Differences and Associations of NLRP3 Inflammasome Levels with Interleukins 1α, 1β, 33 and 37 in Adults with Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Sample Collection and Anthropometrics
2.3. Lipid Profile and Biochemical Estimations
2.4. Serum NLRP3 and ILs (1α, 1β, 33 and 37) Estimations
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, H.-M.; Kim, J.-J.; Kim, H.J.; Shong, M.; Ku, B.J.; Jo, E.-K. Upregulated NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2013, 62, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Daghri, N.M.; Abdi, S.; Sabico, S.; Alnaami, A.M.; Wani, K.A.; Ansari, M.G.A.; Khattak, M.N.K.; Khan, N.; Tripathi, G.; Chrousos, G.P.; et al. Gut-Derived Endotoxin and Telomere Length Attrition in Adults with and without Type 2 Diabetes. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfadul, H.; Sabico, S.; Al-Daghri, N.M. The role of interleukin-1beta in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 901616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainone, V.; Schneider, L.; Saulle, I.; Ricci, C.; Biasin, M.; Al-Daghri, N.M.; Giani, E.; Zuccotti, G.V.; Clerici, M.; Trabattoni, D. Upregulation of inflammasome activity and increased gut permeability are associated with obesity in children and adolescents. Int. J. Obes. 2016, 40, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaboration NCD Risk Factor. Worldwide trends in diabetes since 1980: A pooled analysis of 751 population-based studies with 4.4 million participants. Lancet 2016, 387, 1513–1530. [Google Scholar]
- Wani, K.; AlHarthi, H.; Alghamdi, A.; Sabico, S.; Al-Daghri, N.M. Role of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Obesity-Mediated Metabolic Disorders. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinon, F.; Burns, K.; Tschopp, J. The inflammasome: A molecular platform triggering activation of inflammatory caspases and processing of proIL-beta. Mol. Cell 2002, 10, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Daghri, N.M.; Wani, K.; AlHarthi, H.; Alghamdi, A.; Alnaami, A.M.; Yakout, S.M. Sex-Specific Signature in the Circulating NLRP3 Levels of Saudi Adults with Metabolic Syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, R.C.; Schroder, K.; Pelegrín, P. NLRP3 and pyroptosis blockers for treating inflammatory diseases. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 43, 653–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroja-Mazo, A.; Martín-Sánchez, F.; Gomez, A.I.; Martínez, C.M.; Amores-Iniesta, J.; Compan, V.; Barberà-Cremades, M.; Yagüe, J.; Ruiz-Ortiz, E.; Antón, J.; et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome is released as a particulate danger signal that amplifies the inflammatory response. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Rosa, F.; Saresella, M.; Marventano, I.; Piancone, F.; Ripamonti, E.; Al-Daghri, N.; Bazzini, C.; Zoia, C.P.; Conti, E.; Ferrarese, C.; et al. Stavudine Reduces NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Modulates Amyloid-beta Autophagy. