Development of a Non-Peptide Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Ligand by Structural Modification of Olmesartan as a Biased Agonist
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. AT1 Mutant Receptors
2.3. Cell Cultures, Transfection, and Membrane Preparation
2.4. Competition Binding Study
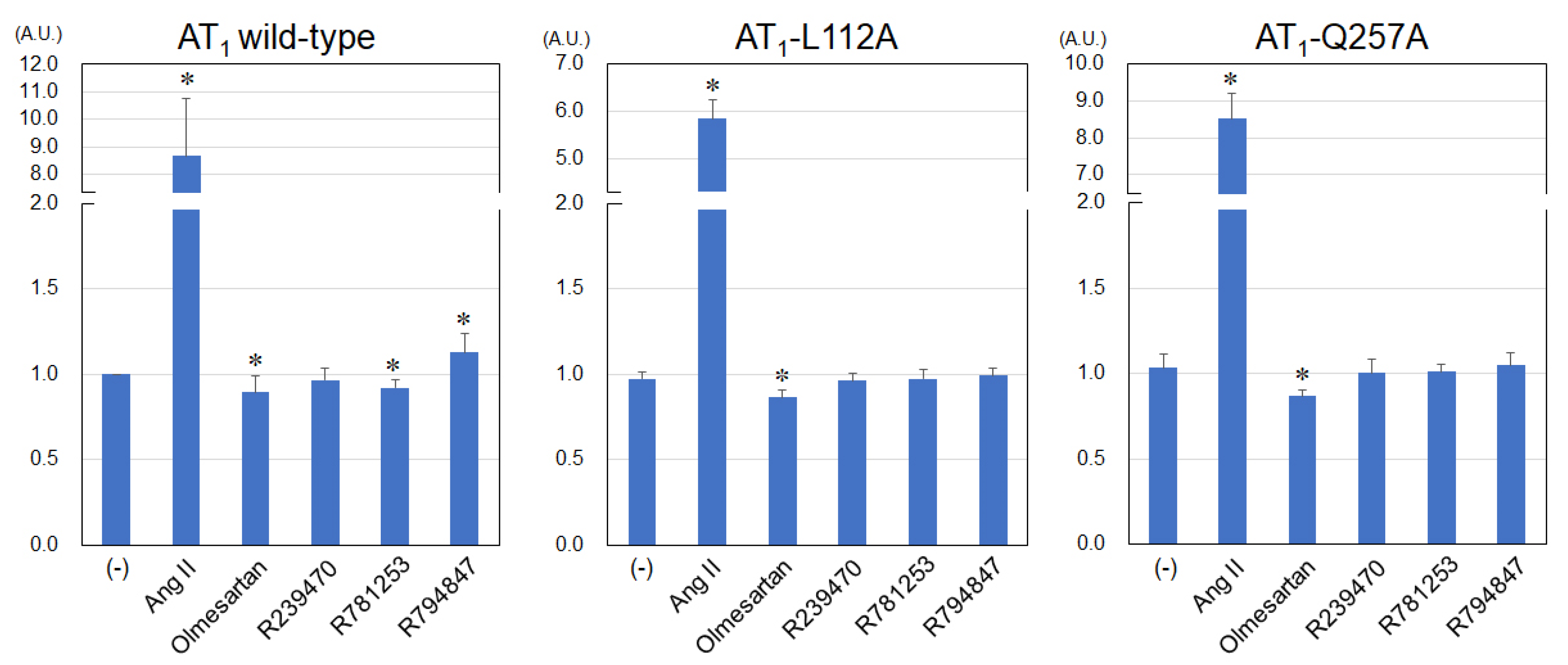
2.5. IP Production Assay
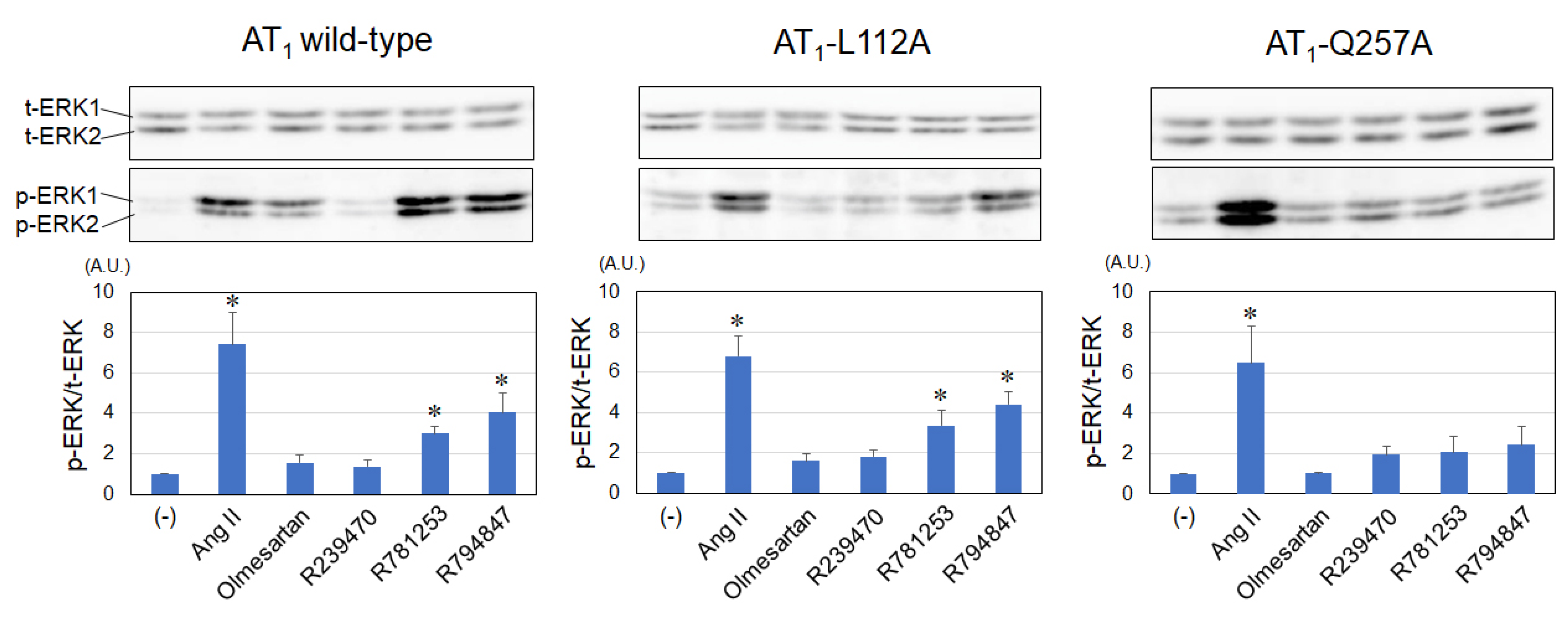
2.6. Immunoblotting of ERK 1/2 Activation
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Binding Affinities of [Sar1,Ile8]Ang II, Olmesartan, R239470, R781253, and R794847 to AT1 Wild-Type and Mutant Receptors
3.2. Levels of IP Production Using Various Ligands in AT1-WT, -L112A and Q257A Receptors
3.3. Levels of ERK Activities Using Various Ligands in AT1-WT, -L112A, and Q257A Receptors
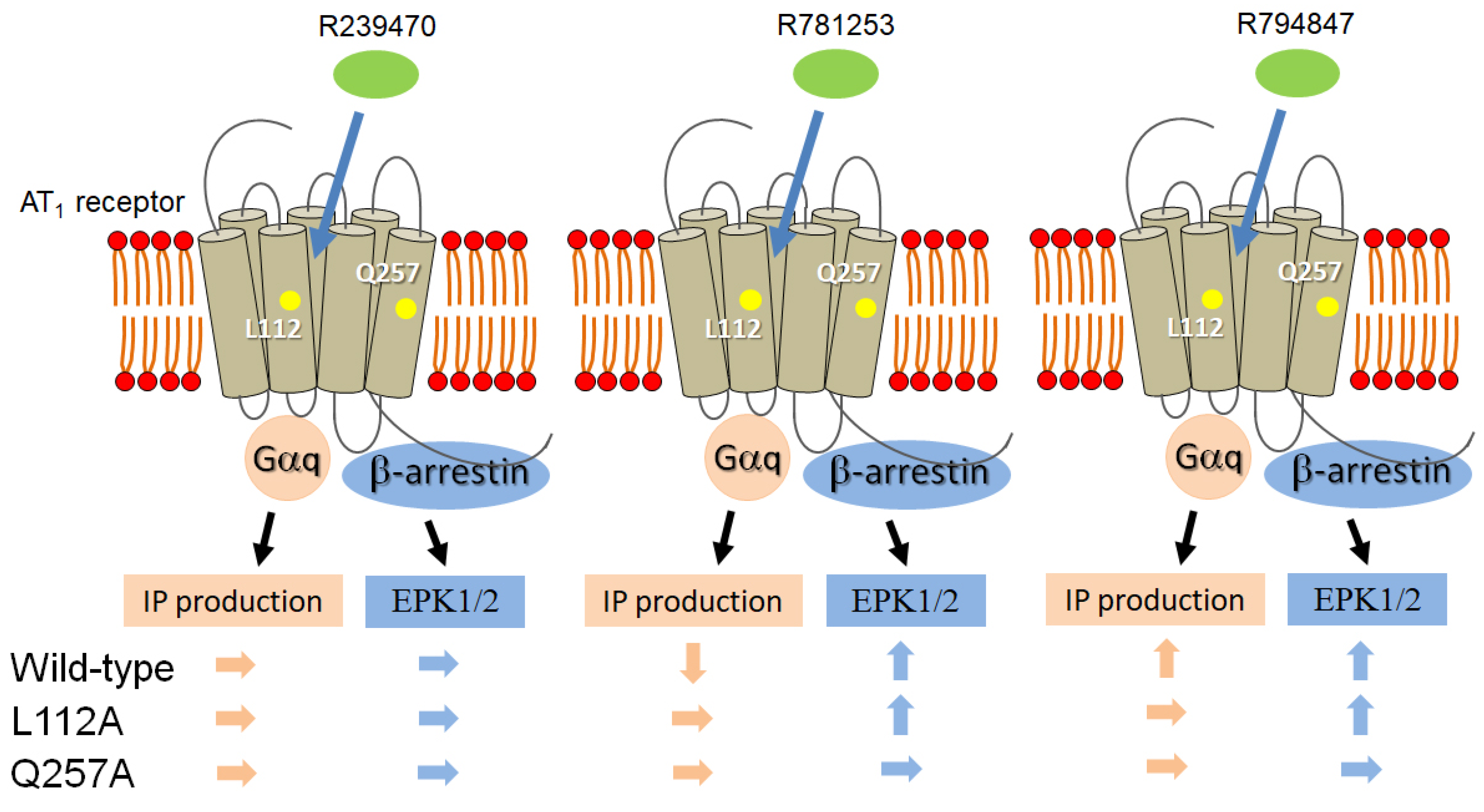
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karnik, S.S.; Unal, H.; Kemp, J.R.; Tirupula, K.C.; Eguchi, S.; Vanderheyden, P.M.; Thomas, W.G. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. XCIX. Angiotensin Receptors: Interpreters of Pathophysiological Angiotensinergic Stimuli [corrected]. Pharmacol. Rev. 2015, 67, 754–819, Erratum in Pharmacol. Rev. 2015, 67, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forrester, S.J.; Booz, G.W.; Sigmund, C.D.; Coffman, T.M.; Kawai, T.; Rizzo, V.; Scalia, R.; Eguchi, S. Angiotensin II Signal Transduction: An Update on Mechanisms of Physiology and Pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1627–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakumar, P.; Jagadeesh, G. A century old renin-angiotensin system still grows with endless possibilities: AT1 receptor signaling cascades in cardiovascular physiopathology. Cell Signal. 