Assessing the Utility of ColabFold and AlphaMissense in Determining Missense Variant Pathogenicity for Congenital Myasthenic Syndromes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Variant Dataset
2.2. ColabFold
2.3. Measuring Variant-Induced Predicted Structural Disruption
2.4. Measuring Variant-Induced Structure Prediction Confidence Changes
2.5. Measuring Variant-Induced Structure Prediction Quality Changes
2.6. AlphaMissense
2.7. AlamutVP
2.8. EVE
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
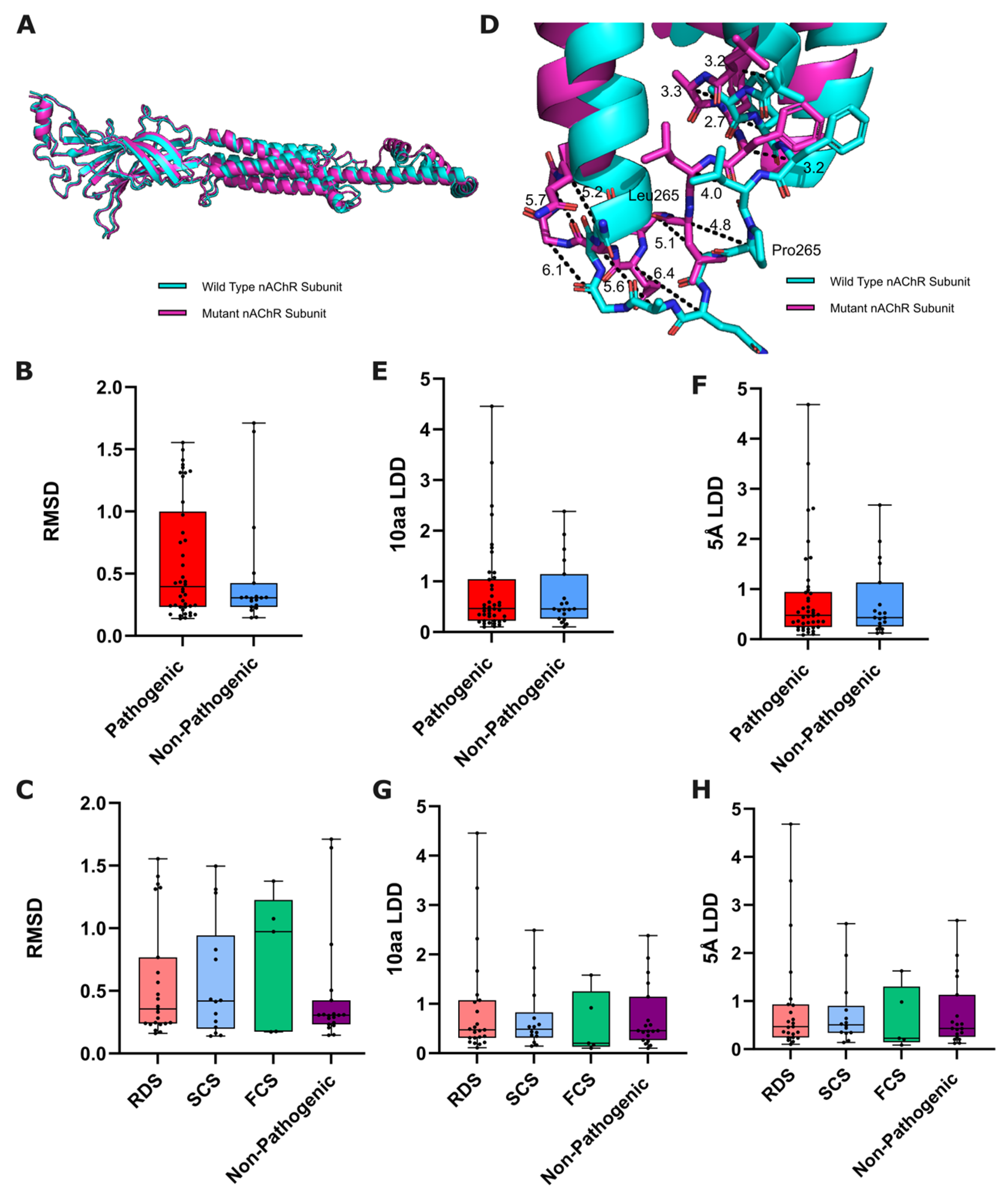
3.1. Variant-Induced ColabFold-Predicted Structural Disruption
