Healing of Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis by Non-Thermal Plasma: Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akintoye, S.; Greenberg, M. Recurrent aphthous stomatitis. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 58, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, C.B.; Smith, G.P. Recurrent aphthous stomatitis: A comprehensive review and recommendations on therapeutic options. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borilova Linhartova, P.; Janos, J.; Slezakova, S.; Bartova, J.; Petanova, J.; Kuklinek, P.; Fassmann, A.; Dusek, L.; Izakovicova Holla, L. Recurrent aphthous stomatitis and gene variability in selected interleukins: A case–control study. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2018, 126, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.; Fang, H.; Li, Q.L.; Cao, Y.; Xia, R.; Zhang, Z.H. Effectiveness of laser therapy in the management of recurrent aphthous stomatitis: A systematic review. Scientifica 2016, 2016, e9062430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, S.I.; Costa, A.M.; de Vasconcelos, B.C.; Amarante, M.V.; Teixeira, P.T.; de Vasconcelos Gurgel, B.C.; Dantas da Silveira, É.J. Recurrent aphthous ulceration: An epidemiological study of etiological factors, treatment and differential diagnosis. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2018, 93, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Bernal, J.; Conejero, C.; Conejero, R. Recurrent aphthous stomatiti. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2020, 111, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasmi, B.A.; Noor, S.; Menzel, A.; Gasmi, A. Oral aphthous: Pathophysiology, clinical aspects and medical treatment. Arch. Razi Inst. 2021, 76, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmeier, L.A.; Fortune, F. Clinical management of oral mucosal disease: A literature review. In Oral Mucosa in Health and Disease; Bergmeier, L., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikaly, S.K.; Saikaly, T.S.; Saikaly, L.E. Recurrent aphthous ulceration: A review of potential causes and novel treatments. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2018, 29, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ng, K.; Kuo, C.; Wu, D. Chinese herbal medicine for recurrent aphthous stomatitis: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, e13681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, S.G.; Cohen, D.M.; Clark, A.N. Ulcerated Lesions of the Oral Mucosa: Clinical and Histologic Review. Head Neck Pathol. 2019, 13, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szyszkowska, B.; Łepecka-Klusek, C.; Kozłowicz, K.; Jazienicka, I.; Krasowska, D. The influence of selected ingredients of dietary supplements on skin condition. Postepy. Dermatol. Alergol. 2014, 31, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belenguer-Guallar, I.; Jiménez-Soriano, Y.; Claramunt-Lozano, A. Treatment of recurrent aphthous stomatitis. A literature review. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2014, 6, e168–e174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafa, M.G.; Ghalwash, D.; El-Kersh, D.M.; Elmazar, M.M. Propolis-based niosomes as oromuco-adhesive films: A randomized clinical trial of a therapeutic drug delivery platform for the treatment of oral recurrent aphthous ulcers. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 18056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hará, Y.; Shiratuchi, H.; Kaneko, T.; Sakagami, H. Search for drugs used in hospitals to treat stomatitis. Medicines 2019, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvaninejad, R.; Navabi, N.; Khoshroo, M.R.; Torabi, N.; Atai, Z. Herbal medicine in treatment of recurrent aphthous stomatitis: A literature review. J. Iran. Dent. Assoc. 2017, 29, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, V.; Gulati, M.; Govila, V.; Anand, B. Low level laser therapy in the treatment of aphthous ulcer. J. Dent. Res. 2013, 24, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasry, S.A.; El Shenawy, H.M.; Mostafa, D.; Ammar, N.M. Different modalities for treatment of recurrent aphthous stomatitis. A randomized clinical trial. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2016, 8, e517–e522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suter, V.G.A.; Sjölund, S.; Bornstein, M.M. Effect of laser on pain relief and wound healing of recurrent aphthous stomatitis: A systematic review. Lasers Med. Sci. 2017, 32, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahromi, N.Z.; Ghapanchi, J.; Pourshahidi, S.; Zahed, M.; Ebrahimi, H. Clinical evaluation of high and low-level laser treatment (CO2 vs InGaAlP diode laser) for Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis. J. Dent. 2017, 18, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Melis, M.; Di Giosia, M.; Colloca, L. Ancillary factors in the treatment of orofacial pain: A topical narrative review. J. Oral Rehabil. 2019, 46, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Avinash, A.; Katiyar, S.; Iyer, A.A.; Jain, S. Dental applications of ozone therapy: A review of literature. Saudi J. Dent. Res. 2017, 8, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbah, F.; Nogales, C.G.; Zaremski, E.; Martinez-Sanchez, G. Ozone therapy in dentistry—Where we are and where we are going to? Rev. Esp. Ozonot. 2018, 8, 37–63. [Google Scholar]
- Bader, K.A.Z. Management of denture-related traumatic ulcers using ozone. J. Prosth. Dent. 2019, 121, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirmala, M.; Smitha, S.G.; Kamath, G. A study to assess the efficacy of local application of oral probiotic in treating recurrent aphthous ulcer and oral Candidiasis. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 71, S113–S117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubin, D.H.E. Effect of correlations on the thermal equilibrium and normal modes of a non-neutral plasma. Phys. Rev. E 1996, 53, 5268–5290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hama-Aziz, K.H.; Miessner, H.; Mueller, S.; Kalass, D.; Moeller, D.; Khorshid, I.; Rashid, M.A.M. Degradation of pharmaceutical diclofenac and ibuprofen in aqueous solution, a direct comparison of ozonation, photocatalysis, and non-thermal plasma. Chem. Engen. J. 2017, 313, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajiyama, H.; Utsumi, F.; Nakamura, K.; Tanaka, H.; Toyokuni, S.; Hori, M.; Kikkawa, F. Future perspective of strategic non-thermal plasma therapy for cancer treatment. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2017, 60, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laroussi, M. Plasma medicine: A brief introduction. Plasma 2018, 1, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubuc, A.; Monsarrat, P.; Virard, F.; Merbahi, N.; Sarrette, J.P.; Laurencin-Dalicieux, S.; Cousty, S. Use of cold-atmospheric plasma in oncology: A concise systematic review. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2018, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.Y.; Hong, Y.J.; Lim, J.; Choi, J.S.; Choi, E.H.; Kang, S.; Rhim, H. Cold atmospheric plasma (CAP), a novel physicochemical source, induces neural differentiation through cross-talk between the specific RONS cascade and Trk/Ras/ERK signaling pathway. Biomaterials 2018, 156, 258–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, H.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, G.C.; Kim, S.S.; Han, S.; Song, K. Non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma is an excellent tool to activate proliferation in various mesoderm-derived human adult stem cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 134, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Cao, Y.; Lu, X. The state of the art of applications of atmospheric-pressure nonequilibrium plasma jets in dentistry. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2016, 44, 134–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancourt-Ángeles, M.; Peña-Eguiluz, R.; López-Callejas, R.; Domínguez-Cadena, N.A.; Mercado-Cabrera, A.; Muñoz-Infante, J.; Rodríguez-Méndez, B.G.; Valencia-Alvarado, R.; Moreno-Tapia, J.A. Treatment in the healing of burns with a cold plasma source. Int. J. Burns Trauma 2017, 7, 142–146. [Google Scholar]