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2019, 72, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, R.; Li, W.; Abdul, Y.; Jackson, L.; Dong, G.; Jamil, S.; Filosa, J.; Fagan, S.C.; Ergul, A. NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition with MCC950 improves diabetes-mediated cognitive impairment and vasoneuronal remodeling after ischemia. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 142, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.J.; Lee, E.K.; Park, T.J.; Kim, W. Damage-associated molecular patterns and their pathological relevance in diabetes mellitus. Ageing Res. Rev. 2015, 24, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kang, Y.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, D.J.; Lee, K.W.; Han, S.J. Acute Glucose Shift Induces the Activation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome in THP-1 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-M.; Hsieh, C.-J.; Huang, J.-C.; Huang, I.-C. Acute and chronic fluctuations in blood glucose levels can increase oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Acta Diabetol. 2012, 49 (Suppl. 1), S171–S177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Shen, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Han, P. Acute blood glucose fluctuation enhances rat aorta endothelial cell apoptosis, oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory cytokine expression in vivo. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2016, 15, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Daghri, N.M.; Al-Attas, O.S.; Alokail, M.S.; Alkharfy, K.M.; Yousef, M.; Sabico, S.L.; Chrousos, G.P. Diabetes mellitus type 2 and other chronic non-communicable diseases in the central region, Saudi Arabia (riyadh cohort 2): A decade of an epidemic. BMC Med. 2011, 9, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Daghri, N.M.; Hussain, S.D.; Ansari, M.G.; Khattak, M.N.; Aljohani, N.; Al-Saleh, Y.; Al-Harbi, M.Y.; Sabico, S.; Alokail, M.S. Decreasing prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in the central region of Saudi Arabia (2008–2017). J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 212, 105920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marathe, P.H.; Gao, H.X.; Close, K.L. American Diabetes Association Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2017. J. Diabetes 2017, 9, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, H.; Li, W.; Chen, S.; Feng, T.; Jiao, W.; Wu, C.; Dong, J.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; et al. Interleukin-37 sensitize the elderly type 2 diabetic patients to insulin therapy through suppressing the gut microbiota dysbiosis. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 112, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Hu, Y.; Long, P.; Li, P.; Chen, P.; Wang, X. The effect of tai chi intervention on NLRP3 and its related antiviral inflammatory factors in the serum of patients with pre-diabetes. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1026509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Bai, G.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; He, Y.; Qiang, D.; Zou, X. Early Predictors in the Onset of Type 2 Diabetes at Different Fasting Blood Glucose Levels. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2021, 14, 1485–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorquera, G.; Russell, J.; Monsalves-Álvarez, M.; Cruz, G.; Valladares-Ide, D.; Basualto-Alarcón, C.; Barrientos, G.; Estrada, M.; Llanos, P. NLRP3 Inflammasome: Potential Role in Obesity Related Low-Grade Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Skeletal Muscle. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coll, R.C.; Robertson, A.A.B.; Chae, J.J.; Higgins, S.C.; Muñoz-Planillo, R.; Inserra, M.C.; Vetter, I.; Dungan, L.S.; Monks, B.G.; Stutz, A.; et al. A small-molecule inhibitor of the NLRP3 inflammasome for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Z.; Fan, Y.; Liu, X.; Xue, J.; Han, Z.; Zhu, C.; Wang, X. NLRP3 inflammasome promotes diabetes-induced endothelial inflammation and atherosclerosis. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2019, 12, 1931–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhong, D.; Chen, H.; Jin, J.; Liu, Q.; Li, G. NLRP3 inflammasome activates interleukin-23/interleukin-17 axis during ischaemia-reperfusion injury in cerebral ischaemia in mice. Life Sci. 2019, 227, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, E.-K.; Kim, J.K.; Shin, D.-M.; Sasakawa, C. Molecular mechanisms regulating NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 13, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinaik, R.; Barayan, D.; Jeschke, M.G. NLRP3 Inflammasome in Inflammation and Metabolism: Identifying Novel Roles in Postburn Adipose Dysfunction. Endocrinology 2020, 161, bqaa116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.-J.; Ren, X.-S.; Xiong, X.-Q.; Chen, Y.-Z.; Zhao, M.-X.; Wang, J.-J.; Zhou, Y.-B.; Han, Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.-H.; et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation contributes to VSMC phenotypic transformation and proliferation in hypertension. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Xu, S.; Ma, Y.; Liu, G.; Jang, H.; Fang, J. Modulatory Mechanisms of the NLRP3 Inflammasomes in Diabetes. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dror, E.; Dalmas, E.; Zeman-Meier, D.; Wueest, S.; Thévenet, J.; Thienel, C.; Timper, K.; Nordmann, T.M.; Traub, S.; Schulze, F.; et al. Postprandial macrophage-derived IL-1β stimulates insulin, and both synergistically promote glucose disposal and inflammation. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanna, S.; Van Zuydam, N.R.; Mahajan, A.; Kurilshikov, A.; Vila, A.V.; Võsa, U.; Mujagic, Z.; Masclee, A.A.M.; Jonkers, D.M.A.E.; Oosting, M.; et al. Causal relationships among the gut microbiome, short-chain fatty acids and metabolic diseases. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Wang, X.; Xie, F.; Zhang, H.; Liu, D. Serum NLRP3: A biomarker for identifying high-risk septic patients. Cytokine 2022, 149, 155725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Guan, H.; Jiao, X.; Yang, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Z. NLRP3 inflammasome mediated pyroptosis is involved in cadmium exposure-induced neuroinflammation through the IL-1beta/IkB-alpha-NF-kappaB-NLRP3 feedback loop in swine. Toxicology 2021, 453, 152720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramunt, B.; Smati, S.; Grandgeorge, N.; Lenfant, F.; Arnal, J.