3.1.1. Global Structural Disruption
3.1.2. Local Structural Disruption
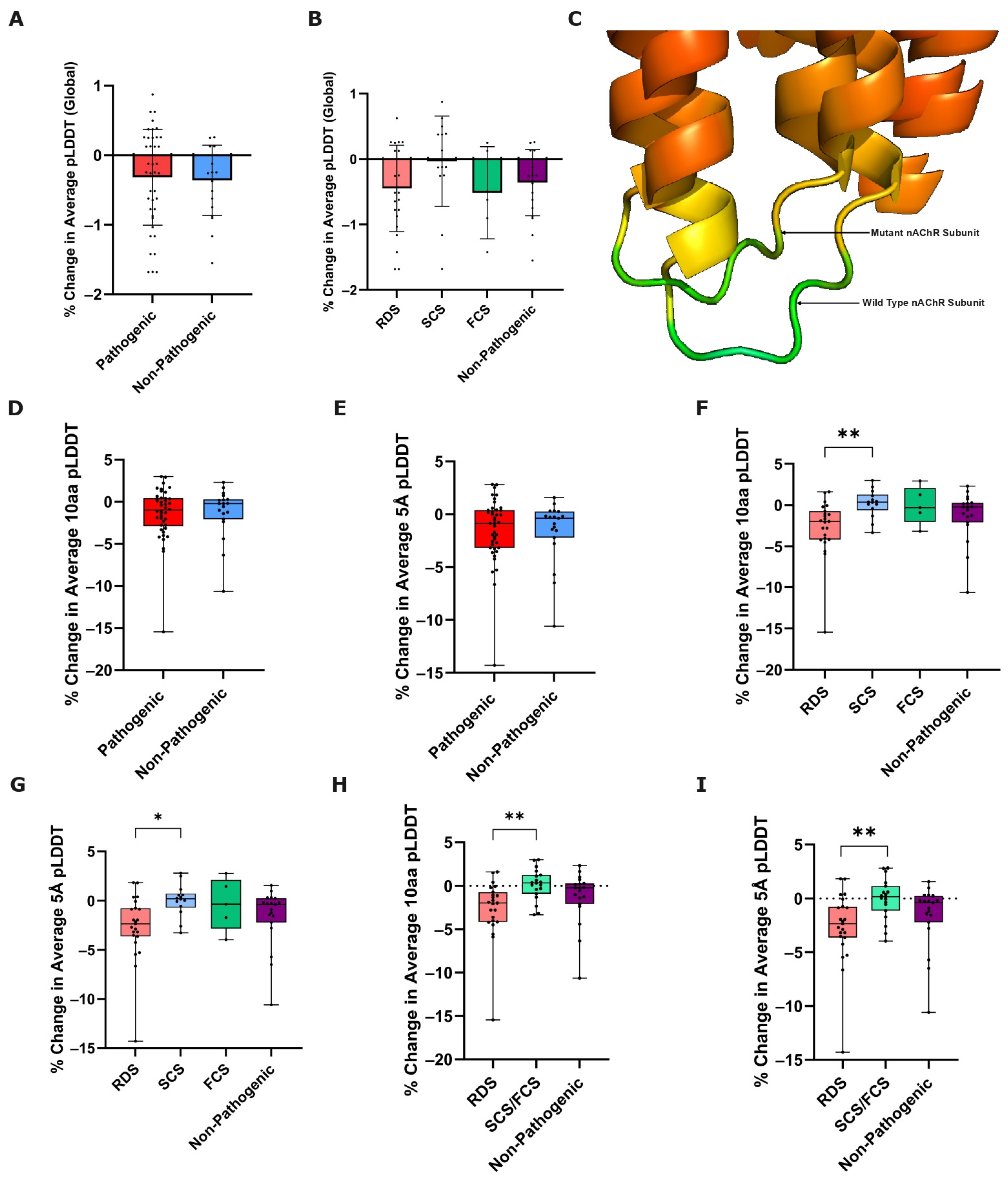
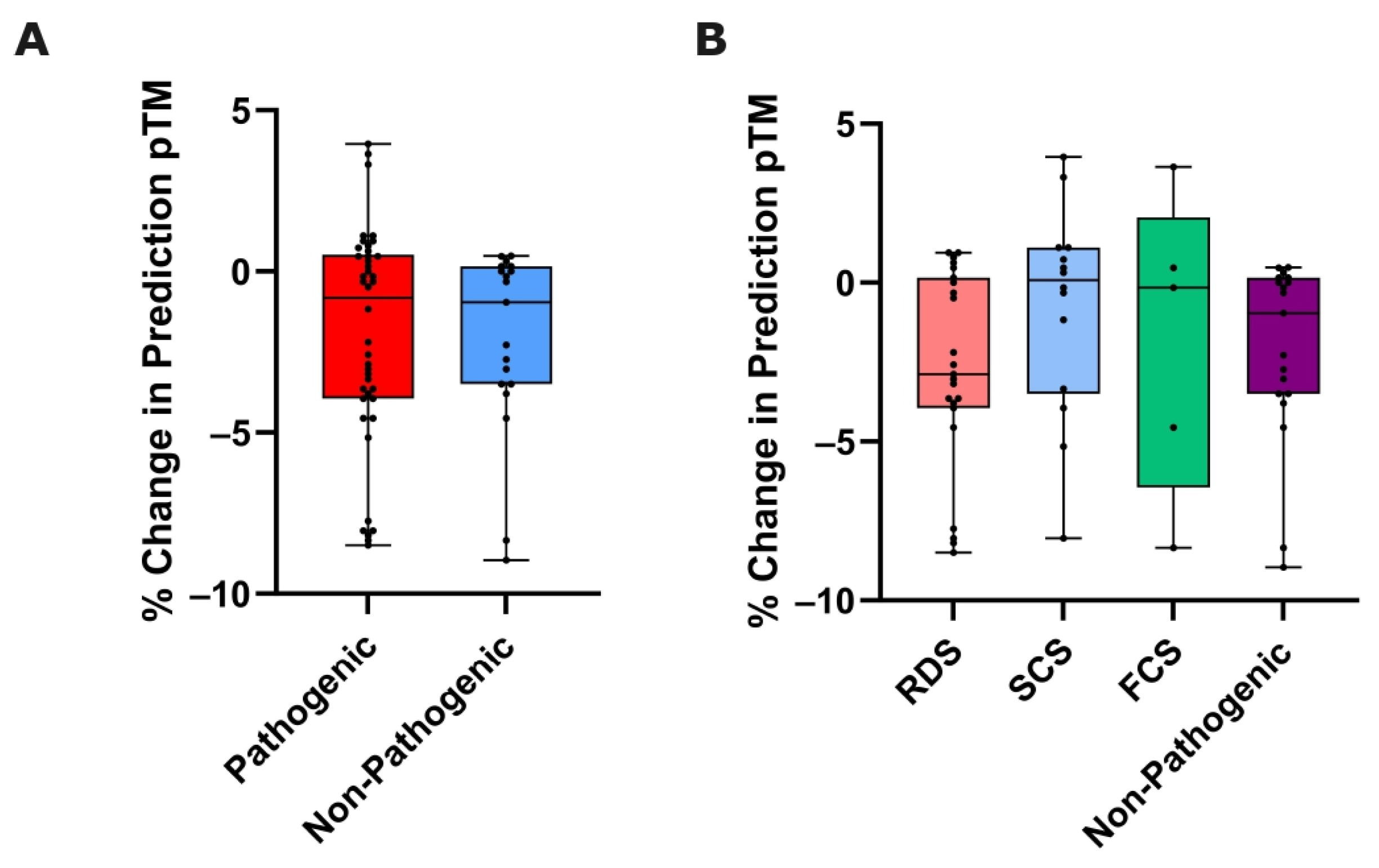
3.2. Variant-Induced ColabFold Prediction Confidence Change
3.2.1. Global Prediction Confidence Change
3.2.2. Local Prediction Confidence Change
3.3. Variant-Induced ColabFold Prediction Quality Change
3.4. AlphaMissense Variant Pathogenicity Prediction
3.5. AlphaMissense Comparison with AlamutVP and EVE
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vanhaesebrouck, A.E.; Beeson, D. The congenital myasthenic syndromes: Expanding genetic and phenotypic spectrums and refining treatment strategies. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2019, 32, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finsterer, J. Congenital myasthenic syndromes. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2019, 14, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez Cruz, P.; Palace, J.; Beeson, D. The Neuromuscular Junction and Wide Heterogeneity of Congenital Myasthenic Syndromes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abicht, A.; Müller, J.S.; Lochmüller, H. Congenital Myasthenic Syndromes Overview. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1168/ (accessed on 7 January 2024).
