Abstract
(1) Background: Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) is a frequently observed clinical manifestation of chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS). This systematic review aimed to evaluate the function of the Eustachian tube following endoscopic sinus surgery (ESS) in adult CRS patients with confirmed preoperative ETD symptoms. (2) Methods: A systematic search of PubMed, Cochrane, Embase, and MEDLINE electronic databases was conducted. The review was performed following the PRISMA guidelines. Studies investigating concurrent ETD in CRS patients who underwent ESS were retrieved. The changes in ETD outcomes were measured by the 7-item Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Questionnaire (ETDQ-7). We employed a random-effects model to conduct the meta-analysis (3) Results: We included seven observational studies that involved a total of 436 CRS patients with concurrent ETD. The pooled results revealed a statistically significant reduction (Standardized mean difference = −1.24; 95% CI = −1.64 to −0.84) in ETDQ-7 scores among the CRS with ETD patient cohort at the 3-month postoperative follow-up. (4) Conclusions: ESS serves as an effective intervention for improving E-tube function in adult CRS patients with concurrent ETD. Future prospective randomized controlled trials that incorporate various outcome predictors should be conducted to explore potential clinical factors for greater ETD improvement and normalization after ESS.
1. Introduction
The Eustachian tube (E-tube) equalizes pressure across the tympanic membrane, supplies air to the middle ear for ventilation, and acts as a channel for mucociliary clearance and sound protection [1]. Paranasal sinuses and nasal cavities are situated in close proximity to the middle ear, which is connected to them by the E-tube. Therefore, considering its anatomic location, Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) is one of the more common otologic manifestations of chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS). The prevalence of otologic symptoms including aural fullness, hearing loss, otalgia, and tinnitus ranged from 15% to 42% in patients diagnosed with chronic rhinosinusitis [2]. The chronic inflammatory response of sinonasal mucosa can lead to the swelling of the E-tube orifice, which can result in the impairment of the pressure equalization and dilatory functions of the E-tube [3,4,5]. Patients who suffer from E-tube dysfunction can report a poorer quality of life due to persistent otologic symptoms. The latest version of the European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps (EPOS 2020) provides evidence-based recommendations for the management of rhinosinusitis, but gives limited attention to CRS-related ETD treatment [6]. Previous studies have investigated the effect of ETD symptoms following endoscopic sinus surgery in CRS patients [5,7]. However, the extent of ETD improvement across different countries has not been thoroughly explored. Therefore, this is the first systematic review to analyze the surgical impact on changes in ETD outcomes in CRS patients worldwide with confirmed preoperative ETD symptoms. The primary objectives of this study are to review the current literature on the prevalence of ETD in CRS and conduct a meta-analysis on the effect of endoscopic sinus surgery for CRS patients with concurrent ETD symptoms.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
The study was developed according to the latest version of Preferred Reporting Item for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines (Supplementary Table S1), [8] and was registered in INPLASY with the registration number (INPLASY202480056). Articles were identified through a comprehensive search of PubMed, Cochrane, Embase, and MEDLINE electronic databases. The search strategies used a combination of medical subject headings (MeSH) and keywords including (‘CRS’ OR ‘chronic rhinosinusitis’ OR ‘chronic sinusitis’ OR ‘sinusitis’ OR ‘rhinosinusitis’) AND (‘ETD’ OR ‘Eustachian tube dysfunction’ OR ‘E tube dysfunction’ OR ‘Eustachian tube’ OR ‘Eustachian tube function’) AND (‘ESS’ OR Endoscopic sinus surgery’ OR ‘nasal surgery’ OR Functional endoscopic sinus surgery’ OR ‘FESS’). The results were limited to the English language only. The search was conducted from the earliest record in each database to the date of inspection (13 March 2024). The detailed search strategy is outlined in Supplementary Table S1.
2.2. Study Selection
Studies describing concurrent ETD in patients with CRS treated by endoscopic sinus surgery were included in the final analysis. The enrolled subjects were adult CRS patients (age > 18) who had an unsatisfactory response to medical therapy and concurrent ETD, which was primarily measured by the 7-item Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Questionnaire (ETDQ-7). ETDQ-7 has been established as a reliable objective measurement for adult patients with ETD. A total item score of ≥14.5 yielded 100% sensitivity and 100% specificity for ETD [9]. Exclusion criteria were studies without either mean preoperative or postoperative ETDQ7 scores with standard deviations, patients receiving concurrent interventions other than ESS, previous history of oncologic management of the head and neck region, pre-existing otologic disease, and positive response to medical therapy. Descriptive studies or review articles published in languages other than English were also excluded.