2014, 26, 2147–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonde, M.M.; Hansen, J.T.; Sanni, S.J.; Haunsø, S.; Gammeltoft, S.; Lyngsø, C.; Hansen, J.L. Biased signaling of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor can be mediated through distinct mechanisms. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, S.; Zhang, J.; Matsuo, Y.; Saku, K.; Karnik, S.S. Activation of extracellular signal-activated kinase by angiotensin II-induced Gq-independent epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation. Hypertens. Res. 2004, 27, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnier, M.; Brunner, H.R. Angiotensin II receptor antagonists. Lancet 2000, 355, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, S.; Fujino, M.; Saku, K. Angiotensin II receptor blocker as an inverse agonist: A current perspective. Curr. Hypertens. Rev. 2005, 1, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Ahn, S.; Ren, X.R.; Whalen, E.J.; Reiter, E.; Wei, H.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Functional antagonism of different G protein-coupled receptor kinases for b-arrestin-mediated angiotensin II receptor signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 1442–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, S.; Okabe, A.; Matsuo, Y.; Karnik, S.S.; Saku, K. Unique binding behavior of the recently approved angiotensin II receptor blocker azilsartan compared with that of candesartan. Hypertens. Res. 2013, 36, 134–139, Erratum in Hypertens Res. 2013, 36, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violin, J.D.; DeWire, S.M.; Yamashita, D.; Rominger, D.H.; Nguyen, L.; Schiller, K.; Whalen, E.J.; Gowen, M.; Lark, M.W. Selectively engaging β-arrestins at the angiotensin II type 1 receptor reduces blood pressure and increases cardiac performance. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 335, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarigopula, M.; Davis, R.T., 3rd; Mungai, P.T.; Ryba, D.M.; Wieczorek, D.F.; Cowan, C.L.; Violin, J.D.; Wolska, B.M.; Solaro, R.J. Cardiac myosin light chain phosphorylation and inotropic effects of a biased ligand, TRV120023, in a dilated cardiomyopathy model. Cardiovasc. Res. 2015, 107, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryba, D.M.; Li, J.; Cowan, C.L.; Russell, B.; Wolska, B.M.; Solaro, R.J. Long-Term Biased β-Arrestin Signaling Improves Cardiac Structure and Function in Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Circulation 2017, 135, 1056–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, P.S.; Butler, J.; Collins, S.P.; Cotter, G.; Davison, B.A.; Ezekowitz, J.A.; Filippatos, G.; Levy, P.D.; Metra, M.; Ponikowski, P.; et al. Biased ligand of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor in patients with acute heart failure: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase IIB, dose ranging trial (BLAST-AHF). Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 2364–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, S.; Karnik, S.S.; Saku, K. Review: Angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockers: Class effects versus molecular effects. J. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Syst. 2011, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, S.; Kiya, Y.; Hanzawa, H.; Nakao, N.; Fujino, M.; Imaizumi, S.; Matsuo, Y.; Yanagisawa, H.; Koike, H.; Komuro, I.; et al. Small molecules with similar structures exhibit agonist, neutral antagonist or inverse agonist activity toward angiotensin II type 1 receptor. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37974, Erratum in PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Unal, H.; Desnoyer, R.; Han, G.W.; Patel, N.; Katritch, V.; Karnik, S.S.; Cherezov, V.; Stevens, R.C. Structural Basis for Ligand Recognition and Functional Selectivity at Angiotensin Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 29127–29139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modestia, S.M.; Malta de Sá, M.; Auger, E.; Trossini, G.H.G.; Krieger, J.E.; Rangel-Yagui, C.O. Biased Agonist TRV027 Determinants in AT1R by Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2019, 59, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, S.; Fujino, M.; Hanzawa, H.; Kiya, Y.; Imaizumi, S.; Matsuo, Y.; Tomita, S.; Uehara, Y.; Karnik, S.S.; Yanagisawa, H.; et al. Molecular mechanism underlying inverse agonist of angiotensin II type 1 receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 19288–19295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suomivuori, C.M.; Latorraca, N.R.; Wingler, L.M.; Eismann, S.; King, M.C.; Kleinhenz, A.L.W.; Skiba, M.A.; Staus, D.P.; Kruse, A.C.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; et al. Molecular mechanism of biased signaling in a prototypical G protein-coupled receptor. Science 2020, 367, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingler, L.M.; Skiba, M.A.; McMahon, C.; Staus, D.P.; Kleinhenz, A.L.W.; Suomivuori, C.M.; Latorraca, N.R.; Dror, R.O.