Anifrolumab for Moderate and Severe Muco-Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus: A Monocentric Experience and Review of the Current Literature
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Case Series
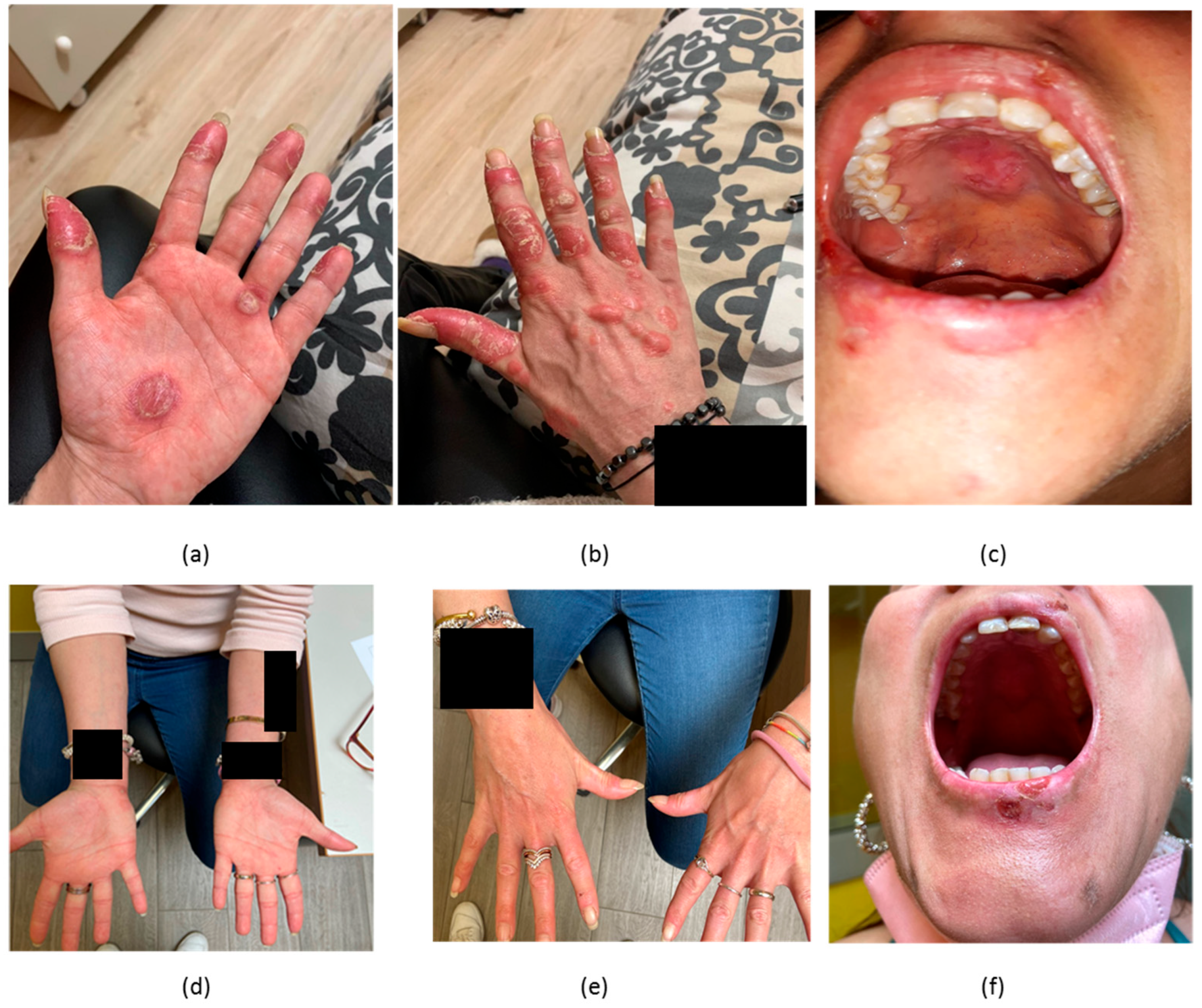
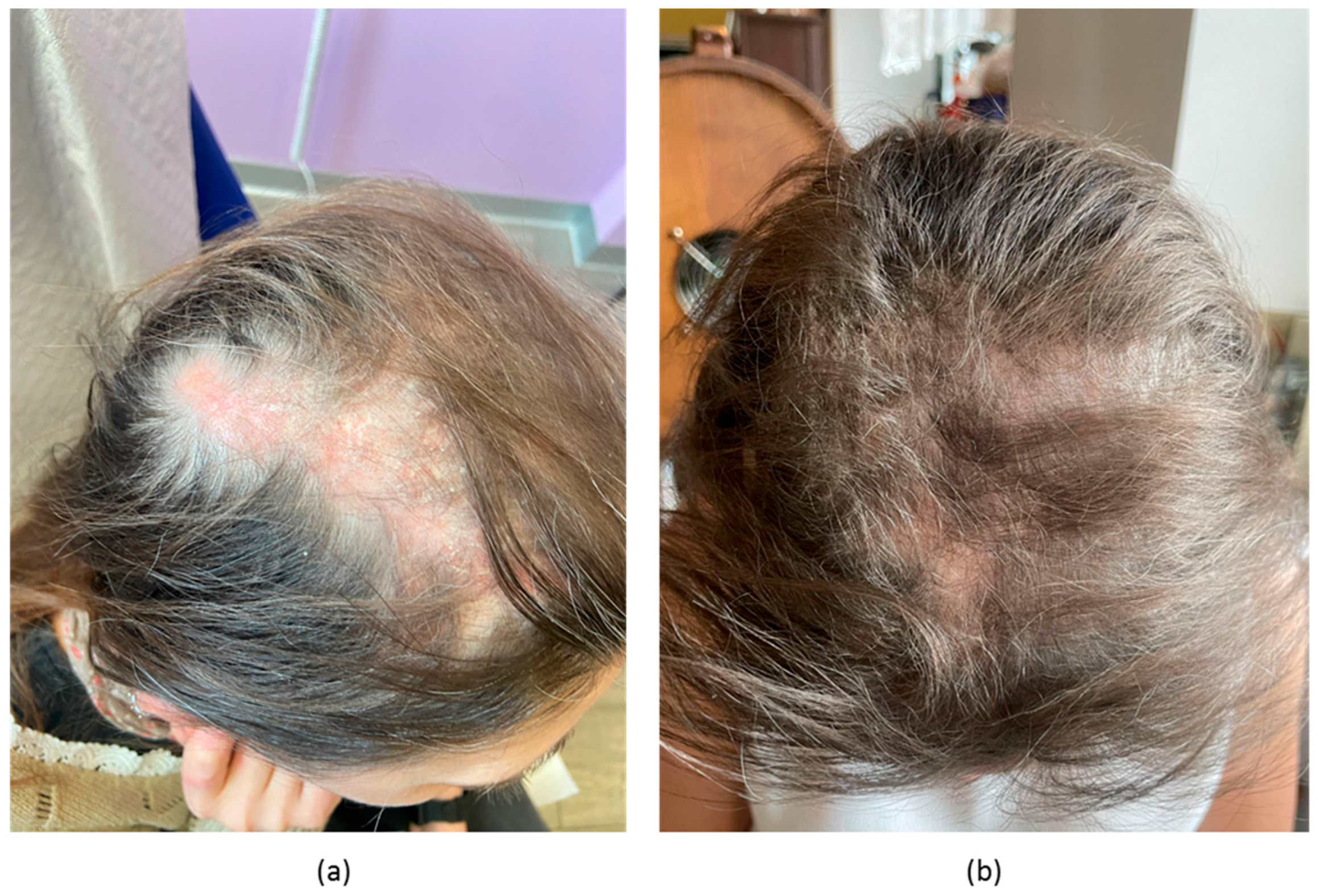
2.1. Case 1
2.2. Case 2
2.3. Case 3
2.4. Case 4
3. Summary of Clinical Data and Review of Literature
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Günther, C. Rapid response of cutaneous lupus erythematosus to treatment with the type I interferon receptor antagonist anifrolumab. Br. J. Dermatol. 2023, 189, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, F.R.; Sampath, A.J.; Foulke, G.T. Anifrolumab for treatment of refractory cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2022, 47, 1998–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, L.M.; Wigston, Z.; Laws, P.; Vital, E.M. Rapid efficacy of anifrolumab across multiple subtypes of recalcitrant cutaneous lupus erythematosus parallels changes in discrete subsets of blood transcriptomic and cellular biomarkers. Br. J. Dermatol. 2023, 189, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morand, E.F.; Furie, R.A.; Bruce, I.N.; Vital, E.M.; Dall’Era, M.; Maho, E. Efficacy of anifrolumab across organ domains in patients with moderate-to-severe systemic lupus erythematosus: A post-hoc analysis of pooled data 28 from the TULIP-1 and TULIP-2 trials. Lancet Rheumatol. 2022, 4, e282–e292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Khan, F.H.; Khan, H.B.; Saadeh, C.; Davey, N. Role of Anifrolumab in Refractory Cutaneous Manifestations of Lupus Erythematosus: A Case Series and Literature Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e39553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, E.H.; Stolarczyk, A.; Richardson, C.T. Successful treatment of severe chronic cutaneous lupus with anifrolumab: A series of 6 cases. JAAD Case Rep. 2023, 37, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chasset, F.; Jaume, L.; Mathian, A.; Abisror, N.; Dutheil, A.; Barbaud, A.; Kottler, D.; Girard, C.; Jousse-Joulin, S.; Tauber, M.; et al. Rapid efficacy of anifrolumab in refractory cutaneous lupus erythematosus. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2023, 89, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, K.; Taylor, D.; Sanchez-Melendez, S.; Barker, J.; Lonowski, S.; Shahriari, N.; Porter, H.J.; Morley, K.; LaChance, A.; Vleugels, R.A. Improvement in Mucosal Discoid Lupus Erythematosus with Anifrolumab. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2023, 27, llad190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, K.; Sanchez-Melendez, S.; Taylor, D.; Barker, J.; LaChance, A.; Shahriari, N.; Vleugels, R.A. Assessment of Clinical Response to Anifrolumab in Patients With Refractory Discoid Lupus Erythematosus. JAMA Dermatol. 2023, 159, 560–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plüß, M.; Piantoni, S.; Wincup, C.; Korsten, P. Rapid Response of Refractory Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Skin Manifestations to Anifrolumab-A Case-Based Review of Clinical Trial Data Suggesting a Domain-Based Therapeutic Approach. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trentin, F.; Tani, C.; Elefante, E.; Stagnaro, C.; Zucchi, D.; Mosca, M. Treatment with Anifrolumab for Discoid Lupus Erythematosus. JAMA Dermatol. 2023, 159, 224–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.N.; Perez-Chada, L.M.; Borucki, R.; Nambudiri, V.E.; Werth, V.P.; Merola, J.F. Development of a working core outcome set for cutaneous lupus erythematosus: A practical approach to an urgent unmet need. Lupus Sci. Med. 2021, 8, e000529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, J.W.H.; Ng, C.H.; Tay, S.H. Biologics targeting type I interferons in SLE: A meta-analysis and systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Lupus 2020, 29, 1845–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furie, R.; Khamashta, M.; Merrill, J.T.; Werth, V.P.; Kalunian, K.; Brohawn, P.; Illei, G.G.; Drappa, J.; Wang, L.; Yoo, S.; et al. Anifrolumab, an Anti-Interferon-alpha Receptor Monoclonal Antibody, in Moderate-to-Severe Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Romo, G.S.; Caielli, S.; Vega, B.; Connolly, J.; Allantaz, F.; Xu, Z.; Punaro, M.; Baisch, J.; Guiducci, C.; Coffman, R.L.; et al. Netting neutrophils are major inducers of type I IFN production in pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 73ra20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jego, G.; Palucka, A.K.; Blanck, J.P.; Chalouni, C.; Pascual, V.; Banchereau, J. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells induce plasma cell differentiation through type I interferon and interleukin 6. Immunity. 2003, 19, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, K.; Beignon, A.S.; Bhardwaj, N. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells: Linking innate and adaptive immunity. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathian, A.; Breillat, P.; Dorgham, K.; Bastard, P.; Charre, C.; Lhote, R.; Quentric, P.; Moyon, Q.; Mariaggi, A.A.; Mouries-Martin, S.; et al. Lower disease activity but higher risk of severe COVID-19 and herpes zoster in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus with pre-existing autoantibodies neutralising IFN-alpha. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 1695–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hile, G.A.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Kahlenberg, J.M. The influence of interferon on healthy and diseased skin. Cytokine 2020, 132, 154605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorio, J.; Meller, S.; Conrad, C.; Di Nardo, A.; Homey, B.; Lauerma, A.; Arai, N.; Gallo, R.L.; Digiovanni, J.; Gilliet, M. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells sense skin injury and promote wound healing through type I interferons. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 2921–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stannard, J.N.; Reed, T.J.; Myers, E.; Lowe, L.; Sarkar, M.K.; Xing, X.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Kahlenberg, J.M. Lupus Skin Is Primed for IL-6 Inflammatory Responses through a Keratinocyte-Mediated Autocrine Type I Interferon Loop. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachdeva, S. Fitzpatrick skin typing: Applications in dermatology. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2009, 75, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Australian_Government. Fitzpatrick Skin Phototype. 2023. Available online: https://www.arpansa.gov.au/sites/default/files/legacy/pubs/RadiationProtection/FitzpatrickSkinType.pdf?acsf_files_redirect (accessed on 13 July 2023).
- Ramirez, G.A.; Canti, V.; Moiola, L.; Magnoni, M.; Rovere-Querini, P.; Coletto, L.A.; Dagna, L.; Manfredi, A.A.; Bozzolo, E.P. Performance of SLE responder index and lupus low disease activity state in real life: A prospective cohort study. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 22, 1752–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morand, E.F.; Furie, R.; Tanaka, Y.; Bruce, I.N.; Askanase, A.D.; Richez, C.; Bae, S.C.; Brohawn, P.Z.; Pineda, L.; Berglind, A.; et al. Trial of Anifrolumab in Active Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furie, R.A.; Morand, E.F.; Bruce, I.N.; Manzi, S.; Kalunian, K.C.; Vital, E.M.; Ford, T.L.; Gupta, R.; Hiepe, F.; Santiago, M. Type I interferon inhibitor anifrolumab in active systemic lupus erythematosus (TULIP-1): A randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Rheumatol. 