- de Masi, G.; Gareri, C.; Cordaro, L.; Fassina, A.; Brun, P.; Zaniol, B.; Cavazzana, R.; Martines, E.; Zuin, M.; Marinaro, G.; et al. Plasma coagulation controller: A low-power atmospheric plasma source for accelerated blood coagulation. Plasma Med. 2018, 8, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Callejas, R.; Peña-Eguiluz, R.; Valencia-Alvarado, R.; Mercado-Cabrera, A.; Rodríguez-Méndez, B.G.; Serment-Guerrero, J.H.; Cabral-Prieto, A.; González-Garduño, A.C.; Domínguez-Cadena, N.A.; Muñoz-Infante, J.; et al. Alternative method for healing the diabetic foot by means of a plasma needle. Clin. Plasma Med. 2018, 9, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, W.J.J.M.; Skorpil, N.E.; Ashton-James, C.E.; Tuinzing, D.B.; Forouzanfar, T. Effect of vasoconstriction on pain after mandibular third molar surgery: A single-blind, randomized controlled trial. Quintessence Int. 2016, 47, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Eguiluz, R.; Serment-Guerrero, J.H.; Azorín-Vega, E.P.; Mercado-Cabrera, A.; Flores-Fuentes, A.A.; Jaramillo-Sierra, B.; Hernández-Arias, A.N.; Girón-Romero, K.; López-Callejas, R.; Rodríguez-Méndez, B.G.; et al. Development and characterization of a non-thermal plasma source for therapeutic treatments. IEEE. Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 68, 1467–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection. Guidelines on limits of exposure to ultraviolet radiation of wavelengths between 180 nm and 400 nm (incoherent optical radiation). Health Phys. 2004, 87, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, J.A.; Normando, A.G.C.; de Toledo, I.P.; Melo, G.; de Luca Canto, G.; Santos-Silva, A.R.; Silva-Guerra, E.N. Laser therapy for recurrent aphthous stomatitis: An overview. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020, 24, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Z.; Tomar, D.; Kaushik, S.; Mittal, S.; Kumar, P. Application of soft tissue laser in the management of recurrent apthous stomatitis: A placebo controlled study. Int. J. Health Sci. 2022, 6, 2590–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagieb, C.S.; Harhash, T.A.E.; Fayed, H.L.; Ali, S. Evaluation of diode laser versus topical corticosteroid in management of Behcet’s disease-associated oral ulcers: A randomized clinical trial. Clin. Oral Investig. 2022, 26, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makvandi, P.; Josic, U.; Delfi, M.; Pinelli, F.; Jahed, V.; Kaya, E.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Zarepour, A.; Rossi, F.; Zarrabi, A.; et al. Drug delivery (nano) platforms for oral and dental applications: Tissue regeneration, infection control, and cancer management. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, e2004014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Wu, N.; Nini Wang, N.; Li, J.; Sun, J.; Peng, Q. Chitosan-based therapeutic systems and their potentials in treatment of oral diseases. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222, 3178–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scully, C.; Porter, S. Oral mucosal disease: Recurrent aphthous stomatitis. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2008, 46, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarom, N.; Zelig, K.; Epstein, J.B.; Gorsky, M. The efficacy of minocycline mouth rinses on the symptoms associated with recurrent aphthous stomatitis: A randomized, double-blind, crossover study assessing different doses of oral rinse. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2017, 123, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekbağrıyanık, T.; Dadas, F.K.; Enhoş, Ş. Effects of non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma on palatal wound healing of free gingival grafts: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin. Oral Investig. 