in Radical Cystectomy and the Effect on Survival in Bladder Cancer Patients. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2020, 3, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dybowski, B. Local Solutions to Shorten Treatment Delays in Bladder Cancer. Results of a Survey among CEJU Authors. Cent. Eur. J. Urol. 2023, 76, 280–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditonno, F.; Veccia, A.; Montanaro, F.; Pettenuzzo, G.; Franco, A.; Manfredi, C.; Triggiani, L.; De Nunzio, C.; De Sio, M.; Cerruto, M.; et al. Trimodal Therapy vs Radical Cystectomy in Patients with Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Comparative Studies. BJU Int. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powles, T.; Assaf, Z.J.; Degaonkar, V.; Grivas, P.; Hussain, M.; Oudard, S.; Gschwend, J.E.; Albers, P.; Castellano, D.; Nishiyama, H.; et al. Updated Overall Survival by Circulating Tumor DNA Status from the Phase 3 IMvigor010 Trial: Adjuvant Atezolizumab Versus Observation in Muscle-Invasive Urothelial Carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 2024, 85, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.B.; Kamat, A.M.; Chamie, K.; Froehner, M.; Wirth, M.P.; Wiklund, P.N.; Black, P.C.; Steinberg, G.D.; Boorjian, S.A.; Daneshmand, S.; et al. Systematic Review of Comorbidity and Competing-Risks Assessments for Bladder Cancer Patients. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2018, 1, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayr, R.; May, M.; Martini, T.; Lodde, M.; Comploj, E.; Pycha, A.; Strobel, J.; Denzinger, S.; Otto, W.; Wieland, W.; et al. Comorbidity and Performance Indices as Predictors of Cancer-Independent Mortality but Not of Cancer-Specific Mortality after Radical Cystectomy for Urothelial Carcinoma of the Bladder. Eur. Urol. 2012, 62, 662–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairey, A.S.; Jacobsen, N.-E.B.; Chetner, M.P.; Mador, D.R.; Metcalfe, J.B.; Moore, R.B.; Rourke, K.F.; Todd, G.T.; Venner, P.M.; Voaklander, D.C.; et al. Associations between Comorbidity, and Overall Survival and Bladder Cancer Specific Survival after Radical Cystectomy: Results from the Alberta Urology Institute Radical Cystectomy Database. J. Urol. 2009, 182, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenberg, M.S.; Boorjian, S.A.; Cheville, J.C.; Thompson, R.H.; Thapa, P.; Kaushik, D.; Frank, I. The SPARC Score: A Multifactorial Outcome Prediction Model for Patients Undergoing Radical Cystectomy for Bladder Cancer. J. Urol. 2013, 190, 2005–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.B.; Huo, J.; Chu, Y.; Baillargeon, J.G.; Daskivich, T.; Kuo, Y.-F.; Kosarek, C.D.; Kim, S.P.; Orihuela, E.; Tyler, D.S.; et al. Cancer and All-Cause Mortality in Bladder Cancer Patients Undergoing Radical Cystectomy: Development and Validation of a Nomogram for Treatment Decision-Making. Urology 2017, 110, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, A.J.; Djaladat, H.; Schuckman, A.; Miranda, G.; Cai, J.; Daneshmand, S. Venous Thromboembolism Following Radical Cystectomy: Significant Predictors, Comparison of Different Anticoagulants and Timing of Events. J. Urol. 2015, 193, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsayed, A.S.; Ozair, S.; Iqbal, U.; Mostowy, M.; Jing, Z.; Gibson, S.; Durrani, M.; Hussein, A.A.; Guru, K.A. Prevalence and Predictors of Venous Thromboembolism After Robot-Assisted Radical Cystectomy. Urology 2021, 149, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAlpine, K.; Breau, R.H.; Mallick, R.; Cnossen, S.; Cagiannos, I.; Morash, C.; Carrier, M.; Lavallée, L.T. Current Guidelines Do Not Sufficiently Discriminate Venous Thromboembolism Risk in Urology. Urol. Oncol. 