The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Liver Fibrosis: Friends or Foes?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Classification, Biogenesis, and Isolation of EVs
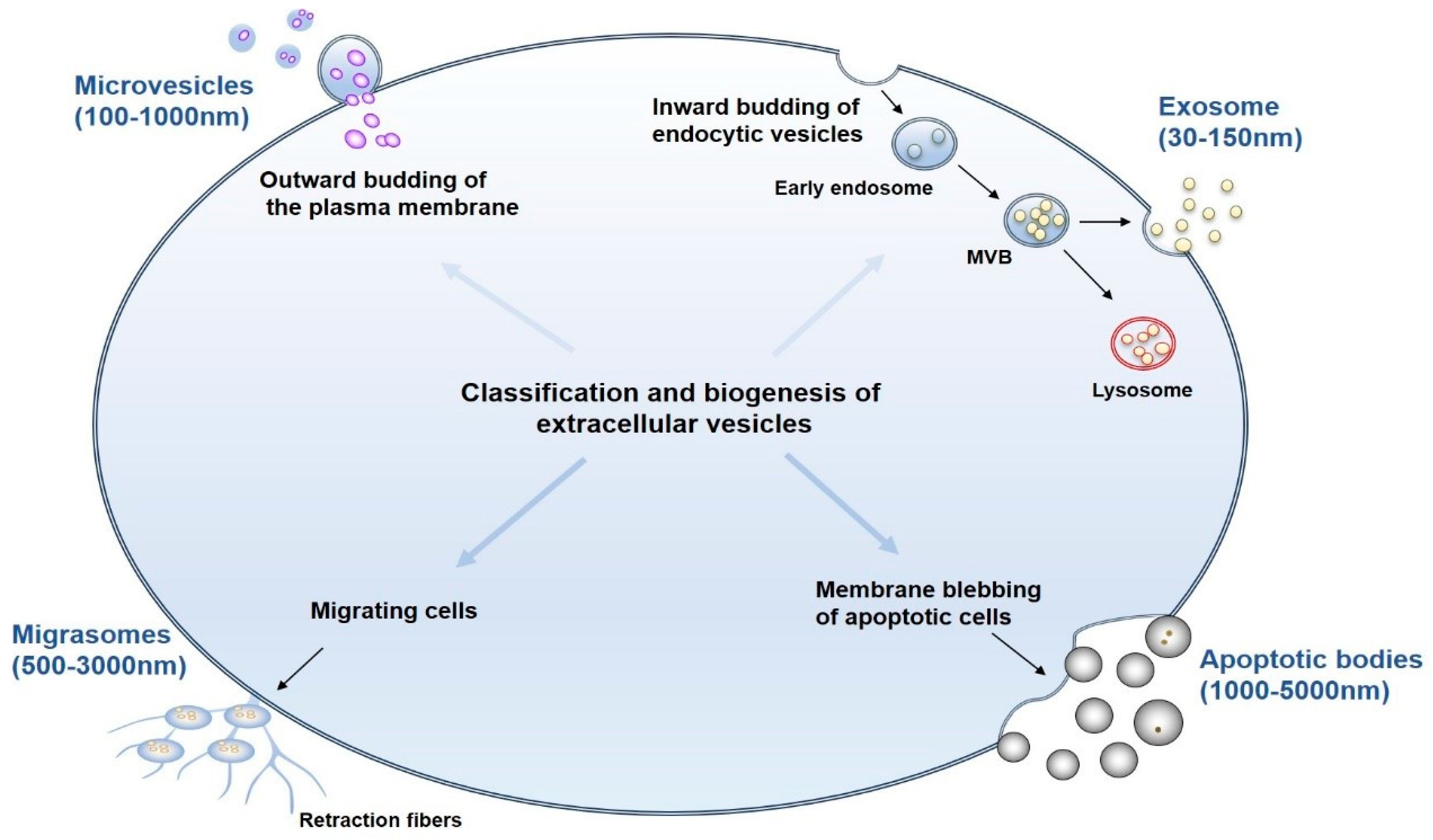
2.1. Classification and Biogenesis of EVs
2.2. Isolation of EVs
3. The Role of EVs (Mainly Exosomes and MVs) in Liver Fibrosis
3.1. EVs as Critical Biomarkers or Mediators in Liver Fibrosis
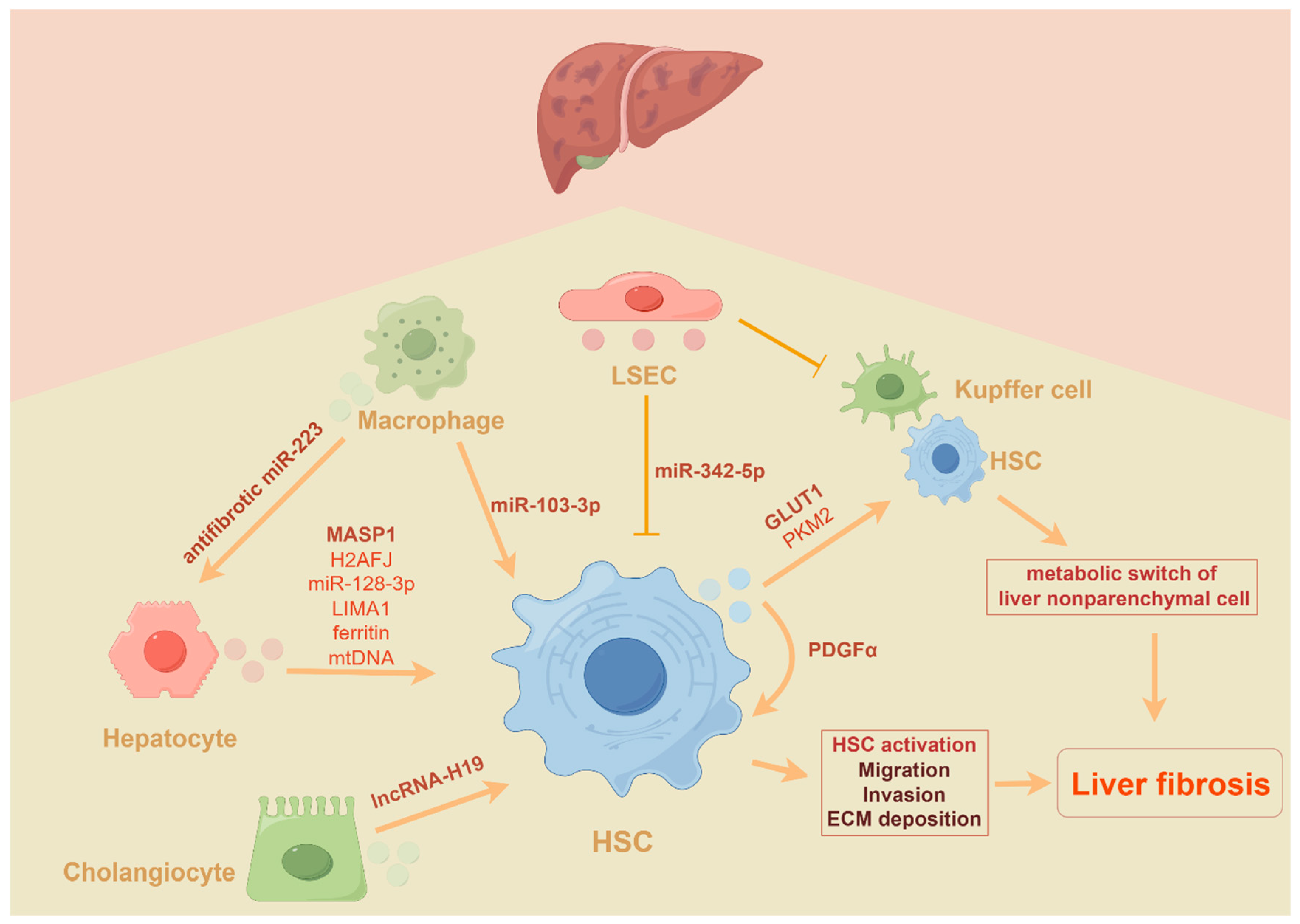
3.2. The Role of EVs in the Progression of Liver Fibrosis
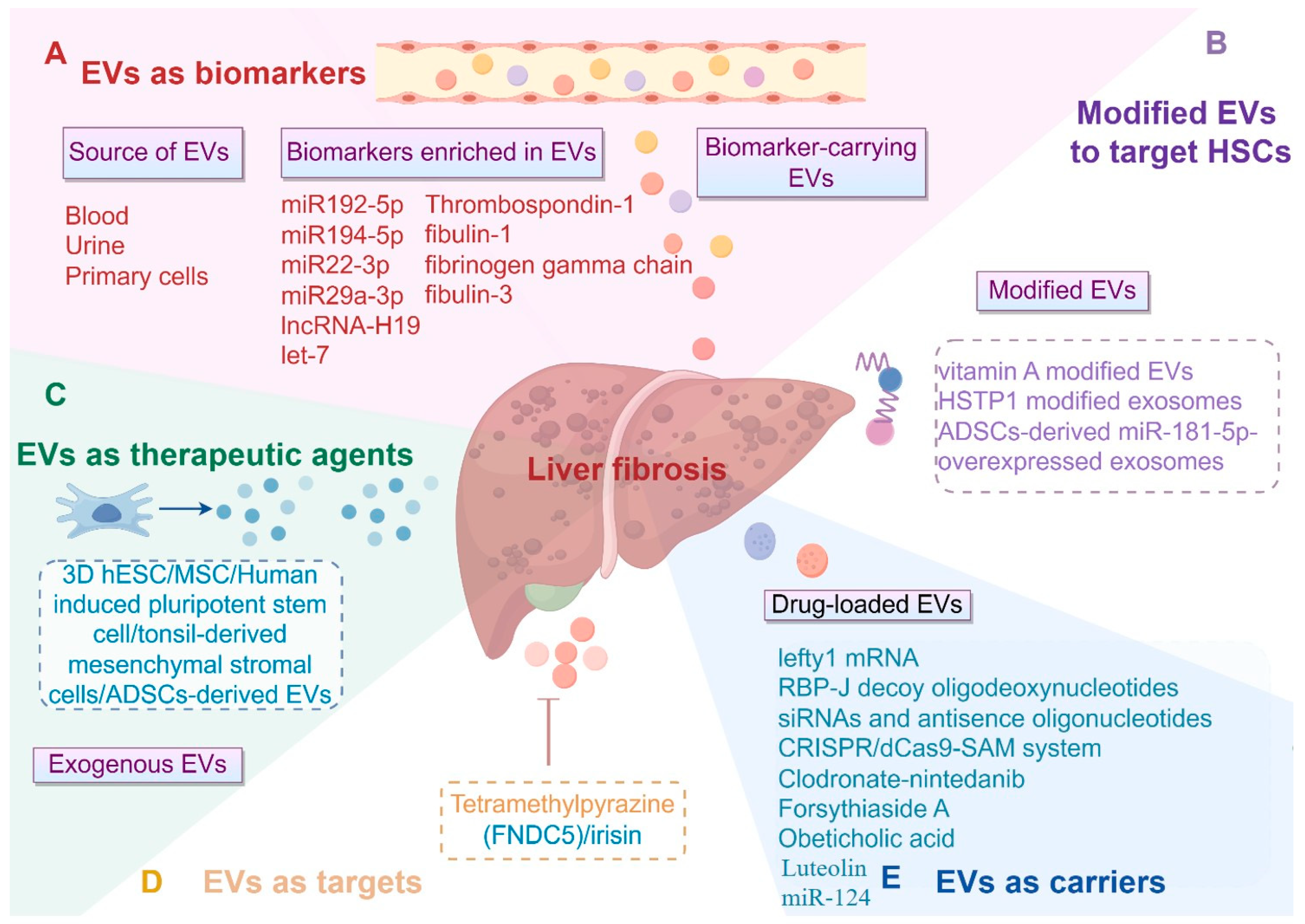
3.3. The Application of EVs (Mainly Exosomes and MVs) in Liver Fibrosis
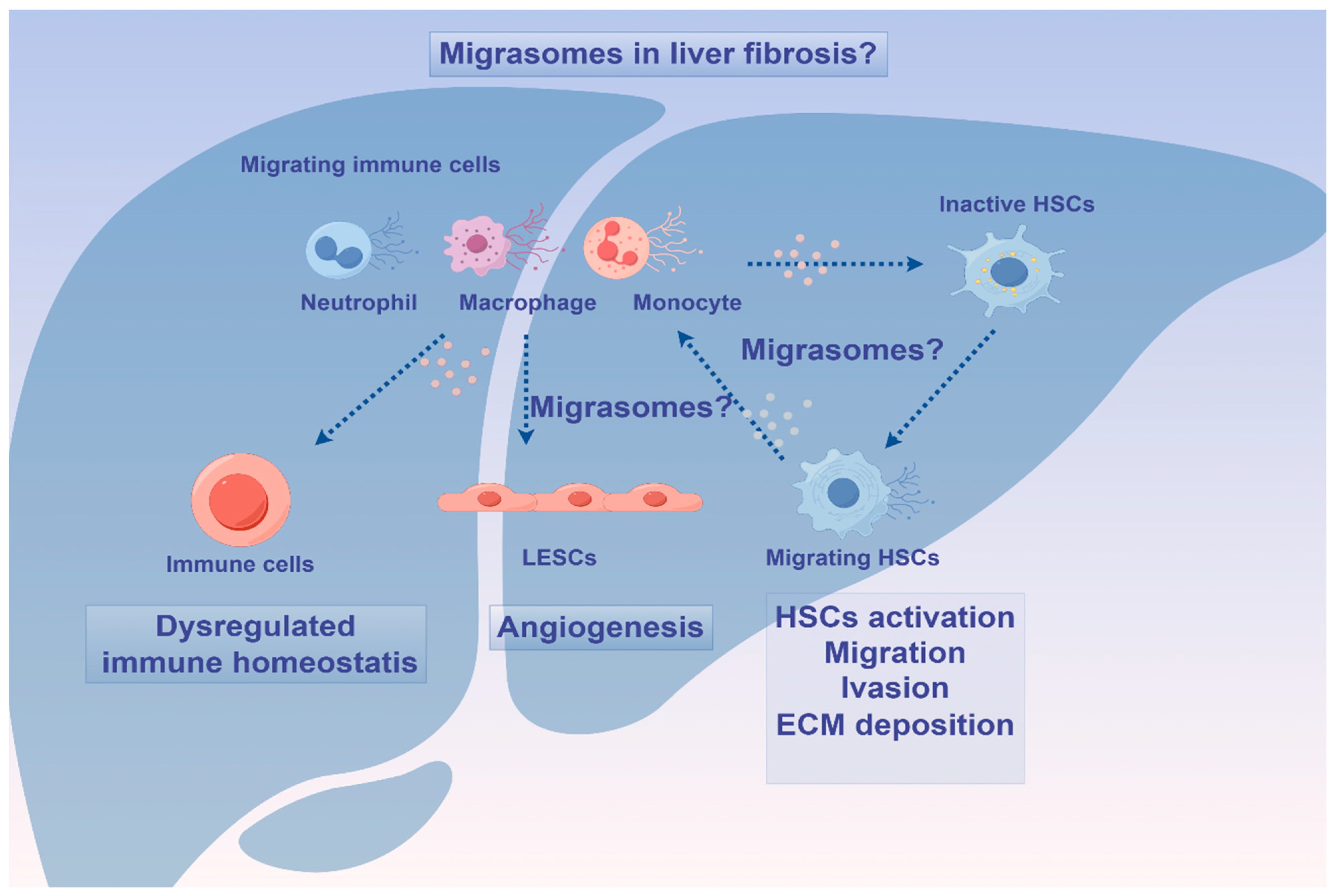
4. Migrasomes in Homeostasis and Diseases: Friends or Foes?
5. Migrasomes: Novel Diagnostic and Therapeutical Opportunities?
6. Clinical Trials of EVs in Liver Fibrosis
7. Discussion and Future Challenges of EVs
7.1. Advantages and Disadvantages of EV Biomarkers Versus Traditional Techniques
7.1.1. Advantages of EV Biomarkers
7.1.2. Disadvantages of EV Biomarkers
7.2. Limitations of EV-Based Therapy
7.3. The Factors Determining the Selection of EVs as a Cargo
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Robinson, M.W.; Harmon, C.; O’Farrelly, C. Liver immunology and its role in inflammation and homeostasis. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2016, 13, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacParland, S.A.; Liu, J.C.; Ma, X.Z.; Innes, B.T.; Bartczak, A.M.; Gage, B.K.; Manuel, J.; Khuu, N.; Echeverri, J.; Linares, I.; et al. Single cell RNA sequencing of human liver reveals distinct intrahepatic macrophage populations. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostallari, E.; Valainathan, S.; Biquard, L.; Shah, V.H.; Rautou, P.E. Role of extracellular vesicles in liver diseases and their therapeutic potential. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 175, 113816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manka, P.; Zeller, A.; Syn, W.K. Fibrosis in Chronic Liver Disease: An Update on Diagnostic and Treatment Modalities. Drugs 2019, 79, 903–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocca, C.; Novo, E.; Miglietta, A.; Parola, M. Angiogenesis and Fibrogenesis in Chronic Liver Diseases. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 1, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.J.; Wang, C. A review of the regulatory mechanisms of extracellular vesicles-mediated intercellular communication. Cell Commun. Signal 2023, 21, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Liu, X.; Ye, J.; Ma, Y.; Mao, J.; Feng, D.; Wang, X. Migrasomes, a new mode of intercellular communication. Cell Commun. Signal 2023, 21, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devhare, P.B.; Ray, R.B. Extracellular vesicles: Novel mediator for cell to cell communications in liver pathogenesis. Mol. Asp. Med. 2018, 60, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, G.; Momen-Heravi, F. Extracellular vesicles in liver disease and potential as biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.R.; Bebawy, M. Circulating biosignatures in multiple myeloma and their role in multidrug resistance. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweij, F.J.; Balaj, L.; Boulanger, C.M.; Carter, D.R.F.; Compeer, E.B.; D’Angelo, G.; El Andaloussi, S.; Goetz, J.G.; Gross, J.C.; Hyenne, V.; et al. The power of imaging to understand extracellular vesicle biology in vivo. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 1013–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaphas, A.; Meyer, J.; Sadoul, R.; Morel, P.; Gonelle-Gispert, C.; Buhler, L.H. Extracellular vesicles: Future diagnostic and therapeutic tools for liver disease and regeneration. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 1801–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomon, C.; Das, S.; Erdbrugger, U.; Kalluri, R.; Kiang Lim, S.; Olefsky, J.M.; Rice, G.E.; Sahoo, S.; Andy Tao, W.; Vader, P.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles and Their Emerging Roles as Cellular Messengers in Endocrinology: An Endocrine Society Scientific Statement. Endocr. Rev. 2022, 43, 441–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Wu, T.; Lin, R.; Zhu, S.; Ji, J.; Jin, D.; Huang, M.; Zheng, W.; Ni, W.; Jiang, F.; et al. Differences between migrasome, a ‘new organelle’, and exosome. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2023, 27, 3672–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yao, L.; Meng, Y.; Li, B.; Yang, Y.; Gao, F. Migrasome: A new functional extracellular vesicle. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Li, Y.; Peng, J.; Wu, D.; Zhao, X.; Cui, Y.; Chen, L.; Yan, X.; Du, Y.; Yu, L. Discovery of the migrasome, an organelle mediating release of cytoplasmic contents during cell migration. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yu, L. Migrasome biogenesis: When biochemistry meets biophysics on membranes. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2024, 49, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, N.; Zhang, W.; Chen, J.; Liu, B.; Du, W.; Liu, X.; et al. The formation of migrasomes is initiated by the assembly of sphingomyelin synthase 2 foci at the leading edge of migrating cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2023, 25, 1173–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinstein, E. The complexity of tetraspanins. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2011, 39, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zucker, B.; Zhang, S.; Elias, S.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, H.; Ding, T.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Lou, J.; et al. Migrasome formation is mediated by assembly of micron-scale tetraspanin macrodomains. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 991–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Yu, L. Calcium ions promote migrasome formation via Synaptotagmin-1. J. Cell Biol. 2024, 223, e202402060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, K.S.; Harris, K.; Arian, K.A.; Ma, L.; Schueng Zancanela, B.; Church, K.A.; McAndrews, K.M.; Kalluri, R. High throughput and rapid isolation of extracellular vesicles and exosomes with purity using size exclusion liquid chromatography. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 40, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Lin, S.; Zhou, C.; Cui, D.; Haick, H.; Tang, N. From Conventional to Microfluidic: Progress in Extracellular Vesicle Separation and Individual Characterization. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, e2202437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Cheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Yang, Q.; Hu, L.; Lou, D.; Li, J.; Dong, X.; et al. Exosome detection via the ultrafast-isolation system: EXODUS. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, R.; Maresh, G.; Zhang, X.; Salomon, C.; Hooper, J.; Margolin, D.; Li, L. The Emerging Roles of Extracellular Vesicles as Communication Vehicles within the Tumor Microenvironment and Beyond. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Takakura, Y. Extracellular vesicle-based therapeutics: Extracellular vesicles as therapeutic targets and agents. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 242, 108352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devarbhavi, H.; Asrani, S.K.; Arab, J.P.; Nartey, Y.A.; Pose, E.; Kamath, P.S. Global burden of Liver Disease: 2023 Update. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 516–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisseleva, T.; Brenner, D. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its regression. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottcher, K.; Pinzani, M. Pathophysiology of liver fibrosis and the methodological barriers to the development of anti-fibrogenic agents. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 121, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotersztajn, S.; Julien, B.; Teixeira-Clerc, F.; Grenard, P.; Mallat, A. Hepatic fibrosis: Molecular mechanisms and drug targets. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2005, 45, 605–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, B.; He, Q.; Weng, Q. Intercellular crosstalk of hepatic stellate cells in liver fibrosis: New insights into therapy. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 155, 104720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thietart, S.; Rautou, P.E. Extracellular vesicles as biomarkers in liver diseases: A clinician’s point of view. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 1507–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X. Extracellular vesicles: Catching the light of intercellular communication in fibrotic liver diseases. Theranostics 2022, 12, 6955–6971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagoonee, S.; Arigoni, M.; Manco, M.; Olivero, M.; Bizzaro, F.; Magagnotti, C.; Andolfo, A.; Miniscalco, B.; Forni, M.; Todeschi, S.; et al. Circulating Extracellular Vesicles Contain Liver-Derived RNA Species as Indicators of Severe Cholestasis-Induced Early Liver Fibrosis in Mice. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2022, 36, 480–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Li, X.; Zhu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Wang, X.; Gurley, E.C.; Liang, G.; Chen, W.; Lai, G.; et al. Cholangiocyte-Derived Exosomal Long Noncoding RNA H19 Promotes Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation and Cholestatic Liver Fibrosis. Hepatology 2019, 70, 1317–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuura, K.; De Giorgi, V.; Schechterly, C.; Wang, R.Y.; Farci, P.; Tanaka, Y.; Alter, H.J. Circulating let-7 levels in plasma and extracellular vesicles correlate with hepatic fibrosis progression in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2016, 64, 732–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payance, A.; Silva-Junior, G.; Bissonnette, J.; Tanguy, M.; Pasquet, B.; Levi, C.; Roux, O.; Nekachtali, O.; Baiges, A.; Hernandez-Gea, V.; et al. Hepatocyte microvesicle levels improve prediction of mortality in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 2018, 68, 1508–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baweja, S.; Bihari, C.; Negi, P.; Thangariyal, S.; Kumari, A.; Lal, D.; Maheshwari, D.; Singh Maras, J.; Nautiyal, N.; Kumar, G.; et al. Circulating extracellular vesicles induce monocyte dysfunction and are associated with sepsis and high mortality in cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2021, 41, 1614–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baweja, S.; Kumari, A.; Negi, P.; Thangariyal, S.; Subudhi, P.D.; Gautam, S.; Mittal, A.; Bihari, C. Vascular Extracellular Vesicles Indicate Severe Hepatopulmonary Syndrome in Cirrhosis. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzzaman, A.; Zhang, X.; Qiao, Z.; Zhan, H.; Sohail, A.; Wahid, A.; Shang, Z.; Guan, X.; Cao, C.X.; Xiao, H. Discovery of small extracellular vesicle proteins from human serum for liver cirrhosis and liver cancer. Biochimie 2020, 177, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakane, S.; Hikita, H.; Shirai, K.; Sakamoto, T.; Narumi, R.; Adachi, J.; Kakita, N.; Yamada, Y.; Toyoda, H.; Takahashi, H.; et al. Proteomic analysis of serum extracellular vesicles reveals Fibulin-3 as a new marker predicting liver-related events in MASLD. Hepatol. Commun. 2024, 8, e0448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Tan, S.; Liu, H.; Jiang, J.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Wu, B. Hepatocyte-derived MASP1-enriched small extracellular vesicles activate HSCs to promote liver fibrosis. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1181–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Jiang, W.; Li, Z.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Pei, Q.; Huang, G.; Wang, L.; et al. Hepatocyte-derived exosomes deliver H2AFJ to hepatic stellate cells and promote liver fibrosis via the MAPK/STMN1 axis activation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 115, 109605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenen, M.T.; Brandt, E.F.; Kaczor, D.M.; Caspers, T.; Heinzmann, A.C.A.; Fischer, P.; Heinrichs, D.; Wirtz, T.H.; Trautwein, C.; Koenen, R.R.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles from Steatotic Hepatocytes Provoke Pro-Fibrotic Responses in Cultured Stellate Cells. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, A.; Reyes, D.; Geng, Y.; Arab, J.P.; Cabrera, D.; Sepulveda, R.; Solis, N.; Buist-Homan, M.; Arrese, M.; Moshage, H. Extracellular vesicles derived from fat-laden hepatocytes undergoing chemical hypoxia promote a pro-fibrotic phenotype in hepatic stellate cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Povero, D.; Panera, N.; Eguchi, A.; Johnson, C.D.; Papouchado, B.G.; de Araujo Horcel, L.; Pinatel, E.M.; Alisi, A.; Nobili, V.; Feldstein, A.E. Lipid-induced hepatocyte-derived extracellular vesicles regulate hepatic stellate cell via microRNAs targeting PPAR-gamma. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 1, 646–663.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Tang, M.; Qian, Y.; Zong, G.; Zhu, G.; Jiang, Y.; Mu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Ding, Q.; Wang, H.; et al. Extracellular vesicles-derived ferritin from lipid-induced hepatocytes regulates activation of hepatic stellate cells. Heliyon 2024, 10, e33741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, W.; Eun, H.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Yi, H.