Serum Adiponectin Is Elevated in Critically Ill Patients with Liver Disease and Associated with Decreased Overall Survival
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Adiponectin Measurements
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
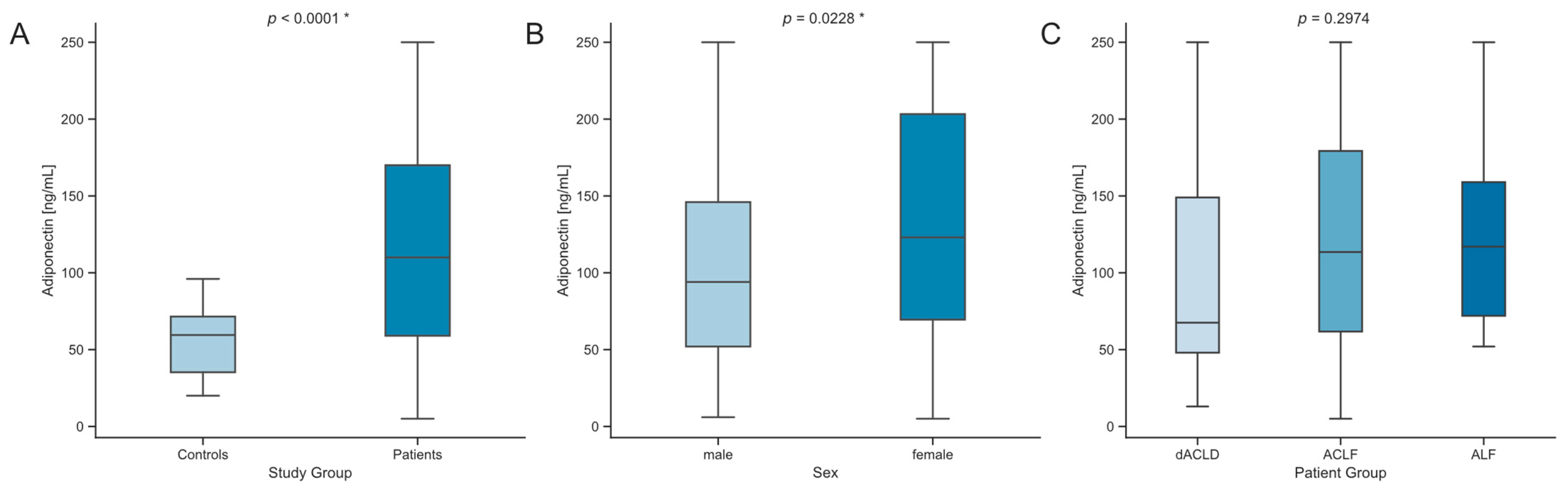
3.2. Serum Levels of Adiponectin Are Elevated in Critically Ill Patients with Liver Dysfunction
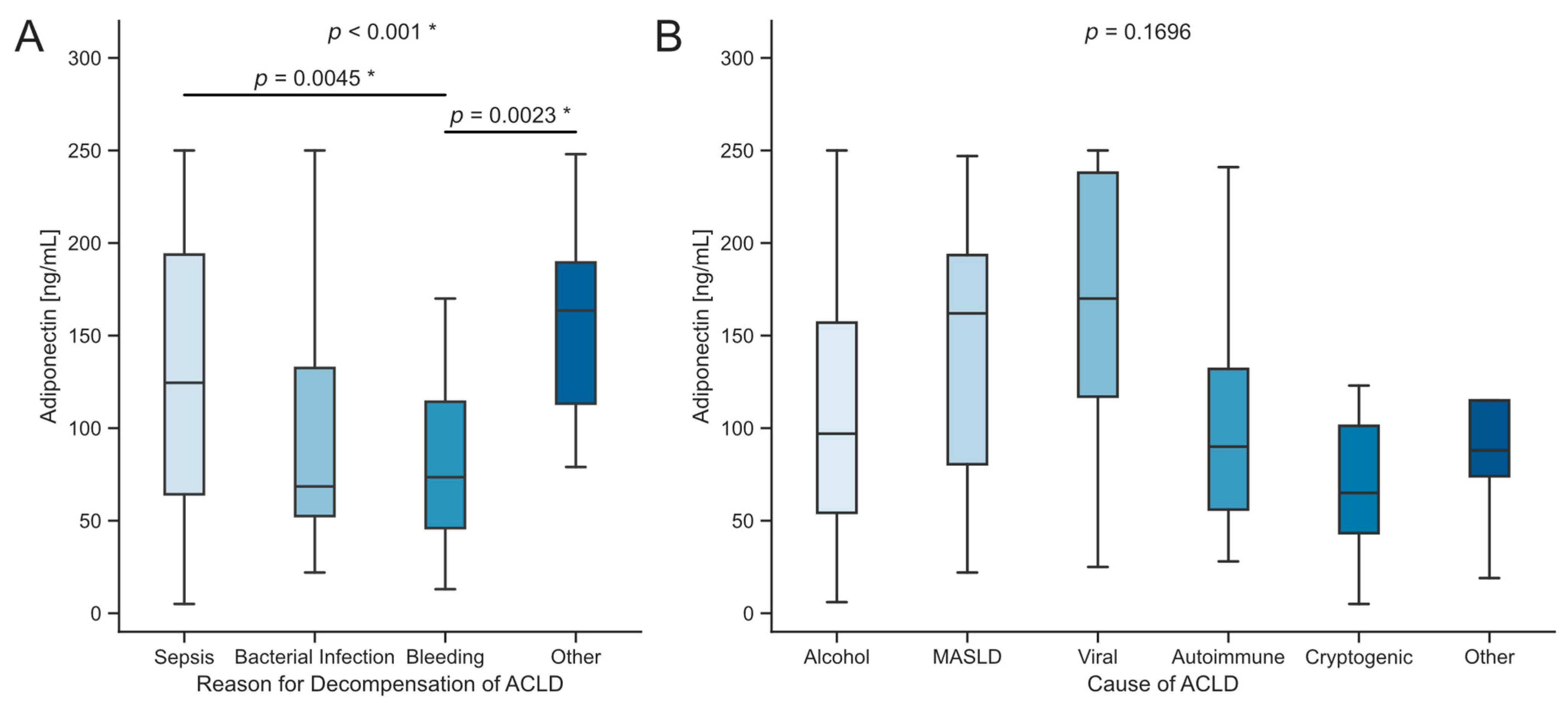
3.3. Impact of Decompensation Events in ACLD
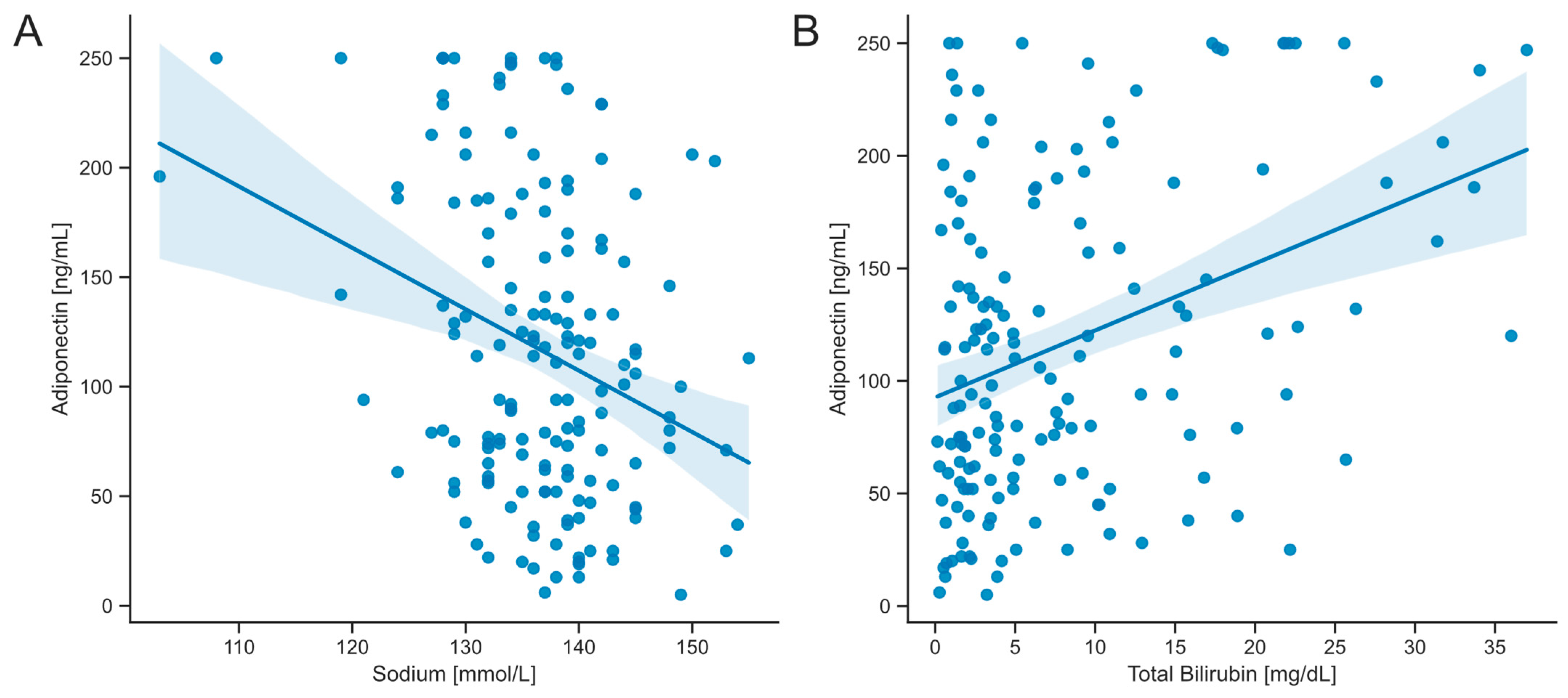
3.4. Serum Concentrations of Adiponectin Correlate with Markers of Hepatic Dysfunction
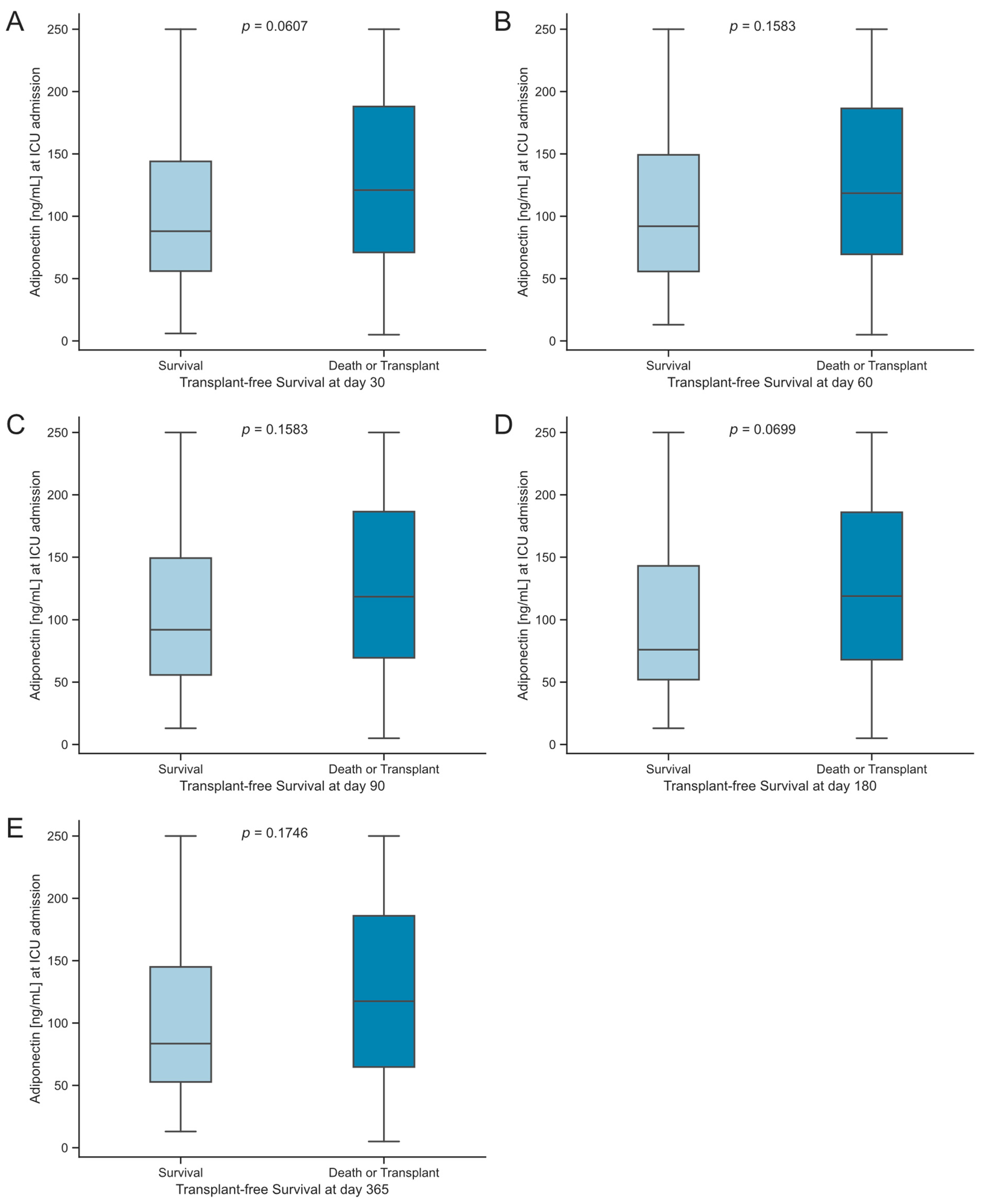
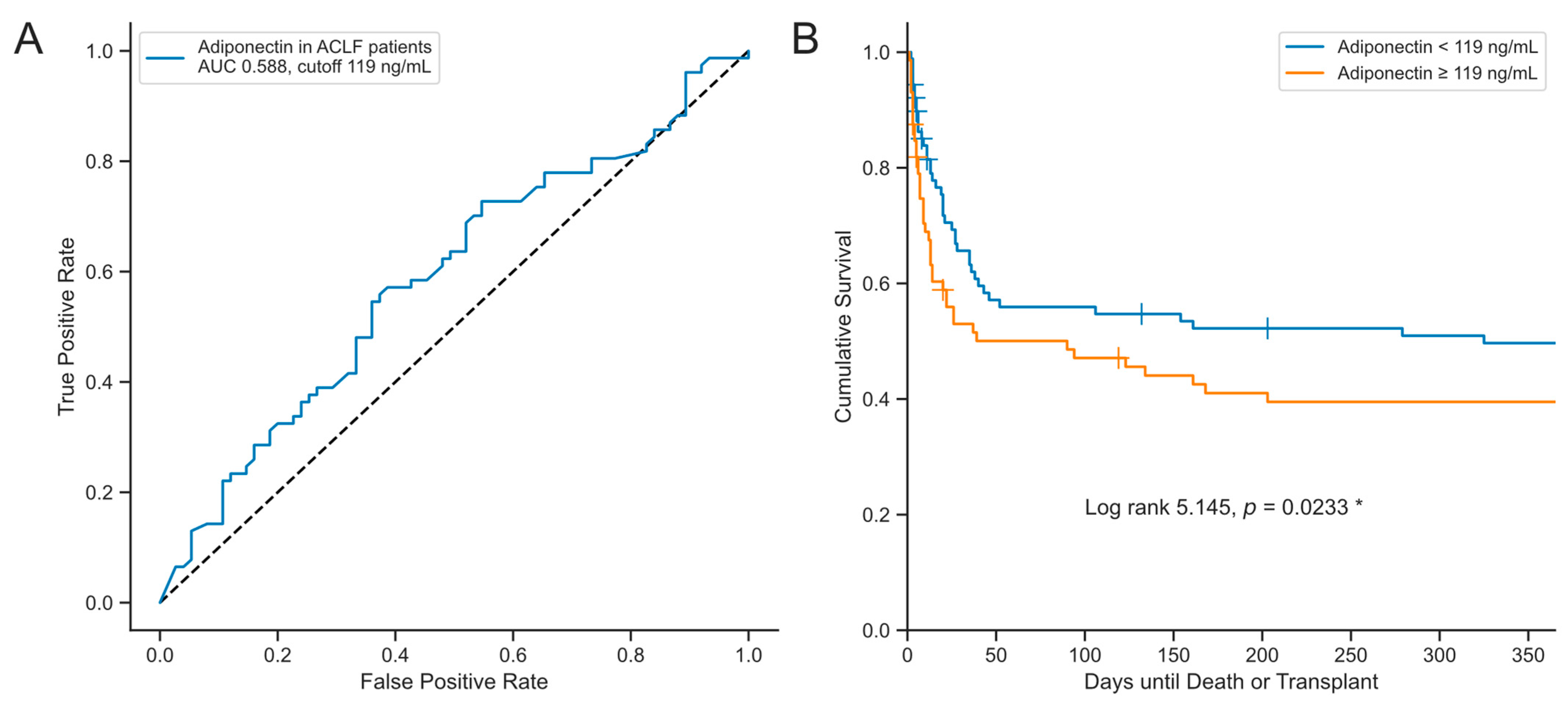
3.5. Serum Concentrations of Adiponectin Are Associated with Transplant-Free Survival in Critically Ill Patients with Acute Liver Dysfunction
3.6. Stability of Serum Adiponectin Levels in the Early Stages of Critical Illness in Patients with Liver Disease
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Adipocytokines: Mediators linking adipose tissue, inflammation and immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 772–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, N.; Parker, J.L.; Lugus, J.J.; Walsh, K. Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, N.; Kihara, S.; Funahashi, T.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Walsh, K. Obesity, adiponectin and vascular inflammatory disease. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2003, 14, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyer, C.; Funahashi, T.; Tanaka, S.; Hotta, K.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Pratley, R.E.; Tataranni, P.A. Hypoadiponectinemia in obesity and type 2 diabetes: Close association with insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 1930–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, A.H.; Combs, T.P.; Scherer, P.E. ACRP30/adiponectin: An adipokine regulating glucose and lipid metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 13, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Ito, Y.; Tsuchida, A.; Yokomizo, T.; Kita, S.; Sugiyama, T.; Miyagishi, M.; Hara, K.; Tsunoda, M.; et al. Cloning of adiponectin receptors that mediate antidiabetic metabolic effects. Nature 2003, 423, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, B.; Iseli, T.; Ramezani-Moghadam, M.; Ho, V.; Wankell, M.; Sun, E.J.; Qiao, L.; George, J.; Hebbard, L.W. The role of AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 in liver fibrosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, V.; Pritchard, M.T.; McMullen, M.R.; Nagy, L.E. Adiponectin normalizes LPS-stimulated TNF-alpha production by rat Kupffer cells after chronic ethanol feeding. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2006, 290, G998–G1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.V.; Scherer, P.E. Adiponectin, the past two decades. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 8, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, P. AMP activated protein kinase: A next generation target for total metabolic control. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2008, 12, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arita, Y.; Kihara, S.; Ouchi, N.; Takahashi, M.; Maeda, K.; Miyagawa, J.; Hotta, K.; Shimomura, I.; Nakamura, T.; Miyaoka, K.; et al. Paradoxical decrease of an adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in obesity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 257, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, T.E.; Colombo, G.; Schiavon, L.L. Adiponectin: A multitasking player in the field of liver diseases. Diabetes Metab. 2014, 40, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, A.; Sanson, E.; Voigt, S.; Helm, A.; Trautwein, C.; Tacke, F. Serum adiponectin upon admission to the intensive care unit may predict mortality in critically ill patients. J. Crit. Care 2011, 26, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, A.M.; Wolf, D.; Avila, M.A.; Moschen, A.R.; Berasain, C.; Enrich, B.; Rumpold, H.; Tilg, H. Up-regulation of the anti-inflammatory adipokine adiponectin in acute liver failure in mice. J. Hepatol. 2006, 44, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, H.; Fujiwara, N.; Tateishi, R.; Arano, T.; Nakagomi, R.; Kondo, M.; Minami, T.; Sato, M.; Uchino, K.; Enooku, K.; et al. Impact of serum levels of interleukin-6 and adiponectin on all-cause, liver-related, and liver-unrelated mortality in chronic hepatitis C patients. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 30, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.M.; Ryu, O.H.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, H.Y.; Seo, J.A.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, N.H.; Choi, D.S.; Baik, S.H. Serum adiponectin, interleukin-10 levels and inflammatory markers in the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2007, 75, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xia, L.