p53 Genetics and Biology in Lung Carcinomas: Insights, Implications and Clinical Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
Other Relevant Tumor Suppressors
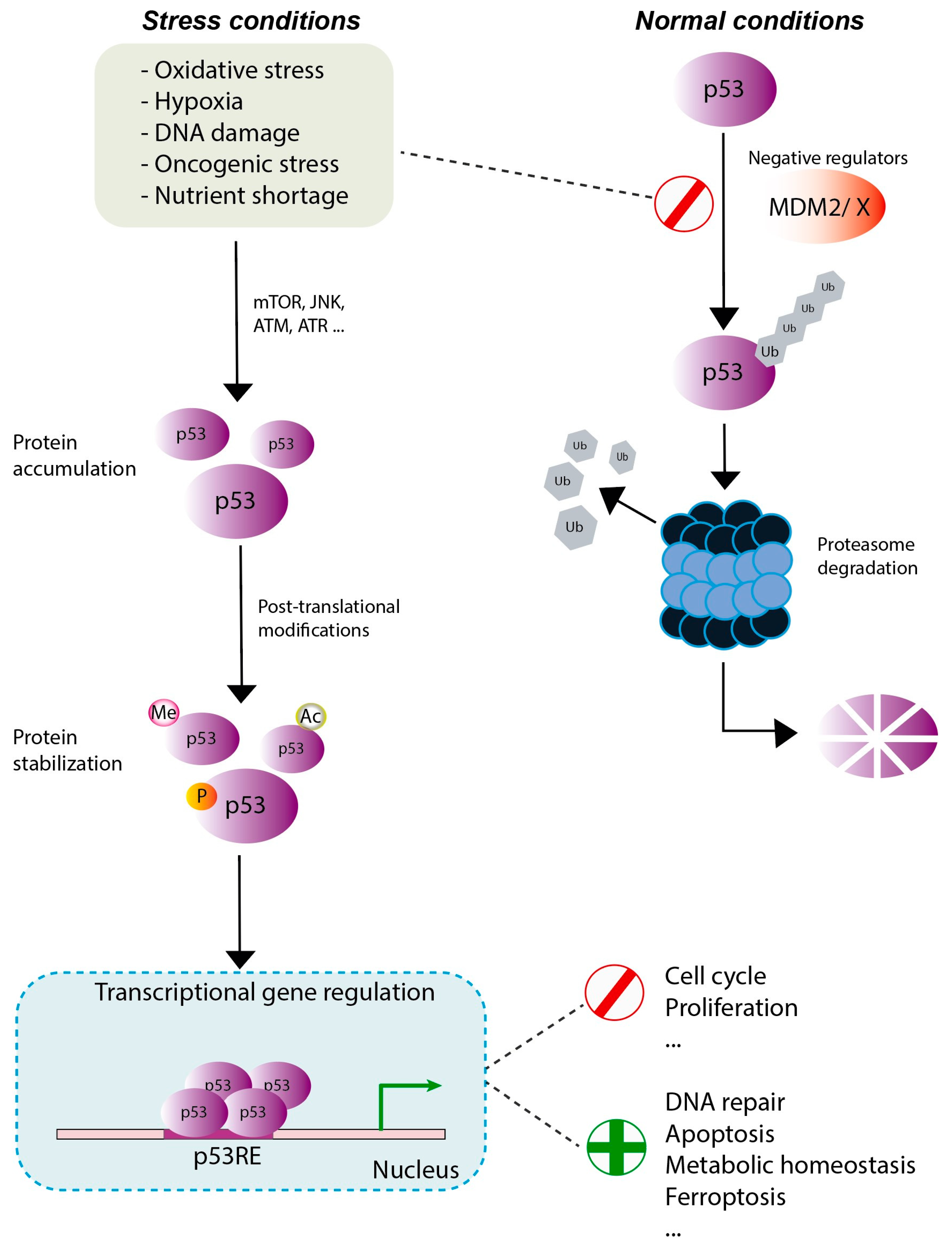
2. p53: Gene and Protein
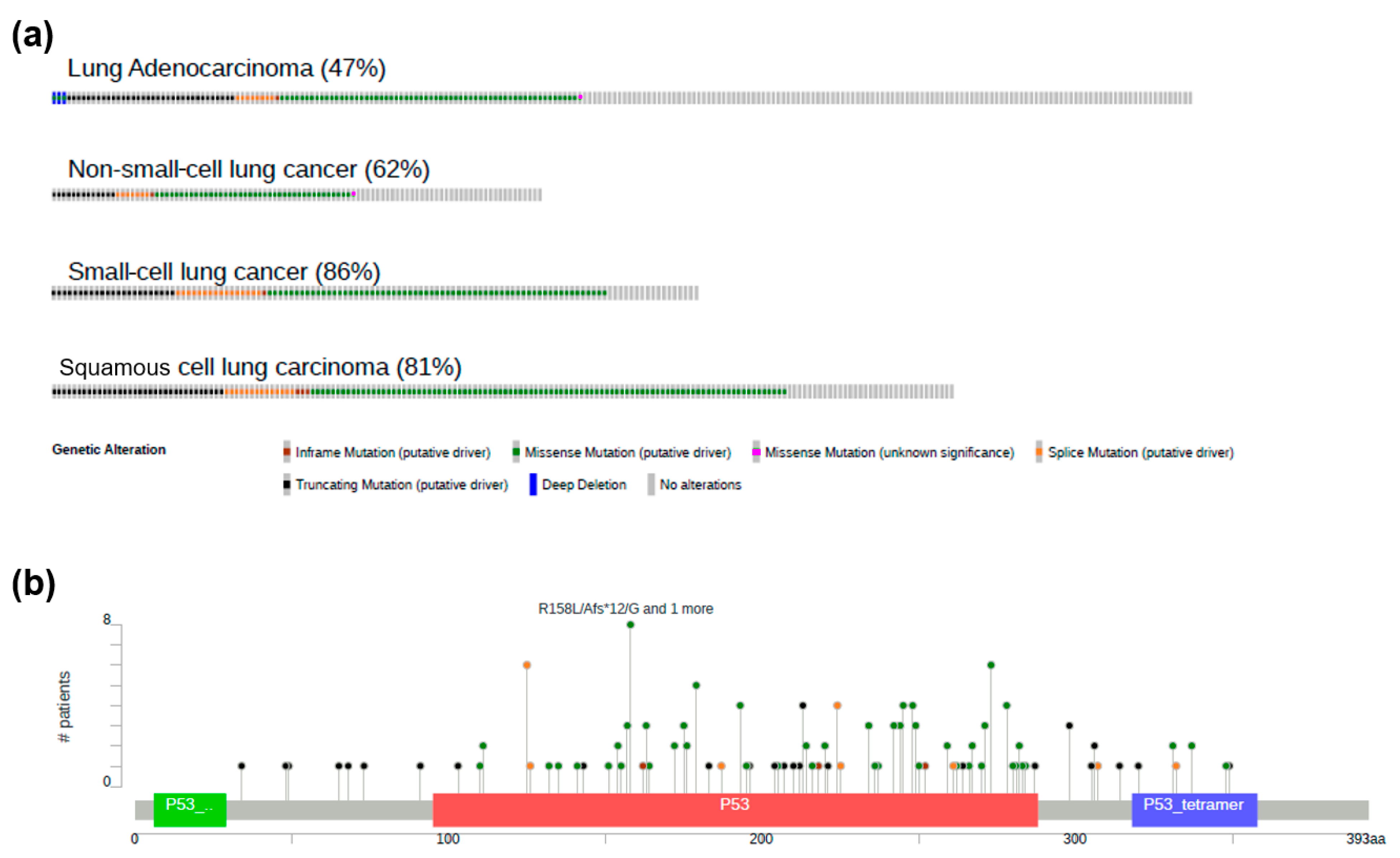
3. LC and p53
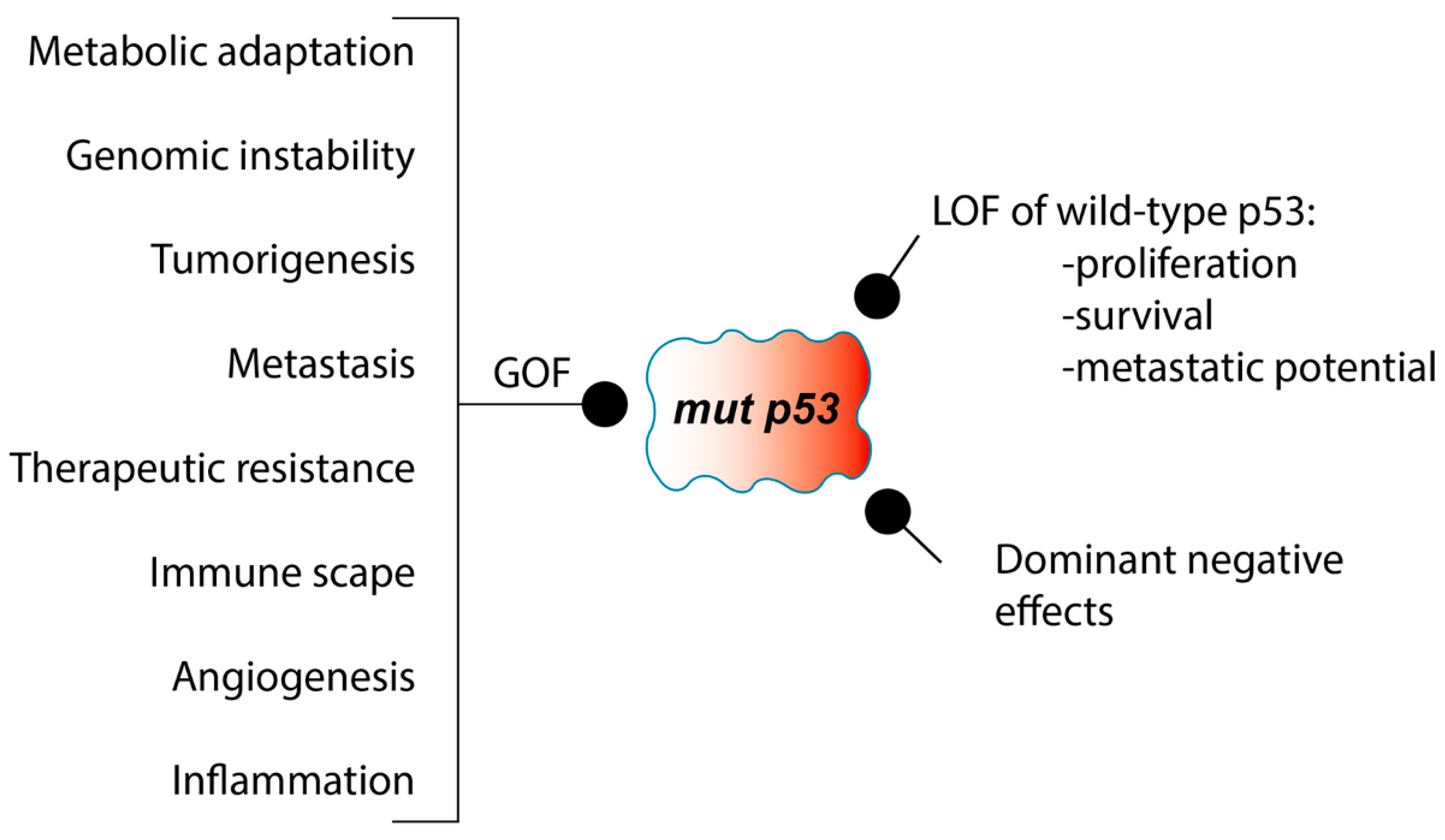
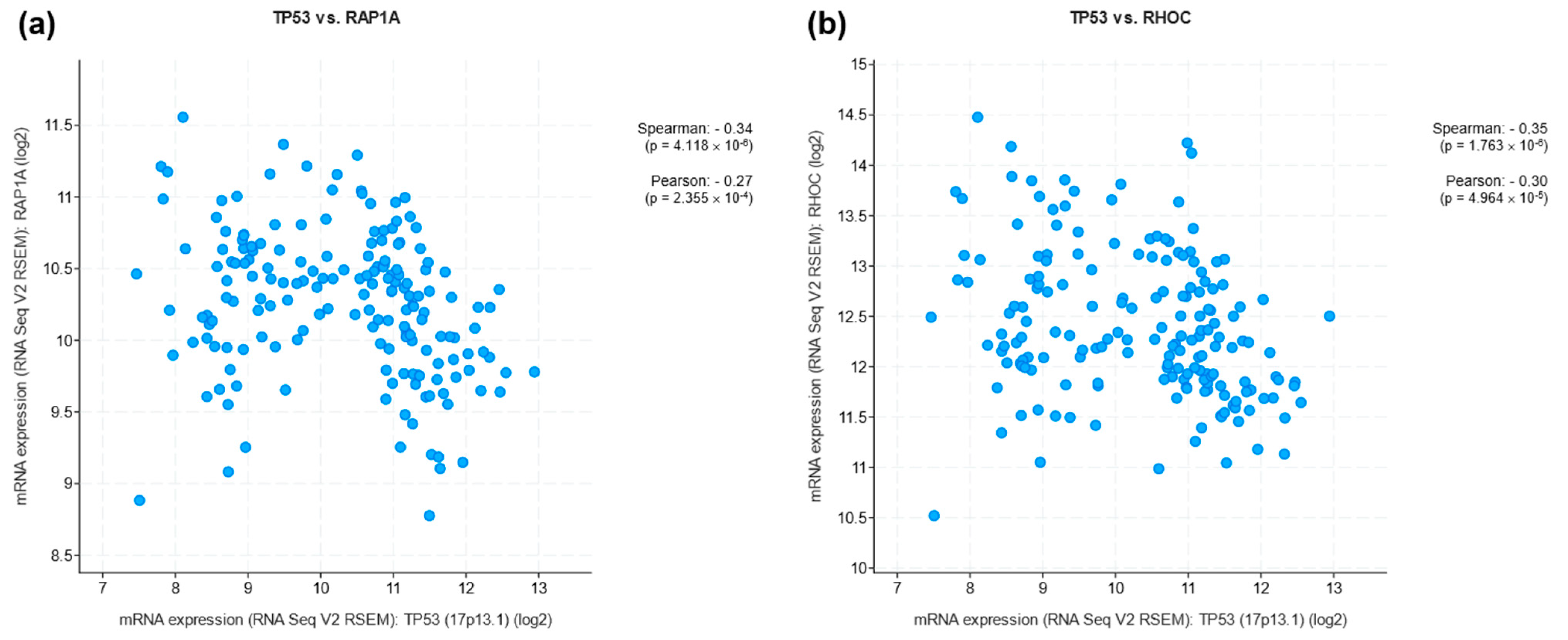
LOF and GOF of p53 in LC
4. p53: Clinical Applications and Therapies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Acronyms
| AKT | Protein kinase B | LUSC | Lung squamous cell carcinoma |
| ALK | Anaplastic lymphoma kinase | MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase | MDM2 | Mouse double minute 2 homolog |
| AT1 | Alveolar type 1 | MDMX | Mouse double minute X |
| AT2 | Alveolar type 2 | mRNA | Messenger RNA |
| ATM | Ataxia telangiectasia mutated | mTOR | Mammalian target of rapamycin |
| ATR | Ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related protein | NGS | Next-generation sequencing |
| CDKN2A | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A | NSCLC | Non-small-cell lung cancer |
| CTD | C-terminal domain | OD | Oligomerization domain |
| ctDNA | Circulating tumor DNA | p53RE | p53-response elements |
| DBD | DNA-binding domain | PARP | Poly-ADP ribose polymerase |
| DLL3 | Delta-like ligand 3 | PD-1 | Programmed cell death protein 1 |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid | PD-L1 | Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 |
| DNMT | DNA methyltransferase | PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor | PRD | Proline-rich domain |
| FLp53 | Full-length p53 | PTEN | Phosphatase and tensin homolog |
| GOF | Gain of function | Rap1A | Ras-associated protein 1A |
| HDAC | Histone deacetylase | Rb1 | Retinoblastoma 1 protein |
| ICIs | Immune checkpoint inhibitors | RhoC | Ras homolog family member C |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase | SCLC | Small-cell lung cancer |
| LC | Lung cancer | TAD | Transactivation domain |
| LOF | Loss of function | YAP | Yes-associated protein |
| LUAD | Lung adenocarcinoma |
References
- Vogelstein, B.; Lane, D.; Levine, A.J. Surfing the P53 Network. Nature 2000, 408, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aylon, Y.; Oren, M. The Paradox of P53: What, How, and Why? Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a026328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dejosez, M.; Ura, H.; Brandt, V.L.; Zwaka, T.P. Safeguards for Cell Cooperation in Mouse Embryogenesis Shown by Genome-Wide Cheater Screen. Science 2013, 341, 1511–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vousden, K.H.; Prives, C. Blinded by the Light: The Growing Complexity of P53. Cell 2009, 137, 413–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenzelmann Broz, D.; Mello, S.S.; Bieging, K.T.; Jiang, D.; Dusek, R.L.; Brady, C.A.; Sidow, A.; Attardi, L.D. Global Genomic Profiling Reveals an Extensive P53-Regulated Autophagy Program Contributing to Key P53 Responses. Genes Dev. 2013, 27, 1016–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoulidis, F.; Heymach, J.V. Co-Occurring Genomic Alterations in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Biology and Therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, A.J.; Oren, M. The First 30 Years of P53: Growing Ever More Complex. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuval, A.; Strandgren, C.; Heldin, A.; Palomar-Siles, M.; Wiman, K.G. Pharmacological Reactivation of P53 in the Era of Precision Anticancer Medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 21, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Sheng, J.; Tang, C.; Nandakumar, V.; Ye, H.; Ji, H.; Tang, H.; Qin, Y.; Guan, H.; Lou, F.; et al. Frequent Mutations in EGFR, KRAS and TP53 Genes in Human Lung Cancer Tumors Detected by Ion Torrent DNA Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopoulos, P.; Dietz, S.; Kirchner, M.; Volckmar, A.L.; Endris, V.; Neumann, O.; Ogrodnik, S.; Heussel, C.P.; Herth, F.J.; Eichhorn, M.; et al. Detection of TP53 Mutations in Tissue or Liquid Rebiopsies at Progression Identifies ALK+ Lung Cancer Patients with Poor Survival. Cancers 2019, 11, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papavassiliou, K.A.; Sofianidi, A.A.; Gogou, V.A.; Anagnostopoulos, N.; Papavassiliou, A.G. P53 and Rb Aberrations in Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC): From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Modulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkhart, D.L.; Sage, J. Cellular Mechanisms of Tumour Suppression by the Retinoblastoma Gene. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.S.; Salmena, L.; Pandolfi, P.P. The Functions and Regulation of the PTEN Tumour Suppressor. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwakawa, R.; Kohno, T.; Totoki, Y.; Shibata, T.; Tsuchihara, K.; Mimaki, S.; Tsuta, K.; Narita, Y.; Nishikawa, R.; Noguchi, M.; et al. Expression and Clinical Significance of Genes Frequently Mutated in Small Cell Lung Cancers Defined by Whole Exome/RNA Sequencing. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velez, M.G.; Kosiorek, H.E.; Egan, J.B.; McNatty, A.L.; Riaz, I.B.; Hwang, S.R.; Stewart, G.A.; Ho, T.H.; Moore, C.N.; Singh, P.; et al. Differential Impact of Tumor Suppressor Gene (TP53, PTEN, RB1) Alterations and Treatment Outcomes in Metastatic, Hormone-Sensitive Prostate Cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022, 25, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, C.; Zhang, B.; Zheng, J.; Singh, P.K.; Bshara, W.; Wang, J.; Gomez, E.C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. PTEN Loss Expands the Histopathologic Diversity and Lineage Plasticity of Lung Cancers Initiated by Rb1/Trp53 Deletion. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2023, 18, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joruiz, S.M.; Bourdon, J.C. P53 Isoforms: Key Regulators of the Cell Fate Decision. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a026039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, D.P.; Cheok, C.F.; Brown, C.; Madhumalar, A.; Ghadessy, F.J.; Verma, C. Mdm2 and P53 Are Highly Conserved from Placozoans to Man. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dumont, P.; Leu, J.I.J.; Della Pietra, A.C.; George, D.L.; Murphy, M. The Codon 72 Polymorphic Variants of P53 Have Markedly Different Apoptotic Potential. Nat. Genet 2003, 33, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garritano, S.; Gemignani, F.; Palmero, E.I.; Olivier, M.; Martel-Planche, G.; Le Calvez-Kelm, F.; Brugiéres, L.; Vargas, F.R.; Brentani, R.R.; Ashton-Prolla, P.; et al. Detailed Haplotype Analysis at the TP53 Locus in p.R337H Mutation Carriers in the Population of Southern Brazil: Evidence for a Founder Effect. Hum. Mutat. 2010, 31, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Chu, H.; Xu, M.; Xue, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Z. Intron 3 Sixteen Base Pairs Duplication Polymorphism of P53 Contributes to Breast Cancer Susceptibility: Evidence from Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendolare, A.; Marzano, F.; Petruzzella, V.; Vacca, R.A.; Guerrini, L.; Pesole, G.; Sbisà, E.; Tullo, A. The Underestimated Role of the P53 Pathway in Renal Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 5733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bykov, V.J.N.; Eriksson, S.E.; Bianchi, J.; Wiman, K.G. Targeting Mutant P53 for Efficient Cancer Therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, H.B.; Mandlik, S.K.; Mandlik, D.S. Role of P53 Suppression in the Pathogenesis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. World J. Gastrointest. Pathophysiol. 