A Computer-Assisted Diagnostic Method for Accurate Detection of Early Nondisplaced Fractures of the Femoral Neck
Abstract
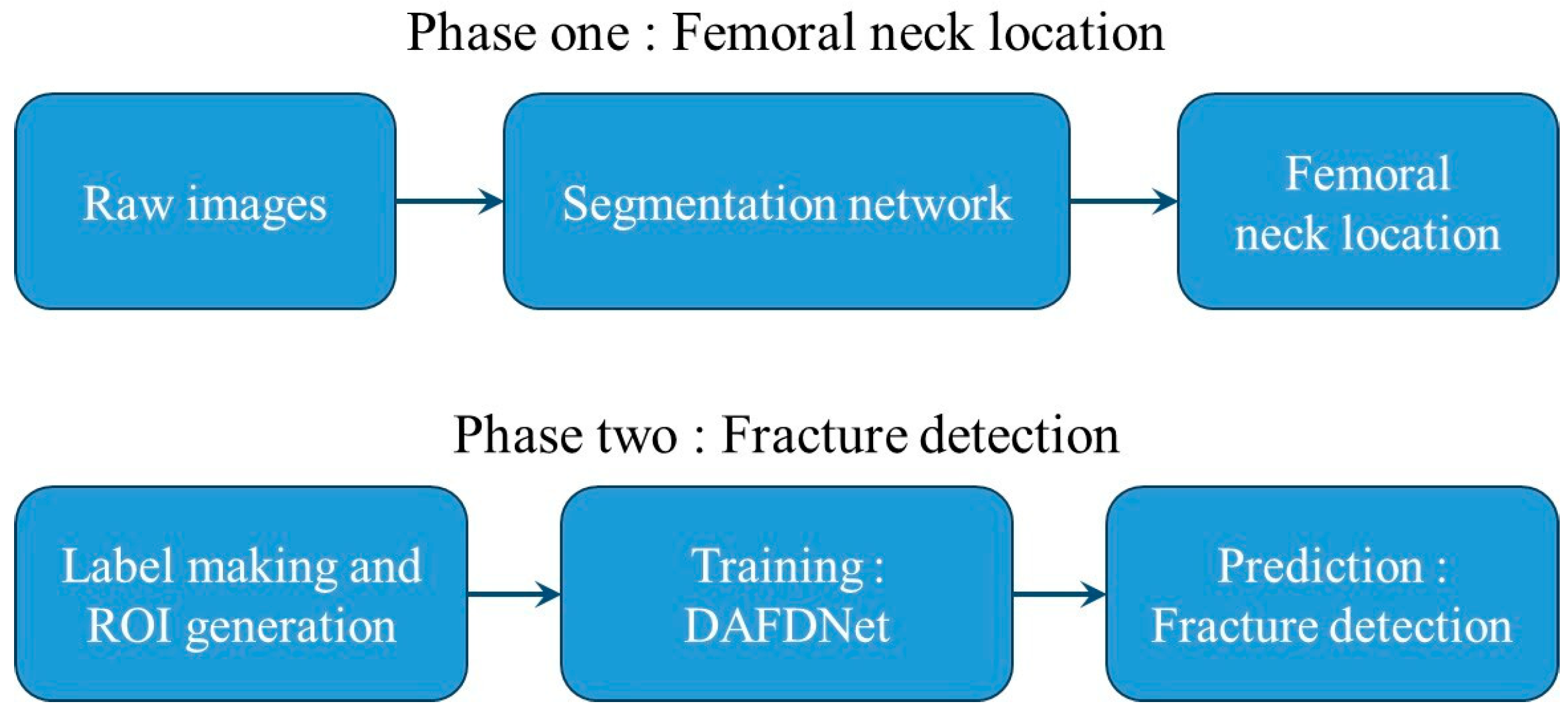
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. DCNN for FNFs
2.2. Gabor Filter
2.3. Attention Mechanism
2.4. Direction-Aware Segmentation Network
2.5. Squeeze-and-Excitation Ghost Convolution
2.6. Model Architecture
3. Experiments and Results
3.1. Dataset and Metrics
3.2. Implementation Details
3.3. Results and Comparison
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Papadimitriou, N.; Tsilidis, K.; Orfanos, P.; Benetou, V.; Ntzani, E.; Soerjomataram, I.; Künn-Nelen, A.; Pettersson-Kymmer, U.; Eriksson, S.; Brenner, H.; et al. Burden of hip fracture using disability-adjusted life-years: A pooled analysis of prospective cohorts in the CHANCES consortium. Lancet Public Health 2017, 2, e239–e246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauer, C.A.; Coca-Perraillon, M.; Cutler, D.M.; Rosen, A.B. Incidence and Mortality of Hip Fractures in the United States. JAMA 2009, 302, 1573–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marks, R. Hip fracture epidemiological trends, outcomes, and risk factors, 1970–2009. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2009, 3, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garden, R.S. Low-Angle Fixation in Fractures of the Femoral Neck. J. Bone Jt. Surgery. Br. Vol. 1961, 43, 647–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florschutz, A.V.; Langford, J.R.; Haidukewych, G.J.; Koval, K.J. Femoral Neck Fractures: Current Management. J. Orthop. Trauma 2015, 29, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoskins, W.; Rayner, J.; Sheehy, R.; Claireaux, H.; Bingham, R.; Santos, R.; Bucknill, A.; Griffin, X. The effect of patient, fracture and surgery on outcomes of high energy neck of femur fractures in patients aged 15–50. HIP Int. 2019, 29, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjertsen, J.; Fevang, J.; Matre, K.; Vinje, T.; Engesæter, L. Clinical outcome after undisplaced femoral neck fractures. Acta Orthop. 2011, 82, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutasa, S.; Varada, S.; Goel, A.; Wong, T.; Rasiej, M. Advanced Deep Learning Techniques Applied to Automated Femoral Neck Fracture Detection and Classification. J. Digit. Imaging 2020, 33, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.C.; Ha, Y.C.; Kim, T.Y.; Choi, J.A.; Koo, K.H. Initially missed occult fractures of the proximal femur in elderly patients: Implications for need of operation and their morbidity. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2010, 130, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevedello, L.M.; Erdal, B.S.; Ryu, J.L.; Little, K.J.; Demirer, M.; Qian, S.; White, R.D. Automated Critical Test Findings Identification and Online Notification System Using Artificial Intelligence in Imaging. Radiology 2017, 285, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Arif, S.M.M.R.; Knapp, K.; Slabaugh, G. Fully automatic cervical vertebrae segmentation framework for X-ray images. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2018, 157, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, W.; Oakden-Rayner, L.; Carneiro, G.; Palmer, L. Detecting hip fractures with radiologist-level performance using deep neural networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.06504. [Google Scholar]