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Park, S.H.; Jang, M.J.; Jo, E.; Kim, S.C.; Han, Y.M.; et al. Exosome-mediated activation of toll-like receptor 3 in stellate cells stimulates interleukin-17 production by gammadelta T cells in liver fibrosis. Hepatology 2016, 64, 616–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Liu, R.P.; Ding, M.N.; Zheng, Q.; Wu, J.Z.; Xue, X.Y.; Gu, Y.Q.; Ma, B.N.; Cai, Y.J.; Li, S.; et al. Tetramethylpyrazine prevents liver fibrotic injury in mice by targeting hepatocyte-derived and mitochondrial DNA-enriched extracellular vesicles. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 2026–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Gao, Y.L.; Jiang, S.; Qian, B.; Che, L.; Wu, J.S.; Du, Z.B.; Wang, M.Z.; Yang, Y.; Lin, Y.C.; et al. Aflatoxin B(1)-exposed hepatocyte-derived extracellular vesicles: Initiating hepatic stellate cell-mediated liver fibrosis through a p53-Parkin-dependent mitophagy pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 277, 116363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostallari, E.; Hirsova, P.; Prasnicka, A.; Verma, V.K.; Yaqoob, U.; Wongjarupong, N.; Roberts, L.R.; Shah, V.H. Hepatic stellate cell-derived platelet-derived growth factor receptor-alpha-enriched extracellular vesicles promote liver fibrosis in mice through SHP2. Hepatology 2018, 68, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, L.; Xia, T.; Du, Y.; Liu, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, F.; Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Shi, C. Exosomes from activated hepatic stellate cells contain GLUT1 and PKM2: A role for exosomes in metabolic switch of liver nonparenchymal cells. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 8530–8542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanal, S.; Liu, Y.; Bamidele, A.O.; Wixom, A.Q.; Washington, A.M.; Jalan-Sakrikar, N.; Cooper, S.A.; Vuckovic, I.; Zhang, S.; Zhong, J.; et al. Glycolysis in hepatic stellate cells coordinates fibrogenic extracellular vesicle release spatially to amplify liver fibrosis. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadn5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Yin, S.; Ren, R.; Liu, S.; Yong, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zheng, M.H.; Kunos, G.; Gao, B.; et al. Myeloid-Cell-Specific IL-6 Signaling Promotes MicroRNA-223-Enriched Exosome Production to Attenuate NAFLD-Associated Fibrosis. Hepatology 2021, 74, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Yao, X.; Yao, H.; Ji, Q.; Ding, G.; Liu, X. Exosomal miR-103-3p from LPS-activated THP-1 macrophage contributes to the activation of hepatic stellate cells. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 5178–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ning, Z.; Xu, Q.; Lin, Y.; Gong, J.; Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Meng, Y.; et al. Autophagic degradation of MVBs in LSECs promotes Aldosterone induced-HSCs activation. Hepatol. Int. 2023, 18, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, Z.; Xia, M.; Salas, S.S.; Ospina, J.A.; Buist-Homan, M.; Harmsen, M.C.; Moshage, H. Extracellular vesicles derived from liver sinusoidal endothelial cells inhibit the activation of hepatic stellate cells and Kupffer cells in vitro. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2024, 1870, 167020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Luo, Y.; Gu, F.; Song, W.; Nie, X.; Yang, Q. Therapeutic role of FNDC5/irisin in attenuating liver fibrosis via inhibiting release of hepatic stellate cell-derived exosomes. Hepatol. Int. 2023, 17, 1659–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, R.; Kemper, S.; Cong, M.; You, H.; Brigstock, D.R. Therapeutic effects of serum extracellular vesicles in liver fibrosis. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1461505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Li, X.; Zhong, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, S.; Wu, H.; Tang, X.; Chen, C.; Fu, Y.; Chen, Q.; et al. 3D hESC exosomes enriched with miR-6766-3p ameliorates liver fibrosis by attenuating activated stellate cells through targeting the TGFbetaRII-SMADS pathway. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Huang, Y.; Mei, R.; Mao, F.; Yang, D.; Liu, J.; Xu, W.; Qian, H.; Yan, Y. HucMSC-derived exosomes delivered BECN1 induces ferroptosis of hepatic stellate cells via regulating the xCT/GPX4 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Shi, C.; Duan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B. Exosomal microRNA-618 derived from mesenchymal stem cells attenuate the progression of hepatic fibrosis by targeting Smad4. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 5915–5927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Wei, J.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, J.; Xiao, E.; Kang, Y.; Kang, Y. Mesenchymal stem cell-originated exosomal circDIDO1 suppresses hepatic stellate cell activation by miR-141-3p/PTEN/AKT pathway in human liver fibrosis. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 440–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, X.; Liu, J.; Yao, X.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Y.; Xie, F. Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviate liver fibrosis through the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Bian, S.; Qiu, S.; Bishop, C.E.; Wan, M.; Xu, N.; Sun, X.; Sequeira, R.C.; Atala, A.; Gu, Z.; et al. Placenta mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles alleviate liver fibrosis by inactivating hepatic stellate cells through a miR-378c/SKP2 axis. Inflamm. Regen. 2023, 43, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Wu, T.; Liu, L.; Luo, B.; Wei, C. Extracellular vesicles-derived miR-150-5p secreted by adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibits CXCL1 expression to attenuate hepatic fibrosis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 701–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shang, J.; Yang, Q.; Dai, Z.; Liang, Y.; Lai, C.; Feng, T.; Zhong, D.; Zou, H.; Sun, L.; et al. Exosomes derived from human adipose mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and remodeling choline metabolism. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohara, M.; Ohnishi, S.; Hosono, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Yuyama, K.; Nakamura, H.; Fu, Q.; Maehara, O.; Suda, G.; Sakamoto, N. Extracellular Vesicles from Amnion-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorate Hepatic Inflammation and Fibrosis in Rats. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 3212643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, M.; Cui, L.; Li, B.; Liu, Y.; Su, R.; Sun, K.; Hu, Y.; Yang, F.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes protect against liver fibrosis via delivering miR-148a to target KLF6/STAT3 pathway in macrophages. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yan, Y.; Wang, B.; Qian, H.; Zhang, X.; Shen, L.; Wang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, W.; Li, W.; et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate liver fibrosis. Stem Cells Dev. 2013, 22, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, N.; Tsuchiya, A.; Mito, M.; Natsui, K.; Natusi, Y.; Koseki, Y.; Tomiyoshi, K.; Yamazaki, F.; Yoshida, Y.; Abe, H.; et al. Analysis of distribution, collection, and confirmation of capacity dependency of small extracellular vesicles toward a therapy for liver cirrhosis. Inflamm. Regen. 2023, 43, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Povero, D.; Pinatel, E.M.; Leszczynska, A.; Goyal, N.P.; Nishio, T.; Kim, J.; Kneiber, D.; de Araujo Horcel, L.; Eguchi, A.; Ordonez, P.M.; et al. Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles reduce hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis. JCI Insight 2019, 5, e125652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiabotto, G.; Ceccotti, E.; Tapparo, M.; Camussi, G.; Bruno, S. Human Liver Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Target Hepatic Stellate Cells and Attenuate Their Pro-fibrotic Phenotype. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 777462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, S.; Pasquino, C.; Herrera Sanchez, M.B.; Tapparo, M.; Figliolini, F.; Grange, C.; Chiabotto, G.; Cedrino, M.; Deregibus, M.C.; Tetta, C.; et al. HLSC-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Attenuate Liver Fibrosis and Inflammation in a Murine Model of Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Mol. Ther. 2020, 28, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, J.; Li, W.; Su, G.; Li, L.; Ran, J. Exosome-derived miR-142-5p from liver stem cells improves the progression of liver fibrosis by regulating macrophage polarization through CTSB. Environ. Toxicol. 