2017, 35, 457.e1–457.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capitanio, U.; Suardi, N.; Shariat, S.F.; Lotan, Y.; Palapattu, G.S.; Bastian, P.J.; Gupta, A.; Vazina, A.; Schoenberg, M.; Lerner, S.P.; et al. Assessing the Minimum Number of Lymph Nodes Needed at Radical Cystectomy in Patients with Bladder Cancer. BJU Int. 2009, 103, 1359–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ślusarczyk, A.; Zapała, P.; Piecha, T.; Rajwa, P.; Moschini, M.; Radziszewski, P. The Association between Lymph Node Dissection and Survival in Lymph Node-Negative Upper Urinary Tract Urothelial Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 4660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruins, H.M.; Veskimae, E.; Hernandez, V.; Imamura, M.; Neuberger, M.M.; Dahm, P.; Stewart, F.; Lam, T.B.; N’Dow, J.; van der Heijden, A.G.; et al. The Impact of the Extent of Lymphadenectomy on Oncologic Outcomes in Patients Undergoing Radical Cystectomy for Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review. Eur. Urol. 2014, 66, 1065–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacciamani, G.E.; Ghodoussipour, S.; Mari, A.; Gill, K.S.; Desai, M.; Artibani, W.; Gill, P.S.; Shariat, S.F.; Gill, I.S.; Djaladat, H. Association between Smoking Exposure, Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Response and Survival Outcomes Following Radical Cystectomy: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Urol. 2020, 204, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ślusarczyk, A.; Zapała, P.; Zapała, Ł.; Radziszewski, P. The Impact of Smoking on Recurrence and Progression of Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 149, 2673–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rink, M.; Zabor, E.C.; Furberg, H.; Xylinas, E.; Ehdaie, B.; Novara, G.; Babjuk, M.; Pycha, A.; Lotan, Y.; Trinh, Q.-D.; et al. Impact of Smoking and Smoking Cessation on Outcomes in Bladder Cancer Patients Treated with Radical Cystectomy. Eur. Urol. 2013, 64, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofner, H.; Laukhtina, E.; Hassler, M.R.; Shariat, S.F. Blood-Based Biomarkers as Prognostic Factors of Recurrent Disease after Radical Cystectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zattoni, F.; Novara, G.; Iafrate, M.; Carletti, F.; Reitano, G.; Randazzo, G.; Ceccato, T.; Betto, G.; Dal Moro, F. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Prognostic Factor for Patients with Urothelial Carcinoma of the Bladder Following Radical Cystectomy. Cent. Eur. J. Urol. 2023, 76, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Chen, D.; Xing, X.-L. Comprehensive Analyses Revealed Eight Immune Related Signatures Correlated With Aberrant Methylations as Prognosis and Diagnosis Biomarkers for Kidney Renal Papillary Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2023, 21, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.; Xu, F.; Zhong, K.; Wang, S.; Xu, Q.; Huang, L.; Cheng, P. The Prognostic Role of Preoperative Circulating Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio in Primary Bladder Cancer Patients Undergoing Radical Cystectomy: A Meta-Analysis. World J. Urol. 2019, 37, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetterlein, M.W.; Seisen, T.; Leow, J.J.; Preston, M.A.; Sun, M.; Friedlander, D.F.; Meyer, C.P.; Chun, F.K.