Regulation of Cancer Stem Cells and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition by CTNNAL1 in Lung Cancer and Glioblastoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Sphere-Formation Assays
2.3. Neutralization Assay
2.4. Antibodies
2.5. Small Interfering RNA (siRNA) Mediated Knockdown of CTNNAL1
2.6. Gene Expression Analysis
2.7. Western Blotting
2.8. Immunocytochemistry
2.9. Single Cell Assay
2.10. Limited Dilution Assay
2.11. Invasion and Migration Assays
2.12. Wound Healing Assay
2.13. Colony-Formation Assay and Irradiation
2.14. Cytokine Array
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of CTNNAL1 as a Potential Target in ALDH1+ Lung Cancer Cells
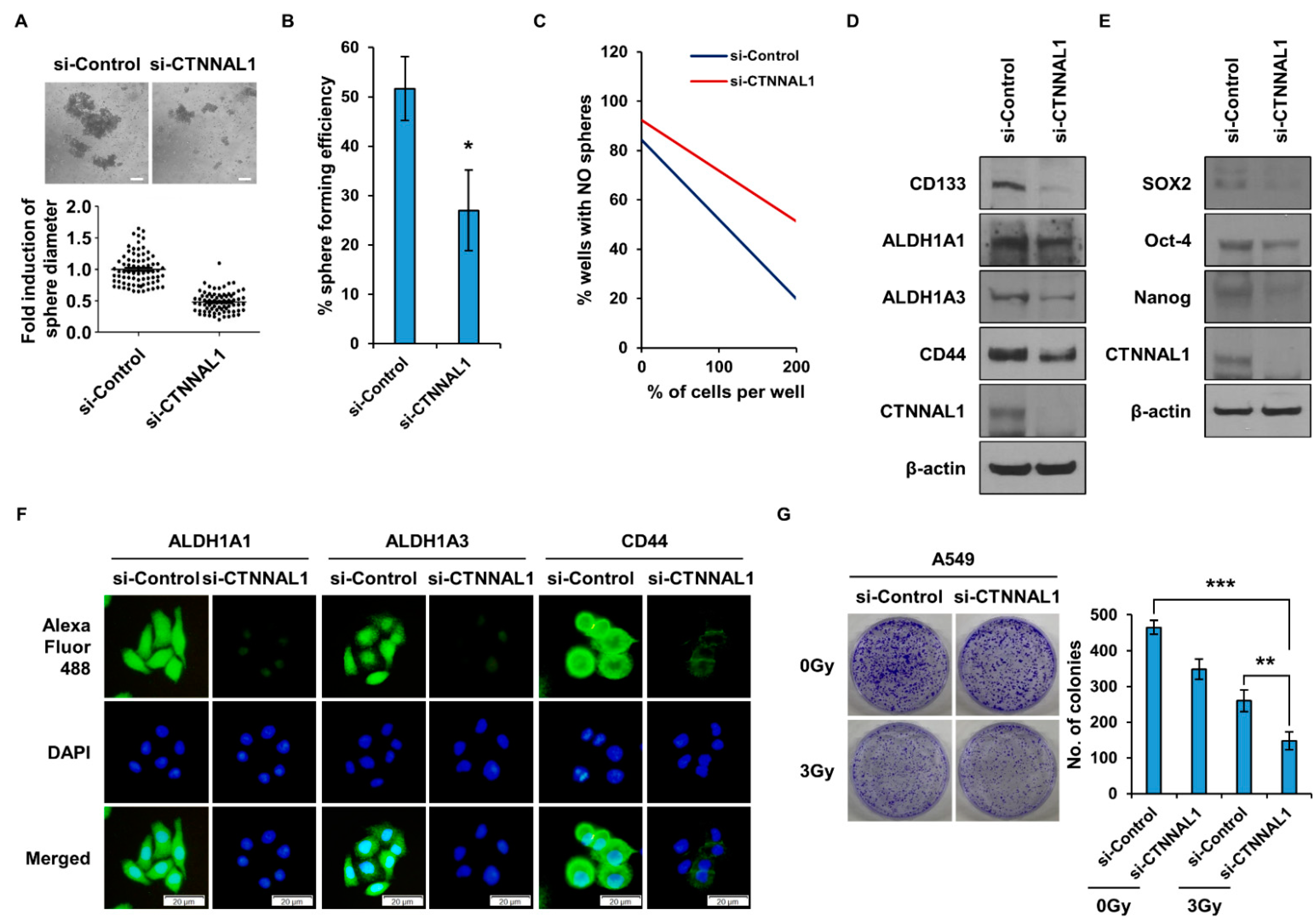
3.2. CTNNAL1 Gene Silencing Reduces Cancer Stem Cell Characteristics and Enhances Sensitivity to Irradiation in Lung Cancer
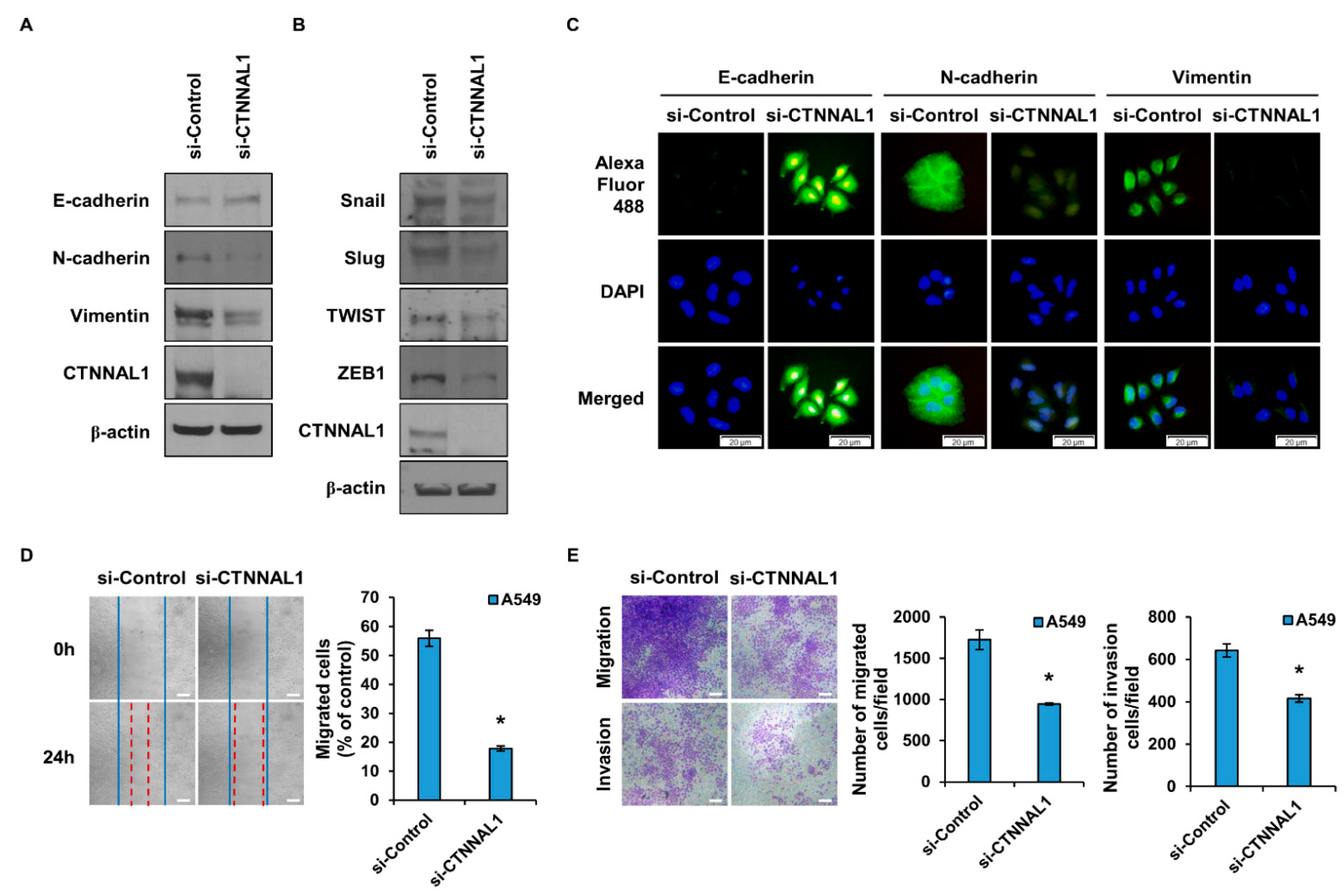
3.3. CTNNAL1 Regulates EMT Phenomena and Cell Motility
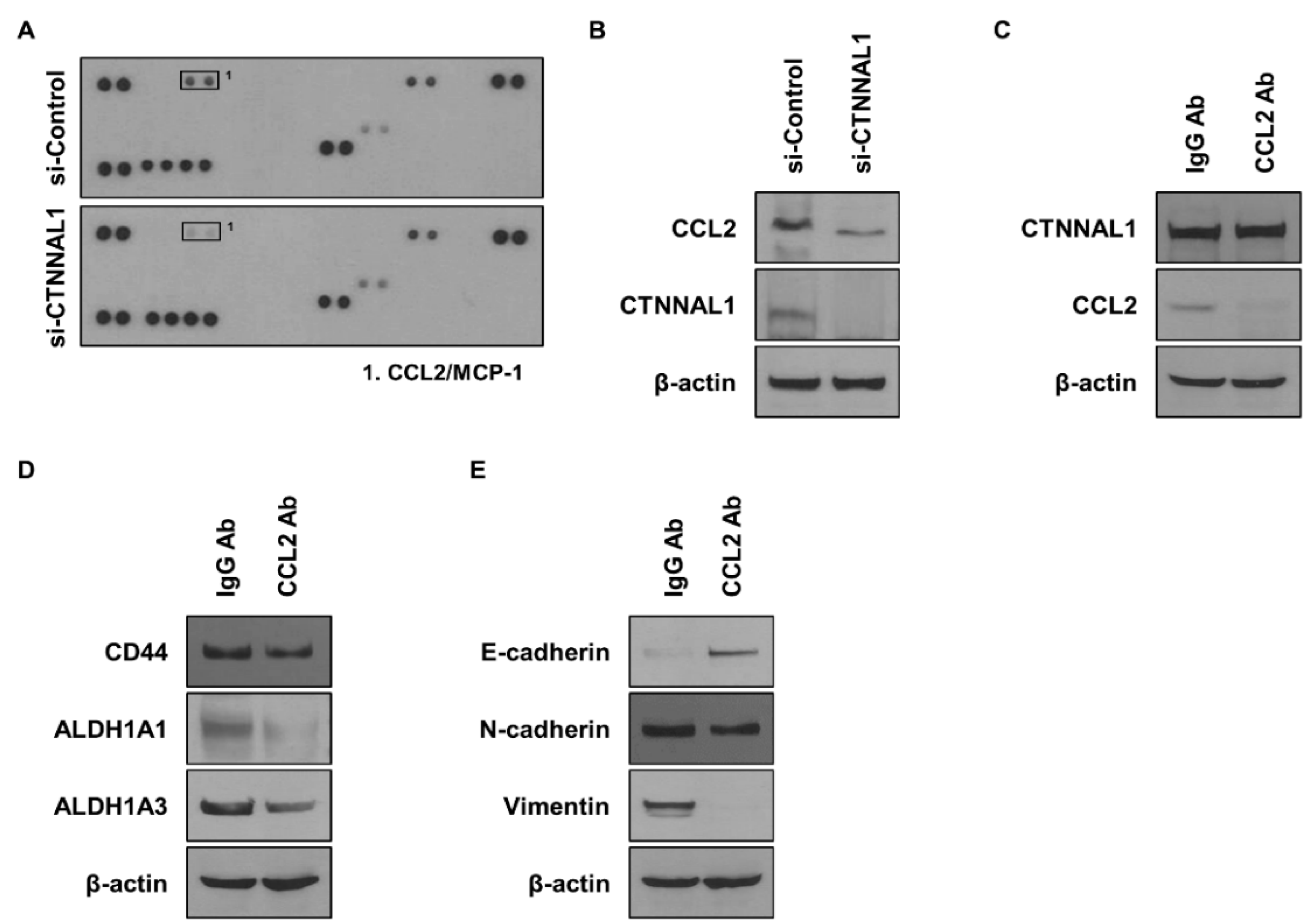
3.4. CTNNAL1 Regulates CCL2 to Affect Cancer Stem Cells and EMT
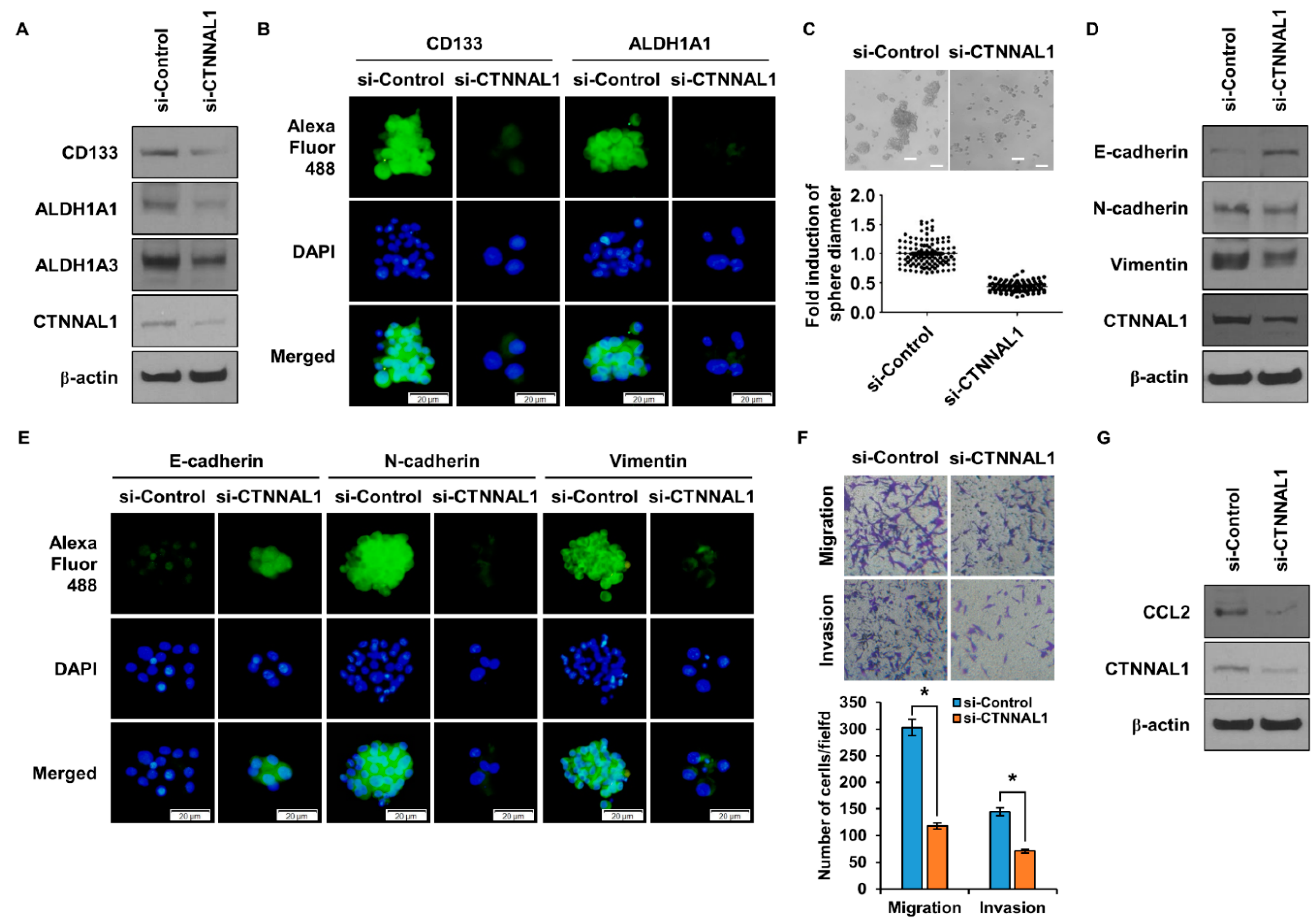
3.5. CTNNAL1 Regulates Stemness and EMT in GBM Cells and Controls CCL2 Secretion
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiang, Y.; Tan, Y.R.; Zhang, J.S.; Qin, X.Q.; Hu, B.B.; Wang, Y.; Qu, F.; Liu, H.J. Wound repair and proliferation of bronchial epithelial cells regulated by CTNNAL1. J. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 103, 920–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merdek, K.D.; Nguyen, N.T.; Toksoz, D. Distinct activities of the alpha-catenin family, alpha-catulin and alpha-catenin, on beta-catenin-mediated signaling. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 24, 2410–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobielak, A.; Fuchs, E. Alpha-catenin: At the junction of intercellular adhesion and actin dynamics. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aberle, H.; Schwartz, H.; Kemler, R. Cadherin-catenin complex: Protein interactions and their implications for cadherin function. J. Cell. Biochem. 1996, 61, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; Weinberg, R.A. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leggett, S.E.; Hruska, A.M.; Guo, M.; Wong, I.Y. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the cytoskeleton in bioengineered systems. Cell Commun. Signal. 2021, 19, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, T.; Ibaragi, S.; Hu, G.F. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cell cooperativity in metastasis. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 7135–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Dong, J.; Haiech, J.; Kilhoffer, M.C.; Zeniou, M. Cancer Stem Cell Quiescence and Plasticity as Major Challenges in Cancer Therapy. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 1740936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, S.P.; Naxerova, K.; Keller, L.; Pantel, K.; Witte, M. Molecular mechanisms of cancer metastasis via the lymphatic versus the blood vessels. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2022, 39, 159–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aponte, P.M.; Caicedo, A. Stemness in Cancer: Stem Cells, Cancer Stem Cells, and Their Microenvironment. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 2017, 5619472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.T.; Ryu, C.J. Cancer stem cell surface markers on normal stem cells. BMB Rep. 2017, 50, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phi, L.T.H.; Sari, I.N.; Yang, Y.G.; Lee, S.H.; Jun, N.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, Y.K.; Kwon, H.Y. Cancer Stem Cells (CSCs) in Drug Resistance and their Therapeutic Implications in Cancer Treatment. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 5416923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, M.; Yaromina, A.; Eicheler, W.; Koch, U.; Baumann, M. Cancer stem cells: Targets and potential biomarkers for radiotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 7224–7229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Sadanandam, A.; Singh, R.K. Chemokines in tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007, 26, 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozga, A.J.; Chow, M.T.; Luster, A.D. Chemokines and the immune response to cancer. Immunity 2021, 54, 859–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triaca, V.; Carito, V.; Fico, E.; Rosso, P.; Fiore, M.; Ralli, M.; Lambiase, A.; Greco, A.; Tirassa, P. Cancer stem cells-driven tumor growth and immune escape: The Janus face of neurotrophins. Aging (Albany NY) 2019, 11, 11770–11792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Q.; Vadgama, J.V.; Wang, P. CCL2/CCR2 signaling in cancer pathogenesis. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadomoto, S.; Izumi, K.; Mizokami, A. Roles of CCL2-CCR2 Axis in the Tumor Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.I.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, R.K.; Jung, U.; Kahm, Y.J.; Cho, E.W.; Kim, I.G. HSPA1L Enhances Cancer Stem Cell-Like Properties by Activating IGF1Rβ and Regulating β-Catenin Transcription. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Ma, L.; Yi, D.; Yoon, J.G.; Diercks, A.; Foltz, G.; Price, N.D.; Hood, L.E.; Tian, Q. A CD133-related gene expression signature identifies an aggressive glioblastoma subtype with excessive mutations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 1591–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Qiu, Q.; Khanna, A.; Todd, N.W.; Deepak, J.; Xing, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Su, Y.; Stass, S.A.; et al. Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 is a tumor stem cell-associated marker in lung cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2009, 7, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Pestell, T.G.; Lisanti, M.P.; Pestell, R.G. Cancer Stem Cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 2144–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.C. Cancer stem cells: Role in tumor growth, recurrence, metastasis, and treatment resistance. Medicine 2016, 95 (Suppl. S1), S20–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thandra, K.C.; Barsouk, A.; Saginala, K.; Aluru, J.S.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology of lung cancer. Contemp. Oncol. 2021, 25, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Jovčevska, I. Genetic secrets of long-term glioblastoma survivors. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2019, 19, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nørøxe, D.S.; Poulsen, H.S.; Lassen, U. Hallmarks of glioblastoma: A systematic review. ESMO Open 2017, 1, e000144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Cui, W.; Yuan, X.; Lin, L.; Cao, Q.; Wang, N.; Li, Y.; Guo, W.; Zhang, X.; et al. Targeting ALDH1A1 by disulfiram/copper complex inhibits non-small cell lung cancer recurrence driven by ALDH-positive cancer stem cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 58516–58530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.S.; Nelson, M.; Wang, L.; Liu, W.; Qian, C.P.; Shridhar, V.; Urrutia, R.; Smith, D.I. Identification and chromosomal localization of CTNNAL1, a novel protein homologous to alpha-catenin. Genomics 1998, 54, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izhak, L.; Wildbaum, G.; Jung, S.; Stein, A.; Shaked, Y.; Karin, N. Dissecting the autocrine and paracrine roles of the CCR2-CCL2 axis in tumor survival and angiogenesis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e28305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawazeer, M.A.; Theoharides, T.C. IL-33stimulateshumanmastcellreleaseof CCL5 and CCL2 via MAPK and NF-κB, inhibited by methoxyluteolin. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 865, 172760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, I.Y.; Chang, S.C.; Wu, H.Y.; Yu, T.C.; Wei, W.C.; Lin, S.; Chien, C.L.; Chang, M.F. Upregulation of the chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 via a severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike-ACE2 signaling pathway. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 7703–7712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatsumi, H.; Matsumoto, M.; Nakayama, K.I. Noncanonical Pathway for Regulation of CCL2 Expression by an mTORC1-FOXK1 Axis Promotes Recruitment of Tumor-Associated Macrophages. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 2471–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kahm, Y.-J.; Jung, U.; Kim, R.-K. Regulation of Cancer Stem Cells and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition by CTNNAL1 in Lung Cancer and Glioblastoma. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051462
Kahm Y-J, Jung U, Kim R-K. Regulation of Cancer Stem Cells and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition by CTNNAL1 in Lung Cancer and Glioblastoma. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(5):1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051462
Chicago/Turabian StyleKahm, Yeon-Jee, Uhee Jung, and Rae-Kwon Kim. 2023. "Regulation of Cancer Stem Cells and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition by CTNNAL1 in Lung Cancer and Glioblastoma" Biomedicines 11, no. 5: 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051462
APA StyleKahm, Y.-J., Jung, U., & Kim, R.-K. (2023). Regulation of Cancer Stem Cells and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition by CTNNAL1 in Lung Cancer and Glioblastoma. Biomedicines, 11(5), 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051462