- Rahman, M.d.M.; Teng, J.; Worrell, B.T.; Noviello, C.M.; Lee, M.; Karlin, A.; Stowell, M.H.B.; Hibbs, R.E. Structure of the Native Muscle-type Nicotinic Receptor and Inhibition by Snake Venom Toxins. Neuron 2020, 106, 952–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omar, A.; Marwaha, K.; Bollu, P.C. Physiology, Neuromuscular Junction. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470413/ (accessed on 7 January 2024).
- Engel, A.G.; Shen, X.-M.; Selcen, D.; Sine, S.M. What Have We Learned from the Congenital Myasthenic Syndromes. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2010, 40, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.; Bonne, G.; Missier, P.; Lochmüller, H. Targeted therapies for congenital myasthenic syndromes: Systematic review and steps towards a treatabolome. Emerg. Top. Life Sci. 2019, 3, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, G. Congenital Myasthenic Syndromes in 2018. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2018, 18, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moult, J.; Fidelis, K.; Kryshtafovych, A.; Schwede, T.; Tramontano, A. Critical assessment of methods of protein structure prediction (CASP)—Round x. Proteins 2013, 82, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Ding, F.; Wang, R.; Shen, R.; Zhang, X.; Luo, S.; Wu, Z.; Xie, Q.; Berger, B.; Ma, J. High-resolution de novo structure prediction from primary sequence. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Akin, H.; Rao, R.; Hie, B.; Zhu, Z.; Lu, W.; Smetanin, N.; Verkuil, R.; Kabeli, O.; Shmueli, Y.; et al. Evolutionary-scale prediction of atomic-level protein structure with a language model. Science 2023, 379, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, M.; DiMaio, F.; Anishchenko, I.; Dauparas, J.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Lee, G.R.; Wang, J.; Cong, Q.; Kinch, L.N.; Schaeffer, R.D.; et al. Accurate prediction of protein structures and interactions using a three-track neural network. Science 2021, 373, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramson, J.; Adler, J.; Dunger, J.; Evans, R.; Green, T.; Pritzel, A.; Ronneberger, O.; Willmore, L.; Ballard, A.J.; Bambrick, J.; et al. Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature 2024, 630, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussad, B.; Roche, R.; Bhattacharya, D. The transformative power of transformers in protein structure prediction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2303499120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlphaFold Protein Structure Database: Frequently Asked Questions. Available online: https://alphafold.ebi.ac.uk/faq (accessed on 7 January 2024).
- Pak, M.A.; Markhieva, K.A.; Novikova, M.S.; Petrov, D.S.; Vorobyev, I.S.; Maksimova, E.S.; Kondrashov, F.A.; Ivankov, D.N. Using AlphaFold to predict the impact of single mutations on protein stability and function. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0282689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buel, G.R.; Walters, K.J. Can AlphaFold2 predict the impact of missense mutations on structure? Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2022, 29, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Xu, M.; Wang, W.; Wu, T.; Zhang, W.; Qin, W.; Sun, B. Utilization of AlphaFold2 to Predict MFS Protein Conformations after Selective Mutation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, J.M.; Polev, K.; Abdirasulov, A.; Reinharz, V.; Grzybowski, B.A.; Tlusty, T. AlphaFold2 Can Predict Single-Mutation Effects. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2023, 131, 218401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirdita, M.; Schütze, K.; Moriwaki, Y.; Heo, L.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Steinegger, M. ColabFold: Making protein folding accessible to all. Nat. Methods 2022, 19, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Novati, G.; Pan, J.; Bycroft, C.; Žemgulytė, A.; Applebaum, T.; Pritzel, A.; Wong, L.H.; Zielinski, M.; Sargeant, T.; et al. Accurate proteome-wide missense variant effect prediction with AlphaMissense. Science 2023, 381, eadg7492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuffield Department of Clinical Neurosciences: Congenital Myasthenia Service. Available online: https://www.ndcn.ox.ac.uk/research/congenital-myasthenia-service (accessed on 19 October 2024).