-F.; Montagner, A.; Gourdy, P. Sex differences in metabolic regulation and diabetes susceptibility. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, X.; Liao, N.; Mi, L.; Peng, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhang, S.; Wen, F. Enhanced Expression of NLRP3 Inflammasome-Related Inflammation in Diabetic Retinopathy. Investig. Ophtalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyer, A.H.; Batten, I.; Reddy, C.; Townsend, L.; Woods, C.P.; O’neill, D.; Gibney, J.; Kennelly, S.P.; Bourke, N.M. Neuropsychological decrements in midlife type-2 diabetes are not associated with peripheral NLRP3 inflammasome responsiveness. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1021351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, D.; Tian, X.; Zhang, H. Analysis of Serum Interleukin-37 Level and Prognosis in Patients with ACS. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2021, 2021, 3755458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Tao, X. Current Understanding of IL-37 in Human Health and Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 696605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.A.; Ad’Hiah, A.H. Interleukin-37 is down-regulated in serum of patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Cytokine 2021, 148, 155702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, R.; Huang, X.; Sun, T.; Wu, Y.; Hambly, B.D.; Bao, S. IL-37 and 38 signalling in gestational diabetes. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2017, 124, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, M.; Xu, Y.; Ye, D.; Zhang, J.; et al. Circulating IL-37 levels are elevated in patients with hypertension. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 21, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harms, R.Z.; Yarde, D.N.; Guinn, Z.; Lorenzo-Arteaga, K.M.; Corley, K.P.; Cabrera, M.S.; Sarvetnick, N.E. Increased expression of IL-18 in the serum and islets of type 1 diabetics. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 64, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Liu, N.; Feng, X.; Yang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Zhuang, S.; Dai, Y.; Liu, M.; Tang, L. Circulating levels of IL-33 are elevated by obesity and positively correlated with metabolic disorders in Chinese adults. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Yao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Gu, X.; Wang, C.; Bao, K.; Sun, Y.; Hong, M. A novel function of NLRP3 independent of inflammasome as a key transcription factor of IL-33 in epithelial cells of atopic dermatitis. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.M. Role of IL-33 in inflammation and disease. J. Inflamm. 2011, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.J.; Azim, A.; Hetty, S.; Jui, B.N.; Kullberg, J.; Lundqvist, M.H.; Eriksson, J.W. Interleukin-33 inhibits glucose uptake in human adipocytes and its expression in adipose tissue is elevated in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Cytokine 2023, 161, 156080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Hao, S.; Dong, X.; Zhang, D.; Jia, Z. Circulating cytokine profile and modulation of regulatory T cells in chronic hepatitis B patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Biomol. Biomed. 