2.3. Data Collection
Abstracts were first screened by two reviewers (K.S. Yang and W.C Chen) for full-text review, then each article was independently assessed for eligibility. A third reviewer (C.N. Wu) was consulted in situations where consensus was not achieved. Primary outcome measures were mean preoperative and postoperative ETDQ7 scores. The ETDQ7 consists of 7 items, with each question being rated on a scale from 1 to 7. Total scores range from 7 to 49, and a total item score cut point of ≥14.5 or a mean item score cut point of ≥2.1 indicates the presence of Eustachian tube dysfunction [9].
2.4. Quality Assessment
The methodological quality and content validity of the recruited studies is assessed using the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS), which is designed to evaluate the risk of bias for nonrandomized studies, including case–control and cohort studies. The NOS contains eight items, which are categorized into three broad perspectives: the selection of the study groups; the comparability of the groups; and the ascertainment of either the exposure (case–control studies) or outcome (cohort studies) of interest [10]. A star system is implemented to allow semi-quantitative assessment of study quality. Two authors (K.S Yang and W.C Chen) used this instrument for study appraisal by awarding a maximum of one star for each item in the selection and outcome section, and a maximum of two in the comparability section if it was fulfilled. Scores on the NOS vary between 0 and 9 points. Studies with a total score of >6 are considered to have good methodological quality. Consensus was reached through discussion when there was a discrepancy between ratings.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Meta-analysis of continuous measures, namely mean preoperative and postoperative ETDQ7 scores, was performed with Cochrane Review Manager (RevMan) version 5.4 (The Cochrane Collaboration 2020). Due to the variation between the enrolled studies such as target populations and mean outcome measures, a random-effects model was used to run the analysis. The proportion was weighted according to the number of subjects in each study. The effect size of the primary study outcome was quantified using the standardized mean difference and 95% confidence intervals (CIs), since not all the included studies employed the same scale to measure ETDQ-7 scores. The degree of statistical heterogeneity across studies was evaluated by I2 and Cochrane’s Q test. I2 statistics of 25%, 50%, and 75% were estimated as low, moderate, and high heterogeneity, respectively [11].
We performed the sensitivity analysis through the one-study removal method to determine whether withdrawing any particular trial could cause a statistically significant difference in summary effect size [12]. Funnel plots were generated and visually inspected for analysis. Potential publication bias could be observed based on asymmetry of the funnel plot. Egger’s regression was not tested as there were less than 10 studies involved. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant for all statistical tests.
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
The literature search process is presented in the PRISMA flowchart (Figure 1). A total of 291 articles were identified through a systematic search of databases. Following the exclusion of 29 duplicate publications and 245 ineligible studies after title and abstract review, we retrieved 17 articles for full-text review. Seven observational studies ultimately met the criteria, and were included in the meta-analysis. Out of the 10 excluded articles in the final stage, one study had no full text available [2], while three studies had insufficient data, either missing postoperative mean ETDQ7 scores or standard deviations [4,13,14]. Four studies were excluded because ETD symptoms were measured with changes in SNOT-22 otologic subdomain scores or the type of tympanometry, thus disallowing useful comparisons to be drawn for the primary outcome [3,15,16]. The remaining two studies were systematic reviews [5,7]. Therefore, seven studies [17,18,19,20,21,22,23] were included in this systematic review and meta-analysis. All studies were observational in design, including five prospective cohort studies [17,19,20,21,22], one prospective case–control study [23], and one retrospective cohort study [18].
Figure 1.
PRISMA flowchart for the current meta-analysis.
3.2. Baseline Characteristics
The summary of the included case series is presented in Table 1. A combined total of 436 patients from these seven studies had concurrent ETD. Four of the studies enrolled a total number of 533 CRS patients that underwent ESS from 2016 to 2019, whereas the remaining three [11,20,22] recruited 155 CRS patients with confirmed diagnoses of ETD admitted for ESS. The prevalence of ETD among CRS patients was 53% (281/533) based on the four studies that enrolled adult CRS patients regardless of ETD status initially. The postoperative evaluations were performed at a range of 2-month to 1-year period. We compared the ETDQ-7 scores at the 3-month interval after ESS as the basis for this analysis, except Higgins et al., which assessed the patients 2 months following operations. With regard to CRS metrics and comorbidities, 197 out of 606 (32.5%) patients had nasal polyposis in six studies. Concomitant allergic rhinitis was recorded in 126 out of 489 (25.7%) CRS patients from three studies. A total of 197 out of 524 (37.6%) patients received revised ESS as documented by four studies. The detailed summary of patient characteristics of the included studies is listed in Table 2.