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, D.; Xin, C.; Wang, H.; Zhang, F.; Guo, X.; Lee, Y.; Zhang, L.; et al. A novel mechanism of diabetic vascular endothelial dysfunction: Hypoadiponectinemia-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 1556–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shingina, A.; Mukhtar, N.; Wakim-Fleming, J.; Alqahtani, S.; Wong, R.J.; Limketkai, B.N.; Larson, A.M.; Grant, L. Acute Liver Failure Guidelines. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 118, 1128–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginès, P.; Krag, A.; Abraldes, J.G.; Solà, E.; Fabrellas, N.; Kamath, P.S. Liver cirrhosis. Lancet 2021, 398, 1359–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, R.; Jalan, R.; Gines, P.; Pavesi, M.; Angeli, P.; Cordoba, J.; Durand, F.; Gustot, T.; Saliba, F.; Domenicali, M.; et al. Acute-on-chronic liver failure is a distinct syndrome that develops in patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 1426–1437.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, V.; Moreau, R.; Jalan, R.; Ginès, P. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: A new syndrome that will re-classify cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, S131–S143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arroyo, V.; Moreau, R.; Jalan, R. Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2137–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, V.; Karvellas, C.J. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: Objective admission and support criteria in the intensive care unit. JHEP Rep. 2019, 1, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trebicka, J.; Sundaram, V.; Moreau, R.; Jalan, R.; Arroyo, V. Liver Transplantation for Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure: Science or Fiction? Liver Transpl. 2020, 26, 906–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPhail, M.J.W.; Parrott, F.; Wendon, J.A.; Harrison, D.A.; Rowan, K.A.; Bernal, W. Incidence and Outcomes for Patients With Cirrhosis Admitted to the United Kingdom Critical Care Units. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 46, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, B.; Hickman, I.; Nisbet, J.; Cohen, J.; Prins, J. Changes in serum adiponectin concentrations in critical illness: A preliminary investigation. Crit. Care 2009, 13, R105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langouche, L.; Vander Perre, S.; Frystyk, J.; Flyvbjerg, A.; Hansen, T.K.; Van den Berghe, G. Adiponectin, retinol-binding protein 4, and leptin in protracted critical illness of pulmonary origin. Crit. Care 2009, 13, R112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mester, P.; Rath, U.; Schmid, S.; Muller, M.; Buechler, C.; Pavel, V. Exploring the Relationship between Plasma Adiponectin, Gender, and Underlying Diseases in Severe Illness. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohlstein, P.; Salvarcioglu, C.; Pollmanns, M.R.; Adams, J.K.; Abu Jhaisha, S.; Kabak, E.; Eisert, A.; Hamesch, K.; Weiskirchen, R.; Koch, A.; et al. Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Serum Leptin in Critically Ill Patients with Acute versus Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendon, J.; Cordoba, J.; Dhawan, A.; Larsen, F.S.; Manns, M.; Samuel, D.; Simpson, K.J.; Yaron, I.; Bernardi, M. EASL Clinical Practical Guidelines on the management of acute (fulminant) liver failure. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 1047–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on acute-on-chronic liver failure. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 461–491. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loosen, S.H.; Koch, A.; Tacke, F.; Roderburg, C.; Luedde, T. The Role of Adipokines as Circulating Biomarkers in Critical Illness and Sepsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreau, R.; Clària, J.; Aguilar, F.; Fenaille, F.; Lozano, J.J.; Junot, C.; Colsch, B.; Caraceni, P.; Trebicka, J.; Pavesi, M.; et al. Blood metabolomics uncovers inflammation-associated mitochondrial dysfunction as a potential mechanism underlying ACLF. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 688–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trebicka, J.; Amoros, A.; Pitarch, C.; Titos, E.; Alcaraz-Quiles, J.; Schierwagen, R.; Deulofeu, C.; Fernandez-Gomez, J.; Piano, S.; Caraceni, P.; et al. Addressing Profiles of Systemic Inflammation Across the Different Clinical Phenotypes of Acutely Decompensated Cirrhosis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffler, A.; Scholmerich, J.; Buchler, C. Mechanisms of disease: Adipocytokines and visceral adipose tissue--emerging role in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Clin. Pract. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005, 2, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emenheiser, J.C.; Greiner, S.P.; Lewis, R.M.; Notter, D.R. Validation of live animal ultrasonic measurements of body composition in market lambs. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 88, 2932–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, T.E.; Costa-Silva, M.; Correa, C.G.; Denardin, G.; Alencar, M.L.A.; Coelho, M.; Muraro-Wildner, L.; Luiza-Bazzo, M.; Gonzalez-Chica, D.A.; Dantas-Correa, E.B.; et al. Clinical Significance of Serum Adiponectin and Resistin Levels in Liver Cirrhosis. Ann. Hepatol. 