2023, 14, 46–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donehower, L.A.; Soussi, T.; Korkut, A.; Liu, Y.; Schultz, A.; Cardenas, M.; Li, X.; Babur, O.; Hsu, T.K.; Lichtarge, O.; et al. Integrated Analysis of TP53 Gene and Pathway Alterations in The Cancer Genome Atlas. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 1370–1384.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Xu, H.; Shi, X.; Ding, G.; Yan, C.; Li, L.; Jian, Z.; Yang, X.; Guo, H.; Li, F.; et al. TP53 Exon 5 Mutation Indicates Poor Progression-Free Survival for Patients with Stage IV NSCLC. Front. Biosci. 2023, 28, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Dong, L.; Liu, H.; Chen, X. TP53, NOTCH2, and STK11 Mutations in a Rare Tumor of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma with Diffuse Coexpression of TTF1 and P40 in the Same Tumor Cells. Int. J. Surg. Pathol. 2023, 31, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.P.; Lozano, G. Mutant P53 Partners in Crime. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marei, H.E.; Althani, A.; Afifi, N.; Hasan, A.; Caceci, T.; Pozzoli, G.; Morrione, A.; Giordano, A.; Cenciarelli, C. P53 Signaling in Cancer Progression and Therapy. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgin, E. The Most Popular Genes in the Human Genome. Nature 2017, 551, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdon, J.C.; Fernandes, K.; Murray-Zmijewski, F.; Liu, G.; Diot, A.; Xirodimas, D.P.; Saville, M.K.; Lane, D.P. P53 Isoforms Can Regulate P53 Transcriptional Activity. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 2122–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcel, V.; Perrier, S.; Aoubala, M.; Ageorges, S.; Groves, M.J.; Diot, A.; Fernandes, K.; Tauro, S.; Bourdon, J.C. Δ160p53 Is a Novel N-Terminal P53 Isoform Encoded by Δ133p53 Transcript. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 4463–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhardt, L.S.; Zhang, X.; Wawruszak, A.; Groen, K.; De Iuliis, G.N.; Avery-Kiejda, K.A. Good Cop, Bad Cop: Defining the Roles of Δ40p53 in Cancer and Aging. Cancers 2020, 12, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candeias, M.M.; Powell, D.J.; Roubalova, E.; Apcher, S.; Bourougaa, K.; Vojtesek, B.; Bruzzoni-Giovanelli, H.; Fåhraeus, R. Expression of P53 and P53/47 Are Controlled by Alternative Mechanisms of Messenger RNA Translation Initiation. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6936–6947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, P.S.; Grover, R.; Das, S. Two Internal Ribosome Entry Sites Mediate the Translation of P53 Isoforms. EMBO Rep. 2006, 7, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, H.; Bräuning, B.; Fainer, I.; Ben-Nissan, G.; Rabani, S.; Goldfinger, N.; Moscovitz, O.; Shakked, Z.; Rotter, V.; Sharon, M. Post-Translational Regulation of P53 Function through 20S Proteasome-Mediated Cleavage. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 2187–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vousden, K.H.; Lane, D.P. P53 in Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momand, J.; Wu, H.H.; Dasgupta, G. MDM2--Master Regulator of the P53 Tumor Suppressor Protein. Gene 2000, 242, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, D.; Oren, M. The P53-Mdm2 Module and the Ubiquitin System. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2003, 13, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, D.; Oren, M. The P53 and Mdm2 Families in Cancer. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2002, 12, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitolli, C.; Wang, Y.; Mancini, M.; Shi, Y.; Melino, G.; Amelio, I. Do Mutations Turn P53 into an Oncogene? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haupt, Y.; Maya, R.; Kazaz, A.; Oren, M. Mdm2 Promotes the Rapid Degradation of P53. Nature 1997, 387, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marvalim, C.; Datta, A.; Lee, S.C. Role of P53 in Breast Cancer Progression: An Insight into P53 Targeted Therapy. Theranostics 2023, 13, 1421–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargonetti, J.; Prives, C. Gain-of-Function Mutant P53: History and Speculation. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 11, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingallina, E.; Sorrentino, G.; Bertolio, R.; Lisek, K.; Zannini, A.; Azzolin, L.; Severino, L.U.; Scaini, D.; Mano, M.; Mantovani, F.; et al. Mechanical Cues Control Mutant P53 Stability through a Mevalonate-RhoA Axis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.; Zeng, S.X.; Zhou, X.; Chen, T.; Zhou, F.; Cao, B.; Jung, J.H.; Del Sal, G.; Luo, S.; Lu, H. Mutant P53 Gains Its Function via C-Myc Activation upon CDK4 Phosphorylation at Serine 249 and Consequent PIN1 Binding. Mol. Cell 2017, 68, 1134–1146.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Maddalena, M.; Lu, Y.Q.; Martinez, S.; Nataraj, N.B.; Noronha, A.; Sinha, S.; Teng, K.; Cohen-Kaplan, V.; Ziv, T.; et al. Cross-Talk between Mutant P53 and P62/SQSTM1 Augments Cancer Cell Migration by Promoting the Degradation of Cell Adhesion Proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2119644119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrales, A.; Ranjan, A.; Iyer, S.V.; Padhye, S.; Weir, S.J.; Roy, A.; Iwakuma, T. DNAJA1 Controls the Fate of Misfolded Mutant P53 through the Mevalonate Pathway. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 18, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilley, S.; Rodriguez, T.A.; Vousden, K.H. Mutant P53 in Cell-Cell Interactions. Genes Dev. 2021, 35, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redman-Rivera, L.N.; Shaver, T.M.; Jin, H.; Marshall, C.B.; Schafer, J.M.; Sheng, Q.; Hongo, R.A.; Beckermann, K.E.; Wheeler, F.C.; Lehmann, B.D.; et al. Acquisition of Aneuploidy Drives Mutant P53-Associated Gain-of-Function Phenotypes. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, C.A.; Singh, S.; Subler, M.A.; Windle, J.J.; Inoue, K.; Fry, E.A.; Pillappa, R.; Grossman, S.R.; Windle, B.; Andrew Yeudall, W.; et al. The Oncogenicity of Tumor-Derived Mutant P53 Is Enhanced by the Recruitment of PLK3. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blagih, J.; Zani, F.; Chakravarty, P.; Hennequart, M.; Pilley, S.; Hobor, S.; Hock, A.K.; Walton, J.B.; Morton, J.P.; Gronroos, E.; et al. Cancer-Specific Loss of P53 Leads to a Modulation of Myeloid and T Cell Responses. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 481–496.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Guo, G. Immunomodulatory Function of the Tumor Suppressor P53 in Host Immune Response and the Tumor Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassin, O.; Nataraj, N.B.; Shreberk-Shaked, M.; Aylon, Y.; Yaeger, R.; Fontemaggi, G.; Mukherjee, S.; Maddalena, M.; Avioz, A.; Iancu, O.; et al. Different Hotspot P53 Mutants Exert Distinct Phenotypes and Predict Outcome of Colorectal Cancer Patients. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Levine, A.J. The P53 Functional Circuit. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 4139–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, A.J. P53, the Cellular Gatekeeper for Growth and Division. Cell 1997, 88, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogan, S.; Carpizo, D.R. Zinc Metallochaperones as Mutant P53 Reactivators: A New Paradigm in Cancer Therapeutics. Cancers 2018, 10, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avery-Kiejda, K.A.; Xu, D.Z.; Adams, L.J.; Scott, R.J.; Vojtesek, B.; Lane, D.P.; Hersey, P. Small Molecular Weight Variants of P53 Are Expressed in Human Melanoma Cells and Are Induced by the DNA-Damaging Agent Cisplatin. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 1659–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anensen, N.; Oyan, A.M.; Bourdon, J.C.; Kalland, K.H.; Bruserud, O.; Gjertsen, B.T. A Distinct P53 Protein Isoform Signature Reflects the Onset of Induction Chemotherapy for Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 3985–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdon, J.C.; Khoury, M.P.; Diot, A.; Baker, L.; Fernandes, K.; Aoubala, M.; Quinlan, P.; Purdie, C.A.; Jordan, L.B.; Prats, A.C.; et al. P53 Mutant Breast Cancer Patients Expressing P53γ Have as Good a Prognosis as Wild-Type P53 Breast Cancer Patients. Breast Cancer Res. 2011, 13, R7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, N.M.; De Oliveira, G.A.P.; Rocha, M.R.; Pedrote, M.M.; Da Silva Ferretti, G.D.; Rangel, L.P.; Morgado-Diaz, J.A.; Silva, J.L.; Gimba, E.R.P. Loss of the P53 Transactivation Domain Results in High Amyloid Aggregation of the Δ40p53 Isoform in Endometrial Carcinoma Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 9430–9439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofstetter, G.; Berger, A.; Fiegl, H.; Slade, N.; Zori, A.; Holzer, B.; Schuster, E.; Mobus, V.J.; Reimer, D.; Daxenbichler, G.; et al. Alternative Splicing of P53 and P73: The Novel P53 Splice Variant P53delta Is an Independent Prognostic Marker in Ovarian Cancer. Oncogene 2010, 29, 1997–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, L.; Hainaut, P.; Blanchet, S.; Ariffin, H. Expression of P53 N-Terminal Isoforms in B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Its Correlation with Clinicopathological Profiles. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, R.; Giannini, C.; Sarkaria, J.N.; Schroeder, M.; Rogers, J.; Mastroeni, D.; Scrable, H. P53 Isoform Profiling in Glioblastoma and Injured Brain. Oncogene 2012, 32, 3165–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofstetter, G.; Berger, A.; Berger, R.; Zorić, A.; Braicu, E.I.; Reimer, D.; Fiegl, H.; Marth, C.; Zeimet, A.G.; Ulmer, H.; et al. The N-Terminally Truncated P53 Isoform Δ40p53 Influences Prognosis in Mucinous Ovarian Cancer. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2012, 22, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandrova, E.M.; Yallowitz, A.R.; Li, D.; Xu, S.; Schulz, R.; Proia, D.A.; Lozano, G.; Dobbelstein, M.; Moll, U.M. Improving Survival by Exploiting Tumour Dependence on Stabilized Mutant P53 for Treatment. Nature 2015, 523, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, A.J. Targeting the P53 Protein for Cancer Therapies: The Translational Impact of P53 Research. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 362–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabapathy, K.; Lane, D.P. Therapeutic Targeting of P53: All Mutants Are Equal, but Some Mutants Are More Equal than Others. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Xu, D.; Zhang, T.; Chang, C.Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Haffty, B.G.; Zong, W.X.; et al. The Ubiquitin Ligase TRIM21 Regulates Mutant P53 Accumulation and Gain of Function in Cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efeyan, A.; Serrano, M. P53: Guardian of the Genome and Policeman of the Oncogenes. Cell Cycle 2007, 6, 1006–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whibley, C.; Pharoah, P.D.P.; Hollstein, M. P53 Polymorphisms: Cancer Implications. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnoud, T.; Parris, J.L.D.; Murphy, M.E. Common Genetic Variants in the TP53 Pathway and Their Impact on Cancer. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 11, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, K.; Xia, J.; Zhu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ye, H.; Wang, P. Prediction of Esophageal Cancer Risk Based on Genetic Variants and Environmental Risk Factors in Chinese Population. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Tan, W.; Zhang, S. P53 Gene Codon 72 Polymorphism and Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Case/Control Study in a Chinese Population. Dis. Esophagus 2008, 21, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.; Shi, T.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xiang, J.; Yu, D.; Liang, Z.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Wang, D.; et al. No Association between TP53 Arg72Pro Polymorphism and Ovarian Cancer Risk: Evidence from 10113 Subjects. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 112761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grochola, L.F.; Zeron-Medina, J.; Mériaux, S.; Bond, G.L. Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms in the P53 Signaling Pathway. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a001032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.M.; Shao, J.; Yin, X.H.; Huang, C.C.; Jia, X.W.; Yuan, Y.D.; Wu, C.J.; Zhen, E.M.; Yao, Z.X.; Zeng, X.T.; et al. Meta-Analysis Results on the Association Between TP53 Codon 72 Polymorphism with the Susceptibility to Oral Cancer. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pim, D.; Banks, L. P53 Polymorphic Variants at Codon 72 Exert Different Effects on Cell Cycle Progression. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 108, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyos, D.; Greenbaum, B.; Levine, A.J. The Genotypes and Phenotypes of Missense Mutations in the Proline Domain of the P53 Protein. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrstka, R.; Coates, P.J.; Vojtesek, B. Polymorphisms in P53 and the P53 Pathway: Roles in Cancer Susceptibility and Response to Treatment. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2009, 13, 440–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Strasser, A.; Kelly, G.L. Should Mutant TP53 Be Targeted for Cancer Therapy? Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansur, M.B.; Greaves, M. Convergent TP53 Loss and Evolvability in Cancer. BMC Ecol. Evol. 2023, 23, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joerger, A.C.; Fersht, A.R. Structural Biology of the Tumor Suppressor P53 and Cancer-Associated Mutants. Adv. Cancer Res. 2007, 97, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corazzari, M.; Collavin, L. Wild-Type and Mutant P53 in Cancer-Related Ferroptosis. A Matter of Stress Management? Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1148192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Guo, M.; Wei, H.; Chen, Y. Targeting P53 Pathways: Mechanisms, Structures, and Advances in Therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollstein, M.; Shomer, B.; Greenblatt, M.; Soussi, T.; Hovig, E.; Montesano, R.; Harris, C.C. Somatic Point Mutations in the P53 Gene of Human Tumors and Cell Lines: Updated Compilation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996, 24, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joerger, A.C.; Fersht, A.R. Structural Biology of the Tumor Suppressor P53. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2008, 77, 557–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogi, A.; Kuwano, H. TP53 Mutations in Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 583929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive Molecular Profiling of Lung Adenocarcinoma. Nature 2014, 511, 543–550, Correction in Nature 2014, 511, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, L.A.; Siegel, R.L.; Jemal, A. Lung Cancer Statistics. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 893, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gridelli, C.; Rossi, A.; Carbone, D.P.; Guarize, J.; Karachaliou, N.; Mok, T.; Petrella, F.; Spaggiari, L.; Rosell, R. Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pikor, L.A.; Ramnarine, V.R.; Lam, S.; Lam, W.L. Genetic Alterations Defining NSCLC Subtypes and Their Therapeutic Implications. Lung Cancer 2013, 82, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, D.; Xu, C.; Wang, C.; Sang, Q. Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma with EML4-ALK Fusion and TP53 Co-Mutation Treated with Ensartinib: A Case Report and Literature Review. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi 2023, 26, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, P.A.J.; Vousden, K.H. P53 Mutations in Cancer. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivier, M.; Hollstein, M.; Hainaut, P. TP53 Mutations in Human Cancers: Origins, Consequences, and Clinical Use. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a001008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivlin, N.; Brosh, R.; Oren, M.; Rotter, V. Mutations in the P53 Tumor Suppressor Gene: Important Milestones at the Various Steps of Tumorigenesis. Genes Cancer 2011, 2, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, P.A.J.; Vousden, K.H. Mutant P53 in Cancer: New Functions and Therapeutic Opportunities. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poeta, M.L.; Manola, J.; Goldwasser, M.A.; Forastiere, A.; Benoit, N.; Califano, J.A.; Ridge, J.A.; Goodwin, J.; Kenady, D.; Saunders, J.; et al. TP53 Mutations and Survival in Squamous-Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2552–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adorno, M.; Cordenonsi, M.; Montagner, M.; Dupont, S.; Wong, C.; Hann, B.; Solari, A.; Bobisse, S.; Rondina, M.B.; Guzzardo, V.; et al. A Mutant-P53/Smad Complex Opposes P63 to Empower TGFbeta-Induced Metastasis. Cell 2009, 137, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkin, D. Li-Fraumeni Syndrome. Genes Cancer 2011, 2, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooks, T.; Pateras, I.S.; Jenkins, L.M.; Patel, K.M.; Robles, A.I.; Morris, J.; Forshew, T.; Appella, E.; Gorgoulis, V.G.; Harris, C.C. Mutant P53 Cancers Reprogram Macrophages to Tumor Supporting Macrophages via Exosomal MiR-1246. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido-Jimenez, S.; Barrera-Lopez, J.F.; Diaz-Chamorro, S.; Mateos-Quiros, C.M.; Rodriguez-Blanco, I.; Marquez-Perez, F.L.; Lorenzo, M.J.; Centeno, F.; Roman, A.C.; Carvajal-Gonzalez, J.M. P53 Regulation by MDM2 Contributes to Self-Renewal and Differentiation of Basal Stem Cells in Mouse and Human Airway Epithelium. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, A.M.; Gatto, A.; Hanson, K.J.; Zhao, R.L.; Raj, N.; Ozawa, M.G.; Seoane, J.A.; Bieging-Rolett, K.T.; Wang, M.; Li, I.; et al. P53 Governs an AT1 Differentiation Programme in Lung Cancer Suppression. Nature 2023, 619, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi-Rad, R.; Li, R.; Paul, M.K.; Dubinett, S.M.; Liu, B. The Biology of Lung Cancer: Development of More Effective Methods for Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Clin. Chest. Med. 2020, 41, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, L.; Ou, W.; Wu, J.; Li, S.; Xu, J.; Feng, J.; Liu, B. TP53 Mutation Is Associated with a Poor Clinical Outcome for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Evidence from a Meta-Analysis. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 5, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.D.; Qin, B.D.; You, P.; Cai, J.; Zang, Y.S. The Prognostic Value of TP53 and Its Correlation with EGFR Mutation in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, an Analysis Based on CBioPortal Data Base. Lung Cancer 2018, 123, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Piha-Paul, S.; Janku, F.; Subbiah, V.; Shi, N.; Hess, K.; Broaddus, R.; Shan, B.; Naing, A.; et al. Outcome Analysis of Phase I Trial Patients with Metastatic KRAS and/or TP53 Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 33258–33270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fregni, M.; Ciribilli, Y.; Zawacka-Pankau, J.E. The Therapeutic Potential of the Restoration of the P53 Protein Family Members in the EGFR-Mutated Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Ji, P.; Shang, A.; Wu, J.; Zhou, H.; Quan, W.; Yao, Y.; Yang, Y.; et al. Novel Evidence for Retinoic Acid-Induced G (Rig-G) as a Tumor Suppressor by Activating P53 Signaling Pathway in Lung Cancer. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 11900–11912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.R.; Yun, J.C.; Ryoo, B.Y.; Im, I.N.; Sung, H.Y.; Cheol, H.K.; Jae, C.L. P53 Enhances Gefitinib-Induced Growth Inhibition and Apoptosis by Regulation of Fas in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Yoon, A.; Kalapurakal, S.K.; Ro, J.Y.; Lee, J.J.; Tu, N.; Hittelman, W.N.; Hong, W.K. Expression of P53 Oncoprotein in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Favorable Prognostic Factor. J. Clin. Oncol. 1995, 13, 1893–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, L.; Wang, L.; Zhou, X.; Han, J.; Li, D.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Zuo, J.; et al. Genomic Landscape and Prognosis of Patients with TP53-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Williams-Villalobo, A.; Godavarthi, J.D.; Shakoor, F.; Xiong, S.; Liu, B. Integrative Bioinformatic Analysis of P53 and Pathway Alterations in Two Different Lung Cancer Subtypes. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2023, 33, 101404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandara, D.R.; Hammerman, P.S.; Sos, M.L.; Lara, P.N.; Hirsch, F.R. Squamous Cell Lung Cancer: From Tumor Genomics to Cancer Therapeutics. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2236–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, D.M.; Anderson, C.M.; Gray, N. Do Changes in Cigarette Design Influence the Rise in Adenocarcinoma of the Lung? Cancer Causes Control 2011, 22, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khuder, S.A.; Mutgi, A.B. Effect of Smoking Cessation on Major Histologic Types of Lung Cancer. Chest 2001, 120, 1577–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dotto, G.P.; Rustgi, A.K. Squamous Cell Cancers: A Unified Perspective on Biology and Genetics. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 622–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammerman, P.S.; Voet, D.; Lawrence, M.S.; Voet, D.; Jing, R.; Cibulskis, K.; Sivachenko, A.; Stojanov, P.; McKenna, A.