Abstract
Liver fibrosis accompanies the development of various chronic liver diseases and promotes their progression. It is characterized by the abnormal accumulation of extracellular matrix proteins (ECM) and impaired ECM degradation. Activated hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) are the major cellular source of ECM-producing myofibroblasts. If liver fibrosis is uncontrolled, it may lead to cirrhosis and even liver cancer, primarily hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Natural killer (NK) cells are a key component of innate immunity and have miscellaneous roles in liver health and disease. Accumulating evidence shows that NK cells play dual roles in the development and progression of liver fibrosis, including profibrotic and anti-fibrotic functions. Regulating NK cells can suppress the activation of HSCs and improve their cytotoxicity against activated HSCs or myofibroblasts to reverse liver fibrosis. Cells such as regulatory T cells (Tregs) and molecules such as prostaglandin E receptor 3 (EP3) can regulate the cytotoxic function of NK cells. In addition, treatments such as alcohol dehydrogenase 3 (ADH3) inhibitors, microRNAs, natural killer group 2, member D (NKG2D) activators, and natural products can enhance NK cell function to inhibit liver fibrosis. In this review, we summarized the cellular and molecular factors that affect the interaction of NK cells with HSCs, as well as the treatments that regulate NK cell function against liver fibrosis. Despite a lot of information about NK cells and their interaction with HSCs, our current knowledge is still insufficient to explain the complex crosstalk between these cells and hepatocytes, liver sinusoidal endothelial cells, Kupffer cells, B cells, and T cells, as well as thrombocytes, regarding the development and progression of liver fibrosis.
1. Introduction
Liver fibrosis is associated with the progression of various chronic liver diseases, such as hepatitis viral infection and alcoholic or non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (ASH or NASH). It is characterized by the abnormal accumulation of extracellular matrix proteins (ECM, e.g., collagen and integrin) and impaired ECM degradation (e.g., metalloproteinases) [1]. Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), the vitamin A-storing cells in the healthy liver, can be activated and differentiated to ECM-producing myofibroblasts in chronic liver diseases, leading to liver fibrosis [2,3]. Without effective treatments, liver fibrosis can progress to cirrhosis, causing liver cancer or failure. Unfortunately, we still lack approved treatments for liver fibrosis. Current strategies for liver fibrosis treatment mainly are limited to the protection and prevention of liver injury and fibrosis-causing factors. These strategies include treatments of anti-etiology (e.g., anti-viral treatment and reduction in alcohol consumption), anti-inflammation, antioxidant stress, inhibition of cell apoptosis, genetic and epigenetic modification, inhibition of HSC activation and proliferation, and promotion of ECM degradation [4,5,6]. Thus, exploration of new treatment options for liver fibrosis is urgently needed.
In the liver, both innate and adaptive immune cells play a pivotal role in the development of liver fibrosis and its associated liver diseases [7], such as alcoholic liver disease (ALD) [8,9], non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) [10,11], and liver cancer [12,13]. Natural killer (NK) cells are an essential component of innate immunity. In humans, NK cells comprise approximately 5–15% of circulating lymphocytes [14]. About half of the intrahepatic lymphocytes (50%) are NK cells, and they modulate the intrahepatic immune response in both physiological and pathological conditions [15]. In laboratory inbred mice, NK cells constitute about 2–5% of lymphocytes in spleens and bone marrows, and the number of NK cells doubles in wild-type mice [16]. In mouse livers, NK cells comprise about 2–5% of non-parenchymal cells (NPCs), and the frequency can be increased to around 10% in NASH livers of mice treated with high-fat and high-sugar diets [17,18].
NK cells have miscellaneous roles in liver health and disease [19,20]. For example, NK cells can be recruited by C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 9 (CXCL9), produced in activated CD103+DCs (dendritic cells), into the tumor microenvironment to express granzyme B, interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) to kill HCC cells [21]. NK cells also have anti-viral infection capabilities. A study showed that there was a negative correlation between the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) titer of hepatitis B viruses and the frequency of CD56brightNK cells in CHB patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB) and peginterferon alpha-2a treatment [22]. In addition, the expression of interferon alpha receptor 2 (IFNAR2) and NK cell p46-related protein (NKp46) in NK cells was remarkably increased in patients with functional cure compared to that in CHB patients without functional cure. Furthermore, NK cells are implicated in the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. The frequency of peripheral blood NK cells (CD3−CD16+CD56+) was increased in patients with alcoholic liver fibrosis (ALF) compared to that in patients without ALF. NK cell frequency was negatively correlated with total T cell frequency but positively associated with the percentage of CD3−CD8+ cells [23]. In the murine NASH model, DX5+ (anti-CD49b antibody) NKp46+NK cells can prevent liver fibrosis progression by suppressing M2-like macrophage polarization and the expression of profibrotic genes (e.g., Tgfb1 encoding transforming growth factor-beta 1) [24].
Several factors impact the phenotype and function of NK cells in liver disease, such as aging [25], calorie restriction [26], hepatitis viral infection [27], primary biliary cholangitis [28], HCC microenvironment [29], etc. In this review, we focus on the roles of NK cells in liver fibrosis, especially for the molecules that impact the interaction of NK cells with HSCs. The cellular and molecular mechanisms of the treatments that regulate NK cell function and phenotype in liver fibrosis are also reviewed and summarized.
2. The Phenotypes of NK Cells in the Liver
In the liver, NK cells can be divided into two main populations: transient conventional NK (cNK) cells and liver resident NK (lr-NK) cells [15]. Mouse lr-NK cells are CD49a+DX5−NK cells, while their cNK cells are CD49a−DX5+NK cells [30]. The phenotype of “memory-like” NK (ml-NK) cells in mice is the same as the phenotype of lr-NK cells or CD49a+DX5−NK cells. Human cNK cells can be subdivided into CD56dimCD16+NK cells and CD56brightCD16−NK cells. In the human liver, CD56dimNK cells and CD56brightNK cells have similar frequencies [31]. Human liver CD56brightlr-NK cells are CCR5+CXCR6+CD69+NK cells, whereas CD56dimcNK cells lack expression of CD69, CCR5, and CXCR6 [32]. Human liver ml-NK cells are CXCR6+CD94/NKG2C+ (killer cell lectin-like receptor C2) NK cells [32]. The maturation of NK cells can be defined for four populations by characterizing the expression of CD11b and CD27 (Figure 1A), including CD11b−CD27−NK cells, CD11b−CD27+NK cells, CD11b+CD27+NK cells, and CD11b+CD27−NK cells [33,34]. CD11b−CD27−NK cells are immature NK cells with differentiation potential, both CD11b−CD27+NK cells and CD11b+CD27+NK cells have the best ability to secrete cytokines, and CD11b+CD27−NK cells display high cytolytic function [33]. Human NK cells can also be classified into three functional subsets (Figure 1B): tolerant NK cells (CD56brightCD27−CD11b−), regulatory NK cells (CD56brightCD27+CD11b+/−), and cytotoxic NK cells (CD56dimCD27−CD11b+) [35].
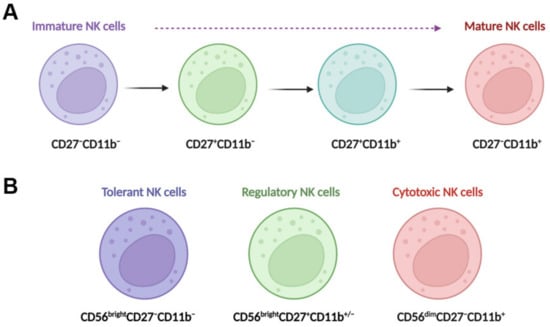
Figure 1.
NK cell maturation and functional subsets. (A) Maturing NK cells can be divided into four populations by characterizing the expression of CD11b and CD27; these populations include CD11b−CD27−NK cells, CD11b−CD27+NK cells, CD11b+CD27+NK cells, and CD11b+CD27−NK cells. CD11b−CD27−NK cells are immature NK cells with differentiation potential, both CD11b−CD27+NK cells and CD11b+CD27+NK cells have the best ability to secrete cytokines, and CD11b+CD27−NK cells display high cytolytic function. (B) Human NK cells can also be classified into three functional subsets, tolerant NK cells (CD56brightCD27−CD11b−), regulatory NK cells (CD56brightCD27+CD11b+/−), and cytotoxic NK cells (CD56dimCD27−CD11b+).
Change in NK phenotypes happens in liver disease. For example, peripheral activated CD56brightNK cells in patients with hepatitis B virus (HBV)-related decompensated liver cirrhosis (HBV-DLC) have been shown to have a phenotype with an increased expression of natural killer group 2, member D (NKG2D), perforin, and granzyme A/B and a decreased expression of inhibitory receptor CD158b1/2 compared NK cells from healthy controls, showing an immune activation status [36]. In contrast, the circulating CD56dimNK cells express low levels of CD107a and perforin with an impaired cytolytic capacity [36].
Single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) data illustrate that there are several subtypes of NK cells in chronic liver disease, which display multiple roles based on the different gene expressions. For example, scRNA-seq data analysis showed that the subpopulation of NK cells expressing SELL, a gene encoding the cell surface adhesion molecule L-selectin, was proliferated in alcohol-induced cirrhotic livers, whereas the subtype of NK cells expressing XCL2 (X-C motif chemokine ligand 2) was enriched in the healthy livers [37]. The heterogeneity of peripheral NK cells has also been shown in the development of NASH from simple steatosis with a decreased expression of NK cell activation marker natural cytotoxicity receptor 3 (NCR3, also known as NKp30) in NASH [38]. In addition, several intracellular signaling mediators were less activated, including in the phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases (pERK) and the phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription (pSTATs) 1, 2, 3, and 5 [38]. In the following sections, we will discuss the functions of NK cells in liver fibrosis and the important molecules involved in the cytotoxicity of NK cells against activated HSCs.