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Kruse, A.C. Angiotensin and biased analogs induce structurally distinct active conformations within a GPCR. Science 2020, 367, 888–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabana, J.; Holleran, B.; Leduc, R.; Escher, E.; Guillemette, G.; Lavigne, P. Identification of Distinct Conformations of the Angiotensin-II Type 1 Receptor Associated with the Gq/11 Protein Pathway and the β-Arrestin Pathway Using Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 15835–15854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingler, L.M.; Elgeti, M.; Hilger, D.; Latorraca, N.R.; Lerch, M.T.; Staus, D.P.; Dror, R.O.; Kobilka, B.K.; Hubbell, W.L.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Angiotensin Analogs with Divergent Bias Stabilize Distinct Receptor Conformations. Cell 2019, 176, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawakami, K.; Yanagawa, M.; Hiratsuka, S.; Yoshida, M.; Ono, Y.; Hiroshima, M.; Ueda, M.; Aoki, J.; Sako, Y.; Inoue, A. Heterotrimeric Gq proteins act as a switch for GRK5/6 selectivity underlying β-arrestin transducer bias. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manglik, A.; Wingler, L.M.; Rockman, H.A.; Lefkowitz, R.J. β-Arrestin-Biased Angiotensin II Receptor Agonists for COVID-19. Circulation 2020, 142, 318–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
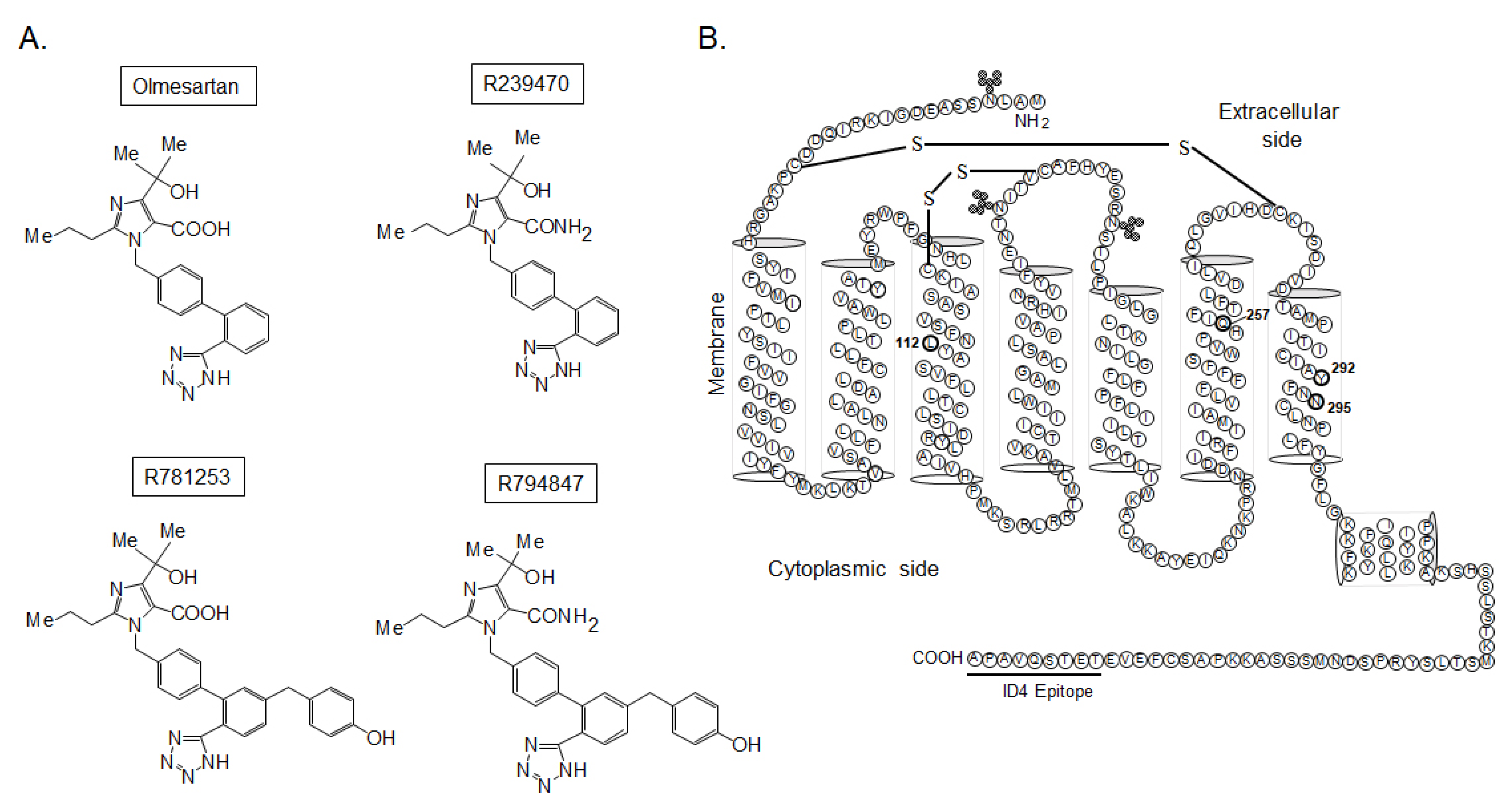
| Receptors | Wild-Type | L112A | Q257A | Y292A | N295A |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands | |||||