- Kazi, A.; Albarqouni, S.; Sanchez, A.J.; Kirchhoff, S.; Biberthaler, P.; Navab, N.; Mateus, D. Automatic Classification of Proximal Femur Fractures Based on Attention Models. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Machine Learning in Medical Imaging, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 10 September 2017; pp. 70–78. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, C.; Ho, T.Y.; Lee, T.Y.; Chang, C.; Chou, C.; Chen, C.; Chung, I.; Liao, C. Application of a deep learning algorithm for detection and visualization of hip fractures on plain pelvic radiographs. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 5469–5477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olczak, J.; Fahlberg, N.; Maki, A.; Razavian, A.S.; Jilert, A.; Stark, A.; Sköldenberg, O.; Gordon, M. Artificial intelligence for analyzing orthopedic trauma radiographs: Deep learning algorithms—Are they on par with humans for diagnosing fractures? Acta Orthop. 2017, 88, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.T.; Chen, C.C.; Cheng, F.J.; Chen, H.W.; Su, Y.S.; Yeh, C.N.; Chung, I.F.; Liao, C. A Human-Algorithm Integration System for Hip Fracture Detection on Plain Radiography: System Development and Validation Study. Psychopharmacology 2020, 8, e19416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, S.; Chen, C.; Zhang, B.; Han, J.; Liu, J. Gabor Convolutional Networks. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 4357–4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Li, C.; Dan, H.; Yu, W. Gabor Feature Based Convolutional Neural Network for Object Recognition in Natural Scene. In Proceedings of the 2016 3rd International Conference on Information Science and Control Engineering (ICISCE), Beijing, China, 8–10 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sarwar, S.S.; Panda, P.; Roy, K. Gabor Filter Assisted Energy Efficient Fast Learning Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Low Power Electronics and Design (ISLPED, Taipei, Taiwan, 24–26 July 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kermany, D.S.; Goldbaum, M.; Wenjia Cai Carolina, C.S.; Valentim Liang, H.; Baxter, S.; McKeown, A.; Yang, G.; Wu, X.; Yan, F.; Dong, J.; et al. Identifying Medical Diagnoses and Treatable Diseases by Image-Based Deep Learning. Cell 2018, 172, 1122–1131.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Laurens, V.; Weinberger, K. Densely Connected Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.; Zhou, D.; Feng, J. Coordinate Attention for Efficient Mobile Network Design. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 13708–13717. [Google Scholar]
- Oktay, O.; Schlemper, J.; Folgoc, L.; Lee, M.; Heinrich, M.; Misawa, K.; Mori, K.; Mcdonagh, S.; Hammerla, N.; Kainz, B. Attention U-Net: Learning Where to Look for the Pancreas. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.03999. [Google Scholar]
- Jie, J.; Li, S.; Samuel, A.; Gang, S.; Wu, E. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, YT, USA, 18–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Woo, S.; Lee, J.Y. BAM: Bottleneck Attention Module. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.06514. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, J.; Nie, L.; Shao, J.; Liu, W.; Chua, T.-S. SCA-CNN: Spatial and Channel-Wise Attention in Convolutional Networks for Image Captioning. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6298–6306. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Gu, J.; Zhang, Z. Attention in Attention Network for Image Super-Resolution. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.09497. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Guo, J.; Xu, C. GhostNet: More Features from Cheap Operations. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Chen, G.; Ci, W. Multiclass objects detection algorithm using DarkNet-53 and DenseNet for intelligent vehicles. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2023, 2023, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakkarinen, D.K.; Banh, K.V.; Hendey, G.W. Magnetic resonance imaging identifies occult hip fractures missed by 64-slice com-puted tomography. J. Emerg. Med. 2012, 43, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.K.; Kalra, S.; Khanna, A.; Thiruvengada, M.M.; Parker, M.J. Timing of surgery for hip fractures: A systematic review of 52 published studies involving 291,413 patients. Injury 2009, 40, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolatowski, F.C.; Frihagen, F.; Bartels, S.; Opland, V.; Benth, J.; Talsnes, O.; Hoelsbrekken, S.E.; Utvåg, S.E. Screw Fixation versus Hemiarthroplasty for Nondisplaced Femoral Neck Fractures in Elderly Patients: A multicenter randomized controlled trial. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Minerva Anestesiol. 2019, 101, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Profession | Misrecognized Fracture Rate | p-Value 1 |
|---|---|---|
| ER doctor | 4.19% | <0.0001 |
| PGY-1 doctor | 7.87% | <0.0001 |
| Senior orthopedic doctor | 2.44% | <0.0001 |
| Stage | Layer | Size | Channel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input | Input | 1024 × 1024 | 1 |
| Gabor | Gab1 | 1024 × 1024 | 32 |
| Gab2 | 512 × 512 | 32 | |
| Gab3 | 256 × 256 | 32 | |
| Ghost | GhoM1 | 1024 × 1024 | 32 |
| GhoM2 | 512 × 512 | 64 | |
| GhoM3 | 256 × 256 | 128 | |
| Gabor + Ghost | GG1 | 1024 × 1024 | 64 |
| GG2 | 512 × 512 | 96 | |
| GG3 | 256 × 256 | 150 | |
| PF | PF1 | 1024 × 1024 | 32 |
| PF2 | 512 × 512 | 64 | |
| PF3 | 256 × 256 | 128 | |
| Attention Module | A1 | 1024 × 1024 | 64 |
| A2 | 512 × 512 | 128 | |
| A3 | 256 × 256 | 256 | |
| Output | Output | 1024 × 1024 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsieh, S.L.; Chiang, J.L.; Chuang, C.H.; Chen, Y.Y.; Hsu, C.J. A Computer-Assisted Diagnostic Method for Accurate Detection of Early Nondisplaced Fractures of the Femoral Neck. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 3100. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11113100
Hsieh SL, Chiang JL, Chuang CH, Chen YY, Hsu CJ. A Computer-Assisted Diagnostic Method for Accurate Detection of Early Nondisplaced Fractures of the Femoral Neck. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(11):3100. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11113100
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsieh, S. L., J. L. Chiang, C. H. Chuang, Y. Y. Chen, and C. J. Hsu. 2023. "A Computer-Assisted Diagnostic Method for Accurate Detection of Early Nondisplaced Fractures of the Femoral Neck" Biomedicines 11, no. 11: 3100. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11113100
APA StyleHsieh, S. L., Chiang, J. L., Chuang, C. H., Chen, Y. Y., & Hsu, C. J. (2023). A Computer-Assisted Diagnostic Method for Accurate Detection of Early Nondisplaced Fractures of the Femoral Neck. Biomedicines, 11(11), 3100. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11113100