3. The Profibrotic Function of NK Cells
NK cells isolated from patients with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection and liver fibrosis (METAVIR fibrosis scores: F1 and F4) compared to NK cells isolated from healthy donors showed a significant reduction in the expression of NK activation markers CD107a (lysosomal-associated membrane protein 1, LAMP-1) and INF-γ [39]. In addition, these NK cells from HCV patients significantly promoted the proliferation of co-cultured human HSC cell line LX-2 cells, especially for the subpopulation that expressed intermediate intensity of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) with small sizes according to the forward scatter profile in flow cytometry gating [39]. In addition, hepatic NKp44+NK cells from patients with HCV infection were positively correlated with liver fibrosis and viral load, producing TNF-α to promote liver injury [40]. In patients with HBV infection, transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) produced by activated HSCs can suppress the anti-fibrotic effect of NK cells by suppressing NK cell degranulation and IFN-γ production [41]. In patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis (SAH), NK cells can induce lysis of endothelial progenitor cells via the CX3CR1/fractalkine axis to promote inflammation and SAH progression [42]. Overall, in different liver disease conditions, NK cells have been demonstrated to be positively associated with the progression of liver fibrosis.
Recent studies showed that NK cells have long-term graft survival in patients with liver transplantation [43]. The recurrence of HCV infection in patients with liver transplantation can cause graft cirrhosis. The mismatch between the killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor, two Ig domains, and long cytoplasmic tail 3 (KIR2DL3) and the ligands of human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class I antigens induces the progression of hepatitis to liver fibrosis [44]. Thus, inhibition of NK cell-mediated HSC activation in liver injury can prevent liver fibrosis.
4. The Anti-Fibrotic Function of NK Cells
NK cells have also been shown to display anti-fibrotic effects in the liver. For example, CD27+CD11b+ NK cells can display cytotoxicity against activated HSCs via the interactions of integrin alpha-4 (Itga4, also known as CD49d)–vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM1), which can be suppressed by depletion of prostaglandin E receptor 3 (EP3) [45]. Mechanistically, activation of EP3 can increase the nuclear translocation of phosphorylated Spi-C transcription factor (Spic) by regulating protein kinase C (PKC) to upregulate Itga4 expression in NK cells. The binding of NK cells and activated HSC cells is mediated by the interaction of Itga4 expressed by NK cells with VCAM1 expressed by activated HSCs [45], as shown in Figure 2. NK cells activated by natural product curcumin induced senescence of LX-2 cells and promoted fibrotic cell clearance by stimulating granule exocytosis [46]. The increased expression of NKG2D ligand major histocompatibility complex class I chain-related gene A (MICA) and UL16-binding protein 2 (ULBP2) on senescent LX-2 cells activate this process [46]. MICA is a polymorphic gene, and its alleles have been demonstrated to be associated with the histologic features of NASH such as liver inflammation and fibrosis [47]. However, the anti-fibrotic effect of NK cells can be suppressed by activated HSCs via producing TGF-β [48]. Therefore, understanding the molecular mechanisms that mediate the interaction of NK cells with activated HSCs or myofibroblasts can improve NK cell-mediated anti-fibrotic effects.
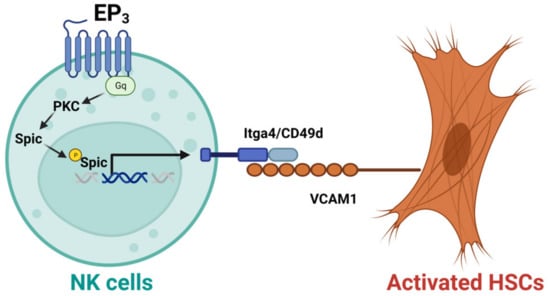
Figure 2.
Activation of EP3 can improve the cytotoxicity of CD27+CD11b+ NK cells against activated hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). Mechanistically, activation of prostaglandin E receptor 3 (EP3) can increase the nuclear translocation of phosphorylated Spi-C transcription factor (Spic) by regulating protein kinase C (PKC) to upregulate integrin alpha-4 (Itga4, or CD49d) in NK cells. The binding of NK cells with activated HSCs is mediated by the interaction of Itga4 with vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM1).
In addition, the anti-fibrotic effects of NK cells, as well as HSC activation, can be regulated by platelets. Platelets contain proteins and growth factors required for liver regeneration and repair [49], playing important roles in chronic liver diseases, including liver fibrosis [50,51]. For example, the platelet count can be used as a simple, non-invasive index to evaluate the degree of liver fibrosis in patients with CHB [52]. In addition, platelet-derived growth factor-β (PDGF-B) can activate HSCs to promote liver fibrosis [53]. PDGF-D not only enhances human NK cell effector functions by binding to the NKp44 receptor, it regulates IL-15-induced human NK cell survival by binding to PDGF receptor-beta [54]. Platelets also play an important role in NASH pathogenesis by promoting inflammatory cell accumulation, steatosis, and liver injury [55]. However, its function on NK cells remains to be further explored.
5. Cellular and Molecular Factors Interfere with the Interaction of NK Cells with HSCs
In chronic liver disease, liver resident and infiltrating cells can impact the function of NK cells and their cytotoxicity to HSCs. For example, mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells can activate the cytotoxicity of NK cells against HSCs in cholestatic mice with liver fibrosis induced by feeding a special diet (0.1%) or bile duct ligation (BDL) [56]. Several important molecules that are associated with the phenotype and function of NK cells are summarized. For example, CD96-expressing NK cells in human HCC tissues are functionally exhausted, with low expression levels of interleukin (IL)-15, IFN-γ, granzyme B, perforin, and TNF-α, but high levels of IL-10 and TGF-β1 [57]. Another study also showed that transcriptional factors such as IRF8 (interferon regulatory factor 8), NR4A2 (nuclear receptor subfamily 4 group A member 2), IKZF3 (IKAROS family zinc finger 3), and REL (REL proto-oncogene, NF-κB subunit) may be implicated in the roles of NK cells during liver fibrosis [58]. In this section, we discuss the impact of liver cells and their secreting factors on the interaction of NK cells with HSCs.
5.1. CD96
CD96, an exhaustion marker for NK cells, can be induced by TGF-β1. Blockade of the interaction of CD96 and its ligand CD155 can restore the function of NK cells [57]. In addition, CD96 shares the ligand CD155 with both CD226 and T cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains (TIGIT). CD226, also known as DNAM-1 (DNAX accessory molecule-1), can competitively bind with CD155 rather than CD96 to activate NK cell-mediated cytotoxic effects, whereas TIGIT controls the CD226-mediated effect on NK cells [59]. Multiparameter flow cytometry analysis showed that TIGIT expression was significantly increased and CD226 expression was suppressed in intrahepatic CD56brightNK cells compared to matched peripheral blood CD56brightNK cells [60]. Co-culture of peripheral blood CD56brightNK cells with human hepatoma cells or primary human hepatocyte organoids can increase the expression of TIGIT but suppress the expression of CD226 in NK cells, showing the phenotype of intrahepatic CD56brightNK cells [60]. Therefore, in the tumor microenvironment, the cytotoxicity of NK cells against cancer cells and activated HSCs can be suppressed due to the increased expression of CD96 and TIGIT.
5.2. CTLA-4
Regulatory T cells (Tregs) play a vital role in chronic liver diseases, including liver fibrosis and cancer [61]. Tregs can inhibit the activation of NK cells when co-cultured with HSCs in a cell-contact-dependent manner [62]. The cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4) expressed by Tregs can suppress the activation of NK cells by producing cytokines such as IL-8 and TGF-β1 to suppress the expression of NKG2D ligand MHC class I chain-related proteins A and B (MIC-A/B) and HLA class I on HSCs [62]. Therefore, reducing the number and function of Tregs or suppressing their expression of CTLA-4 may restore the cytotoxic function of NK cells against activated HSCs to prevent liver fibrosis.
5.3. EP3
The expression of EP3 was dramatically decreased in NK cells from mice with liver fibrosis and patients with liver cirrhosis [45]. Specific depletion of EP3 in NK cells can aggregate carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) or BDL–induced mouse liver fibrosis. The cytotoxicity of CD27+CD11b+NK cells against activated HSCs is suppressed by EP3 deletion [45]. In contrast, activating EP3 can increase the interaction of CD27+CD11b+NK cells and activate HSCs via Itga4-VCAM1 binding to promote NK cell cytotoxicity to ECM-producing HSCs [45]. Thus, EP3, as a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR), can be targeted to increase NK cell function.
5.4. KIR
Killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) is expressed on the surface of NK cells and regulates their cytotoxicity by interacting with HLA class I molecules [63]. The expression ratio of activating and inhibitory KIRs (a/iKIR) in NK cells changes in liver injury. Co-culture of lymphocytes from human patients with HCV infection can stimulate LX-2 cell activation and increase the expression of α-SMA compared with healthy lymphocytes. The α-SMA production in co-cultured cells was suppressed when HCV lymphocytes were treated with small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) against iKIR [64]. Adoptive transfer of splenocytes (enriched with NK cells) from naive SCID mice (lacking B and T cells) that underwent iKIR knockdown by siRNAs can reduce CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in BALB/c male SCID-Beige mice (lacking B/T/NK cells), which is evidenced by reduced expression of collagen and α-SMA production [64]. In addition, the interactions of KIR/HLA-I are associated with graft survival times of patients with liver transplantation, as well as NK cell alloreactivity [43].