2018, 17, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsochatzis, E.; Papatheodoridis, G.V.; Hadziyannis, E.; Georgiou, A.; Kafiri, G.; Tiniakos, D.G.; Manesis, E.K.; Archimandritis, A.J. Serum adipokine levels in chronic liver diseases: Association of resistin levels with fibrosis severity. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 43, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, R.F.; Atta, A.M.; de Oliveira, I.S.; Santos, T.P.S.; Santos, J.P.A.; Schinoni, M.I.; de Sousa-Atta, M.L.B. Adiponectin levels and insulin resistance among patients with chronic hepatitis C. Acta Trop. 2018, 178, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korah, T.E.; El-Sayed, S.; Elshafie, M.K.; Hammoda, G.E.; Safan, M.A. Significance of serum leptin and adiponectin levels in Egyptian patients with chronic hepatitis C virus associated hepatic steatosis and fibrosis. World J. Hepatol. 2013, 5, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbetta, S.; Redaelli, A.; Pozzi, M.; Bovo, G.; Ratti, L.; Redaelli, E.; Pellegrini, C.; Beck-Peccoz, P.; Spada, A. Fibrosis is associated with adiponectin resistance in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 41, 898–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buechler, C.; Schäffler, A.; Johann, M.; Neumeier, M.; Köhl, P.; Weiss, T.; Wodarz, N.; Kiefer, P.; Hellerbrand, C. Elevated adiponectin serum levels in patients with chronic alcohol abuse rapidly decline during alcohol withdrawal. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 24, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierksma, A.; Patel, H.; Ouchi, N.; Kihara, S.; Funahashi, T.; Heine, R.J.; Grobbee, D.E.; Kluft, C.; Hendriks, H.F. Effect of moderate alcohol consumption on adiponectin, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and insulin sensitivity. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaser, S.; Moschen, A.; Kaser, A.; Ludwiczek, O.; Ebenbichler, C.F.; Vogel, W.; Jaschke, W.; Patsch, J.R.; Tilg, H. Circulating adiponectin reflects severity of liver disease but not insulin sensitivity in liver cirrhosis. J. Intern. Med. 2005, 258, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacke, F.; Wüstefeld, T.; Horn, R.; Luedde, T.; Srinivas Rao, A.; Manns, M.P.; Trautwein, C.; Brabant, G. High adiponectin in chronic liver disease and cholestasis suggests biliary route of adiponectin excretion in vivo. J. Hepatol. 