2019, 1, e208–e219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastard, P.; Rosen, L.B.; Zhang, Q.; Michailidis, E.; Hoffmann, H.H.; Zhang, Y.; Dorgham, K.; Philippot, Q.; Rosain, J.; Beziat, V.; et al. Autoantibodies against type I IFNs in patients with life-threatening COVID-19. Science 2020, 370, eabd4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalunian, K.C.; Furie, R.; Morand, E.F.; Bruce, I.N.; Manzi, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Winthrop, K.; Hupka, I.; Zhang, L.J.; Werther, S.; et al. A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Phase III Extension Trial of the Long-Term Safety and Tolerability of Anifrolumab in Active Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023, 75, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ref. | n | Age, Gender | Phototype | Body Area | CLE Subtypes | Mucosal Involvement | Disease Duration (years) | CLASI-A | SLEDAI | Concomitant Therapies | Side Effects | Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Khan et al. [5] | 2 | 39, F | II | Chest | SCLE | No | 18 | NR | NR | PDN | No | Yes |
| 28, F | II | Hands | CCLE | No | NR | NR | NR | PDN | No | Yes | ||
| Chasset et al. [7] | 11 | 35 | I–IV (7) V–VI (4) | NR | DLE (10), SCLE (4), Chilblain lupus (1), | Yes (4) | 12 (3–23) | 15 (4–35) | 8 (4–22) | HCQ (10) CQ (1) MTX (2) MM (2) Thalidomide (2) Steroids (9) | COVID-19 (1), herpes zoster (1), palmar warts (1), mucosal candidiasis (1) | Yes |
| Kowalski et al. [6] | 6 | 48 (37–66) | I–III (3) V–VI (3) | Trunk, limbs, head/neck | DLE (4) CCLE (2) | No | 10.5 (2–26) | NR | NR | HCQ (3), AZA (1), steroids (2), CQ (1) | VZV (1) | Yes |
| Pluss et al. [10] | 1 | 30, F | II | Chest and upper limbs | SCLE | No | 15 | 17 | 10 | MM | No | Yes |
| Trentin et al. [11] | 2 | 31 59 | III III | Head/Neck Head/Neck with scarring alopecia | DLE DLE, chilblain | No No | NR NR | 26 24 | 13 10 | MTX + steroids No | No | Yes Yes |
| No | ||||||||||||
| Shaw et al. [9] | 8 | 42.5 (19–75) | I–III (2) IV–V (3) VI (3) | NR | DLE | NR | NR | 17.1 | NR | Steroids (1), HCQ (4), MMF (2), IVIG (2), THL (1), ACT (1), None (2) | None | Yes |
| Shaw et al. [8] | 7 | 28 (30–40) | IV (3) V (4) | Lips (6), Hard palate (6), Tongue (1), nasal mucosa (1) | SLE + DLE | Yes | NR | NR | 8 (4–12) | HCQ (6), MMF (3), ACT (1), THL (1), PDN (1) None | No | CR 86% PR 14% |