5.5. KLRG1
The frequency of killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily G member 1 (KLRG1)-expressing NK cells in the liver and blood of patients with CHB has been found to be negatively associated with liver fibrosis. Osteopontin derived from HSCs can stimulate the activation of NK cells to express CD44 and IFN-γ and increase NK cell degranulation activity [65]. In addition, KLRG1+ NK cells play an anti-fibrotic role in patients with CHB, which showed an increased production of IFN-γ and cytolytic activity against HSCs compared to KLRG1− NK cells [65]. KLRG1 is a maturation marker of NK cells. Memory KLRG1+ NK cells post-HCV infection play an essential role in HCV clearance and mediate antigen-specific response against HCV infection [66].
5.6. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5
Mice with NK cell-specific knockout metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGluR5) had aggravated CCl4-induced liver fibrosis and decreased IFN-γ production compared to wild-type mice [67]. In contrast, activation of mGluR5 can increase NK cell cytotoxicity against activated HSCs by upregulating the expression of anti-fibrotic genes, such as IFGN, PRF1 (perforin), and KLRK1 (killer cell lectin-like receptor K1), and increasing IFN-γ production through the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway [67]. mGluR5 plays multiple roles in cell stress and metabolic regulation [68,69], making it a potential target for regulating NK cell function.
5.7. NKG2D Ligands or Stimulators
The expression of retinoic acid early inducible 1 (RAE-1), an NKG2D ligand, is undetectable in quiescent HSCs but highly expressed in activated HSCs [70]. Treatments such as polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid (poly(I:C)) or IFN-γ can increase the expression of NKG2D and TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligands on liver NK cells to increase their cytotoxicity against activated HSCs [70]. Stimulated NK cells from patients with HCV or HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) with CD4+ T cell supernatants can enhance their cytotoxicity against HSCs compared to unstimulated NK cells. IL-2 secreted from CD4+ T cells contributes to the activation of NK cells and the upregulated expression of NKG2D in NK cells [71]. In addition, the frequency of circulating NK cells expressing NKG2D was also shown to decrease in patients with HCC [72]. IL-30 treatment has been shown to enhance the anti-fibrotic activity of NKT cells against activated HSCs by upregulating the expression of NKG2D and its binding with the ligand retinoic acid early inducible 1 (RAE-1) [73]. IL-30, a subunit of IL-27 (IL27p28), can also regulate both NK and T cell function by binding cytokine-like factor 1 [74]. Thus, IL-30 treatment may also enhance NK cell cytotoxicity against activated HSCs.
5.8. PD-1
The programmed death 1 (PD-1)/PD-ligand 1 (PD-L1) axis is involved in the pathogenesis of chronic liver diseases [75], such as hepatitis, liver fibrosis, and HCC. The frequency of NK cells was reduced in patients with HIV and HCV co-infection, which advanced the progression of liver fibrosis. In addition, an increased exhaustion marker PD-1 expression in NK cells was positively associated with advanced liver fibrosis and NK cell dysfunction [76]. Cancer-associated fibroblasts play a key role in liver cancer progression by inducing immune tolerance, chemoresistance, expression of growth factors, etc. [77]. Tumor cells can inhibit the function of NK cells via the interaction of PD-L1/PD-1 [78]. Therefore, inhibition of PD-1 expression in NK cells can improve their cytotoxicity against cancer and fibrotic cells.
5.9. Siglecs
Sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectins (Siglecs) play an important role in the regulation of immune cell functions [79,80], including in NK cells [81]. Siglec-7 and Siglec-9 are highly expressed by NK cells. In patients with NAFLD and different stages of liver fibrosis, the frequency of peripheral blood Siglec-7+CD56dimNK cells was suppressed, whereas the frequency of dysfunctional Siglec-7−PD-1+CD57+CD56dimNK cells was increased [11]. The expression of Siglec-9 on NK cells in patients with CHB was decreased, which was negatively correlated with serum hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) and HBV DNA titer [8]. Therefore, regulating Siglec expression in NK cells can improve their function.
5.10. STATs
The signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) is a transcription factor that regulates NK cell proliferation and activation. NK cell dysfunction is mediated by STAT1 by downregulating NKG2D expression. Cellular studies show that STAT1 deletion in human NK cell line NK-92 cells can inhibit cell proliferation, promote cell apoptosis, and impair their cytotoxicity [27]. Treatment of dihydromyricetin (DHM) can inhibit HSC activation in vitro and decrease CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in C57BL/6 mice. Further molecular studies show that DHM treatment can improve NK cell-killing ability by enhancing IFN-γ expression through the NF-κB/STAT3 pathway [82]. Therefore, regulation of the expression of transcription factor STAT may be applied to regulate NK cell function.
5.11. TIGIT
In addition to the suppressive effect of TIGIT on CD226-mediated activation of NK cells [59], TIGIT deficiency can suppress parasite (Schistosoma japonicum) infection-induced liver fibrosis [83]. A cellular mechanism study showed that NK cells from TIGIT-deficient mice compared to NK cells from wild-type mice can induce more co-cultured HSC apoptosis [83].
Overall, these molecules (Table 1) contribute to the regulation of the cytotoxicity of NK cells against HSCs. Regulation of these genes could provide therapeutic strategies against liver fibrosis.

Table 1.
Molecules regulate the interaction of NK cells with HSCs.
Table 1.
Molecules regulate the interaction of NK cells with HSCs.
| Molecules | Function | References |
|---|---|---|
| CD96 | CD96, an exhaustion marker for NK cells, can be induced by TGF-β1. Blockade of the interaction of CD96 and its ligand CD155 can restore the function of NK cells. | [57] |
| CTLA-4 | CTLA-4 expressed by Tregs can suppress NK cell activation by releasing cytokines such as IL-8 and TGF-β1 to suppress the expression of NKG2D ligand MHC class I chain-related proteins A and B (MIC-A/B) and HLA class I on HSCs. | [62] |
| EP3 | Specific depletion of E-prostanoid 3 receptor (EP3) in NK cells can aggregate carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)- or bile duct ligation (BDL)-induced mouse liver fibrosis. The cytotoxicity of CD27+CD11b+NK cells against activated HSCs is suppressed by EP3 deletion. | [45] |
| KIR | Adoptive transfer of splenocytes enriched with NK cells that have undergone inhibitory killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (iKIR) knockdown by small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) can reduce CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in BALB/c male SCID-Beige mice (lacking B/T/NK cells), evidenced by reduced expression of collagen and α-SMA. | [64] |
| KLRG1 | The frequency of killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily G member 1 (KLRG1)-expressing NK cells displayed anti-fibrotic effects in patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB). | [65] |
| mGluR5 | Mice with NK cell-specific knockout metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGluR5) have aggravated CCl4-induced liver fibrosis compared to wild-type mice. In contrast, activation of mGluR5 can increase NK cell cytotoxicity against activated HSCs by upregulating the expression of anti-fibrotic genes, such as PRF1 (perforin), KLRK1 (killer cell lectin-like receptor K1), and IFN-γ production. | [67] |
| NKG2D | Treatments such as poly(I:C) or IFN-γ can stimulate the expression of NKG2D on NK cells to increase its cytotoxicity against activated HSCs. | [70] |
| PD-1 | The expression of exhaustion marker PD-1 in NK cells was positively associated with advanced liver fibrosis and NK cell dysfunction. | [76] |
| Siglec-7 | The frequency of peripheral blood Siglec-7+CD56dimNK cells was decreased in patients with NAFLD with different stages of liver fibrosis, whereas the frequency of dysfunctional Siglec-7−PD-1+CD57+CD56dimNK cells was increased. | [11] |
| STAT1 | STAT1 deletion in human NK cell line NK-92 cells can inhibit cell proliferation, promote cell apoptosis, and impair cell cytotoxicity. | [27] |
| STAT3 | Treatment of dihydromyricetin (DHM) can inhibit HSC activation in vitro and decrease CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in C57BL/6 mice by improving NK cell killing ability and IFN-γ expression through the NF-κB/STAT3 pathway. | [82] |
| TIGIT | TIGIT deficiency can inhibit parasite (Schistosoma japonicum) infection-induced liver fibrosis by increasing NK cell-mediated apoptosis HSCs. | [83] |
Abbreviations: α-SMA: α-smooth muscle actin; CTLA-4: cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4; HSCs: hepatic stellate cells; NF-κB: nuclear factor-κB; NKG2D: natural killer group 2, member D; Siglec-7: sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin 7; Poly(I:C): polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid; Tregs: regulatory T cells; STAT1/3: signal transducer and activator of transcription 1/3; TIGIT: T cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains.
6. Treatments Improve the Cytolytic Function of NK Cells to HSCs
Factors such as pathogenic infection (e.g., infection of Echinococcus multilocularis), liver metabolic disorder (e.g., NAFLD), and tumor development can induce NK cell dysfunction, leading to liver fibrosis [11,84,85]. Some treatments have been shown to regulate NK cell function to inhibit liver fibrosis, such as alcohol dehydrogenase 3 (ADH3) inhibitors, microRNAs, NKG2D activators, and natural products. For example, treatment with cultured mycelium of Cordyceps sinensis can significantly inhibit CCl4 treatment-induced NK cell reduction and dysfunction in mice with liver fibrosis [86]. Here, we review some treatments that regulate NK cell function against fibrosis.