3.3. Methodological Quality Assessment of the Included Studies
We presented the quality appraisal of studies using NOS in Table 3. All the included studies were considered to have good methodological quality (total scores > 6). No stars were awarded to two studies, Chang et al. and Hsieh et al., for the adequacy of the follow-up because they did not document whether any participants were lost to follow-up [18,22]. The funnel plot demonstrated all studies were within the funnel distribution except for two without symmetry, suggesting some publication bias based on visual inspection (Supplementary Figure S1).

Table 1.
Summary of the retrieved trials investigating the effect of endoscopic sinus surgery on improving ETD in the enrolled participants.
Table 1.
Summary of the retrieved trials investigating the effect of endoscopic sinus surgery on improving ETD in the enrolled participants.
| First Author and Year | Country | Study Period | Study Design | Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria | Total CRS Patients (n) | CRS + ETD (n) | Definition of ETD | Pre-op ETDQ-7 Score | Post-op ETDQ-7 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bowles 2019 [17] | United Kingdom | August 2016– November 2017 | Prospective cohort study | Adult patients with refractory CRS despite a minimum of 6 months of medical therapy | Pre-existing otological disease, adequate response to medical therapy, patient preference for continuing medical therapy, contraindication to general anesthetic | 57 | 39 | ETDQ-7 ≥ 13.5 | 20.6 ± 10.34 | 11.4 ± 5.65 |
| Chang 2020 [18] | United States | December 2016–December 2018 | Retrospective cohort study | Adult patients diagnosed with CRS or RARS delineated by International Consensus Statement on Allergy and Rhinology | Known otologic comorbidities apart from ETD, prior otologic surgery, sinonasal diagnoses other than sinusitis | 302 | 180 | ETDQ-7 ≥ 14.5 | 25.5 ± 7.6 | 16.8 ± 8.5 |
| Higgins, 2020 [23] | United States | November 2016–December 2017 | Prospective case–control study | Adult CRS patients with persistent ETD without MEE despite a period of 6–8 weeks of maximum medical therapy | Ear surgery, adenoidectomy, Eustachian tube dilation, MEE, cholesteatoma, history of major ear surgery, severe atelectasis, congenital ear disorder, prior head and neck surgery | 60 | 60 | Mean ETDQ-7 ≥ 2.1 | 3.45 ± 1.061 | 2.164 ± 1.206 |
| Wu, 2020 [21] | United States | September 2018–March 2019 | Prospective cohort study | Adult patients with CRS after failed medical therapy according to International Consensus Statement on Allergy and Rhinology | Failure to complete preoperative ETDQ-7 and SNOT-22 questionnaires | 82 | 39 | ETDQ-7 ≥ 14.5 | 16.8 ± 8.2 | 12.7 ± 6.8 |
| Chen, 2021 [20] | China | December 2019–December 2020 | Prospective cohort study | Adult CRS patients with concurrent ETD and were refractory to conservative treatment for at least 12 weeks | Meniere’s disease, low-frequency sensorineural hearing loss, patulous Eustachian tube, chronic suppurative otitis media, acute upper respiratory infection and temporomandibular joint dysfunction | 70 | 70 | ETDQ-7 ≥ 14.5 + Tympanogram B/C ETDQ-7 ≥ 14.5 + ETS ≤ 5 | 20.13 ± 6.18 | 8.63 ± 3.62 |
| Chen, 2022 [19] | Taiwan | December 2016–December 2017 | Prospective cohort study | Adult CRS patients with unsatisfactory response to medical treatment for at least 2 months | History of radiotherapy of the head and neck region, ear surgery, pharyngeal surgery | 92 | 23 | ETDQ-7 ≥ 14.5 | 25.52 ± 7.7 | 10.6 ±8.31 |
| Hsieh, 2024 [22] | Taiwan | July 2018–June 2022 | Prospective cohort study 1 | Adult CRS patients with at least ethmoid and maxillary sinuses involved and diagnosis of ETD for at least 3 months | Elderly individuals, pregnant women, history of head and neck cancer, previous ear surgery, septoplasty, turbinate reduction procedures, TMJ disorder, aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease | 25 | 25 | ETDQ-7 ≥ 14.5 + Inflation–deflation: (p) 2 Grade II-IV endoscopic inflammation score | 22.84 ± 7.39 | 16.24 ± 7.74 |
| Total (n) | - | - | - | - | - | 688 | 436 | - | - |
Abbreviations: CRS, chronic rhinosinusitis; Pre-op, preoperative; ETD, Eustachian tube dysfunction; ETDQ-7, 7-item Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Questionnaire; Post-op, postoperative; MEE: middle ear effusion; TMJ: Temporomandibular joint; ETS: Eustachian tube score. 1 Hsieh, 2024 was a prospective randomized controlled trial comparing the treatment effect of ESS alone with combined balloon Eustachian tuboplasty (BET) in patients with CRS and ETD. Only the ESS group was extracted from the study to be included in this meta-analysis for comparative purposes. Thus, we defined the study as prospective cohort study here. 2 (p) represents a poor result on the inflation–deflation test.