-H.; Lipsitz, S.R.; Menon, M.; et al. Effect of Nonurothelial Histologic Variants on the Outcomes of Radical Cystectomy for Nonmetastatic Muscle-Invasive Urinary Bladder Cancer. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2017, 16, e129–e139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naspro, R.; La Croce, G.; Finati, M.; Roscigno, M.; Pellucchi, F.; Sodano, M.; Manica, M.; Gianatti, A.; Da Pozzo, L.F. Oncological Outcomes of Concomitant Carcinoma in Situ at Radical Cystectomy in Pure Urothelial Bladder Cancer and in Histological Variants. Urol. Oncol. 2022, 40, 61.e9–61.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variables | Whole Cohort | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Pts/Median | % of Patients/IQR | ||
| Gender | male | 152 | 70.7 |
| female | 63 | 29.3 | |
| Age | years | 68 | 64–73 |
| BMI | kg/m2 | 25.3 | 22.2–29.3 |
| pT stage | 0 | 17 | 7.91 |
| 1 | 19 | 8.84 | |
| 2 | 52 | 24.19 | |
| 3 | 66 | 30.70 | |
| 4 | 39 | 18.14 | |
| Ta | 5 | 2.33 | |
| CIS | 17 | 7.91 | |
| Tumor grade | HG | 204 | 94.88 |
| LG | 11 | 5.12 | |
| Maximal staging | NMIBC | 29 | 13.49 |
| MIBC | 186 | 86.51 | |
| pN stage | 0 | 156 | 72.56 |
| 1 | 32 | 14.88 | |
| 2 | 24 | 11.16 | |
| 3 | 3 | 1.4 | |
| Lymph node density | 0 | 156 | 72.56 |
| 0–0.33 | 48 | 22.33 | |
| 0.34–0.49 | 4 | 1.86 | |
| ≥0.50 | 7 | 3.26 | |
| Lymph node yield | number | 10 | 6–15 |
| Concomitant CIS | no | 210 | 97.67 |
| yes | 5 | 2.33 | |
| Histology | TCC | 206 | 95.81 |
| SCC | 6 | 2.79 | |
| other | 3 | 1.40 | |
| Surgical margin status | R0 | 180 | 83.72 |
| R1 | 30 | 13.95 | |
| R2 | 5 | 2.33 | |
| Ureteral margin | negative | 201 | 93.49 |
| positive | 14 | 6.51 | |
| Urethral margin | negative | 202 | 93.95 |
| positive | 13 | 6.05 | |
| Length of hospitalization | days | 15 | 10–19 |
| Smoking status | never | 26 | 12.09 |
| former | 107 | 49.77 | |
| active | 71 | 33.02 | |
| unknown | 11 | 5.12 | |
| Blood transfusion | no | 95 | 44.19 |
| yes | 120 | 55.81 | |
| Neoadjuvant chemotherapy | no | 151 | 70.23 |
| yes | 64 | 29.77 | |
| Variables | Whole Cohort | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Pts/Median | % of Patients/IQR | ||
| AJCC system | 0 | 38 | 17.67 |
| I | 17 | 7.91 | |
| II | 40 | 18.60 | |
| IIIa | 92 | 42.79 | |
| IIIb | 27 | 12.56 | |
| COBRA nomogram | 0 | 53 | 24.65 |
| 1 | 42 | 19.53 | |
| 2 | 15 | 6.98 | |
| 3 | 55 | 25.58 | |
| 4 | 34 | 15.81 | |
| 5 | 9 | 4.19 | |
| 6 | 7 | 3.26 | |
| Simplified COBRA | low risk | 95 | 44.19 |
| intermediate risk | 104 | 48.37 | |
| high risk | 16 | 7.44 | |
| ASA scale | 1 | 18 | 8.37 |
| 2 | 79 | 36.74 | |
| 3 | 102 | 47.44 | |
| 4 | 16 | 7.44 | |
| Charlson comorbidity index | score | 5 | 4–6 |
| Charlson comorbidity index | ≤5 | 135 | 62.79 |
| >5 | 80 | 37.21 | |
| Caprini score | ≤12 | 166 | 77.21 |
| >12 | 49 | 22.79 | |
| Improve score | ≤3 | 180 | 83.72 |
| >3 | 35 | 16.28 | |
| Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio | ≤3.5 | 86 | 40 |
| >3.5 | 129 | 60 | |