6.1. ADH Inhibitor
The activity of alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) has been shown to be positively associated with liver fibrosis in mice, as well as the expression of HSC activation markers collagen (Col)1a1 and α-SMA [87]. Treatment with 4-methylpyrazole (4-MP), a broad inhibitor ADH, can attenuate CCl4- and BDL-induced liver fibrosis in mice by regulating IFN-γ production in NK cells to increase the apoptosis of activated HSCs [88]. Meanwhile, HSCs isolated from ADH3-deficient mice expressed lower levels of collagen and TGF-β1 compared with those in wild-type mice. In contrast, the expression of IFN-γ was increased in NK cells from ADH3-deficient mice compared to that in NK cells from wild-type mice [89].
6.2. MicroRNAs
Exosomes derived from NK cells can reduce TGF-β1-induced HSC activation. A molecular mechanism study demonstrates that microRNA-233 (miR-233) expressed in NK cell exosomes can block autophagy during HSC activation by inhibiting autophagy-related 7 (ATG7) expression [90]. Similarly, one study shows that miR-96-5p can block the autophagy activity of LX-2 cells by targeting ATG7 to suppress the mRNA expression levels of ECM genes [91]. Another study also shows that miR-155 can upregulate the expression of IFN-γ in NK cells from patients with HCV by suppressing the expression of T cell immunoglobulin- and mucin-domain-containing molecule 3 (Tim-3) [92]. Thus, microRNAs can be applied to improve NK cell cytotoxicity against activated HSCs and directly inhibit HSC activation.
6.3. NKG2D Stimulators
The expression of NK cell activating ligand RAE-1, a ligand for NKG2D receptor, was upregulated on early activated HSCs but lost in fully activated HSCs. Lacking RAE-1 expression makes fully activated HSCs resistant to NK cell cytotoxicity [93]. In mice with primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), NK cells can be activated by Kupffer cells, a process mediated by NKG2D/RAE-1 interaction to produce IFN-γ synergistically with Kupffer cell-derived TNF-α, resulting in liver inflammation [94]. In patients with HIV and HCV co-infection, CD4+ T cells can stimulate the anti-fibrotic activity of NK cells via IL-2-induced upregulation of NKG2D [71]. Overall, NKG2D can be targeted to induce NK cell activation and increase their anti-fibrotic activity.
6.4. NLRP3 Inflammasome Regulation
The NLRP3 (NOD-, LRR-, and pyrin domain-containing protein 3) inflammasome is comprised of a sensor (NLRP3), an adaptor (apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase recruitment domain/ACS), and an effector (caspase 1) [95]. NLRP3 is an intracellular sensor that detects a wide range of microbial- and host-derived signals [96]. NLRP3 ablation in HCC cells can upregulate their expression of MIC-A, which interacts with NKG2D in NK cells to enhance NK cytotoxicity. In addition, mice xenografted with NLRP3-knockout HCC cells developed tumors slowly, and tumor cells were sensitive to NK cell cytotoxicity [97]. In contrast, the NLRP3 inflammasome-IL18 signaling pathway in Kupffer cells can prime hepatic NK cell maturation and anti-cancer activity [98]. The function of NLRP3 inflammasome on NK cell activation is cell-dependent.
6.5. Ras Homology Family Member A (RhoA) Kinase Inhibitor
The Ras homolog gene family member A (RhoA) is a Rho GTPase superfamily member, and it plays a vital role in signal transduction and regulation of gene transcription. Therefore, RhoA is involved in many cellular functions, such as cell division, proliferation, and migration [99]. Treatment with Fasudil, a RhoA kinase inhibitor, can ameliorate thioacetamide (TAA)-induced liver fibrosis in mice by stimulating NK cell activation and suppressing HSC activation and proliferation [100]. RhoA is also involved in the PDGF-BB (platelet-derived growth factor-BB) or TGF-β1-induced activation of HSCs, which can be suppressed by anti-fibrotic treatment [101]. Therefore, RhoA is a potential target for the treatment of liver fibrosis.
6.6. γδT Cells
In addition to their direct killing ability against activated HSCs, γδT cells can increase the cytotoxicity of cNK and lr-NK cells against activated HSCs to improve liver fibrosis. A molecular study further shows that the crosstalk between γδT and NK cells is mediated partly by CD137, the co-stimulatory receptor 4-1BB [102].
6.7. Tim-3
The expression of Tim-3 in circulating NK cells and liver infiltrating lymphocytes in patients with CHB was significantly increased compared to that in healthy controls [103]. Upregulation of Tim-3 suppressed NK cell cytotoxicity and IFN-γ production [103]. Rosuvastatin, a lipid-lowering agent, can significantly reduce the percentage of Tim-3+ cells in NK cells of patients with CHB compared with the placebo group [104]. A higher frequency of NK cells co-expressing Tim-3 and TIGIT was found in patients with chronic HCV with advanced fibrosis, with increased susceptibility to HCC development [105]. As an immune checkpoint receptor, Tim-3 can suppress the effects of NK cells, which may be targeted to improve NK cell cytotoxicity to activated HSCs.
7. Liver Resident NK Cells
In the human liver, NK cells account for about 50% of intrahepatic lymphocytes and play important roles in liver immune responses [15]. Lr-NK cells (liver-resident NK cells) are a heterogeneous population and exhibit phenotypical differences from cNK (conventional NK) cells [106]. The features of lr-NK and cNK cells in mice and humans are summarized [106], as shown in Figure 3.
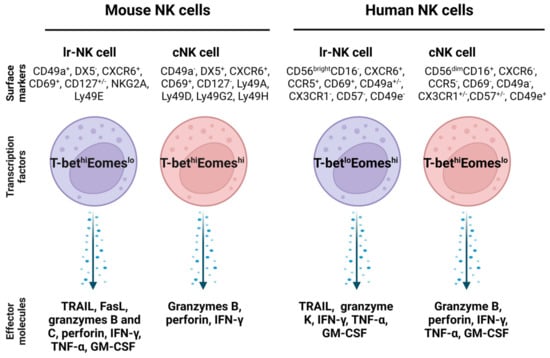
Figure 3.
Comparison of mouse and human liver resident NK cells and conventional NK cells. The transcription factors in lr-NK cells and cNK cells are different, and they also express different surface markers and effector molecules. Abbreviations: cNK: conventional NK cell; Eomes: eomesodermin; FasL: Fas ligand; GM-CSF: granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; lr-NK: liver resident NK; NKG2A: killer cell lectin-like receptor C1; T-bet: T-box transcription factor; TRAIL: TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand.
Lr-NK cells have been shown to have distinct gene expression profiles and display important roles in autoimmune cholangitis [107] and liver fibrosis [108]. One study shows that the frequency of intrahepatic NKp44+ NK cells producing TNF-α is correlated with both HCV infection level and stage of liver fibrosis [40]. Another study reveals that human lr-NK (CD49a+CD25+) cells expressing CD25, CD34, and CXCR3 display high proliferative capacity in vitro [109]. In contrast, recruited CXCR3+ NK cells in the livers of mice with diet-induced NASH display a protective role against liver fibrosis. However, the distinct roles of both lr-NK and cNK cells in the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis remain to be explored.
Accumulating studies reveal that targeting lr-NK cells can prevent liver fibrosis and cancer progression. For example, treatment with Ecballium elateriumone, a medicinal plant, increased the number of lr-NK cells and their expression of CD107a and IFN-γ and inhibited thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis in mice [108]. Treatment with low doses of IL-2 can increase the proliferation of CD49a+CD25+lr-NK cells in cirrhotic livers [109]. γδT cell subset (γδT1) cells expressing IFN-γ directly display cytotoxicity against activated HSCs, which can also enhance the cytotoxicity of lr-NK cells against activated HSCs [102]. Some molecules can be targeted to enhance the activity of lr-NK cells. One study showed that lr-NK cells expressed TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL), distinguishing them from cNK cells. Treatment with Everolimus, a mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitor, can improve the anti-tumor activity of lr-NK cells by upregulating TRAIL expression [110]. Another study shows that retinoid-related orphan nuclear receptor alpha (RORα) is highly expressed in lr-NK cells, and its agonist can activate lr-NK cells to prevent colorectal cancer liver metastasis [111]. In addition, chemokine receptors such as CXCR6 and CCR5 (Figure 3) are also only expressed by human lr-NK cells, but not human cNK cells, which could be targeted to modulate lr-NK cell function to inhibit liver fibrosis [32]. For example, treatment with cytokines such as IL-12 and IL-15 can increase the expression of CXCR6 and CD49a in circulating NK cells to display comparable phenotypic and functional features of lr-NK cells [112]. Furthermore, some factors such as aryl hydrocarbon receptors are required for the maintenance of lr-NK cells [113], and can be targeted for regulating lr-NK cell functions. Overall, targeting molecules such as TRAIL, RORα, and chemokine receptors can increase the cytotoxicity of lr-NK cells against cancer cells and activated HSCs.
8. Clinical Evaluations
In clinical trials, some treatments have been evaluated to treat liver diseases by regulating NK cell frequency and function, including lipid-lowing agents (e.g., rosuvastatin) [104], immune regulators (e.g., Toll-like receptor 8 agonist GS-9688) [114,115], antiviral agents (e.g., pegylated interferon-alpha) [116,117,118], anticancer agents (e.g., Sorafenib) [119], microRNAs (e.g., RG-101) [120], and combined therapies (e.g., IL-2 and IFN) [121], as well as organisms (e.g., Arthrospira, a genus of free-floating filamentous cyanobacteria) [122]. In Table 2, we review the functions of different treatments in NK cell regulation. However, studies that target NK cells for liver fibrosis treatment are rare, and more investigations are expected.

Table 2.
Treatments regulate NK cells.
Table 2.