2005, 42, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, P.; Wong, F.; Watson, H.; Ginès, P. Hyponatremia in cirrhosis: Results of a patient population survey. Hepatology 2006, 44, 1535–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginès, P.; Guevara, M. Hyponatremia in cirrhosis: Pathogenesis, clinical significance, and management. Hepatology 2008, 48, 1002–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balmer, M.L.; Joneli, J.; Schoepfer, A.; Stickel, F.; Thormann, W.; Dufour, J.F. Significance of serum adiponectin levels in patients with chronic liver disease. Clin. Sci. 2010, 119, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasztelan-Szczerbinska, B.; Surdacka, A.; Slomka, M.; Rolinski, J.; Celinski, K.; Smolen, A.; Szczerbinski, M. Association of serum adiponectin, leptin, and resistin concentrations with the severity of liver dysfunction and the disease complications in alcoholic liver disease. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 148526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietge, U.J.; Böker, K.H.; Manns, M.P.; Bahr, M.J. Elevated circulating adiponectin levels in liver cirrhosis are associated with reduced liver function and altered hepatic hemodynamics. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 287, E82–E89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalafateli, M.; Triantos, C.; Tsochatzis, E.; Michalaki, M.; Koutroumpakis, E.; Thomopoulos, K.; Kyriazopoulou, V.; Jelastopulu, E.; Burroughs, A.; Lambropoulou-Karatza, C.; et al. Adipokines levels are associated with the severity of liver disease in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 3020–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzaghi, C.; Xu, M.; Salvemini, L.; De Bonis, C.; Palladino, G.; Huang, T.; Copetti, M.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Fini, G.; et al. Circulating adiponectin and cardiovascular mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Evidence of sexual dimorphism. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2014, 13, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollerits, B.; Fliser, D.; Heid, I.M.; Ritz, E.; Kronenberg, F.; Group, M.S. Gender-specific association of adiponectin as a predictor of progression of chronic kidney disease: The Mild to Moderate Kidney Disease Study. Kidney Int. 2007, 71, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameter | dACLD | ACLF | ALF | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number, n | 20 | 124 | 17 | |
| Sex, female, n (%) | 9 (45%) | 50 (40.3%) | 9 (52.9%) | 0.5924 |