2023, 23, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salti, T.; Khazim, K.; Haddad, R.; Campisi-Pinto, S.; Bar-Sela, G.; Cohen, I. Glucose Induces IL-1α-Dependent Inflammation and Extracellular Matrix Proteins Expression and Deposition in Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paolo, N.C.; Shayakhmetov, D.M. Interleukin 1α and the inflammatory process. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagvadorj, J.; Mikulska-Ruminska, K.; Tumurkhuu, G.; Ratsimandresy, R.A.; Carriere, J.; Andres, A.M.; Marek-Iannucci, S.; Song, Y.; Chen, S.; Lane, M.; et al. Recruitment of pro-IL-1alpha to mitochondrial cardiolipin, via shared LC3 binding domain, inhibits mitophagy and drives maximal NLRP3 activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2015632118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Ai, C.; Bai, M.; Niu, J.; Zhang, Z. NLRP3 Inflammasome/Pyroptosis: A Key Driving Force in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wirtz, S. Does Pyroptosis Play a Role in Inflammasome-Related Disorders? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

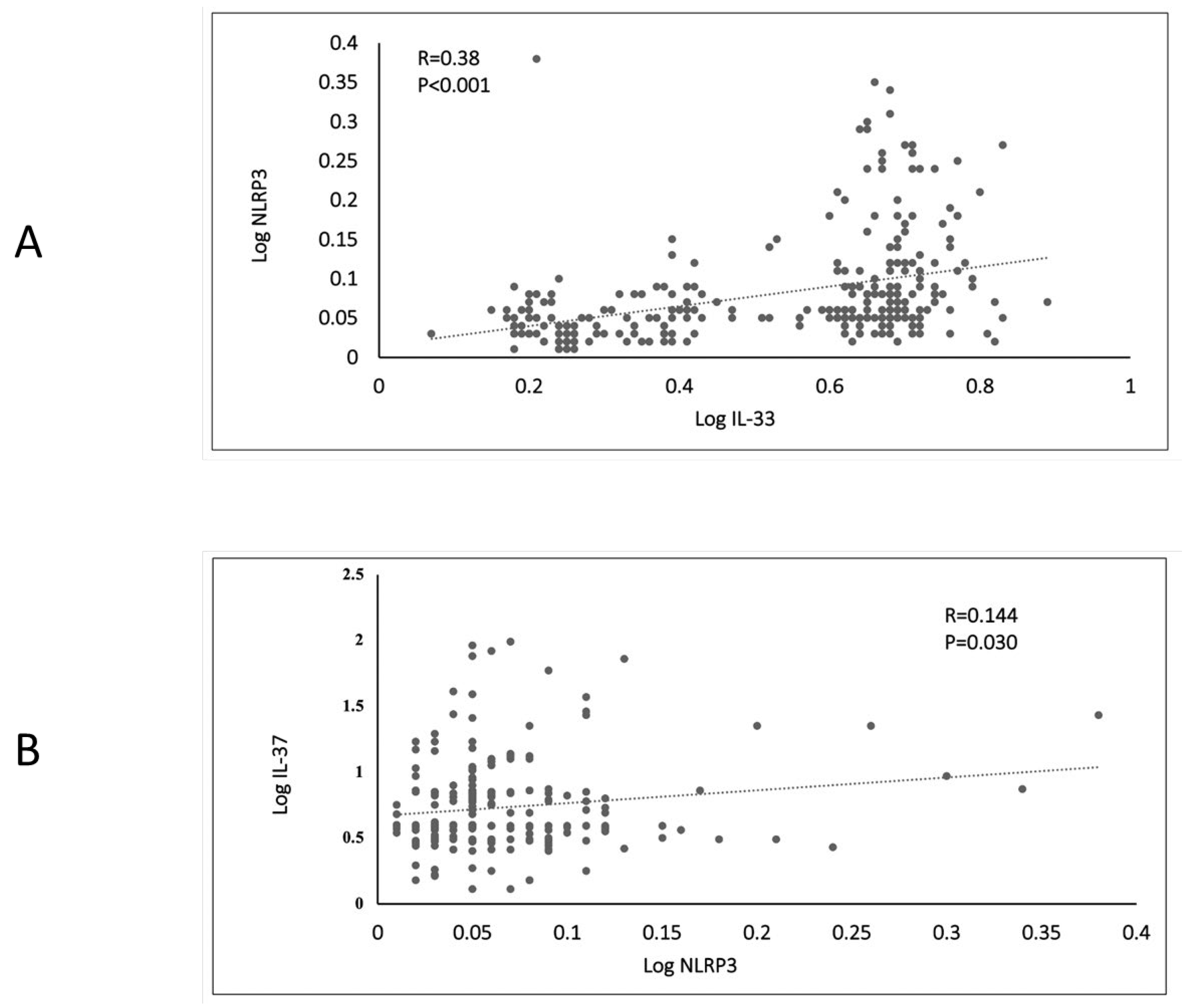
| Parameters | HC | PD | T2DM | p-Value | p-Value (Age and BMI Adjusted) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (M/F) | 198 (87/111) | 88 (38/50) | 121 (26/95) | ||
| Age (year) | 39.3 ± 8.9 | 42.3 ± 8.8 A | 44.0 ± 8.7 A | <0.001 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 28.7 ± 5.3 | 32.7 ± 5.9 A | 32.6 ± 7.2 A | <0.001 | |
| WHR | 0.85 ± 0.09 | 0.87 ± 0.08 | 0.90 ± 0.09 A | 0.001 | |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 119.2 ± 12.0 | 122.4 ± 12.7 | 127.5 ± 16.2 AB | <0.001 | 0.001 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 74.8 ± 9.9 | 76.6 ± 9.9 | 78.5 ± 10.3 | 0.009 | 0.16 |
| Fasting glucose (mmol/L) | 4.81 ± 0.50 | 5.98 ± 0.30 A | 8.62 ± 2.50 AB | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Hb1AC (%) | 5.0 ± 0.7 | 5.6 ± 0.5 A | 7.2 ± 1.4 AB | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Insulin (uU/mL) | 12.7 (6.3–18.9) | 15.9 (15.6–16.7) | 19.4 (15.9–19.8) AB | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 5.2 ± 0.9 | 5.1 ± 0.9 | 5.3 ± 1.3 | 0.268 | 0.24 |
| HDL cholesterol (mmol/L) | 1.3 ± 0.4 | 1.1 ± 0.3 A | 1.2 ± 0.4 A | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 1.2 (0.9–1.7) | 1.7 (1.2–2.3) A | 1.7 (1.3–2.2) A | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| NLRP3 | IL-1α | IL-33 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adjusted R2 (explained variation) | 0.46 | 0.43 | 0.11 |
| Independent predictors | IL-1α (β = 0.18), Triglycerides (β = 0.09) | NLRP3 (β = 2.45), Triglycerides (β = 0.09) | Diastolic BP (β = −0.01) |
| Dependent Variable | NLRP3 | IL-1α | IL-33 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Independent Variables | β ± S.E. | p-Value | β ± S.E. | p-Value | β ± S.E. | p-Value |
| Group status | ||||||
| HC | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||