2023, 38, 1860–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, C.; Shin, Y.; Wang, S.; Han, J.; Kim, M.; Kim, J.M.; Shin, S.C.; Lee, B.J.; Kim, T.J.; et al. sEVs from tonsil-derived mesenchymal stromal cells alleviate activation of hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis through miR-486-5p. Mol. Ther. 2021, 29, 1471–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Feng, J.; Guo, J.; Wang, J.; Xiu, G.; Xu, J.; Ning, K.; Ling, B.; Fu, Q.; Xu, J. ADSCs-derived exosomes ameliorate hepatic fibrosis by suppressing stellate cell activation and remodeling hepatocellular glutamine synthetase-mediated glutamine and ammonia homeostasis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, E.; Dominguez, L.M.; Bayo, J.; Malvicini, M.; Atorrasagasti, C.; Rodriguez, M.; Cantero, M.J.; Garcia, M.; Yannarelli, G.; Mazzolini, G. Human umbilical cord perivascular cells-derived extracellular vesicles mediate the transfer of IGF-I to the liver and ameliorate hepatic fibrogenesis in mice. Gene Ther. 2020, 27, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.J.; Cao, J.; Lee, C.Y.; Wu, Y.M. Umbilical cord blood plasma-derived exosomes as a novel therapy to reverse liver fibrosis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wu, J.; Cao, H.; Ma, C.; Wu, Z.; Tian, Y.; Ma, C.; Qiu, H.; Pan, G. Human-Induced Hepatocytes-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Ameliorated Liver Fibrosis in Mice via Suppression of TGF-beta1/Smad Signaling and Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling. Stem Cells Dev. 2023, 32, 638–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reif, S.; Atias, A.; Musseri, M.; Koroukhov, N.; Gerstl, R.G. Beneficial Effects of Milk-Derived Extracellular Vesicles on Liver Fibrosis Progression by Inhibiting Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, H.; Dong, B.; Zhu, D.; Fu, Z.; Liu, J.; Jin, Y. Sja-let-7 suppresses the development of liver fibrosis via Schistosoma japonicum extracellular vesicles. PLoS Pathog. 2024, 20, e1012153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, D.G.; Oh, B.H.; Nguyen, V.Q.; Lim, G.T.; Um, W.; Jung, J.M.; Jeon, J.; Choi, J.S.; Choi, Y.C.; Jung, Y.J.; et al. Vitamin A-coupled stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles regulate the fibrotic cascade by targeting activated hepatic stellate cells in vivo. J. Control Release 2021, 336, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Yan, M.; Bai, Z.; Xie, Y.; Ren, L.; Wei, J.; Zhu, D.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Luo, J.; et al. Huc-MSC-derived exosomes modified with the targeting peptide of aHSCs for liver fibrosis therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, X.; Li, F.; Ma, Z.; Xu, M.; Lu, L. Exosomes derived from miR-181-5p-modified adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells prevent liver fibrosis via autophagy activation. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 2491–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Teng, L. Small extracellular vesicles encapsulating lefty1 mRNA inhibit hepatic fibrosis. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 17, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Li, W.N.; Li, X.X.; Yue, K.Y.; Duan, J.L.; Ruan, B.; Liu, J.J.; Song, P.; Yue, Z.S.; Tao, K.S.; et al. Exosome-mediated delivery of RBP-J decoy oligodeoxynucleotides ameliorates hepatic fibrosis in mice. Theranostics 2022, 12, 1816–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.; Chen, Y.; Li, B.; Sugimoto, H.; Yang, S.; Yang, C.; LeBleu, V.S.; McAndrews, K.M.; Kalluri, R. Therapeutic targeting of STAT3 with small interference RNAs and antisense oligonucleotides embedded exosomes in liver fibrosis. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, N.; Zhong, W.; Li, J.; Zhai, Z.; Lu, J.; Dong, R. Targeted activation of HNF4alpha/HGF1/FOXA2 reverses hepatic fibrosis via exosome-mediated delivery of CRISPR/dCas9-SAM system. Nanomedicine 2022, 17, 1411–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, K.; Fan, M.; Huang, D.; Sun, L.; Li, B.; Xu, R.; Zhang, J.; Shao, X.; Chen, Y. Clodronate-nintedanib-loaded exosome-liposome hybridization enhances the liver fibrosis therapy by inhibiting Kupffer cell activity. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C.; Fu, K.; Ma, C.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, C.; Li, Y. CD44-Targeting Drug Delivery System of Exosomes Loading Forsythiaside A Combats Liver Fibrosis via Regulating NLRP3-Mediated Pyroptosis. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, e2202228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizsoltani, A.; Hatami, B.; Zali, M.R.; Mahdavi, V.; Baghaei, K.; Alizadeh, E. Obeticholic acid-loaded exosomes attenuate liver fibrosis through dual targeting of the FXR signaling pathway and ECM remodeling. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 168, 115777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashour, A.A.; El-Kamel, A.H.; Mehanna, R.A.; Mourad, G.; Heikal, L.A. Luteolin-loaded exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells: A promising therapy for liver fibrosis. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 3270–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niknam, B.; Baghaei, K.; Mahmoud Hashemi, S.; Hatami, B.; Reza Zali, M.; Amani, D. Human Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem cells derived-exosomes enriched by miR-124 promote an anti-fibrotic response in an experimental model of liver fibrosis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 119, 110294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Sun, Z.; Wei, J.; Zhang, Y.; An, W.; Lin, Y.; Li, X. BMP7-Loaded Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Ameliorate Liver Fibrosis by Targeting Activated Hepatic Stellate Cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 3475–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, H.; Jiang, D.; Hu, X.; Du, W.; Ji, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Sho, T.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; et al. Mitocytosis, a migrasome-mediated mitochondrial quality-control process. Cell 2021, 184, 2896–2910.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lu, Z.; Jiang, D.; Guo, Y.; Qiao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, T.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhanghao, K.; et al. Iterative tomography with digital adaptive optics permits hour-long intravital observation of 3D subcellular dynamics at millisecond scale. Cell 2021, 184, 3318–3332.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Jiao, L.; Li, Q.; Xie, R.; Jia, H.; Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Huang, D.; Zheng, J.; et al. Neutrophil-derived migrasomes are an essential part of the coagulation system. Nat. Cell Biol. 2024, 26, 1110–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Li, T.; Ma, X.; Liu, S.; Li, C.; Huang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Wu, R.; Wang, S.; Lu, D.; et al. Macrophage lineage cells-derived migrasomes activate complement-dependent blood-brain barrier damage in cerebral amyloid angiopathy mouse model. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, D.; Zhang, Y.; Song, W. The M2 Macrophages Derived Migrasomes from the Surface of Titania Nanotubes Array as a New Concept for Enhancing Osteogenesis. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, e2400257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, T.; Yin, S.; Gao, M.; He, H.; Li, Y.; Jiang, D.; Shi, M.; Wang, J.; Yu, L. Monocytes deposit migrasomes to promote embryonic angiogenesis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2022, 24, 1726–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellicoro, A.; Ramachandran, P.; Iredale, J.P.; Fallowfield, J.A. Liver fibrosis and repair: Immune regulation of wound healing in a solid organ. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastore, M.; Caligiuri, A.; Raggi, C.; Navari, N.; Piombanti, B.; Di Maira, G.; Rovida, E.; Piccinni, M.P.; Lombardelli, L.; Logiodice, F.; et al. Macrophage MerTK promotes profibrogenic cross-talk with hepatic stellate cells via soluble mediators. JHEP Rep. 2022, 4, 100444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Zhu, Z.; Jia, R.; Wang, N.A.; Shi, M.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, L. CD151-enriched migrasomes mediate hepatocellular carcinoma invasion by conditioning cancer cells and promoting angiogenesis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 43, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Peng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, K.; Chen, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, T.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, S.; et al. Pancreatic Cancer Cell-derived Migrasomes Promote Cancer Progression by Fostering an Immunosuppressive Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Lett. 2024, 605, 217289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniz, I.A.; Karbanova, J.; Wobus, M.; Bornhauser, M.; Wimberger, P.; Kuhlmann, J.D.; Corbeil, D. Mesenchymal stromal cell-associated migrasomes: A new source of chemoattractant for cells of hematopoietic origin. Cell Commun. Signal 2023, 21, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Su, X.; Lu, P.; Kang, X.; Hu, M.; Li, C.; Wang, S.; Lu, D.; Shen, S.; Huang, H.; et al. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Dermcidin-Containing Migrasomes enhance LC3-Associated Phagocytosis of Pulmonary Macrophages and Protect against Post-Stroke Pneumonia. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2206432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Hu, D.; Dong, Z.; Lu, F. Migrasomes from adipose derived stem cells enrich CXCL12 to recruit stem cells via CXCR4/RhoA for a positive feedback loop mediating soft tissue regeneration. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Lei, Y.; Zheng, J.; Peng, J.; Li, Y.; Yu, L.; Chen, Y. Identification of markers for migrasome detection. Cell Discov. 2019, 5, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Rong, W.; Zeng, C.; Zhu, X.; Chen, Q.; Li, L.; Liu, Z.H.; Zen, K. Podocyte-Released Migrasomes in Urine Serve as an Indicator for Early Podocyte Injury. Kidney Dis. 2020, 6, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Zhang, H.; Chen, S.; Lou, K.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, M.; Lu, R.; Zheng, C.; Li, L.; Chen, Q.; et al. Quantification of urinary podocyte-derived migrasomes for the diagnosis of kidney disease. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkrief, L.; Ganne-Carrie, N.; Manceau, H.; Tanguy, M.; Valainathan, S.R.; Riescher-Tuczkiewicz, A.; Biquard, L.; Barget, N.; Chaffaut, C.; Louvet, A.; et al. Hepatocyte-derived biomarkers predict liver-related events at 2 years in Child-Pugh class A alcohol-related cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 910–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momen-Heravi, F.; Getting, S.J.; Moschos, S.A. Extracellular vesicles and their nucleic acids for biomarker discovery. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 192, 170–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sources/Type | Cargos | Target or Outcomes | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3D-hESCs; exosomes | miR-6766-3p | HSCs; TGFβRII-SMADs, anti-fibrotic | [60] |
| HucMSCs; exosomes | BECN1 | HSCs; xCT/GPX4, HSCs ferroptosis | [61] |
| MSCs; exosomes | miR-618 | HSCs; Smad4, inactivate HSCs | [62] |
| MSC; exosomes | circDIDO1 | HSCs; miR-141-3p/PTEN/AKT | [63] |
| hBM-MSCs; exosomes | / | HSCs; Wnt/β-catenin, inactivate HSCs | [64] |
| Placenta MSCs; EVs | miR-378c | HSCs; SKP2, inactivate HSCs | [65] |
| ADSCs; EVs | miR-150-5p | HSCs; CXCL1, inhibit HSC activation | [66] |
| Human ADSCs; exosomes | / | PI3K/AKT/mTOR, choline metabolism | [67] |
| Amnion-derived MSCs; EVs | / | HSCs, Kupffer cells | [68] |
| MSCs; exosomes | miR-148a | Macrophages; KLF6/STAT3, modulate macrophage phenotype | [69] |
| HucMSCs; exosomes | / | Hepatocytes; EMT | [70] |
| Human iPSCs; EVs | miR-92a-3p | HSCs; reduce HSC activation | [72] |
| Human LSCs; EVs | miR-146a-5p | Anti-fibrotic | [73] |
| Human LSCs; EVs | / | Anti-fibrotic | [74] |
| LSCs; exosomes | miR-142-5p | Macrophages; CTSB, regulate macrophage polarization | [75] |
| T-MSCs; small EVs | miR-486-5p | HSCs; hedgehog signaling | [76] |
| ASCs; exosomes | / | HSCs; inactivate HSCs, remodel glutamine metabolism | [77] |
| HUCPVCs; EVs | IGF-I | HSCs, macrophages | [78] |
| Human UCB; exosomes | / | HSCs; TGF-β/ID1 | [79] |
| HiHep; EVs | / | TGF-β1/Smad, Nrf2/HO-1 | [80] |
| Milk; EVs | / | HSCs; inactivate HSCs | [81] |
| Schistosoma japonicum; EVs | Sja-let-7 | HSCs; Col1α2/TGF-β/Smad | [82] |
| MSCs; vitamin A-coupled EV | / | activated HSCs; anti-fibrotic | [83] |
| HucMSCs; HSTP1-exosomes | / | inactivate HSCs | [84] |
| miR-181-5p-modified ADSCs; exosomes | miR-181-5p | HSCs; autophagy activation | [85] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tao, X.; Chen, C.; Liu, M. The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Liver Fibrosis: Friends or Foes? Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2665. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122665
Tao X, Chen C, Liu M. The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Liver Fibrosis: Friends or Foes? Biomedicines. 2024; 12(12):2665. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122665
Chicago/Turabian StyleTao, Xiang, Can Chen, and Mei Liu. 2024. "The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Liver Fibrosis: Friends or Foes?" Biomedicines 12, no. 12: 2665. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122665
APA StyleTao, X., Chen, C., & Liu, M. (2024). The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Liver Fibrosis: Friends or Foes? Biomedicines, 12(12), 2665. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122665