| Systemic immune-inflammation index | ≤650 | 76 | 35.35 |
| >650 | 139 | 64.65 | |
| Neutrophil to erythrocyte ratio | ≤1.2 | 81 | 37.67 |
| >1.2 | 134 | 62.33 | |
| Hemoglobin concentration | <12 g/dL | 121 | 56.28 |
| ≥12 g/dL | 94 | 43.72 | |
| Variables | HR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | female | ref | ||
| male | 1.14 | 0.61–2.13 | 0.69 | |
| Age | years | 1.03 | 0.99–1.06 | 0.17 |
| BMI | kg/m2 | 0.95 | 0.88–1.03 | 0.21 |
| pT Stage | 0 | ref | ||
| 1 | 2.01 | 0.37–10.96 | 0.42 | |
| 2 | 1.56 | 0.34–7.23 | 0.57 | |
| 3 | 2.57 | 0.59–11.15 | 0.21 | |
| 4 | 5.07 | 1.18–21.86 | 0.03 | |
| Ta | 1.47 | 0.13–16.3 | 0.75 | |
| CIS | 0.53 | 0.05–5.8 | 0.6 | |
| Tumor grade | LG | ref | ||
| HG | 3.09 | 0.43–22.37 | 0.26 | |
| pN stage | 0 | ref | ||
| 1 | 1.77 | 0.86–3.62 | 0.12 | |
| 2 | 5.83 | 2.85–11.95 | <0.01 | |
| 3 | 2.29 | 0.31–16.91 | 0.42 | |
| Lymph node density | 0 | ref | ||
| 0–0.33 | 2.31 | 1.27–4.2 | 0.01 | |
| 0.34–0.49 | 5.83 | 0.76–44.67 | 0.09 | |
| ≥0.50 | 8.17 | 2.81–23.79 | <0.01 | |
| Lymph node yield | number | 0.96 | 0.92–1.01 | 0.1 |
| Concomitant CIS | no | ref | ||
| yes | 3.14 | 0.75–13.15 | 0.12 | |
| Histology | TCC | ref | ||
| other | 5.7 | 1.36–23.93 | 0.02 | |
| SCC | 0.71 | 0.1–5.16 | 0.73 | |
| Surgical margin status | R0 | ref | ||
| R1 | 2.19 | 1.14–4.21 | 0.02 | |
| R2 | 13.89 | 2.91–66.37 | <0.01 | |
| Ureteral margin | negative | ref | ||
| positive | 1.71 | 0.77–3.83 | 0.19 | |
| Urethral margin | negative | ref | ||
| positive | 2.45 | 1.1–5.44 | 0.03 | |
| Length of hospitalization | days | 1.02 | 1–1.03 | 0.03 |
| Smoking status | former | ref | ||
| never | 1.89 | 0.81–4.42 | 0.14 | |
| active | 2.61 | 1.41–4.85 | <0.01 | |
| unknown | 1.33 | 0.18–10.16 | 0.78 | |
| Blood transfusion | no | ref | ||
| yes | 1.98 | 1.1–3.57 | 0.02 | |
| Neoadjuvant chemotherapy | no | ref | ||
| yes | 0.9 | 0.48–1.7 | 0.75 | |
| AJCC system | 0 | ref | ||
| I | 1.62 | 0.27–9.72 | 0.6 | |
| II | 2.21 | 0.55–8.85 | 0.26 | |
| IIIa | 4.11 | 1.25–13.5 | 0.02 | |
| IIIb | 12.92 | 3.61–46.27 | <0.01 | |
| COBRA nomogram | 1.46 | 1.22–1.74 | <0.01 | |
| Simplified COBRA | low risk | ref | ||
| intermediate risk | 2.27 | 1.19–4.33 | 0.01 | |
| high risk | 7.67 | 3–19.58 | <0.01 | |
| ASA | 2 | ref | ||
| 1 | 0.75 | 0.17–3.24 | 0.7 | |
| 3 | 1.17 | 0.64–2.14 | 0.61 | |
| 4 | 1.91 | 0.75–4.85 | 0.17 | |
| Caprini score | ≤12 | ref | ||
| >12 | 0.83 | 0.44–1.55 | 0.55 | |
| Improve score | ≤3 | ref | ||
| >3 | 1.17 | 0.58–2.36 | 0.65 | |
| Charlson comorbidity index | 1.18 | 1.01–1.37 | 0.04 | |
| Non-age-adjusted Charlson Comorbidity Index | 1.21 | 1.00–1.46 | 0.05 | |
| High Charlson comorbidity index | ≤5 | ref | ||
| >5 | 1.95 | 1.12–3.37 | 0.02 | |
| Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio | ≤3.5 | ref | ||
| >3.5 | 1.87 | 1.09–3.23 | 0.02 | |
| Systemic immune-inflammation index | ≤650 | ref | ||
| >650 | 2.63 | 1.28–5.41 | 0.01 | |
| Neutrophil to erythrocyte ratio | ≤1.2 | ref | ||
| >1.2 | 2.035 | 1.07–3.88 | 0.03 | |
| Hemoglobin concentration | ≥12 g/dL | ref | ||
| <12 g/dL | 1.38 | 0.8–2.39 | 0.25 |
| Multivariable Analysis for Cancer-Specific Mortality | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | HR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| AJCC system | 0 | ref | ||
| I | 1.3 | 0.20–8.31 | 0.78 | |
| II | 2.59 | 0.62–10.74 | 0.19 | |