| Age (years) | 59.5 (15.25) | 58 (15.25) | 52 (32) | 0.1947 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.1 (4.5) | 27.6 (8.5) | 25.7 (6.5) | 0.0044 * |
| APACHE II score | 16.5 (12) | 27 (14) | 15 (11) | <0.001 * |
| SOFA score | 8 (4) | 14 (5) | 9 (3) | <0.001 * |
| MELD score | 13 (6) | 28 (12.25) | 30 (11) | <0.001 * |
| Liver transplantation, n (%) | 3 (15.0%) | 13 (10.5%) | 6 (35.5%) | 0.0199 * |
| Mechanical ventilation, n (%) | 3 (15.0%) | 64 (51.6%) | 2 (11.8%) | <0.001 * |
| Vasopressor demand, n (%) | 1 (5.0%) | 100 (80.6%) | 4 (23.5%) | <0.001 * |
| ICU days, n | 3 (1.25) | 6 (10) | 6 (11) | <0.001 * |
| Death in ICU, n (%) | 0 (0%) | 70 (56.5%) | 4 (23.5%) | <0.001 * |
| 30-day mortality, n (%) | 0 (0%) | 60 (52.2%) | 2 (11.8%) | <0.001 * |
| 1-year mortality, n (%) | 3 (15.8%) | 76 (66.7%) | 5 (31.2%) | <0.001 * |
| Adiponectin (ng/mL) | 67.5 (101) | 113.5 (117.5) | 117 (87) | 0.2974 |
| Parameter | Spearman’s r | p |
|---|---|---|
| Demographics | ||
| Age | −0.0072 | 0.928 |
| BMI | 0.11449 | 0.149 |
| Blood count and markers of inflammation | ||
| WBC | −0.059 | 0.457 |
| Hemoglobin | 0.09237 | 0.244 |
| Platelets | 0.00758 | 0.924 |
| CRP | −0.00721 | 0.364 |
| PCT | 0.03524 | 0.672 |
| IL-6 | 0.02512 | 0.781 |
| Electrolytes and renal system | ||
| Sodium | −0.2652 | 0.001 * |
| Potassium | −0.0659 | 0.407 |
| pH | 0.12674 | 0.109 |
| Urea | −0.0002 | 0.998 |
| Creatinine | 0.10018 | 0.206 |
| eGFR | −0.1247 | 0.115 |
| Diuresis per day | 0.0925 | 0.252 |
| Coagulation and hepato-pancreatico-biliary system | ||
| Albumin | −0.1243 | 0.116 |
| INR | 0.15482 | 0.05 |
| Bilirubin, total | 0.29116 | <0.001 * |
| AST | 0.03012 | 0.705 |
| ALT | 0.08779 | 0.268 |
| gGT | −0.1174 | 0.138 |
| AP | 0.14077 | 0.075 |
| Cholesterol | −0.0958 | 0.237 |
| Cardiopulmonary system | ||
| NT-pro BNP | −0.0891 | 0.31 |
| Norepinephrine demand | −0.0931 | 0.345 |
| Horovitz quotient (PaO2/FiO2) | 0.14989 | 0.058 |
| FiO2 | −0.1844 | 0.019 * |
| Lactate | 0.09991 | 0.207 |
| Disease severity and clinical scores | ||
| Length of stay in ICU | −0.0246 | 0.757 |
| Length of stay in hospital | 0.04102 | 0.605 |
| SOFA score | 0.05352 | 0.5 |
| APACHE II score | −0.0302 | 0.703 |
| SAPS II score | −0.0817 | 0.303 |
| MELD score | 0.27912 | <0.001 * |
| Child–Pugh points | 0.22967 | 0.006 * |
| CLIF-C OF score | 0.0506 | 0.556 |
| CLIF-C ACLF score | 0.06008 | 0.507 |
| Univariate Regression | Multivariate Regression | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Covariate | β Coefficient | Coefficient | 95 % CI | p | Coefficient | 95 % CI | p |
