TRAP-Induced Platelet Reactivity Is Inhibited by Omega-3 Fatty Acid-Derived Prostaglandin E3 (PGE3)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
Blood Collection
2.3. Platelet Aggregation
2.4. P-Selectin (CD62P)
2.5. Measurement of VASP Phosphorylation
2.6. Data Presentation
3. Results
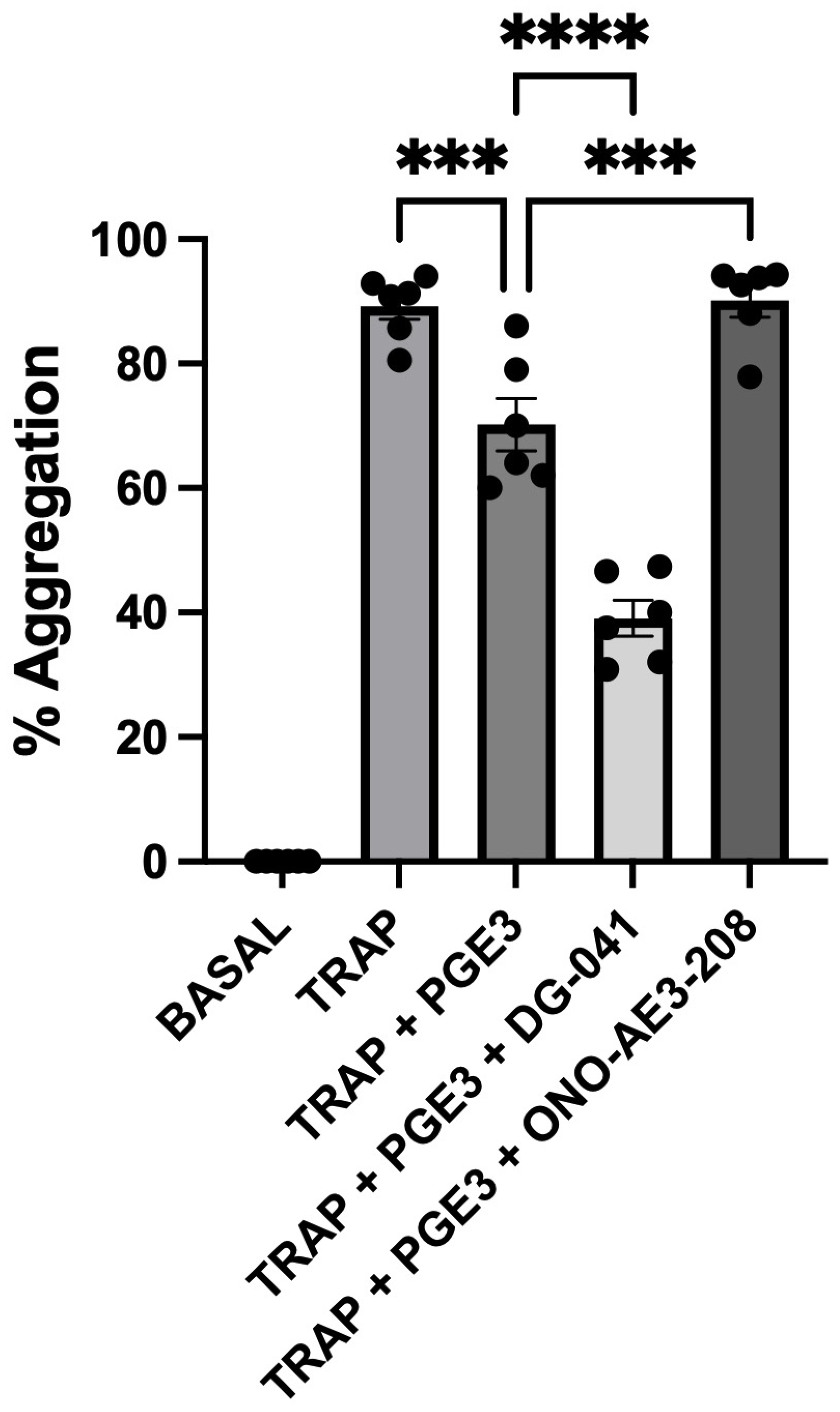
3.1. TRAP-6-Induced Platelet Aggregation
3.2. TRAP-6-Induced P-Selectin Expression
3.3. TRAP-6-Induced VASP Phosphorylation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vaduganathan, M.; Mensah, G.A.; Turco, J.V.; Fuster, V.; Roth, G.A. The global burden of cardiovascular diseases and risk: A compass for future health. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 80, 2361–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braune, S.; Küpper, J.H.; Jung, F. Effect of prostanoids on human platelet function: An overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beccacece, L.; Abondio, P.; Bibi, C.; Pelotti, S.; Luiselli, D. The link between prostanoids and cardiovascular diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crescente, M.; Menke, L.; Chan, M.V.; Armstrong, P.C.; Warned, T.D. Eicosanoids in platelets and the effect of their modulation by aspirin in the cardiovascular system (and beyond). Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 988–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, H.; Williams, J.O.; Ferekidis, N.; Ismail, A.; Chan, Y.H.; Michael, D.R.; Guschina, I.A.; Tyrrell, V.J.; O’Donnell, V.B.; Harwood, J.L.; et al. Dihomo-γ-linolenic acid inhibits several key cellular processes associated with atherosclerosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2019, 1865, 2538–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, S.; Tilly, P.; Hentsch, D.; Vonesch, J.L.; Fabre, J.E. Vascular wall-produced prostaglandin E2 exacerbates arterial thrombosis and atherothrombosis through platelet EP3 receptors. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Zeller, W.; Zhou, N.; Hategan, G.; Mishra, R.; Polozov; Yu, P.; Onua, E.; Zhang, J.; Zembower, D.; et al. Identification of DG-041, a potent and selective, prostanoid EP3 receptor antagonist, as a novel anti-platelet agent. ACS Chem. Biol. J. 2009, 4, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heptinstall, S.; Espinosa, D.I.; Manolopoulos, P.; Glenn, J.R.; White, A.E.; Johnson, A.; Dovlatova, N.; Fox, S.C.; May, J.A.; Hermann, D.; et al. DG-041 inhibits the EP3 prostanoid receptor-a new target for inhibition of platelet function in atherothrombotic disease. Platelets 2008, 19, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherratt, S.C.; Libby, P.; Budoff, M.J.; Bhatt, D.L.; Mason, R.P. Role of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Cardiovascular Disease: The Debate Continues. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2023, 25, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, J.R.; Budoff, M.J.; Wanic, O.R.; Le, V.; Patele, D.K.; Nelson, A.; Richard, L. Nemiroff RL. EPA’s pleiotropic mechanisms of action: A narrative review. Postgrad. Med. 2021, 133, 651–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Shan, K.; Yang, Q.; Qi, Y.; Qu, H.; Li, J.; Wang, R.; Jia, L.; Chen, W.; Feng, N.; et al. Prostaglandin E3 attenuates macrophage-associated inflammation and prostate tumour growth by modulating polarization. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 5586–5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Jiang, Y.; Fischer, S.M. Prostaglandin E3 metabolism and cancer. Cancer Lett. 2014, 348, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyú, D.; Glenn, J.R.; White, A.E.; Johnson, A.; Heptinstall, S.; Fox, S.C. The role of prostanoid receptors in mediating the effects of PGE3 on human platelet function. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 107, 797–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khana, S.U.; Lonea, A.N.; Khanb, M.S.; Salim, S.; Virani, S.S.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Nasir, K.; Miller, M.; Michos, E.D.; Ballantyne, C.M.; et al. Effect of omega-3 fatty acids on cardiovascular outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 38, 100997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, D.L.; Steg, P.G.; Miller, M.; Brinton, E.A.; Jacobson, T.A.; Ketchum, S.B.; Doyle, R.T., Jr.; Juliano, R.A.; Jiao, L.; Granowitz, C.; et al. Cardiovascular risk reduction with Icosapent Ethyl for hypertriglyceridemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budoff, M.J.; Bhatt, D.L.; Kinninger, A.; Lakshmanan, S.; Muhlestein, J.B.; Le, V.T.; May, H.T.; Shaikh, K.; Shekar, C.; Roy, S.K.; et al. Effect of icosapent ethyl on progression of coronary atherosclerosis in patients with elevated triglycerides on statin therapy: Final results of the EVAPORATE trial. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 3925–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, M.; Origasa, H.; Matsuzaki, M.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Saito, Y.; Ishikawa, Y.; Oikawa, S.; Sasaki, J.; Hishida, H.; Itakura, H.; et al. Effects of eicosapentaenoic acid on major coronary events in hypercholesterolaemic patients (JELIS): A randomised open- label, blinded endpoint analysis. Lancet 2007, 369, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, R.P.; Libby, P.; Bhatt, D.L. Emerging Mechanisms of Cardiovascular Protection for the Omega-3 Fatty Acid Eicosapentaenoic Acid. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 1135–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adili, R.; Hawley, M.; Holinstat, M. Regulation of platelet function and thrombosis by omega-3 and omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2018, 139, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, C.N.; Levy, B.D. Resolvins in inflammation: Emergence of the pro-resolving superfamily of mediators. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 2657–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oner, F.; Alvarez, C.; Yaghmoor, W.; Stephens, D.; Hasturk, H.; Firatli, E.; Kantarci, A. Resolvin E1 Regulates Th17 Function and T Cell Activation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 637983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymanska, P.; Luzak, B.; Miłowska, K.; Golanski, J. The Anti-Aggregative Potential of Resolvin E1 on Human Platelets. Molecules 2023, 28, 5323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyú, D.; Glenn, J.R.; White, A.E.; Johnson, A.J.; Fox, S.C.; Heptinstall, S. The role of prostanoid receptors in mediating the effects of PGE2 on human platelet function. Platelets 2010, 21, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyú, D.; Jüttner, M.; Glenn, J.R.; White, A.E.; Johnson, A.J.; Fox, S.C.; Heptinstall, S. PGE1 and PGE2 modify platelet function through different prostanoid receptors. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2011, 94, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, J.R.; Whie, A.; Iyu, D.; Heptinstall, S. PGE2 reverses Gs-mediated inhibition of platelet aggregation by interaction with EP3 receptors but adds to non-Gs-mediated inhibition of platelet aggregation by interaction with EP4 receptors. Platelets 2012, 23, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyu, D.; Glenn, J.R.; White, A.; Fox Sc Dovlatova, N.; Heptinstall, S. P2Y12 and EP3 antagonists promote the inhibitory effects of natural modulators of platelet aggregation that act via cAMP. Platelets 2011, 22, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, D.L.; Bryson, T.D.; Taube, D.; Xu, J.; Peterson, E.; Harding, P. Deleterious effects of cardiomyocyte-specific prostaglandin E2 EP3 receptor overexpression on cardiac function after myocardial infarction. Life Sci. 2023, 313, 121277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryson, T.D.; Gu, X.; Khalil, R.M.; Khan, S.; Zhu, L.; Xu, J.; Peterson, E.; Yang, X.P.; Harding, P. Overexpression of Prostaglandin E2 EP4 Receptor Improves Cardiac Function after Myocardial Infarction. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2018, 118, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, J.B.; Hvas, A.M. Thrombin: A Pivotal Player in Hemostasis and Beyond. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2021, 47, 759–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Meijden, P.E.J.; Heemskerk, J.W.M. Platelet biology and functions: New concepts and clinical perspectives. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.-S.; Kwon, H.-W.; Shin, J.-H.; Rhee, M.H.; Park, C.-E.; Lee, D.-H. Anti-Thrombotic Effects of Artesunate through Regulation of cAMP and PI3K/MAPK Pathway on Human Platelets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, E.; Abel, K.; Krieger, M.; Palm, D.; Hoppe, V.; Hoppe, J.; Walter, U. cAMP- and cGMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylation sites of the focal adhesion vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) in vitro and in intact human platelets. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 14509–14517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, J.R.; Dovlatova, N.; White, A.E.; Dhillon, K.; Heptinstall, S.; Fox, S.C. ‘VASPFix’ for measurement of VASP phosphorylation in platelets and for monitoring effects of P2Y12 antagonists. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 111, 539–548. [Google Scholar]
- Ungerer, M.; Munch, G. Novel antiplatelet drugs in clinical development. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 110, 868–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Z.; Zhao, G.; He, X.; Yu, X.; Fu, Q.; Wu, N.; Ding, Z.; Sun, H.; et al. Endothelial YAP Mediates Hyperglycemia-Induced Platelet Hyperactivity and Arterial Thrombosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2024, 44, 254–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipose, S.; Konya, V.; Sreckovic, I.; Marsche, G.; Lippe, I.T.; Peskar, B.A.; Heinemann, A.; Schuligoi, R. The prostaglandin E2 receptor EP4 is expressed by human platelets and potently inhibits platelet aggregation and thrombus formation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 2416–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Fang, B.; Du, S.; Wang, S.; Li, O.; Jia, X.; Bao, C.; Ye, L.; Sui, X.; Qian, L.; et al. Endothelial cell prostaglandin E2 receptor EP4 is essential for blood pressure homeostasis. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e138505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Xu, C.; Huo, X.; Hao, H.; Wan, Q.; Chen, H.; Zhang, X.; Breyer, R.M.; Huang, Y.; Cao, X.; et al. The cyclooxygenase-1/mPGES-1/endothelial prostaglandin EP4 receptor pathway constrains myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aung, T.; Halsey, J.; Kromhout, D.; Gerstein, H.C.; Marchioli, R.; Tavazzi, L.; Geleijnse, J.M.; Rauch, B.; Ness, A.; Galan, P.; et al. Associations of omega-3 fatty acid supplement use with cardiovascular disease risks: Meta-analysis of 10 trials involving 77,917 individuals. JAMA Cardiol. 2018, 3, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, S.J.; Lincoff, A.M.; Garcia, M.; Bash, D.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Barter, P.J.; Davidson, M.H.; Kastelein, J.J.P.; Koenig, W.; McGuire, D.K.; et al. Effect of High-Dose Omega-3 Fatty Acids vs Corn Oil on Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Patients at High Cardiovascular Risk: The STRENGTH Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2020, 324, 2268–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, P.; Flaumenhaft, R. Platelet α–granules: Basic biology and clinical correlates. Blood Rev. 2009, 23, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finsterbusch, M.; Schrottmaier, W.C.; Kral-Pointner, J.B.; Salzmann, M.; Assinger, A. Measuring and interpreting platelet-leukocyte aggregates. Platelets 2018, 29, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, I.I.; Apta, B.H.R.; Bonna, A.M.; Harper, M.T. Platelet P-selectin triggers rapid surface exposure of tissue factor in monocytes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyú, D.; Glenn, J.R.; White, A.E.; Fox, S.C.; van Giezen, H.; Nylander, S.; Heptinstall, S. Mode of action of P2Y12 antagonists as inhibitors of platelet function. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 105, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iyú, D.; Glenn, J.R.; White, A.E.; Fox, S.C.; Heptinstall, S. Adenosine derived from ADP can contribute to inhibition of platelet aggregation in the presence of a P2Y12 antagonist. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Osete, J.-M.; García-Candel, F.; Fernández-Gómez, F.-J.; Blanquer, M.; Atucha, N.M.; García-Estañ, J.; Iyú, D. TRAP-Induced Platelet Reactivity Is Inhibited by Omega-3 Fatty Acid-Derived Prostaglandin E3 (PGE3). Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2855. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122855
Osete J-M, García-Candel F, Fernández-Gómez F-J, Blanquer M, Atucha NM, García-Estañ J, Iyú D. TRAP-Induced Platelet Reactivity Is Inhibited by Omega-3 Fatty Acid-Derived Prostaglandin E3 (PGE3). Biomedicines. 2024; 12(12):2855. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122855
Chicago/Turabian StyleOsete, José-Miguel, Faustino García-Candel, Francisco-José Fernández-Gómez, Miguel Blanquer, Noemí M. Atucha, Joaquín García-Estañ, and David Iyú. 2024. "TRAP-Induced Platelet Reactivity Is Inhibited by Omega-3 Fatty Acid-Derived Prostaglandin E3 (PGE3)" Biomedicines 12, no. 12: 2855. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122855
APA StyleOsete, J.-M., García-Candel, F., Fernández-Gómez, F.-J., Blanquer, M., Atucha, N. M., García-Estañ, J., & Iyú, D. (2024). TRAP-Induced Platelet Reactivity Is Inhibited by Omega-3 Fatty Acid-Derived Prostaglandin E3 (PGE3). Biomedicines, 12(12), 2855. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122855