Treatments regulate NK cells.
| Treatment | Function | References |
|---|---|---|
| Rosuvastatin (RSV) | RSV administration can significantly increase CD3+ CD16+ CD56+ NKT cells and reduce the percentage of Tim-3+NK cells in patients with CHB compared to the controls. | [104] |
| TLR-8 agonist GS-9688 | In vitro treatment with GS-9688 can induce the expression of interferon-γ and TNF-α in NK cells to enhance their cytolytic function against hepatocytes. In addition, GS-9688 can increase the frequency of activated NK cells in patients with HBV. | [114] |
| TLR 7 agonist GS-9620 | Administration of GS-9620 increased NK cell activation and function but did not decrease the levels of HBsAg in patients with suppression of HBV infection by nucleos(t)ide analogue (NA) therapy. | [115] |
| A combination of pegylated interferon-alpha (peg-IFN-α) and NA therapy | The combined treatment can effectively reduce HBsAg by increasing the frequency and absolute number of circulating CD56brightNK cells, compared with the NA treatment group, whereas the CD56dimNK cells were decreased. | [116] |
| Peg-IFN-α and sequential NA treatment | CHB patients receiving Peg-IFN-α and sequential NA treatment showed a decrease in HBsAg due to an increase in a subset of distinct NK cells, expressing NK cell activation receptors NKp30 and NKp46 with increased IFN-γ production and cytotoxicity. | [117] |
| Peg-IFN-α-2b monotherapy or combination therapy with adefovir dipivoxil | The frequency and the absolute number of NKp30+NK cells were significantly increased, which was accompanied by increased expression of CD107a and IFN-γ in patients with CHB during Peg-IFN-α-2b monotherapy or combination therapy with adefovir dipivoxil. | [118] |
| Sorafenib | Sorafenib treatment can reduce the percentage of CD56brightCD16−NK cells and increase the frequency of CD56dimCD16+NK cells and the expression of granzyme B and perforin in total NK cells and both subsets of cells, improving the overall survival in HCC patients. | [119] |
| RG-101, an N-acetylgalactosamine-conjugated anti-microRNA-122 oligonucleotide | A single subcutaneous administration of RG-101 (2 mg/kg) increased the frequency of NK cells in PBMCs and decreased plasma HCV RNA and IFN-γ-induced protein 10 (IP-10) levels in patients. | [120] |
| IFN or IL-2 and therapeutic vaccine with IFN | Combination therapy with IFN and other immunomodulators such as IL-2 can enhance HBeAg in patients with entecavir treatment by significantly increasing peripheral CD56brightCD16−NK cells and decreasing regulatory T cells. | [121] |
| Arthrospira | Treatment with Arthrospira, a genus of free-floating filamentous cyanobacteria, increased serum IFN-γ levels but decreased serum TNF-α and IL-6 and hepatic fibrosis and steatosis in CHB patients receiving NA therapy. | [122] |
Abbreviations: CHB: chronic hepatitis B (CHB); HBeAg: hepatitis B e antigen; HBsAg: hepatitis B surface antigen; IFN: interferon; PBMCs: peripheral blood mononuclear cells; TLR-8: Toll-like receptor 8.
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) engineered NK cells are potent strategies for the treatment of liver cancer and fibrosis in the new decade due to their specificity and lower side effects [123]. Several recruiting clinical trials aim to study the efficacy of NK cells in treatments against HCC and hepatitis viral infection (ClinicalTrials.gov.; e.g., NCT05040438, NCT04162158, NCT05171309, and NCT03761875, accession date: 28 March 2023).
In the future, combined therapies will advance the efficacy and safety of NK cell-mediated treatment. One clinical trial reveals that a combined therapy of short-term irreversible electroporation and allogenic NK cell immunotherapy significantly reduces circulating tumor cells and increases immune function in patients with unresectable primary liver cancer [124]. Another clinical trial shows that the combination of locoregional high-dose autologous NK cell therapy with hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy is a safe and effective therapy in patients with locally advanced HCC who are refractory to the standard treatment [125]. However, the development of NK cells targeting activated HSCs to treat liver fibrosis is less investigated.
9. Summary
Uncontrolled progression of liver fibrosis advances the development and progression of liver cirrhosis and HCC. However, there are no currently available FDA-approved anti-fibrotic treatments, even though there has been great progress in understanding the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Activated HSCs and differentiated myofibroblasts contribute to liver fibrosis through excessive ECM production. Cellular crosstalk between HSCs and surrounding cells, including both liver parenchymal and non-parenchymal cells, is involved in the activation of HSCs. Among them, NK cells play a crucial role in combating liver fibrosis and its causative factors, such as viral infections. Regulating the role of NK cells can suppress the activation of HSCs and improve their cytolytic function against activated HSCs or myofibroblasts to reverse liver fibrosis. Cells such as Tregs and molecules such as EP3 can regulate the cytotoxic function of NK cells. In addition, treatments such as ADH3 inhibitors, microRNAs, NKG2D activators, and natural products have been shown to regulate NK cell function to inhibit liver fibrosis. To date, the only available treatments, such as lipid-lowing agents, immune regulators, antiviral and anti-cancer agents, microRNAs, and combined therapies (e.g., IL-2 and IFN), regulate NK cell activation to inhibit fibrosis-causing factors. Therapeutic NK cells (e.g., CAR NK cells) or NK cell function regulators are limited. Overall, a better understanding of the cellular and molecular factors that interfere with the interaction between NK cells (especially lr-NK cells) and HSCs will provide new therapeutic targets for liver fibrosis. Meanwhile, more clinical trials are expected to investigate the roles of NK cells and NK cell-mediated factors in liver fibrosis treatment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, investigation, data curation, writing—original draft preparation, M.Y.; writing—review and editing, M.Y., E.V., E.T.K., K.F.S.-O. and G.L.; supervision, E.T.K., K.F.S.-O. and G.L.; funding acquisition, E.T.K., K.F.S.-O. and G.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors were funded by grants from NIH R01DK130340 (G.L., K.S.O., R.S.R.), NIH R01CA208396 (G.L., M.K., K.S.O.), and NIH R01CA250536 (G.L. and K.S.O.); partly supported by VA Merit Award I01 BX004065-1 (E.T.K. and K.S.O.) and Ellis Fischel Cancer Center Pilot Project Grant (G.L.).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data supporting reported results can be found in this paper.
Acknowledgments
The figures in the present manuscript were prepared using Biorender (https://biorender.com, accessed on 14 March 2023).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhao, X.; Chen, J.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, D. New insights into fibrosis from the ECM degradation perspective: The macrophage-MMP-ECM interaction. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Dong, W.; Kang, A.; Kuai, Y.; Xu, T.; Fan, Z.; Shi, L.; Sun, D.; Lu, Y.; Li, Z.; et al. Regulatory role and translational potential of CCL11 in liver fibrosis. Hepatology, 2023; Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knorr, J.; Kaufmann, B.; Inzaugarat, M.E.; Holtmann, T.M.; Geisler, L.; Hundertmark, J.; Kohlhepp, M.S.; Boosheri, L.M.; Chilin-Fuentes, D.R.; Birmingham, A.; et al. Interleukin-18 signaling promotes activation of hepatic stellate cells in mouse liver fibrosis. Hepatology, 2022; Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Sun, H.; Xue, T.; Gan, C.; Liu, H.; Xie, Y.; Yao, Y.; Ye, T. Liver Fibrosis: Therapeutic Targets and Advances in Drug Therapy. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 730176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shao, J.; Zhang, F.; Yin, G.; Chen, A.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, S. N(6)-methyladenosine modification regulates ferroptosis through autophagy signaling pathway in hepatic stellate cells. Redox. Biol. 2021, 47, 102151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, Y.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Brenner, D.A. New Developments on the Treatment of Liver Fibrosis. Dig. Dis. 2016, 34, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huby, T.; Gautier, E.L. Immune cell-mediated features of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 22, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Jiang, J.; Xie, L.; Shen, H.; Wu, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; et al. Interplay Between Liver Type 1 Innate Lymphoid Cells and NK Cells Drives the Development of Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 15, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Little, A.; Zhang, H. Chronic alcohol consumption inhibits peripheral NK cell development and maturation by decreasing the availability of IL-15. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 101, 1015–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiglund, N.; Strand, K.; Cornillet, M.; Stål, P.; Thorell, A.; Zimmer, C.L.; Näslund, E.; Karlgren, S.; Nilsson, H.; Mellgren, G.; et al. Retained NK Cell Phenotype and Functionality in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, Y.; Yoshio, S.; Doi, H.; Mori, T.; Matsuda, M.; Kawai, H.; Shimagaki, T.; Yoshikawa, S.; Aoki, Y.; Osawa, Y.; et al. Increased Frequency of Dysfunctional Siglec-7(−)CD57(+)PD-1(+) Natural Killer Cells in Patients With Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 603133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.F.; Gao, C.; Huang, X.Y.; Lu, J.C.; Guo, X.J.; Shi, G.M.; Cai, J.B.; Ke, A.W. Cancer cell-derived exosomal circUHRF1 induces natural killer cell exhaustion and may cause resistance to anti-PD1 therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.J.; Sung, P.S.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, G.W.; Jang, J.W.; Jung, E.S.; Bae, S.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Yoon, S.K. EpCAM-high liver cancer stem cells resist natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity by upregulating CEACAM1. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freud, A.G.; Mundy-Bosse, B.L.; Yu, J.; Caligiuri, M.A. The Broad Spectrum of Human Natural Killer Cell Diversity. Immunity 2017, 47, 820–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikulak, J.; Bruni, E.; Oriolo, F.; Di Vito, C.; Mavilio, D. Hepatic Natural Killer Cells: Organ-Specific Sentinels of Liver Immune Homeostasis and Physiopathology. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, A.M.; Yang, C.; Thakar, M.S.; Malarkannan, S. Natural Killer Cells: Development, Maturation, and Clinical Utilization. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Kimchi, E.T.; Staveley-O’Carroll, K.F.; Li, G. Astaxanthin Prevents Diet-Induced NASH Progression by Shaping Intrahepatic Immunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Qi, X.; Li, N.; Kaifi, J.T.; Chen, S.; Wheeler, A.A.; Kimchi, E.T.; Ericsson, A.C.; Scott Rector, R.; Staveley-O’Carroll, K.F.; et al. Western diet contributes to the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in male mice via remodeling gut microbiota and increasing production of 2-oleoylglycerol. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Sun, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Yan, H.; Pu, Q.; Xie, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Du, J.; Yang, Z. The imbalance between NKG2A and NKG2D expression is involved in NK cell immunosuppression and tumor progression of patients with hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2023, 53, 417–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.J.; Yang, N.; Mu, X.; Tang, L.; Wang, S.S.; Zhou, C.B.; Yuan, J.H.; Wang, H.Y.; Yu, Y.Y.; Li, J.; et al. Reduction of natural killer cells is associated with poor outcomes in patients with hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure. Hepatol. Int. 2022, 16, 1398–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wu, Q.; Chen, T.; Su, R.; Pan, C.; Qian, J.; Huang, H.; Yin, S.; Xie, H.; Zhou, L.; et al. Blocking CD47 promotes antitumour immunity through CD103(+) dendritic cell-NK cell axis in murine hepatocellular carcinoma model. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.; Lu, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Deng, W.; Jiang, T.; Lin, Y.; Yang, L.; Bi, X.; Lu, Y.; et al. Functional molecular expression of nature killer cells correlated to HBsAg clearance in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients during PEG-IFN α-2a therapy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1067362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuluaga, P.; Teniente-Serra, A.; Fuster, D.; Quirant-Sánchez, B.; Hernandez-Rubio, A.; Martínez-Cáceres, E.; Muga, R. Increased Natural Killer Cells Are Associated with Alcohol Liver Fibrosis and with T Cell and Cytotoxic Subpopulations Change. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosello-Trampont, A.C.; Krueger, P.; Narayanan, S.; Landes, S.G.; Leitinger, N.; Hahn, Y.S. NKp46(+) natural killer cells attenuate metabolism-induced hepatic fibrosis by regulating macrophage activation in mice. Hepatology 2016, 63, 799–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beli, E.; Duriancik, D.M.; Clinthorne, J.F.; Lee, T.; Kim, S.; Gardner, E.M. Natural killer cell development and maturation in aged mice. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2014, 135, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.J.; Beaver, C.M.; Goodier, M.R.; Bottomley, C.; Nielsen, C.M.; Wolf, A.F.; Boldrin, L.; Whitmore, C.; Morgan, J.; Pearce, D.J.; et al. Calorie Restriction Attenuates Terminal Differentiation of Immune Cells. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Mo, Q.; Fu, T.; Liu, Y.; Diao, B. STAT1 is associated with NK cell dysfunction by downregulating NKG2D transcription in chronic HBV-infected patients. Immunobiology 2022, 227, 152272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Fu, H.; Yang, Y.; Yu, H.; Ai, X.; Lei, Y.; Bao, W.; Tang, Y. Modulation of CXCR1 and CXCR3 expression on NK cells via Tim-3 in a murine model of primary biliary cholangitis. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 135, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rennert, C.; Tauber, C.; Fehrenbach, P.; Heim, K.; Bettinger, D.; Sogukpinar, Ö.; Schuch, A.; Zecher, B.F.; Bengsch, B.; Lang, S.A.; et al. Adaptive Subsets Limit the Anti-Tumoral NK-Cell Activity in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cells 2021, 10, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Jiang, X.; Chen, Y.; Sojka, D.K.; Wei, H.; Gao, X.; Sun, R.; Yokoyama, W.M.; Tian, Z. Liver-resident NK cells confer adaptive immunity in skin-contact inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1444–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Highton, A.J.; Schuster, I.S.; Degli-Esposti, M.A.; Altfeld, M. The role of natural killer cells in liver inflammation. Semin. Immunopathol. 2021, 43, 519–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudspeth, K.; Donadon, M.; Cimino, M.; Pontarini, E.; Tentorio, P.; Preti, M.; Hong, M.; Bertoletti, A.; Bicciato, S.; Invernizzi, P.; et al. Human liver-resident CD56(bright)/CD16(neg) NK cells are retained within hepatic sinusoids via the engagement of CCR5 and CXCR6 pathways. J. Autoimmun. 2016, 66, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, B.; Wang, F.; Sun, R.; Ling, B.; Tian, Z.; Wei, H. CD11b and CD27 reflect distinct population and functional specialization in human natural killer cells. Immunology 2011, 133, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiossone, L.; Chaix, J.; Fuseri, N.; Roth, C.; Vivier, E.; Walzer, T. Maturation of mouse NK cells is a 4-stage developmental program. Blood 2009, 113, 5488–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Tian, Z.; Wei, H. Subsets of human natural killer cells and their regulatory effects. Immunology 2014, 141, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, L.; Yao, W.; Guan, J.; Liu, X.; Wei, X.; Lin, X. Impaired circulating CD56(dim) NK cells are associated with decompensation of HBV-related cirrhosis. Hum. Immunol. 2020, 81, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, A.; He, W.; Rao, J.; Ye, D.; Cheng, P.; Jian, Q.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Deng, R.; Gao, Y.; et al. Dysregulation of innate cell types in the hepatic immune microenvironment of alcoholic liver cirrhosis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1034356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waller, K.J.; Saihi, H.; Li, W.; Brindley, J.H.; De Jong, A.; Syn, W.K.; Bessant, C.; Alazawi, W. Single-cell phenotypes of peripheral blood immune cells in early and late stages of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2023, 29, 417–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amer, J.; Salhab, A.; Doron, S.; Morali, G.; Safadi, R. A novel flow cytometry tool for fibrosis scoring through hepatic stellate cell differentiation. Cytometry A 2018, 93, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, I.; Lucar, O.; Petitdemange, C.; Béziat, V.; Lapalus, M.; Bédossa, P.; Debré, P.; Asselah, T.; Marcellin, P.; Vieillard, V. Accumulation of Intrahepatic TNF-α-Producing NKp44+ NK Cells Correlates With Liver Fibrosis and Viral Load in Chronic HCV Infection. Medicine 2016, 95, e3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, Y.; Hu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Shang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Tu, B.; et al. Activated hepatic stellate cells impair NK cell anti-fibrosis capacity through a TGF-β-dependent emperipolesis in HBV cirrhotic patients. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehgal, R.; Kaur, S.; Shasthry, S.M.; Agrawal, T.; Dwivedi, V.; Seth, D.; Ramakrishna, G.; Sarin, S.K.; Trehanpati, N. Natural Killer Cells Contribute to Pathogenesis of Severe Alcoholic Hepatitis by Inducing Lysis of Endothelial Progenitor Cells. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2020, 44, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legaz, I.; Bolarín, J.M.; Campillo, J.A.; Moya-Quiles, M.R.; Miras, M.; Muro, M.; Minguela, A.; Álvarez-López, M.R. Killer Cell Immunoglobulin-like Receptors (KIR) and Human Leucocyte Antigen C (HLA-C) Increase the Risk of Long-Term Chronic Liver Graft Rejection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Arias, A.E.; Haworth, S.E.; Belli, L.S.; Burra, P.; Pinzello, G.; Vangeli, M.; Minola, E.; Guido, M.; Boccagni, P.; De Feo, T.M.; et al. Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor genotype and killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor-human leukocyte antigen C ligand compatibility affect the severity of hepatitis C virus recurrence after liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2009, 15, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, X.; Zhang, R.; Du, R.; Yu, T.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zuo, S.; Wang, X.; et al. EP3 enhances adhesion and cytotoxicity of NK cells toward hepatic stellate cells in a murine liver fibrosis model. J. Exp. Med. 2022, 219, e20212414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Jia, Y.; Yao, Z.; Huang, J.; Hao, M.; Yao, S.; Lian, N.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; et al. Hepatic stellate cell interferes with NK cell regulation of fibrogenesis via curcumin induced senescence of hepatic stellate cell. Cell Signal. 2017, 33, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karrar, A.; Rajput, B.; Hariharan, S.; Abdelatif, D.; Houry, M.; Moosvi, A.; Ali, I.; Tan, D.; Noor, S.; Esmaeili, D.; et al. Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I-Related Chain a Alleles and Histology of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatol. Commun. 2021, 5, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, W.I.; Park, O.; Suh, Y.G.; Byun, J.S.; Park, S.Y.; Choi, E.; Kim, J.K.; Ko, H.; Wang, H.; Miller, A.M.; et al. Suppression of innate immunity (natural killer cell/interferon-γ) in the advanced stages of liver fibrosis in mice. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1342–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurokawa, T.; Ohkohchi, N. Platelets in liver disease, cancer and regeneration. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 3228–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czajka, P.; Przybyłkowski, A.; Nowak, A.; Postula, M.; Wolska, M.; Mirowska-Guzel, D.; Czlonkowska, A.; Eyileten, C. Antiplatelet drugs and liver fibrosis. Platelets 2022, 33, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisman, T.; Luyendyk, J.P. Platelets as Modulators of Liver Diseases. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2018, 44, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, L.K.; Zhang, G.; Luo, S.Y.; Yin, W.; Song, H.Y. The value of platelet count in evaluating the degree of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Ikenaga, N.; Liu, S.B.; Peng, Z.W.; Chung, J.; Sverdlov, D.Y.; Miyamoto, M.; Kim, Y.O.; Ogawa, S.; Arch, R.H.; et al. Extrahepatic platelet-derived growth factor-β, delivered by platelets, promotes activation of hepatic stellate cells and biliary fibrosis in mice. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 1378–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Tang, T.; Wu, X.; Mansour, A.G.; Lu, T.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.S.; Caligiuri, M.A.; Yu, J. PDGF-D-PDGFRβ signaling enhances IL-15-mediated human natural killer cell survival. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2114134119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malehmir, M.; Pfister, D.; Gallage, S.; Szydlowska, M.; Inverso, D.; Kotsiliti, E.; Leone, V.; Peiseler, M.; Surewaard, B.G.J.; Rath, D.; et al. Platelet GPIbα is a mediator and potential interventional target for NASH and subsequent liver cancer. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 641–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Peng, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Li, W.; Huang, F.; Zheng, C.; Xu, F.; Hu, Q.; et al. MAIT cells ameliorate liver fibrosis by enhancing the cytotoxicity of NK cells in cholestatic murine models. Liver Int. 2022, 42, 2743–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Huang, Q.; Huang, M.; Wen, H.; Lin, R.; Zheng, M.; Qu, K.; Li, K.; Wei, H.; Xiao, W.; et al. Human CD96 Correlates to Natural Killer Cell Exhaustion and Predicts the Prognosis of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2019, 70, 168–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Niu, J. Identification of Immune Microenvironment Changes and the Expression of Immune-Related Genes in Liver Cirrhosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 918445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.J.; Martinet, L.; Gilfillan, S.; Souza-Fonseca-Guimaraes, F.; Chow, M.T.; Town, L.; Ritchie, D.S.; Colonna, M.; Andrews, D.M.; Smyth, M.J. The receptors CD96 and CD226 oppose each other in the regulation of natural killer cell functions. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, A.E.; Fittje, P.; Müller, L.M.; Ahrenstorf, A.E.; Hagemann, K.; Hagen, S.H.; Hess, L.U.; Niehrs, A.; Poch, T.; Ravichandran, G.; et al. The co-inhibitory receptor TIGIT regulates NK cell function and is upregulated in human intrahepatic CD56(bright) NK cells. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1117320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Liu, S.; Yang, M. Regulatory T cells and their associated factors in hepatocellular carcinoma development and therapy. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 3346–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhans, B.; Alwan, A.W.; Krämer, B.; Glässner, A.; Lutz, P.; Strassburg, C.P.; Nattermann, J.; Spengler, U. Regulatory CD4+ T cells modulate the interaction between NK cells and hepatic stellate cells by acting on either cell type. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auer, E.D.; Tong, H.V.; Amorim, L.M.; Malheiros, D.; Hoan, N.X.; Issler, H.C.; Petzl-Erler, M.L.; Beltrame, M.H.; Boldt, A.B.W.; Toan, N.L.; et al. Natural killer cell receptor variants and chronic hepatitis B virus infection in the Vietnamese population. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 96, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhanna, N.; Abu Tair, L.; Doron, S.; Amer, J.; Azzeh, M.; Mahamid, M.; Friedman, S.; Safadi, R. Amelioration of hepatic fibrosis by NK cell activation. Gut 2011, 60, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijaya, R.S.; Read, S.A.; Schibeci, S.; Eslam, M.; Azardaryany, M.K.; El-Khobar, K.; van der Poorten, D.; Lin, R.; Yuen, L.; Lam, V.; et al. KLRG1+ natural killer cells exert a novel antifibrotic function in chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijaya, R.S.; Read, S.A.; Selvamani, S.P.; Schibeci, S.; Azardaryany, M.K.; Ong, A.; van der Poorten, D.; Lin, R.; Douglas, M.W.; George, J.; et al. Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Eradication With Interferon-Free Direct-Acting Antiviral-Based Therapy Results in KLRG1+ HCV-Specific Memory Natural Killer Cells. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 223, 1183–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, W.M.; Ryu, T.; Lee, J.H.; Shim, Y.R.; Kim, M.H.; Kim, H.H.; Kim, Y.E.; Yang, K.; Kim, K.; Choi, S.E.; et al. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 in Natural Killer Cells Attenuates Liver Fibrosis by Exerting Cytotoxicity to Activated Stellate Cells. Hepatology 2021, 74, 2170–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanshiashvili, L.; Tsitsilashvili, E.; Dabrundashvili, N.; Kalandadze, I.; Mikeladze, D. Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 may be involved in macrophage plasticity. Biol. Res. 2017, 50, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chantong, B.; Kratschmar, D.V.; Lister, A.; Odermatt, A. Inhibition of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 induces cellular stress through pertussis toxin-sensitive Gi-proteins in murine BV-2 microglia cells. J. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 11, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radaeva, S.; Sun, R.; Jaruga, B.; Nguyen, V.T.; Tian, Z.; Gao, B. Natural killer cells ameliorate liver fibrosis by killing activated stellate cells in NKG2D-dependent and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-dependent manners. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 435–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glässner, A.; Eisenhardt, M.; Kokordelis, P.; Krämer, B.; Wolter, F.; Nischalke, H.D.; Boesecke, C.; Sauerbruch, T.; Rockstroh, J.K.; Spengler, U.; et al. Impaired CD4⁺ T cell stimulation of NK cell anti-fibrotic activity may contribute to accelerated liver fibrosis progression in HIV/HCV patients. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassouna, M.M.; Radwan, E.M.; Abdelsameea, E.; Estaphan, S.; Abd Elrhman, H.E.; Abdel-Samiee, M.; Naguib, M. The Putative Role of Natural Killer Cells in Patients with Hepatitis C Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2021, 22, 2559–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, A.; Satelli, A.; Yan, J.; Xueqing, X.; Gagea, M.; Hunter, C.A.; Mishra, L.; Li, S. IL-30 (IL27p28) attenuates liver fibrosis through inducing NKG2D-rae1 interaction between NKT and activated hepatic stellate cells in mice. Hepatology 2014, 60, 2027–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crabé, S.; Guay-Giroux, A.; Tormo, A.J.; Duluc, D.; Lissilaa, R.; Guilhot, F.; Mavoungou-Bigouagou, U.; Lefouili, F.; Cognet, I.; Ferlin, W.; et al. The IL-27 p28 subunit binds cytokine-like factor 1 to form a cytokine regulating NK and T cell activities requiring IL-6R for signaling. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 7692–7702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Khurana, A.; Allawadhi, P.; Banothu, A.K.; Bharani, K.K.; Weiskirchen, R. Emerging Role of PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors in Chronic Liver Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 790963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo, M.L.; Ghiglione, Y.A.; Salido, J.P.; Urioste, A.; Poblete, G.; Sisto, A.E.; Martinez, A.; Rolón, M.J.; Ojeda, D.S.; Cahn, P.E.; et al. Liver cirrhosis in HIV/HCV-coinfected individuals is related to NK cell dysfunction and exhaustion, but not to an impaired NK cell modulation by CD4(+) T-cells. J. Int. AIDS Soc. 2019, 22, e25375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Zhu, E.; Zhang, Y. Advances of cancer-associated fibroblasts in liver cancer. Biomark. Res. 2022, 10, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.; Hodgins, J.J.; Marathe, M.; Nicolai, C.J.; Bourgeois-Daigneault, M.C.; Trevino, T.N.; Azimi, C.S.; Scheer, A.K.; Randolph, H.E.; Thompson, T.W.; et al. Contribution of NK cells to immunotherapy mediated by PD-1/PD-L1 blockade. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 4654–4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, M.; Ericsson, A.C. Function of Macrophages in Disease: Current Understanding on Molecular Mechanisms. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 620510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Arooj, S.; Wang, H. NK Cell-Based Immune Checkpoint Inhibition. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstock, P.; Horstkorte, R.; Gnanapragassam, V.S.; Harth, J.; Kielstein, H. Siglec-7 expression is reduced on a natural killer (NK) cell subset of obese humans. Immunol. Res. 2017, 65, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yu, L.; Zhou, M.; Hou, P.; Yi, L.; Mi, M. Dihydromyricetin ameliorates liver fibrosis via inhibition of hepatic stellate cells by inducing autophagy and natural killer cell-mediated killing effect. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 18, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, T.; Zhou, H.; Liu, H.; Hu, Y.; Cao, J. Inhibition of hepatic natural killer cell function via the TIGIT receptor in schistosomiasis-induced liver fibrosis. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayindala, X.; Huang, H.; Gao, S.; Xu, X. Echinococcus multilocularis induces surface high expression of inhibitory killer immunoglobulin-like receptor on natural killer cells. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2021, 49, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Kim, E.; Ryu, J.; Lee, H.; Shin, E.A.; Lee, M.; Lee, H.; Lee, J.H.; Yoon, J.H.; Song, D.G.; et al. TM4SF5-mediated liver malignancy involves NK cell exhaustion-like phenotypes. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 79, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Huang, K.; Shen, L.; Tao, Y.Y.; Liu, C.H. Cultured Mycelium Cordyceps sinensis allevi¬ates CCl4-induced liver inflammation and fibrosis in mice by activating hepatic natural killer cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2016, 37, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Han, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ding, Y.; Chen, J.; Qiao, H.; Gao, N. Effect of ADHI on hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 651, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.S.; Eun, H.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Jung, J.Y.; Park, S.H.; Park, K.G.; Choi, H.S.; Suh, J.M.; Jeong, W.I. Treatment with 4-methylpyrazole modulated stellate cells and natural killer cells and ameliorated liver fibrosis in mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Byun, J.S.; Seo, W.; Jeong, J.M.; Park, O.; Duester, G.; Haseba, T.; Kim, S.C.; Park, K.G.; et al. Alcohol dehydrogenase III exacerbates liver fibrosis by enhancing stellate cell activation and suppressing natural killer cells in mice. Hepatology 2014, 60, 1044–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Quan, J. Exosomal miR-223 derived from natural killer cells inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation by suppressing autophagy. Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Li, N.; Cheng, Q.; Zheng, J.; Zhu, M.; Bao, S.; Chen, M.; Shi, G. miR-96-5p prevents hepatic stellate cell activation by inhibiting autophagy via ATG7. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 96, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.Q.; Ren, J.P.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, G.Y.; Moorman, J.P.; Yao, Z.Q. MicroRNA-155 regulates interferon-γ production in natural killer cells via Tim-3 signalling in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Immunology 2015, 145, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radaeva, S.; Wang, L.; Radaev, S.; Jeong, W.I.; Park, O.; Gao, B. Retinoic acid signaling sensitizes hepatic stellate cells to NK cell killing via upregulation of NK cell activating ligand RAE1. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2007, 293, G809–G816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, H.Y.; Bao, W.M.; Yang, C.X.; Lai, W.J.; Xu, J.M.; Yu, H.Y.; Yang, Y.N.; Tan, X.; Gupta, A.K.; Tang, Y.M. Kupffer Cells Regulate Natural Killer Cells Via the NK group 2, Member D (NKG2D)/Retinoic Acid Early Inducible-1 (RAE-1) Interaction and Cytokines in a Primary Biliary Cholangitis Mouse Model. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26, e923726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, K.V.; Deng, M.; Ting, J.P.Y. The NLRP3 inflammasome: Molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, C.M.; Coll, R.C. NLRP3 inflammasome priming: A riddle wrapped in a mystery inside an enigma. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 108, 937–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.H.; Kim, D.; Jung, J.; Kang, H.; Cho, H. NLRP3 Deficiency in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Enhances Surveillance of NK-92 through a Modulation of MICA/B. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupaul-Chicoine, J.; Arabzadeh, A.; Dagenais, M.; Douglas, T.; Champagne, C.; Morizot, A.; Rodrigue-Gervais, I.G.; Breton, V.; Colpitts, S.L.; Beauchemin, N.; et al. The Nlrp3 Inflammasome Suppresses Colorectal Cancer Metastatic Growth in the Liver by Promoting Natural Killer Cell Tumoricidal Activity. Immunity 2015, 43, 751–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilian, L.S.; Voran, J.; Frank, D.; Rangrez, A.Y. RhoA: A dubious molecule in cardiac pathophysiology. J. Biomed. Sci. 2021, 28, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.J.; Mu, Y.L.; Zhao, H.J.; Zhao, R.R.; Guo, Q.J.; Su, Y.H.; Zhang, J. Fasudil prevents liver fibrosis via activating natural killer cells and suppressing hepatic stellate cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 3581–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L. Endostatin attenuates PDGF-BB- or TGF-β1-induced HSCs activation via suppressing RhoA/ROCK1 signal pathways. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Hu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, C. γδT Cells Suppress Liver Fibrosis via Strong Cytolysis and Enhanced NK Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity Against Hepatic Stellate Cells. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.; Hou, N.; Meng, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, F.; Zhang, L.; Sun, W.; et al. T cell immunoglobulin- and mucin-domain-containing molecule-3 (Tim-3) mediates natural killer cell suppression in chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2010, 52, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norouzi, A.; Taziki, S.; Najafipasandi, A.; Mohammadi, S.; Roshandel, G. Rosuvastatin Intervention Decreased the Frequencies of the TIM-3+ Population of NK Cells and NKT Cells among Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B. Iran. J. Immunol. 2022, 19, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okwor, C.I.A.; Oh, J.S.; Crawley, A.M.; Cooper, C.L.; Lee, S.H. Expression of Inhibitory Receptors on T and NK Cells Defines Immunological Phenotypes of HCV Patients with Advanced Liver Fibrosis. iScience 2020, 23, 101513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Sun, R. Liver-resident NK cells and their potential functions. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 14, 890–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.B.; Lu, F.T.; Ma, H.D.; Wang, Y.H.; Yang, W.; Long, J.; Miao, Q.; Zhang, W.; Tian, Z.; Ridgway, W.M.; et al. Liver-resident NK cells suppress autoimmune cholangitis and limit the proliferation of CD4(+) T cells. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanim, M.; Amer, J.; Salhab, A.; Jaradat, N. Ecballium elaterium improved stimulatory effects of tissue-resident NK cells and ameliorated liver fibrosis in a thioacetamide mice model. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 150, 112942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martrus, G.; Kautz, T.; Lunemann, S.; Richert, L.; Glau, L.; Salzberger, W.; Goebels, H.; Langeneckert, A.; Hess, L.; Poch, T.; et al. Proliferative capacity exhibited by human liver-resident CD49a+CD25+ NK cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saparbay, J.; Tanaka, Y.; Tanimine, N.; Ohira, M.; Ohdan, H. Everolimus enhances TRAIL-mediated anti-tumor activity of liver resident natural killer cells in mice. Transpl. Int. 2020, 33, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Song, H.; Wei, H.; Sun, R.; Tian, Z.; Peng, H. Requirement of RORα for maintenance and antitumor immunity of liver-resident natural killer cells/ILC1s. Hepatology 2022, 75, 1181–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hydes, T.; Noll, A.; Salinas-Riester, G.; Abuhilal, M.; Armstrong, T.; Hamady, Z.; Primrose, J.; Takhar, A.; Walter, L.; Khakoo, S.I. IL-12 and IL-15 induce the expression of CXCR6 and CD49a on peripheral natural killer cells. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2018, 6, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.H.; Shin, J.H.; Haggadone, M.D.; Sunwoo, J.B. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor is required for the maintenance of liver-resident natural killer cells. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 2249–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, O.E.; Colbeck, E.J.; Daffis, S.; Khan, S.; Ramakrishnan, D.; Pattabiraman, D.; Chu, R.; Micolochick Steuer, H.; Lehar, S.; Peiser, L.; et al. Therapeutic Potential of TLR8 Agonist GS-9688 (Selgantolimod) in Chronic Hepatitis B: Remodeling of Antiviral and Regulatory Mediators. Hepatology 2021, 74, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boni, C.; Vecchi, A.; Rossi, M.; Laccabue, D.; Giuberti, T.; Alfieri, A.; Lampertico, P.; Grossi, G.; Facchetti, F.; Brunetto, M.R.; et al. TLR7 Agonist Increases Responses of Hepatitis B Virus-Specific T Cells and Natural Killer Cells in Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B Treated With Nucleos(T)Ide Analogues. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1764–1777.e1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, N.; Liu, B.; Chen, Z.; Li, H.; Chen, M.; Peng, M.; Ren, H.; Hu, P. Combination of pegylated interferon-alpha and nucleos(t)ide analogue treatment enhances the activity of natural killer cells in nucleos(t)ide analogue experienced chronic hepatitis B patients. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2020, 202, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, U.S.; Peppa, D.; Micco, L.; Singh, H.D.; Carey, I.; Foster, G.R.; Maini, M.K.; Kennedy, P.T. Interferon Alpha Induces Sustained Changes in NK Cell Responsiveness to Hepatitis B Viral Load Suppression In Vivo. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Fu, B.; Liu, Y.; Guo, C.; Ye, Y.; Sun, R.; Li, J.; Tian, Z.; Wei, H. NKp30(+) NK cells are associated with HBV control during pegylated-interferon-alpha-2b therapy of chronic hepatitis B. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Wang, E.; Liu, L.; Wang, Q.; Xia, D.; Bai, W.; Tie, J.; Li, X.; Yuan, J.; Yang, S.; et al. Sorafenib may enhance antitumour efficacy in hepatocellular carcinoma patients by modulating the proportions and functions of natural killer cells. Investig. New Drugs 2020, 38, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stelma, F.; van der Ree, M.H.; Sinnige, M.J.; Brown, A.; Swadling, L.; de Vree, J.M.L.; Willemse, S.B.; van der Valk, M.; Grint, P.; Neben, S.; et al. Immune phenotype and function of natural killer and T cells in chronic hepatitis C patients who received a single dose of anti-MicroRNA-122, RG-101. Hepatology 2017, 66, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Wang, P.; Han, M.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Xia, Q.; Yan, W.; Wan, X.; Zhu, C.; Xie, Q.; et al. Sequential combination therapy with interferon, interleukin-2 and therapeutic vaccine in entecavir-suppressed chronic hepatitis B patients: The Endeavor study. Hepatol. Int. 2019, 13, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiue, S.J.; Cheng, C.L.; Shiue, H.S.; Chen, C.N.; Cheng, S.W.; Wu, L.W.; Jargalsaikhan, G.; Chan, T.S.; Lin, H.Y.; Wu, M.S. Arthrospira Enhances Seroclearance in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Receiving Nucleos(t)ide Analogue through Modulation of TNF-α/IFN-γ Profile. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajid, M.; Liu, L.; Sun, C. The Dynamic Role of NK Cells in Liver Cancers: Role in HCC and HBV Associated HCC and Its Therapeutic Implications. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 887186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Qin, Z.; Du, D.; Wu, Y.; Qiu, S.; Mu, F.; Xu, K.; Chen, J. Safety and Short-Term Efficacy of Irreversible Electroporation and Allogenic Natural Killer Cell Immunotherapy Combination in the Treatment of Patients with Unresectable Primary Liver Cancer. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2019, 42, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, W.K.; Lee, B.C.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.J.; Chung, I.J.; Cho, S.B.; Koh, Y.S. A Phase I Study of Locoregional High-Dose Autologous Natural Killer Cell Therapy With Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy in Patients With Locally Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 879452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).