| Sodium | −20.88 | −2.8030 | −4.2150–−1.3910 | <0.001 * | −2.6195 | −4.007–−1.232 | <0.001 * |
| Bilirubin, total | 25.44 | 2.9733 | 1.7727–4.1739 | <0.001 * | 1.7467 | 0.226–3.267 | 0.025 * |
| MELD score | 18.92 | 2.1481 | 0.9433–3.3528 | <0.001 * | 0.8322 | −0.734–2.398 | 0.295 |
| FiO2 | −10.26 | −0.4424 | −0.9125–0.0276 | 0.0649 | |||
| Child–Pugh points | 17.57 | 8.4181 | 2.9556–13.8812 | 0.003 * | 2.3704 | −3.813–8.554 | 0.450 |
| Covariate | Hazard Ratio | 95 % CI | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adiponectin | 1.002897 | 1.00179–1.005623 | 0.0367 * |
| Age | 1.001946 | 0.988774–1.015295 | 0.7734 |
| Sex | 0.873853 | 0.589472–1.1595429 | 0.5020 |
| Sex, male | 1.002670 | 0.998934–1.006420 | 0.1612 |
| Sex, female | 1.003799 | 0.999622–1.007995 | 0.0747 |
| Sodium | 1.010828 | 0.984609–1.037745 | 0.4219 |
| Bilirubin | 1.053230 | 1.031838–1.075065 | <0.001* |
| APACHE II score | 1.028431 | 1.009198–1.048031 | 0.0036 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pollmanns, M.R.; Pajaziti, Q.; Hohlstein, P.; Adams, J.K.; Abu Jhaisha, S.; Kabak, E.; Hamesch, K.; Nusser, S.H.A.; Weiskirchen, R.; Wirtz, T.H.; et al. Serum Adiponectin Is Elevated in Critically Ill Patients with Liver Disease and Associated with Decreased Overall Survival. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2173. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12102173
Pollmanns MR, Pajaziti Q, Hohlstein P, Adams JK, Abu Jhaisha S, Kabak E, Hamesch K, Nusser SHA, Weiskirchen R, Wirtz TH, et al. Serum Adiponectin Is Elevated in Critically Ill Patients with Liver Disease and Associated with Decreased Overall Survival. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(10):2173. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12102173
Chicago/Turabian StylePollmanns, Maike R., Qendrim Pajaziti, Philipp Hohlstein, Jule K. Adams, Samira Abu Jhaisha, Elena Kabak, Karim Hamesch, Sophie H. A. Nusser, Ralf Weiskirchen, Theresa H. Wirtz, and et al. 2024. "Serum Adiponectin Is Elevated in Critically Ill Patients with Liver Disease and Associated with Decreased Overall Survival" Biomedicines 12, no. 10: 2173. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12102173
APA StylePollmanns, M. R., Pajaziti, Q., Hohlstein, P., Adams, J. K., Abu Jhaisha, S., Kabak, E., Hamesch, K., Nusser, S. H. A., Weiskirchen, R., Wirtz, T. H., & Koch, A. (2024). Serum Adiponectin Is Elevated in Critically Ill Patients with Liver Disease and Associated with Decreased Overall Survival. Biomedicines, 12(10), 2173. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12102173