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Comprehensive Genomic Characterization of Squamous Cell Lung Cancers. Nature 2012, 489, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Hammerman, P.S.; Kim, J.; Yoon, J.A.; Lee, Y.; Sun, J.M.; Wilkerson, M.D.; Pedamallu, C.S.; Cibulskis, K.; Yoo, Y.K.; et al. Integrative and Comparative Genomic Analysis of Lung Squamous Cell Carcinomas in East Asian Patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Egeren, D.; Kohli, K.; Warner, J.L.; Bedard, P.L.; Riely, G.; Lepisto, E.; Schrag, D.; Lenoue-Newton, M.; Catalano, P.; Kehl, K.L.; et al. Genomic Analysis of Early-Stage Lung Cancer Reveals a Role for TP53 Mutations in Distant Metastasis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robles, A.I.; Linke, S.P.; Harris, C.C. The P53 Network in Lung Carcinogenesis. Oncogene 2002, 21, 6898–6907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hainaut, P.; Pfeifer, G.P. Patterns of P53 G-->T Transversions in Lung Cancers Reflect the Primary Mutagenic Signature of DNA-Damage by Tobacco Smoke. Carcinogenesis 2001, 22, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denissenko, M.F.; Pao, A.; Tang, M.S.; Pfeifer, G.P. Preferential Formation of Benzo[a]Pyrene Adducts at Lung Cancer Mutational Hotspots in P53. Science 1996, 274, 430–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, L.E.; Denissenko, M.F.; Bennett, W.P.; Li, H.; Amin, S.; Tang, M.S.; Pfeifer, G.P. Targeting of Lung Cancer Mutational Hotspots by Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2000, 92, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heist, R.S.; Sequist, L.V.; Engelman, J.A. Genetic Changes in Squamous Cell Lung Cancer: A Review. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The CBio Cancer Genomics Portal: An Open Platform for Exploring Multidimensional Cancer Genomics Data. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Bruijn, I.; Kundra, R.; Mastrogiacomo, B.; Tran, T.N.; Sikina, L.; Mazor, T.; Li, X.; Ochoa, A.; Zhao, G.; Lai, B.; et al. Analysis and Visualization of Longitudinal Genomic and Clinical Data from the AACR Project GENIE Biopharma Collaborative in CBioPortal. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, 3861–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative Analysis of Complex Cancer Genomics and Clinical Profiles Using the CBioPortal. Sci. Signal 2013, 6, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Carlsen, L.; Hernandez Borrero, L.; Seyhan, A.A.; Tian, X.; El-Deiry, W.S. Advanced Strategies for Therapeutic Targeting of Wild-Type and Mutant P53 in Cancer. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamath, D.; Iwakuma, T.; Bossmann, S.H. Therapeutic Potential of Combating Cancer by Restoring Wild-Type P53 through MRNA Nanodelivery. Nanomedicine 2024, 56, 102732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Burigotto, M.; Ghetti, S.; Vaillant, F.; Tan, T.; Capaldo, B.D.; Palmieri, M.; Hirokawa, Y.; Tai, L.; Simpson, D.S.; et al. Loss-of-Function but Not Gain-of-Function Properties of Mutant TP53 Are Critical for the Proliferation, Survival and Metastasis of a Broad Range of Cancer Cells. Cancer Discov. 2023, 14, 362–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Wang, T.; Gleber-Netto, F.O.; Chen, Z.; Mcgrail, D.J.; Gomez, J.A.; Ju, W.; Gadhikar, M.A.; Ma, W.; Shen, L.; et al. Mutant P53 Gains Oncogenic Functions through a Chromosomal Instability-Induced Cytosolic DNA Response. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, M.; Rotter, V. Mutant P53 Gain-of-Function in Cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a001107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olive, K.P.; Tuveson, D.A.; Ruhe, Z.C.; Yin, B.; Willis, N.A.; Bronson, R.T.; Crowley, D.; Jacks, T. Mutant P53 Gain of Function in Two Mouse Models of Li-Fraumeni Syndrome. Cell 2004, 119, 847–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado-Ortiz, E.; de la Cruz-López, K.G.; Becerril-Rico, J.; Sarabia-Sánchez, M.A.; Ortiz-Sánchez, E.; García-Carrancá, A. Mutant P53 Gain-of-Function: Role in Cancer Development, Progression, and Therapeutic Approaches. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 8, 607670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Jiao, Z.; Fu, Y.; Hou, Y.; Sun, J.; Hu, F.; Yu, S.; Gong, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, G. An Overview of the Functions of P53 and Drugs Acting Either on Wild- or Mutant-Type P53. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 265, 116121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, M.; Feng, Z.; Hu, W. Mutant P53 in Cancer: Accumulation, Gain-of-Function, and Therapy. J. Mol. Biol. 2017, 429, 1595–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, H.; Choudhary, M.; Sharma, H.; Chowdhury, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Chowdhury, R. Chloroquine Induces Transitory Attenuation of Proliferation of Human Lung Cancer Cells through Regulation of Mutant P53 and YAP. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 1045–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandinova, A.; Lee, S.W. The P53 Pathway as a Target in Cancer Therapeutics: Obstacles and Promise. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 64rv1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barta, J.A.; Pauley, K.; Kossenkov, A.V.; McMahon, S.B. The Lung-Enriched P53 Mutants V157F and R158L/P Regulate a Gain of Function Transcriptome in Lung Cancer. Carcinogenesis 2020, 41, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.W.; Wu, M.F.; Wang, J.; Yeh, K.T.; Goan, Y.G.; Chiou, H.L.; Chen, C.Y.; Lee, H. Human Papillomavirus 16/18 E6 Oncoprotein Is Expressed in Lung Cancer and Related with P53 Inactivation. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 10686–10693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.R.; Ong, R.W.; Tan, T.Z.; Mohamed Salleh, N.A.B.; Thangavelu, M.; Chan, J.V.; Koh, L.Y.J.; Periyasamy, G.; Lau, J.A.; Le, T.B.U.; et al. Targeting Codon 158 P53-Mutant Cancers via the Induction of P53 Acetylation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.W.; Liu, W.S.; Wang, J.; Chen, C.Y.; Cheng, Y.W.; Lee, H. Reduced P21(WAF1/CIP1) via Alteration of P53-DDX3 Pathway Is Associated with Poor Relapse-Free Survival in Early-Stage Human Papillomavirus-Associated Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 1895–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldser, D.M.; Kostova, K.K.; Winslow, M.M.; Taylor, S.E.; Cashman, C.; Whittaker, C.A.; Sanchez-Rivera, F.J.; Resnick, R.; Bronson, R.; Hemann, M.T.; et al. Stage-Specific Sensitivity to P53 Restoration during Lung Cancer Progression. Nature 2010, 468, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Estecio, M.R.; Chen, R.; Reuben, A.; Wang, L.; Fujimoto, J.; Carrot-Zhang, J.; McGranahan, N.; Ying, L.; Fukuoka, J.; et al. Evolution of DNA Methylome from Precancerous Lesions to Invasive Lung Adenocarcinomas. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, V.H.; Pipinikas, C.P.; Pennycuick, A.; Lee-Six, H.; Chandrasekharan, D.; Beane, J.; Morris, T.J.; Karpathakis, A.; Feber, A.; Breeze, C.E.; et al. Deciphering the Genomic, Epigenomic, and Transcriptomic Landscapes of Pre-Invasive Lung Cancer Lesions. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; El-Deiry, W.S. Restoration of P53 to Limit Tumor Growth. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2008, 20, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreeff, M.; Kelly, K.R.; Yee, K.; Assouline, S.; Strair, R.; Popplewell, L.; Bowen, D.; Martinelli, G.; Drummond, M.W.; Vyas, P.; et al. Results of the Phase I Trial of RG7112, a Small-Molecule MDM2 Antagonist in Leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.D.; Tang, Q.; Kong, Y.; Rong, T.; Wang, Q.; Li, N.; Fang, X.; Gu, J.; Xiong, D.; Yin, Y.; et al. MDM2 Inhibitor APG-115 Exerts Potent Antitumor Activity and Synergizes with Standard-of-Care Agents in Preclinical Acute Myeloid Leukemia Models. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, F.E. Small-Molecule MDM2 Inhibitors in Clinical Trials for Cancer Therapy. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 236, 114334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Hiran, T.; Holden, S.A.; Chafai-Fadela, K.; Rogers, S.; Ram, S.; Menon, K. Abstract 4470: KevetrinTM, a Novel Small Molecule, Activates P53, Enhances Expression of P21, Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in a Human Cancer Cell Line. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Brennan, D.P.; Chafai-Fadela, K.; Holden, S.A.; Ram, S.; Shapiro, G.I.; Menon, K. Abstract 3221: Kevetrin Induces P53-Dependent and Independent Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Ovarian Cancer Cell Lines Representing Heterogeneous Histologies. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kumar, A.; Holden, S.A.; Chafai-Fadela, K.; Ram, S.; Menon, K. KevetrinTM Targets Both MDM2 P53 and Rb E2F Pathways in Tumor Suppression KevetrinTM Targets Both MDM2-P53 and Rb-E2F Pathways in Tumor Suppression. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangatia, J.; Vangala, R.K.; Singh, S.M.; Peer Zada, A.A.; Elsässer, A.; Kohlmann, A.; Haferlach, T.; Tenen, D.G.; Hiddemann, W.; Behre, G. Elevated C-Jun Expression in Acute Myeloid Leukemias Inhibits C/EBPalpha DNA Binding via Leucine Zipper Domain Interaction. Oncogene 2003, 22, 4760–4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; An, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhong, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ma, F.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; et al. A Novel Naphthalimide Compound Restores P53 Function in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by Reorganizing the Bak·Bcl-Xl Complex and Triggering Transcriptional Regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 4211–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Du, W.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Zeng, S.; Zhang, G. Small-Molecule MX-C2/3 Suppresses Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Progression via P53 Activation. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 366, 110142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Fillmore, C.M.; Hammerman, P.S.; Kim, C.F.; Wong, K.K. Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancers: A Heterogeneous Set of Diseases. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Huang, L.L.; Chen, J.H.; Wu, J.; Xu, Q. The Emerging Treatment Landscape of Targeted Therapy in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2019, 4, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, R.S.; Morgensztern, D.; Boshoff, C. The Biology and Management of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Nature 2018, 553, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.C.M.; Pan, Y.; Velcheti, V.; Wong, K.K. Squamous Cell Lung Cancer: Current Landscape and Future Therapeutic Options. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 1279–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.Y.; Yang, J.C.H.; Yang, P.C. Precision Management of Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Annu. Rev. Med. 2020, 71, 117–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paik, P.K.; Pillai, R.N.; Lathan, C.S.; Velasco, S.A.; Papadimitrakopoulou, V. New Treatment Options in Advanced Squamous Cell Lung Cancer. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2019, 39, e198–e206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socinski, M.A.; Obasaju, C.; Gandara, D.; Hirsch, F.R.; Bonomi, P.; Bunn, P.A.; Kim, E.S.; Langer, C.J.; Natale, R.B.; Novello, S.; et al. Current and Emergent Therapy Options for Advanced Squamous Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumplido-Laso, G.; Benitez, D.A.; Mulero-Navarro, S.; Carvajal-Gonzalez, J.M. Transcriptional Regulation of Airway Epithelial Cell Differentiation: Insights into the Notch Pathway and Beyond. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Z.; Jin, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H. Signaling Pathways and Targeted Therapies in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Mechanisms and Clinical Trials. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelland, L. The Resurgence of Platinum-Based Cancer Chemotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rottenberg, S.; Disler, C.; Perego, P. The Rediscovery of Platinum-Based Cancer Therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brower, V. Predicting Response to Cisplatin in NSCLC. Lancet Oncol. 2007, 8, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbour, K.C.; Riely, G.J. Systemic Therapy for Locally Advanced and Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Review. JAMA 2019, 322, 764–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Pan, C.; Bei, J.X.; Li, B.; Liang, C.; Xu, Y.; Fu, X. Mutant P53 in Cancer Progression and Targeted Therapies. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 595187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Lin, H.; He, P.; He, L.; Chen, J.; Lin, L.; Chen, Y. A TP53-Associated Gene Signature for Prediction of Prognosis and Therapeutic Responses in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Oncoimmunology 2020, 9, 1731943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J. Current Developments of Targeting the P53 Signaling Pathway for Cancer Treatment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 220, 107720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; Schenker, M.; Lee, K.H.; Provencio, M.; Nishio, M.; Lesniewski-Kmak, K.; Sangha, R.; Ahmed, S.; Raimbourg, J.; Feeney, K.; et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab versus Chemotherapy as First-Line Treatment in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with High Tumour Mutational Burden: Patient-Reported Outcomes Results from the Randomised, Open-Label, Phase III CheckMate 227 Trial. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 116, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Goh, K.Y.; Chen, Z.; Lee, W.X.; Choy, S.M.; Fong, J.X.; Wong, Y.K.; Li, D.; Hu, F.; Tang, H.W. A Novel TP53 Gene Mutation Sustains Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer through Mitophagy. Cells 2022, 11, 3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, D.J.; Crawford, E.L.; Chen, H.; Grogan, E.L.; Deppen, S.A.; Morrison, T.; Antic, S.L.; Massion, P.P.; Willey, J.C. TP53 Mutation Prevalence in Normal Airway Epithelium as a Biomarker for Lung Cancer Risk. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budczies, J.; Romanovsky, E.; Kirchner, M.; Neumann, O.; Blasi, M.; Schnorbach, J.; Shah, R.; Bozorgmehr, F.; Savai, R.; Stiewe, T.; et al. Abstract 2487: KRAS and TP53 Co-Mutation Predicts Benefit of Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2024, 84, 2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Xu, Z.; Liu, G.; Jiang, B.; de Bock, G.H.; Groen, H.J.M.; Vliegenthart, R.; Xie, X. Simultaneous Identification of Egfr, Kras, Erbb2, and Tp53 Mutations in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by Machine Learning-Derived Three-Dimensional Radiomics. Cancers 2021, 13, 1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, H.; Ding, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Xiao, B.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, Q. Quantitative Analysis of TP53-Related Lung Cancer Based on Radiomics. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2022, 15, 8481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canale, M.; Andrikou, K.; Priano, I.; Cravero, P.; Pasini, L.; Urbini, M.; Delmonte, A.; Crinò, L.; Bronte, G.; Ulivi, P. The Role of TP53 Mutations in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Clinical Significance and Implications for Therapy. Cancers 2022, 14, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jiang, M.; Yang, Z.; Huang, X.; Li, N. The Role of Distinct Co-Mutation Patterns with TP53 Mutation in Immunotherapy for NSCLC. Genes Dis. 2022, 9, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ricciuti, B.; Nguyen, T.; Li, X.; Rabin, M.S.; Awad, M.M.; Lin, X.; Johnson, B.E.; Christiani, D.C. Association between Smoking History and Tumor Mutation Burden in Advanced Non⇓small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 2566–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.K.H.; Skoulidis, F.; Kerr, K.M.; Ahn, M.J.; Kapp, J.R.; Soares, F.A.; Yatabe, Y. KRAS G12C in Advanced NSCLC: Prevalence, Co-Mutations, and Testing. Lung Cancer 2023, 184, 107293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caron, E. Cellular Functions of the Rap1 GTP-Binding Protein: A Pattern Emerges. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, A.B.; Hall, A. Rho GTPases: Biochemistry and Biology. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2005, 21, 247–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, A.; Lotfi, P.; Chavan, A.J.; Montaño, N.M.; Bolourani, P.; Weeks, G.; Shen, Z.; Briggs, S.P.; Pots, H.; Van Haastert, P.J.M.; et al. The Small GTPases Ras and Rap1 Bind to and Control TORC2 Activity. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croft, D.R.; Crighton, D.; Samuel, M.S.; Lourenco, F.C.; Munro, J.; Wood, J.; Bensaad, K.; Vousden, K.H.; Sansom, O.J.; Ryan, K.M.; et al. P53-Mediated Transcriptional Regulation and Activation of the Actin Cytoskeleton Regulatory RhoC to LIMK2 Signaling Pathway Promotes Cell Survival. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 666–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncbag, N.; Kar, G.; Gursoy, A.; Keskin, O.; Nussinov, R. Towards Inferring Time Dimensionality in Protein-Protein Interaction Networks by Integrating Structures: The P53 Example. Mol. Biosyst. 2009, 5, 1770–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.; Lim, J.S.; Jang, S.J.; Cun, Y.; Ozretia, L.; Kong, G.; Leenders, F.; Lu, X.; Fernández-Cuesta, L.; Bosco, G.; et al. Comprehensive Genomic Profiles of Small Cell Lung Cancer. Nature 2015, 524, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, S.B.; Crosbie, P.A.; Balata, H.; Chudziak, J.; Hussell, T.; Dive, C. Progress and Prospects of Early Detection in Lung Cancer. Open Biol. 2017, 7, 170070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Cheng, H.; Yu, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Lou, F.; Wang, H.; Cao, S. Mutation Patterns and Evolutionary Action Score of TP53 Enable Identification of a Patient Population with Poor Prognosis in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 6649–6658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Liang, X.; Wang, J.; Ding, G.; Tang, J.; Xue, J.; He, X.; Ge, J.; Jin, X.; Yang, Z.; et al. Identification of Key Biomarkers and Candidate Molecules in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer by Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis. Genet. Res. 2023, 2023, e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hainaut, P.; Pfeifer, G.P. Somatic TP53 Mutations in the Era of Genome Sequencing. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a026179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.J.; Lee, K.; Lee, S.Y.; Kwon, Y.; Woo, J.; Jeon, C.Y.; Ko, S.G. P53 Activation Enhances the Sensitivity of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer to the Combination of SH003 and Docetaxel by Inhibiting de Novo Pyrimidine Synthesis. Cancer Cell Int. 2024, 24, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wu, P.; Shen, Z.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, F.; Chen, K.; Zhao, J. An Immune Checkpoint-Based Signature Predicts Prognosis and Chemotherapy Response for Patients with Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 117, 109827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza, R.P.; Chen-Yost, H.I.H.; Wanjari, P.; Wang, P.; Symes, E.; Johnson, D.N.; Reeves, W.; Mueller, J.; Antic, T.; Biernacka, A. Lung Adenocarcinomas with Isolated TP53 Mutation: A Comprehensive Clinical, Cytopathologic and Molecular Characterization. Cancer Med. 2024, 13, e6873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.; Hasan, G.M.; Eldin, S.M.; Adnan, M.; Riyaz, M.B.; Islam, A.; Khan, I.; Hassan, M.I. Investigating Regulated Signaling Pathways in Therapeutic Targeting of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 161, 114452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basse, C.; Trabelsi-Grati, O.; Masliah, J.; Callens, C.; Kamal, M.; Freneaux, P.; Klijanienko, J.; Bieche, I.; Girard, N. Gain of Aggressive Histological and Molecular Patterns after Acquired Resistance to Novel Anti-EGFR Therapies in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Ding, X.; Ding, J.; Wang, X. Histological Transformation into SCLC: An Important Resistance Mechanism of NSCLC upon Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1275957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Martinez, L. Harnessing P53 to Improve Immunotherapy for Lung Cancer Treatment. Cancer Res. 2023, 84, OF1–OF2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Kim, J.; Deng, Q.; Ricciuti, B.; Alessi, J.V.; Eglenen-Polat, B.; Bender, M.E.; Huang, H.C.; Kowash, R.R.; Cuevas, I.; et al. Loss of P53 and Mutational Heterogeneity Drives Immune Resistance in an Autochthonous Mouse Lung Cancer Model with High Tumor Mutational Burden. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 1731–1748.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, T.; Kunimasa, K.; Hirotsu, Y.; Nakagomi, T.; Yokoyama, Y.; Higuchi, R.; Otake, S.; Oyama, T.; Amemiya, K.; Mochizuki, H.; et al. Association of Mutation Profiles with Postoperative Survival in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jager, V.D.; Timens, W.; Bayle, A.; Botling, J.; Brcic, L.; Büttner, R.; Fernandes, M.G.O.; Havel, L.; Hochmair, M.; Hofman, P.; et al. Future Perspective for the Application of Predictive Biomarker Testing in Advanced Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2024, 38, 100839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, A.; Chen, M.; Yeung, S.; Parsa, C.; Orlando, R.; Huang, Y. The Medicinal Mushroom Ganoderma Lucidum Prevents Lung Tumorigenesis Induced by Tobacco Smoke Carcinogens. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1244150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudrapal, M.; Maji, S.; Prajapati, S.K.; Kesharwani, P.; Deb, P.K.; Khan, J.; Ismail, R.M.; Kankate, R.S.; Sahoo, R.K.; Khairnar, S.J.; et al. Protective Effects of Diets Rich in Polyphenols in Cigarette Smoke (CS)-Induced Oxidative Damages and Associated Health Implications. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boța, M.; Vlaia, L.; Jîjie, A.-R.; Marcovici, I.; Crişan, F.; Oancea, C.; Dehelean, C.A.; Mateescu, T.; Moacă, E.-A. Exploring Synergistic Interactions between Natural Compounds and Conventional Chemotherapeutic Drugs in Preclinical Models of Lung Cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Hou, R.; Yu, J.; Xing, C.; Zhuang, C.; Qu, Z. Dietary Phytochemicals as Potential Chemopreventive Agents against Tobacco-Induced Lung Carcinogenesis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sompel, K.; Smith, A.J.; Hauer, C.; Elango, A.P.; Clamby, E.T.; Keith, R.L.; Tennis, M.A. Precision Cut Lung Slices as a Preclinical Model for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Chemoprevention. Cancer Prev. Res. 2023, 16, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordiak, J.; Bielec, F.; Jabłoński, S.; Pastuszak-Lewandoska, D. Role of Beta-Carotene in Lung Cancer Primary Chemoprevention: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benusiglio, P.R.; Fallet, V.; Sanchis-Borja, M.; Coulet, F.; Cadranel, J. Lung Cancer Is Also a Hereditary Disease. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2021, 30, 210045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezquita, L.; Jové, M.; Nadal, E.; Kfoury, M.; Morán, T.; Ricordel, C.; Dhooge, M.; Tlemsani, C.; Léna, H.; Teulé, A.; et al. High Prevalence of Somatic Oncogenic Driver Alterations in Patients with NSCLC and Li-Fraumeni Syndrome. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, H.; Munchel, A.; York, T.; Macatangay, R. Multi-Generational Review of Oncologic Tumors in a Family with TP53 Mutation Presenting with a Pediatric Patient with Osteosarcoma and Lung Acinar Adenocarcinoma. Cureus 2021, 13, e17271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nierengarten, M.B. Updated American Cancer Society Lung Cancer Screening Guidelines: The New Guidelines Offer Expanded Criteria Recommended for Lung Cancer Screening Based on Age, Smoking Status, and Smoking History. Cancer 2024, 130, 656–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, J.; Lee, E.; Lim, J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, C.T.; Jang, S.H.; Paek, Y.J.; Lee, W.C.; Lee, C.W.; et al. Strategies to Improve Smoking Cessation for Participants in Lung Cancer Screening Program: Analysis of Factors Associated with Smoking Cessation in Korean Lung Cancer Screening Project (K-LUCAS). Cancer Res. Treat. 2024, 56, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandi, P.; Star, J.; Ashad-Bishop, K.; Kratzer, T.; Smith, R.; Jemal, A. Lung Cancer Screening in the US, 2022. JAMA Intern. Med. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.; Murray, R.L.; Crosbie, P.A. Integrated Stop Smoking Interventions Are Essential to Maximise the Health Benefits from Lung Cancer Screening. Thorax 2024, 79, 198–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillay, J.; Rahman, S.; Klarenbach, S.; Reynolds, D.L.; Tessier, L.A.; Thériault, G.; Persaud, N.; Finley, C.; Leighl, N.; McInnes, M.D.F.; et al. Screening for Lung Cancer with Computed Tomography: Protocol for Systematic Reviews for the Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care. Syst. Rev. 2024, 13, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toumazis, I.; Cao, P.; de Nijs, K.; Bastani, M.; Munshi, V.; Hemmati, M.; ten Haaf, K.; Jeon, J.; Tammemägi, M.; Gazelle, G.S.; et al. Risk Model-Based Lung Cancer Screening: A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2023, 176, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Huang, H.Y.; Lin, Z.; Ranieri, M.; Li, S.; Sahu, S.; Liu, Y.; Ban, Y.; Guidry, K.; Hu, H.; et al. Genome-Wide CRISPR Screens Identify Multiple Synthetic Lethal Targets That Enhance KRASG12C Inhibitor Efficacy. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, 4095–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Xin, M.; Feng, H.; Zhang, W.; Liao, Z.; Sheng, T.; Wen, P.; Wu, Q.; Liang, T.; Shi, J.; et al. Cryo-Shocked Tumor Cells Deliver CRISPR-Cas9 for Lung Cancer Regression by Synthetic Lethality. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadk8264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liang, S.Q.; Zhao, L.; Yang, H.; Marti, T.M.; Hegedüs, B.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, B.; Chen, C.; Wang, W.; et al. Metabolic Synthetic Lethality by Targeting NOP56 and MTOR in KRAS-Mutant Lung Cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, L.L.; Ma, S.C.; Guo, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.P.; Fan, Z.; Liu, L.J.; Liu, L.; Han, D.D.; Leng, M.X.; Wang, J.; et al. PARP Inhibition Induces Synthetic Lethality and Adaptive Immunity in LKB1-Mutant Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, 568–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.S.; Nagasaka, M. Spotlight on Sotorasib (AMG 510) for KRAS G12C Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 2021, 12, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riganti, C.; Giampietro, R.; Kopecka, J.; Costamagna, C.; Abatematteo, F.S.; Contino, M.; Abate, C. MRP1-Collateral Sensitizers as a Novel Therapeutic Approach in Resistant Cancer Therapy: An In Vitro and In Vivo Study in Lung Resistant Tumor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandarana, C.; Tiwari, A. A Review of Clinical Trials of Cancer and Its Treatment as a Vaccine. Rev. Recent Clin. Trials 2024, 19, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, D.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhang, B.; Ma, W.; Cheng, B.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Mu, Y.; Xu, H.; et al. An Engineered Influenza Virus to Deliver Antigens for Lung Cancer Vaccination. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathish, G.; Monavarshini, L.K.; Sundaram, K.; Subramanian, S.; Kannayiram, G. Immunotherapy for Lung Cancer. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2024, 254, 155104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Malviya, R.; Uniyal, P. Vaccine for Targeted Therapy of Lung Cancer: Advances and Developments. Curr. Drug Targets 2024, 25, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Huang, J.; Shen, C.; Jiang, W.; Yang, X.; Huang, J.; Gu, Y.; Li, Z.; Ma, Y.; Bian, J. Tumor-Targeted Metabolic Inhibitor Prodrug Labelled with Cyanine Dyes Enhances Immunoprevention of Lung Cancer. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2024, 14, 751–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Pan, J.; Fang, Z.; Jia, J.; Zhang, R.; He, M.; Zhong, H.; He, J.; Yang, X.; Shi, Y.; et al. A Novel PD-L1-Containing MSLN Targeting Vaccine for Lung Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 925217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Clowers, M.J.; Velasco, W.V.; Peng, S.; Peng, Q.; Shi, Y.; Ramos-Castaneda, M.; Zarghooni, M.; Yang, S.; Babcock, R.L.; et al. Targeting IL-1β as an Immunopreventive and Therapeutic Modality for K-Ras-Mutant Lung Cancer. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e157788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Benitez, D.A.; Cumplido-Laso, G.; Olivera-Gómez, M.; Del Valle-Del Pino, N.; Díaz-Pizarro, A.; Mulero-Navarro, S.; Román-García, A.; Carvajal-Gonzalez, J.M. p53 Genetics and Biology in Lung Carcinomas: Insights, Implications and Clinical Applications. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071453
Benitez DA, Cumplido-Laso G, Olivera-Gómez M, Del Valle-Del Pino N, Díaz-Pizarro A, Mulero-Navarro S, Román-García A, Carvajal-Gonzalez JM. p53 Genetics and Biology in Lung Carcinomas: Insights, Implications and Clinical Applications. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(7):1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071453
Chicago/Turabian StyleBenitez, Dixan A., Guadalupe Cumplido-Laso, Marcos Olivera-Gómez, Nuria Del Valle-Del Pino, Alba Díaz-Pizarro, Sonia Mulero-Navarro, Angel Román-García, and Jose Maria Carvajal-Gonzalez. 2024. "p53 Genetics and Biology in Lung Carcinomas: Insights, Implications and Clinical Applications" Biomedicines 12, no. 7: 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071453
APA StyleBenitez, D. A., Cumplido-Laso, G., Olivera-Gómez, M., Del Valle-Del Pino, N., Díaz-Pizarro, A., Mulero-Navarro, S., Román-García, A., & Carvajal-Gonzalez, J. M. (2024). p53 Genetics and Biology in Lung Carcinomas: Insights, Implications and Clinical Applications. Biomedicines, 12(7), 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071453