Table 2.
Summary of the characteristics of recruited patients.
Table 2.
Summary of the characteristics of recruited patients.
| First Author and Year | Total Number of CRS Patients | Nasal Polyposis | Allergic Rhinitis | Asthma | Revised ESS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bowles 2019 [17] | 57 | 23 | - | 16 | - |
| Chang 2020 [18] | 302 | 60 | 63 | 114 | 136 |
| Higgins, 2020 [23] | 60 | 18 | - | - | 32 |
| Wu, 2020 [21] | 82 | - | - | - | - |
| Chen, 2021 [20] | 70 | 51 | 25 | 3 | 17 |
| Chen, 2022 [19] | 92 | 39 | 30 | 5 | 12 |
| Hsieh, 2024 [22] | 25 | 6 | 8 | 3 | - |
| Total, n (%) | 688 | 197 (32.5) | 126 (25.7) | 141 (25.8) | 197 (37.6) |

Table 3.
Detailed quality assessment of the included studies using the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) A. Cohort studies. B. Case–control study.
Table 3.
Detailed quality assessment of the included studies using the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) A. Cohort studies. B. Case–control study.
| A. First Author | Selection | Comparability | Outcomes | Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Representativeness of Exposed Cohort | Selection of Nonexposed Cohort | Ascertainment of Exposure | Outcome not Present at the Start of the Study | Comparability Based on the Design or Analysis | Assessment of Outcomes | Length of Follow-Up | Adequacy of Follow-Up | ||
| Bowles 2019 [17] | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | 8 |
| Chang 2020 [18] | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | - | 7 |
| Wu 2020 [21] | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | 8 |
| Chen 2021 [20] | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | 8 |
| Chen 2022 [19] | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | 8 |
| Hsieh 2024 [22] | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | - | 7 |
| B. First Author | Selection | Comparability | Exposure | Total | |||||
| Representativeness of cases | Selection of controls | Definition of controls | Adequate cases definition | Comparability based on the design or analysis | Ascertainment of exposure | Same method of ascertainment | Non-response rate | ||
| Higgins 2020 [23] | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | ✵ | 8 |
Good quality: A total of 3 or 4 stars in the selection domain AND 1 or 2 stars in comparability domain AND 2 or 3 stars in the outcome/exposure domain. Fair quality: A total of 2 stars in the selection domain AND 1 or 2 stars in comparability domain AND 2 or 3 stars in the outcome/exposure domain. Poor quality: A total of 0 or 1 star in the selection domain OR 0 stars in comparability domain OR 0 or 1 stars in the outcome/exposure domain.
3.4. Primary Outcomes
Following endoscopic sinus surgery, the ETDQ-7 score showed a statistically significant reduction (standardized mean difference = −1.24; 95% CI = −1.64 to −0.84, I2 = 84%) in the CRS with ETD patient cohort (Figure 2). High heterogeneity was observed nonetheless. A sensitivity analysis was conducted by employing the one-study-removal method [12]. No statistically significant change in the standard difference in mean was found when any one of the studies was excluded.
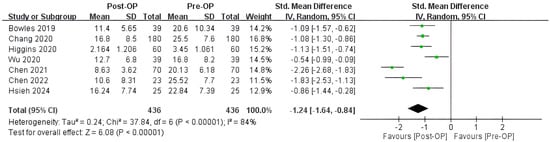
Figure 2.
Forest plot showing the effect of endoscopic sinus surgery (ESS) on reducing ETDQ-7 scores in CRS patients. Surgical treatment of CRS was associated with relief of ETD symptoms. SD, standard deviation; Total, total number of subjects; Std, standard; CI, confidence interval; Op, operation; The green dot represents the point estimate of the study result. The horizontal line extending from each green dot represents the 95% confidence interval (CI) for the effect estimate. The black diamond symbol represents the overall effect estimate from all the studies included in the meta-analysis, with the width of the diamond reflects the 95% CI around the pooled effect estimate. Bowles 2019 [17]; Chang 2020 [18]; Higgins 2020 [23]; Wu 2020 [21]; Chen 2021 [20]; Chen 2022 [19]; Hsieh 2024 [22].