| PD | −0.014 ± 0.01 | 0.33 | −0.01 ± 0.04 | 0.84 | 0.140 ± 0.075 | 0.06 |
| T2DM | −0.037 ± 0.02 | 0.028 | 0.08 ± 0.03 | 0.018 | 0.057 ± 0.065 | 0.38 |
| Gender | ||||||
| Female | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||
| Male | 0.008 ± 0.01 | 0.51 | −0.047 ± 0.03 | 0.07 | −0.062 ± 0.051 | 0.22 |
| Age | −0.001 ± 0.0006 | 0.037 | 0.002 ± 0.001 | 0.20 | 0.003 ± 0.002 | 0.25 |
| BMI | 0.0001 ± 0.001 | 0.59 | −0.001 ± 0.002 | 0.45 | −0.004 ± 0.002 | 0.11 |
| WHR | −0.032 ± 0.06 | 0.59 | 0.122 ± 0.14 | 0.38 | −0.008 ± 0.27 | 0.98 |
| Systolic BP | 0.0001 ± 0.0003 | 0.65 | 0.00001 ± 0.0007 | 0.46 | 0.00001 ± 0.001 | 0.83 |
| Diastolic BP | 0.0002 ± 0.0005 | 0.84 | 0.00001 ± 0.001 | 0.71 | −0.002 ± 0.002 | 0.44 |
| Glucose | 0.003 ± 0.004 | 0.40 | −0.007 ± 0.008 | 0.40 | −0.008 ± 0.016 | 0.64 |
| HbA1C (%) | 0.008 ± 0.006 | 0.17 | 0.004 ± 0.013 | 0.74 | −0.045 ± 0.025 | 0.07 |
| Cholesterol | −0.005 ± 0.004 | 0.24 | 0.003 ± 0.010 | 0.81 | −0.007 ± 0.021 | 0.72 |
| HDL cholesterol | −0.002 ± 0.02 | 0.86 | 0.011 ±0.032 | 0.75 | −0.163 ± 0.062 | 0.009 |
| Triglycerides | 0.071 ± 0.04 | 0.07 | −0.026 ± 0.093 | 0.78 | −0.016 ± 0.179 | 0.93 |
| IL-18 | −0.022 ± 0.007 | 0.005 | 0.015 ± 0.018 | 0.41 | −0.062 ± 0.034 | 0.08 |
| IL-1α | 0.132 ± 0.046 | 0.004 | ---- | --- | −0.577 ± 0.202 | 0.004 |
| IL-1β | 0.0001 ± 0.024 | 0.99 | 0.098 ± 0.056 | 0.08 | 0.009 ± 0.110 | 0.93 |
| IL-33 | 0.064 ± 0.023 | 0.007 | −0.156 ± 0.054 | 0.004 | --- | --- |
| IL-37 | −0.002 ± 0.016 | 0.92 | 0.002 ± 0.037 | 0.96 | −0.068 ± 0.072 | 0.35 |
| NLRP3 | ---- | --- | 0.702 ± 0.243 | 0.004 | 1.269 ± 0.470 | 0.007 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alfadul, H.; Sabico, S.; Ansari, M.G.A.; Alnaami, A.M.; Amer, O.E.; Hussain, S.D.; Wani, K.; Khattak, M.N.K.; Clerici, M.; Al-Daghri, N.M. Differences and Associations of NLRP3 Inflammasome Levels with Interleukins 1α, 1β, 33 and 37 in Adults with Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051315
Alfadul H, Sabico S, Ansari MGA, Alnaami AM, Amer OE, Hussain SD, Wani K, Khattak MNK, Clerici M, Al-Daghri NM. Differences and Associations of NLRP3 Inflammasome Levels with Interleukins 1α, 1β, 33 and 37 in Adults with Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(5):1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051315
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlfadul, Hend, Shaun Sabico, Mohammed G. A. Ansari, Abdullah M. Alnaami, Osama E. Amer, Syed D. Hussain, Kaiser Wani, Malak N. K. Khattak, Mario Clerici, and Nasser M. Al-Daghri. 2023. "Differences and Associations of NLRP3 Inflammasome Levels with Interleukins 1α, 1β, 33 and 37 in Adults with Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus" Biomedicines 11, no. 5: 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051315
APA StyleAlfadul, H., Sabico, S., Ansari, M. G. A., Alnaami, A. M., Amer, O. E., Hussain, S. D., Wani, K., Khattak, M. N. K., Clerici, M., & Al-Daghri, N. M. (2023). Differences and Associations of NLRP3 Inflammasome Levels with Interleukins 1α, 1β, 33 and 37 in Adults with Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Biomedicines, 11(5), 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051315