| Blum et al. [2] | 3 | 35 (22–51) | VI (3) | Head/neck (3), limbs (1) | SLE + CLE | No | 11.3 (9–13) | NR | NR | HCQ (3), MM (2), AZA (1) | No | Yes |
| Carter et al. [3] | 7 | 46 (33–64) | NR | Head/neck, trunk, limbs (3) | DLE (5), chilblain lupus (1), SCLE (1) | NR | 17 (6–26) | 17 | NR | PDN (3) | UTI (2), URI/bronchitis (1) and otitis externa (1). COVID-19 + polydermatomal shingles and VZV oticus (1) | Yes 1 |
| Our case series | 4 | 35.5 (25–44) | II 2 III 2 | Trunk (4), head/neck region (4), hands (1), scarring alopecia (1), oral (2), genital (1) | SLE with muco-cutaneous involvement (3), DLE (1) | Yes | 9 (5 years–12 years) | 19.5 (12–27) | 10.25 | HCQ (4), MMF (4), PDN (3) | Genital candidiasis (2), HSV1 (1) | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paolino, G.; Ramirez, G.A.; Calabrese, C.; Moroni, L.; Bianchi, V.G.; Bozzolo, E.P.; Mercuri, S.R.; Dagna, L. Anifrolumab for Moderate and Severe Muco-Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus: A Monocentric Experience and Review of the Current Literature. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2904. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11112904
Paolino G, Ramirez GA, Calabrese C, Moroni L, Bianchi VG, Bozzolo EP, Mercuri SR, Dagna L. Anifrolumab for Moderate and Severe Muco-Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus: A Monocentric Experience and Review of the Current Literature. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(11):2904. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11112904
Chicago/Turabian StylePaolino, Giovanni, Giuseppe A. Ramirez, Chiara Calabrese, Luca Moroni, Vittoria Giulia Bianchi, Enrica P. Bozzolo, Santo Raffaele Mercuri, and Lorenzo Dagna. 2023. "Anifrolumab for Moderate and Severe Muco-Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus: A Monocentric Experience and Review of the Current Literature" Biomedicines 11, no. 11: 2904. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11112904
APA StylePaolino, G., Ramirez, G. A., Calabrese, C., Moroni, L., Bianchi, V. G., Bozzolo, E. P., Mercuri, S. R., & Dagna, L. (2023). Anifrolumab for Moderate and Severe Muco-Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus: A Monocentric Experience and Review of the Current Literature. Biomedicines, 11(11), 2904. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11112904