4. Discussion
According to previous studies, around 48.5% of CRS patients had clinically significant ETD, defined as an ETDQ-7 score of 14.5 or higher [4]. The preoperative prevalence rates of ETD in our enrolled studies varied from 25% to 68% [17,18,19,21]. This study corroborated the finding of ETD being a common comorbidity of CRS. Inflammatory changes and mucosal edema characterized in CRS may extend to the nasopharyngeal region, which could lead to swelling and obstruction of the E-tube orifice [24]. Impairment in E-tube dilatory function and increased nasal airway resistance give rise to negative middle ear pressure. The resulting pressure gradient contributes to ETD, which is associated with otologic manifestations, including aural fullness, cracking/popping, otalgia, and otitis media effusion [2,25,26]. Treating underlying sinonasal diseases may thereby alleviate ETD symptoms.
In this meta-analysis, ESS was shown to statistically reduce ETD symptoms in CRS patients, and statistical significance was maintained in the sensitivity analysis. A retrospective case series by Adams et al. found a mean reduction of 5.1 ± 8.4 points in the ETDQ-7 score among CRS participants with concurrent ETD after receiving ≥4 weeks of medical treatment [27]. Additionally, the pilot study by Stoikes et al. reported a significant postoperative treatment effect on all otologic symptoms associated with CRS [2]. Recent studies have sought to evaluate the surgical approach for CRS patients with concurrent ETD. Sinus epithelization is typically completed at 3–6 months following operation, when nasal mucosa has returned to its normal state [28]. Hence, the recruited studies were assessed and compared at a baseline of 3 months postoperatively. Based on this meta-analysis, endoscopic sinus surgery has proven to be effective in improving Eustachian tube function in CRS patients with ETD, as evidenced by a significant reduction in postoperative ETDQ-7 scores.
Although there was one prior meta-analysis that studied the impact of ESS on ETD in CRS patients, this is the first systematic review to date to recruit the largest number of case series from Asia, Europe, and the United States to demonstrate this promising effect. This suggests the applicability of our findings to both Eastern and Western populations, which may display differences in the inflammatory phenotypes and endotypes of CRS [29]. Compared to the Western population, a lower prevalence of CRS comorbid with eosinophilic disease was found in the East Asian population. This might reflect a lower inflammatory burden in the Eastern population [19]. Additionally, this is the first analysis to discuss the response of ETD improvement in CRS patients following ESS based on clinical predictors. However, more outcome data are needed to conduct a subgroup analysis.
A high degree of heterogeneity was observed in the reported outcomes. One contributing factor might be that studies had different definitions for significant preoperative ETD scores and cut-off values for clinical improvement. Higgins et al. defined clinically significant ETD as a mean ETDQ-7 item score of at least 2.1. However, this value equated to a total item score cut point of 14.5, which was adopted by the rest of the studies, except for Bowles et al., who used a preoperative score of 13.5 to indicate the presence of ETD [9,23]. The minimal clinically important difference (MCID), the extent of symptom improvement that reached clinical significance, was defined as a reduction in ETDQ-7 score by ≥3.5 postoperatively according to Chang et al. and Chen et al. [18,20], and >3.7 as reported by Hsieh et al. [22]. Higgins et al. assigned this cut-off value at 0.5, whereas the other studies did not provide figures that constituted significant ETD improvement based on the MCID [23]. Second, the etiology of ETD was likely multifactorial, with potential contributors represented by gastrointestinal reflux, allergy, temporomandibular joint disorder, obstructive lesions, or pressure dysregulation, apart from upper respiratory inflammation [30,31]. Since the reported ETD among CRS patients could be attributable to other pathologies, a detailed preoperative evaluation of other predisposing factors to ETD is warranted before study inclusion.
Clinical predictors of ETD improvement following ESS in CRS patients were discussed in previous studies [19,20,23]. A greater preoperative disease burden, delineated by higher ETDQ-7 or SNOT-22 score, revealed a consistent significance in affecting ETD outcome. Higgins et al. indicated that a high preoperative ETDQ-7 score, defined by a mean item score ≥ 4, was negatively associated with ETDQ-7 normalization [23]. A strong link was also found in Chen et al., where a preoperative SNOT-22 score ≥ 40 was correlated to failure of ETDQ-7 score normalization after ESS [20]. In addition, Chen et al. showed that compared with patients who underwent primary surgery, revision surgery was an independent clinical factor in persistent ETD symptoms [19]. Higher inflammatory burden in the sinonasal and middle ear cavity for an extended period thus explained the recalcitrant ETD despite surgical treatments.