| IIIa | 3.39 | 1.01–11.39 | 0.05 | |
| IIIb | 23.25 | 6.06–89.26 | <0.01 | |
| Charlson comorbidity index | ≤5 | ref | ||
| >5 | 2.72 | 1.45–5.11 | <0.01 | |
| Smoking status | former | ref | ||
| never | 2.71 | 1.06–6.9 | 0.04 | |
| active | 2.85 | 1.47–5.53 | <0.01 | |
| unknown | 2.98 | 0.35–25.03 | 0.32 | |
| Concomitant CIS | no | ref | ||
| yes | 18.09 | 3.41–96.03 | <0.01 | |
| Histology | TCC | ref | ||
| other | 21.24 | 3.97–113.73 | <0.01 | |
| SCC | 2.31 | 0.27–20.18 | 0.45 | |
| Lymph node yield | 0.91 | 0.86–0.97 | <0.01 | |
| Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio | >3.5 | ref | ||
| ≤3.5 | 1.80 | 1.01–3.21 | 0.046 | |
| Multivariable Analysis for Overall Mortality | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | HR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| AJCC system | 0 | ref | ||
| I | 2.34 | 0.56–9.88 | 0.25 | |
| II | 1.79 | 0.49–6.56 | 0.38 | |
| IIIa | 3.02 | 1.06–8.63 | 0.04 | |
| IIIb | 18.34 | 5.47–61.51 | <0.01 | |
| Charlson comorbidity index | ≤5 | ref | ||
| >5 | 1.82 | 1–3.3 | 0.05 | |
| Smoking status | former | ref | ||
| never | 2.02 | 0.87–4.71 | 0.10 | |
| active | 2.55 | 1.36–4.78 | <0.01 | |
| unknown | 2.1 | 0.26–17.08 | 0.49 | |
| Concomitant CIS | no | ref | ||
| yes | 9.49 | 1.92–46.94 | 0.01 | |
| Histology | TCC | ref | ||
| other | 10.84 | 2.13–55.13 | 0.01 | |
| SCC | 2.31 | 0.26–20.94 | 0.46 | |
| Lymph node yield | 0.92 | 0.87–0.96 | <0.01 | |
| Age | 1.04 | 1–1.08 | 0.09 | |
| Systemic immune-inflammation index | ≤650 | ref | ||
| >650 | 1.99 | 1.03–3.87 | 0.04 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ślusarczyk, A.; Wolański, R.; Miłow, J.; Piekarczyk, H.; Lipiński, P.; Zapała, P.; Niemczyk, G.; Kurzyna, P.; Wróbel, A.; Różański, W.; et al. Can We Go beyond Pathology? The Prognostic Role of Risk Scoring Tools for Cancer-Specific Survival of Patients with Bladder Cancer Undergoing Radical Cystectomy. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1541. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071541
Ślusarczyk A, Wolański R, Miłow J, Piekarczyk H, Lipiński P, Zapała P, Niemczyk G, Kurzyna P, Wróbel A, Różański W, et al. Can We Go beyond Pathology? The Prognostic Role of Risk Scoring Tools for Cancer-Specific Survival of Patients with Bladder Cancer Undergoing Radical Cystectomy. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(7):1541. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071541
Chicago/Turabian StyleŚlusarczyk, Aleksander, Rafał Wolański, Jerzy Miłow, Hanna Piekarczyk, Piotr Lipiński, Piotr Zapała, Grzegorz Niemczyk, Paweł Kurzyna, Andrzej Wróbel, Waldemar Różański, and et al. 2024. "Can We Go beyond Pathology? The Prognostic Role of Risk Scoring Tools for Cancer-Specific Survival of Patients with Bladder Cancer Undergoing Radical Cystectomy" Biomedicines 12, no. 7: 1541. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071541
APA StyleŚlusarczyk, A., Wolański, R., Miłow, J., Piekarczyk, H., Lipiński, P., Zapała, P., Niemczyk, G., Kurzyna, P., Wróbel, A., Różański, W., Radziszewski, P., & Zapała, Ł. (2024). Can We Go beyond Pathology? The Prognostic Role of Risk Scoring Tools for Cancer-Specific Survival of Patients with Bladder Cancer Undergoing Radical Cystectomy. Biomedicines, 12(7), 1541. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071541