- Masson, E.; Zou, W.-B.; Génin, E.; Cooper, D.N.; Le Gac, G.; Fichou, Y.; Pu, N.; Rebours, V.; Férec, C.; Liao, Z.; et al. Expanding ACMG variant classification guidelines into a general framework. Hum. Genom. 2022, 16, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alamut Visual Plus. Available online: https://www.sophiagenetics.com/platform/alamut-visual-plus/ (accessed on 3 April 2024).
- Frazer, J.; Notin, P.; Dias, M.; Gomez, A.; Min, J.K.; Brock, K.; Gal, Y.; Marks, D.S. Disease variant prediction with deep generative models of evolutionary data. Nature 2021, 599, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, A.; Inan, T.; Shehu, A. Analysis of AlphaFold2 for Modelling Structures of Wildtype and Variant Protein Sequences. EPiC Ser. Comput. 2022, 83, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Pan, F.; Liu, H.; Hong, P.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J. Applications of AlphaFold beyond Protein Structure Prediction. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Skolnick, J. Scoring function for automated assessment of protein structure template quality. Proteins 2004, 57, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.-B.; Perminov, A.; Bekele, S.; Kedziora, G.; Farajollahi, S.; Varaljay, V.; Hinkle, K.; Molinero, V.; Meister, K.; Hung, C.; et al. AlphaFold2 models indicate that protein sequence determines both structure and dynamics. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruff, K.M.; Pappu, R.V. AlphaFold and Implications for Intrinsically Disordered Proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 2021, 433, 167208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljungdahl, A.; Kohani, S.; Page, N.F.; Wells, E.S.; Wigdor, E.M.; Dong, S.; Sanders, S.J. AlphaMissense is better correlated with functional assays of missense impact than earlier prediction algorithms. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondi, D.; Tanyalcin, I.; Ferté, J.; Gazzo, A.; Orlando, G.; Lenaerts, T.; Rooman, M.; Vranken, W. DEOGEN2: Prediction and interactive visualization of single amino acid variant deleteriousness in human proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W201–W206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, M.F.; Shihab, H.A.; Mort, M.; Cooper, D.N.; Gaunt, T.R.; Campbell, C. FATHMM-XF: Accurate prediction of pathogenic point mutations via extended features. Bioinformatics 2017, 34, 511–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentzsch, P.; Witten, D.; Cooper, G.M.; Shendure, J.; Kircher, M. CADD: Predicting the deleteriousness of variants throughout the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 47, D886–D894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munsamy, G.; Bohnuud, T.; Lorenz, P. Improving alphafold2 performance with A global metagenomic & biological data supply chain. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| MSA Mode | MMseqs2 (UniRef + Environmental) |
| Number of Models | 5 |
| Number of Recycles | 3 |
| Stop at Score | 100 |
| Use Amber | No |
| Use Templates | No |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ryan-Phillips, F.; Henehan, L.; Ramdas, S.; Palace, J.; Beeson, D.; Dong, Y.Y. Assessing the Utility of ColabFold and AlphaMissense in Determining Missense Variant Pathogenicity for Congenital Myasthenic Syndromes. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2549. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12112549
Ryan-Phillips F, Henehan L, Ramdas S, Palace J, Beeson D, Dong YY. Assessing the Utility of ColabFold and AlphaMissense in Determining Missense Variant Pathogenicity for Congenital Myasthenic Syndromes. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(11):2549. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12112549
Chicago/Turabian StyleRyan-Phillips, Finlay, Leighann Henehan, Sithara Ramdas, Jacqueline Palace, David Beeson, and Yin Yao Dong. 2024. "Assessing the Utility of ColabFold and AlphaMissense in Determining Missense Variant Pathogenicity for Congenital Myasthenic Syndromes" Biomedicines 12, no. 11: 2549. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12112549
APA StyleRyan-Phillips, F., Henehan, L., Ramdas, S., Palace, J., Beeson, D., & Dong, Y. Y. (2024). Assessing the Utility of ColabFold and AlphaMissense in Determining Missense Variant Pathogenicity for Congenital Myasthenic Syndromes. Biomedicines, 12(11), 2549. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12112549