Furthermore, Higgins et al. retrospectively explored the variables that were attributed to ETDQ-7 normalization in its study group, and nasal polyposis was one of the preoperative factors that showed a statistical significance to ETDQ-7 normalization [23]. No significant link in regression analysis, however, was found in either Chang et al., Chen et al., or Hsieh et al. [18,19,22]. The inconsistency of statistical significance implied that no definitive conclusions could be drawn regarding the effect of ESS on ETD based on CRS endotypes. Thus, further research is needed to determine whether different inflammatory endotypes contribute to ETD improvement following ESS.
While the surgical efficacy for comorbid ETD might be independent of polyp status, biologic treatment may result in greater improvements in ETDQ-7 scores for patients with CRS with nasal polyps (CRSwNP), which is predominantly characterized by type II inflammation. In particular, one retrospective cohort study reported that Dupilumab, a monoclonal antibody inhibiting interleukin-4 (IL-4) and interleukin-13 (IL-13) pathways, alleviated ETD at a similar magnitude as ESS in Th2-driven CRS [32]. Compared to other biologics, previous studies have proposed Dupilumab as an effective treatment for eosinophilic otitis media (EOM) by relieving Eustachian tube obstruction, with cases of the Eustachian tube opening after Dupilumab having been reported [33]. The pathophysiology behind how Dupilumab resolved CRSwNP and EOM may involve periostin expression in the granulation tissue of nasal polyps and the middle ear [34]. Triggered by type 2 cytokines such as IL-4 and IL-13, periostin is found in thickened mucosa and is thought to prolong inflammation [34,35]. Therefore, by reducing IL-4 and/or IL-13 levels, Dupilumab may inhibit periostin production, thus suppressing inflammation, and consequently improving Eustachian tube obstruction. Since biologics are currently administered as adjunctive therapy for uncontrolled CRSwNP, they are likely to show therapeutic potential in patients with persistent ETD following sinus surgery within the CRSwNP cohort.
There are several limitations to the study. First, although the ETDQ-7 score has been utilized as a reliable clinical instrument for E-tube dysfunction, it is nonetheless reported based on individuals’ subjective symptoms. The result was not supported by comparing with other outcome measure tools, including the Sino-Nasal Outcome Test (SNOT-22), tympanometry, or tubomanometry. Despite not including SNOT-22 as the study measurement, prior studies have consistently shown a strong correlation between ETDQ-7 and SNOT-22 ear subdomains for ETD evaluation [18,21]. A consensus statement released by an European multi-institutional panel of experts has recommended that the diagnosis of Eustachian tube dysfunction be based on both subjective symptoms and objective findings from tympanometry or otoscopy [1]. Although tympanometry demonstrates high sensitivity and specificity for assessing the functional integrity of the middle ear, its effectiveness in diagnosing ETD is limited [36]. Approximately 60% of patients with ETD exhibit normal tympanometry results, highlighting its limitation in detecting mild ETD cases [22]. So far, no universally accepted set of diagnostic means has been validated as a gold standard for measuring ET function. Thus, patient’s subjective reports of improvement in ET function hold greater value for physicians in assessing clinical response. In addition, ETDQ-7 has also been widely implemented for recognizing ETD due to its well-established sensitivity and specificity, as well as its ease of administration [9].
Second, few studies have investigated independent predictors of ESS outcomes on CRS-related ETD, so only parallel comparisons could be drawn from the literature. Lastly, the forest plot was pooled from single-arm observational cohorts, with no control group to compare the outcome of those who did not receive surgery. This could potentially bias the impact of ESS on relieving ETD. Therefore, future randomized controlled trials are encouraged to gain a more accurate understanding of the role of ESS in treating CRS with ETD.