| [Sar1,Ile8]Ang II | 0.8 ± 0.4 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | 3.3 ± 1.5 | 2.1 ± 0.9 | 7.0 ± 2.0 |
| Olmesartan | 2.3 ± 0.8 | 27 ± 7 | 228 ± 38 | 47 ± 15 | 334 ± 105 |
| R239470 | 0.8 ± 0.3 | 37 ± 12 | 20 ± 2 | 6.3 ± 3.8 | 69 ± 8 |
| R781253 | 21 ± 10 | 23 ± 7 | 14 ± 6 | 95 ± 7 | >10,000 |
| R794847 | 48 ± 12 | 31 ± 5 | 2.7 ± 0.8 | 30 ± 8 | >10,000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matsuo, Y.; Suematsu, Y.; Morita, H.; Miura, S.-i. Development of a Non-Peptide Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Ligand by Structural Modification of Olmesartan as a Biased Agonist. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051486
Matsuo Y, Suematsu Y, Morita H, Miura S-i. Development of a Non-Peptide Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Ligand by Structural Modification of Olmesartan as a Biased Agonist. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(5):1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051486
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatsuo, Yoshino, Yasunori Suematsu, Hidetaka Morita, and Shin-ichiro Miura. 2023. "Development of a Non-Peptide Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Ligand by Structural Modification of Olmesartan as a Biased Agonist" Biomedicines 11, no. 5: 1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051486
APA StyleMatsuo, Y., Suematsu, Y., Morita, H., & Miura, S.-i. (2023). Development of a Non-Peptide Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Ligand by Structural Modification of Olmesartan as a Biased Agonist. Biomedicines, 11(5), 1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051486