5. Conclusions
CRS patients had a high prevalence of concomitant ETD, of which symptoms were significantly improved following ESS at the 3-month postoperative interval. Based on selected studies, greater disease burden, represented by higher preoperative scores or those receiving revision surgery, was shown to be negatively associated with ETD improvement. Larger prospective case studies are encouraged to analyze the change in ETD, stratified by CRS subgroup for statistical purposes. Moreover, future research should incorporate control groups, allowing for a comparison between surgical and conservative treatments to better reflect the actual efficacy of ESS.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biomedicines12112484/s1, Table S1: PRISMA Checklist; Table S2: Keywords and search results in different databases; Figure S1: The funnel plot of the included studies evaluating the effect of endoscopic sinus surgery on improving ETD symptoms among CRS patients.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.-S.Y. and S.-D.L.; methodology, K.-S.Y. and C.-C.W.; software, K.-S.Y.; validation, W.-C.C., C.-N.W. and S.-D.L.; formal analysis, K.-S.Y. and W.-C.C.; investigation, K.-S.Y., Y.-S.W. and W.-C.C.; resources, W.-C.C., C.-N.W. and C.-S.W.; data curation, K.-S.Y., Y.-S.W. and S.-D.L.; writing—K.-S.Y., W.-C.C. and C.-N.W.; writing—review and editing, K.-S.Y., C.-C.W. and S.-D.L.; visualization, Y.-S.W. and C.-S.W.; supervision, C.-C.W. and S.-D.L.; project administration, K.-S.Y., C.-C.W. and S.-D.L.; funding acquisition, S.-D.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The author Sheng-Dean Luo is the host of a research plan in Chang Gung Memorial Hospital and received research grants (CORPG8K0151) and (CORPG8L0521).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Schilder, A.G.M.; Bhutta, M.F.; Butler, C.C.; Holy, C.; Levine, L.H.; Kvaerner, K.J.; Norman, G.; Pennings, R.J.; Poe, D.; Silvola, J.T.; et al. Eustachian tube dysfunction: Consensus statement on definition, types, clinical presentation and diagnosis. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2015, 40, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoikes, N.F.; Dutton, J.M. The effect of endoscopic sinus surgery on symptoms of Eustachian tube dysfunction. Am. J. Rhinol. 2005, 19, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, M.J.; Ling, L.C.; Yao, W.C.; Luong, A.; Citardi, M.J. Eustachian tube dysfunction symptoms in patients treated in a tertiary rhinology clinic. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2017, 7, 1135–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangbumrungtham, N.; Patel, V.S.; Thamboo, A.; Patel, Z.M.; Nayak, J.V.; Ma, Y.; Choby, G.; Hwang, P.H. The prevalence of Eustachian tube dysfunction symptoms in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2018, 8, 620–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Shih, M.C.; Edwards, T.S.; Nguyen, S.A.; Meyer, T.A.; Soler, Z.M.; Schlosser, R.J. Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) in chronic rhinosinusitis with comparision to primary ETD: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2022, 12, 942–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokkens, W.J.; Lund, V.J.; Hopkins, C.; Hellings, P.W.; Kern, R.; Reitsma, S.; Toppila-Salmi, S.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M.; Mullol, J. Executive summary of EPOS 2020 including integrated care pathways. Rhinology 2020, 58, 82–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotimi, O.; Mohamed, N.; Steele, K.B.P.; Bowles, P. Impact of endoscopic sinus surgery on Eustachian tube dysfunction in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Rhinol. Online 2022, 5, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoul, E.D.; Anand, V.K.; Christos, P.J. Validating the clinical assessment of eustachian tube dysfunction: The Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Questionnaire (ETDQ-7). Laryngoscope 2012, 122, 1137–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stang, A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 25, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeks, J.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Altman, D.G. Chapter 10: Analysing Data and Undertaking Meta-Analyses. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; Version 6.4; Cochrane: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, I.H.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, S.W. Changes in symptoms of Eustachian tube dysfunction after nasal surgery. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 279, 5017–5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.Y.; Jang, S.; Seo, G.; Park, S.K. Effect of endoscopic sinus surgery on Eustachian tube function in adult sinusitis patients: A prospective case-control study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teo, N.W.; Mace, J.C.; Smith, T.L.; Hwang, P.H. Impact of endoscopic sinus surgery on otologic symptoms associated with chronic rhinosinusitis. World J. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2017, 3, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniakas, A.; Desrosiers, M.; Asmar, M.H.; Al Falasi, M.; Mfuna Endam, L.; Hopkins, C.; Philpott, C.; Erskine, S.; Smith, R.; Kilty, S. Eustachian tube symptoms are frequent in chronic rhinosinusitis and respond well to endoscopic sinus surgery. Rhinology 2018, 56, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowles, P.F.; Agrawal, S.; Salam, M.A. Eustachian Tube dysfunction in chronic rhinosinusitis: Pre and post-operative results following endoscopic sinus surgery, a prospective study. Rhinology 2019, 57, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.T.; Hosseini, D.K.; Song, S.H.; Nayak, J.V.; Patel, Z.M.; Lee, J.Y.; Hwang, P.H. The Effect of Endoscopic Sinus Surgery on Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Symptoms. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2020, 163, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.C.; Yang, K.L.; Lin, W.C.; Fang, K.C.; Wu, C.N.; Luo, S.D. Clinical outcomes of Eustachian tube dysfunction in chronic rhinosinusitis following endoscopic sinus surgery. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2022, 85, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Dang, H.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Z.; Ma, Y.; Liu, X.; Lin, P.; Zou, H.; Xiong, H. Endoscopic sinus surgery improves Eustachian tube function in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis: A multicenter prospective study. Rhinology 2021, 59, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.W.; Walgama, E.S.; Higgins, T.S.; Borrelli, M.; Vardanyan, N.; Hopp, S.; Shamsian, A.; Hopp, M.L. Eustachian Tube Quality of Life and Severity of Disease in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2020, 34, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.Y.; Lin, W.C.; Lin, C.C.; Chou, Y.F. Combined balloon Eustachian tuboplasty endoscopic sinus surgery for patients with chronic rhinosinusitis and Eustachian tube dysfunction. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2024, 14, 1327–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, T.S.; Cappello, Z.J.; Wu, A.W.; Ting, J.Y.; Sindwani, R. Predictors of eustachian tube dysfunction improvement and normalization after endoscopic sinus surgery. Laryngoscope 2020, 130, E721–E726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuraola, O.A.; Afolabi, A.O.; Ologe, F.E. Tympanometry and endoscopic diagnosis of eustachian tube dysfunction in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Niger. Postgrad. Med. J. 2023, 30, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkelstein, Y.; Talmi, Y.P.; Rubel, Y.; Bar-Ziv, J.; Zohar, Y. Otitis media with effusion as a presenting symptom of chronic sinusitis. J. Laryngol. Otol. 1989, 103, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, R.D.; Ort, H.; Leong, A.B.; Cook, D.A.; Street, D.; Hamburger, R.N. Tympanometric changes following nasal antigen challenge in children with allergic rhinitis. Ann. Allergy 1984, 53, 468–471. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, S.M.; Derbarsegian, A.; Sedaghat, A.R.; Phillips, K.M. Impact of medical treatment for chronic rhinosinusitis on eustachian tube dysfunction. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2023, 14, 850–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OuYang, Z.; Lou, Z.; Lou, Z.; Jin, K.; Sun, J.; Chen, Z. The effect of concurrent nasal surgery on the eustachian tube function and myringoplasty outcomes. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2021, 42, 102926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, G.; Kim, H.Y.; Jung, Y.G.; Hong, S.D. Endotypes of Asian chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: A narrative review. Precis. Future Med. 2022, 6, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juszczak, H.M.; Loftus, P.A. Role of Allergy in Eustachian Tube Dysfunction. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2020, 20, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernkopf, E.; Cristalli, G.; de Vincentiis, G.C.; Bernkopf, G.; Capriotti, V. Temporomandibular Joint and Otitis Media: A Narrative Review of Implications in Etiopathogenesis and Treatment. Medicina 2022, 58, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.T.; Roozdar, P.; Lin, Y.T.; Lee, J.Y.; Nayak, J.V.; Patel, Z.M.; Hwang, P.H. Effect of dupilumab on Eustachian tube dysfunction in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2023, 13, 1561–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashima, D.; Nakayama, T.; Minagawa, S.; Adachi, T.; Mitsuyama, C.; Shida, Y.; Nakajima, T.; Haruna, S.I.; Matsuwaki, Y. Dupilumab improves eosinophilic otitis media associated with eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergol. Int. 2023, 72, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishizawa, H.; Matsubara, A.; Nakagawa, T.; Ohta, N.; Izuhara, K.; Shirasaki, T.; Abe, T.; Takeda, I.; Shinkawa, H. The role of periostin in eosinophilic otitis media. Acta Otolaryngol. 2012, 132, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, A.; Ohta, N.; Suzuki, Y.; Kakehata, S.; Okubo, K.; Ikeda, H.; Shiraishi, H.; Izuhara, K. Expression of pendrin and periostin in allergic rhinitis and chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergol. Int. 2012, 61, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Anwar, M.W.; Elnabtity, N.M.; Nada, E.; Abdelmonem, S. Relationship between nasal polyposis and Eustachian tube function. Egypt. J. Otolaryngol. 2022, 38, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).