2021, 25, 6269–6278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, M.; Hemalatha, V.T.; Sundar, N.M.; Nisha, A. Applications of cold atmospheric pressure plasma in dentistry—A review. J. Pharm. Res. Int. 2022, 34, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, H.G.; Albaba, M.R.; Caygur, A.; Cengiz, E.; Boke-Karacaoglu, F.; Tumer, H. Treatment of recurrent aphthous stomatitis with Er,Cr:YSGG laser irradiation: A randomized controlled split mouth clinical study. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 170, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, H.; Singh, M.P.; Nahar, P.; Mathur, H.; Sowmya, G.V. Efficacy of low-level laser therapy in treatment of recurrent aphthous ulcers—A sham controlled, split mouth follow up study. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2014, 8, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalabonova, H.; Daskalov, H. Clinical assessment of the therapeutic effect of low-level laser therapy on chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2014, 28, 929–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa, A.C.T.; da Rocha, Í.B.P.; de Carvalho, A.F.M.; de Freitas Coelho, N.P.M.; Feitosa, M.C.P.; Barros, E.M.L.; Arisawa, E.A.L.; de Amorim, M.R.L. Comparative study between low level laser and therapeutic ultrasound in second intertion ulcers repair in mice. J. Laser Med. Sci. 2018, 9, 14–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamishehkar, H.; Nokhodchi, A.; Ghambarzadeh, S.; Kouhsoltani, M. Triamcinolone acetonide oromucoadhesive paste for treatment of aphthous stomatitis. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 5, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, H.; Meng, Y.; Wu, C.; Sun, Y.; Xu, Y.; Deng, X.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L. Role of biologics in refractory recurrent aphthous stomatitis. J. Oral Path. Med. 2022, 51, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shavakhi, M.; Sahebkar, A.; Shirban, F.; Bagherniya, M. The efficacy of herbal medicine in the treatment of recurrent aphthous stomatitis: A systematic review of randomized clinical trials. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 672–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, M.R.; Hosseini, M.S.; Fatollah, S.; Mirpour, S.; Ghoranneviss, M.; Larijani, B.; Mohajeri-Tehrani, M.R.; Khorramizadeh, M.R. Beneficial effects of cold atmospheric plasma on inflammatory phase of diabetic foot ulcers; a randomized clinical trial. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2020, 19, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, N.; Ryu, J.J.; Choi, E.H.; Kaushik, N.K. Generation and role of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species induced by plasma, lasers, chemical agents, and other systems in dentistry. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 7542540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
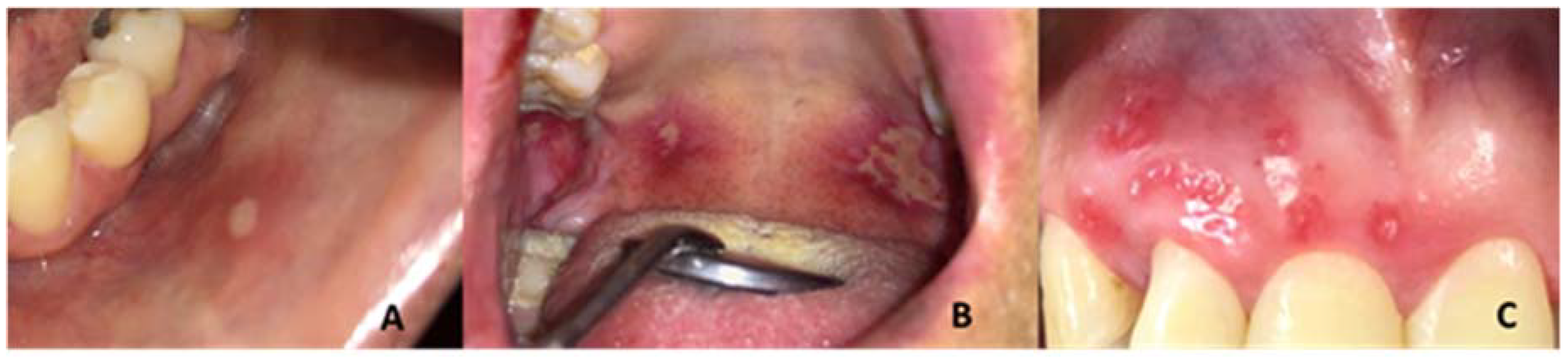



| Recurrent Herpetiform Ulcers | Major Recurrent Ulcers | Minor Recurrent Ulcers | Fisher’s Exact | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 10 | 0.01 | ||
| Female | 1 | 10 | 9 | |
| Age | ||||
| 18–30 | 2 | 9 | 0.005 | |
| 31–50 | 1 | 7 | ||
| 51–67 | 8 | 3 | ||
| Marital status | ||||
| Married | 1 | 8 | 6 | 0.02 |
| Single | 2 | 13 | ||
| Scholarship | ||||
| High school | 2 | 3 | 0.04 | |
| Basic | 1 | 8 | 6 | |
| Bachelor’s degree | 10 | |||
| Occupation | ||||
| Unemployed | 3 | 1 | 0.003 | |
| Student | 2 | 3 | ||
| Homework | 1 | 5 | 1 | |
| Employee | 14 | |||
| Medication consumption | ||||
| Not | 1 | 2 | 11 | 0.08 |
| Yes | 8 | 8 | ||
| Smoking | ||||
| Cigarette | 3 | 4 | 0.73 | |
| No | 1 | 7 | 15 | |
| Alcohol consumption | ||||
| 2 to 4 times a month | 1 | 0.02 | ||
| Never | 1 | 8 | 4 | |
| Once a year | 1 | 8 | ||
| Once a month | 7 | |||
| Ulcers evolution time | ||||
| Two to five days | 1 | 4 | 10 | 0.69 |
| Six to ten days | 6 | 8 | ||
| One day | 1 | |||
| Ulcers recurrence period | ||||
| Zero | 1 | 0.07 | ||
| One for year | 1 | 5 | 2 | |
| One for month | 5 | 5 | ||
| One for week | 3 | |||
| More than a year | 8 | |||
| Mean and Standard Deviation of Ulcer Size | ||
|---|---|---|
| Initial | 6.9 ± 4.51 A | 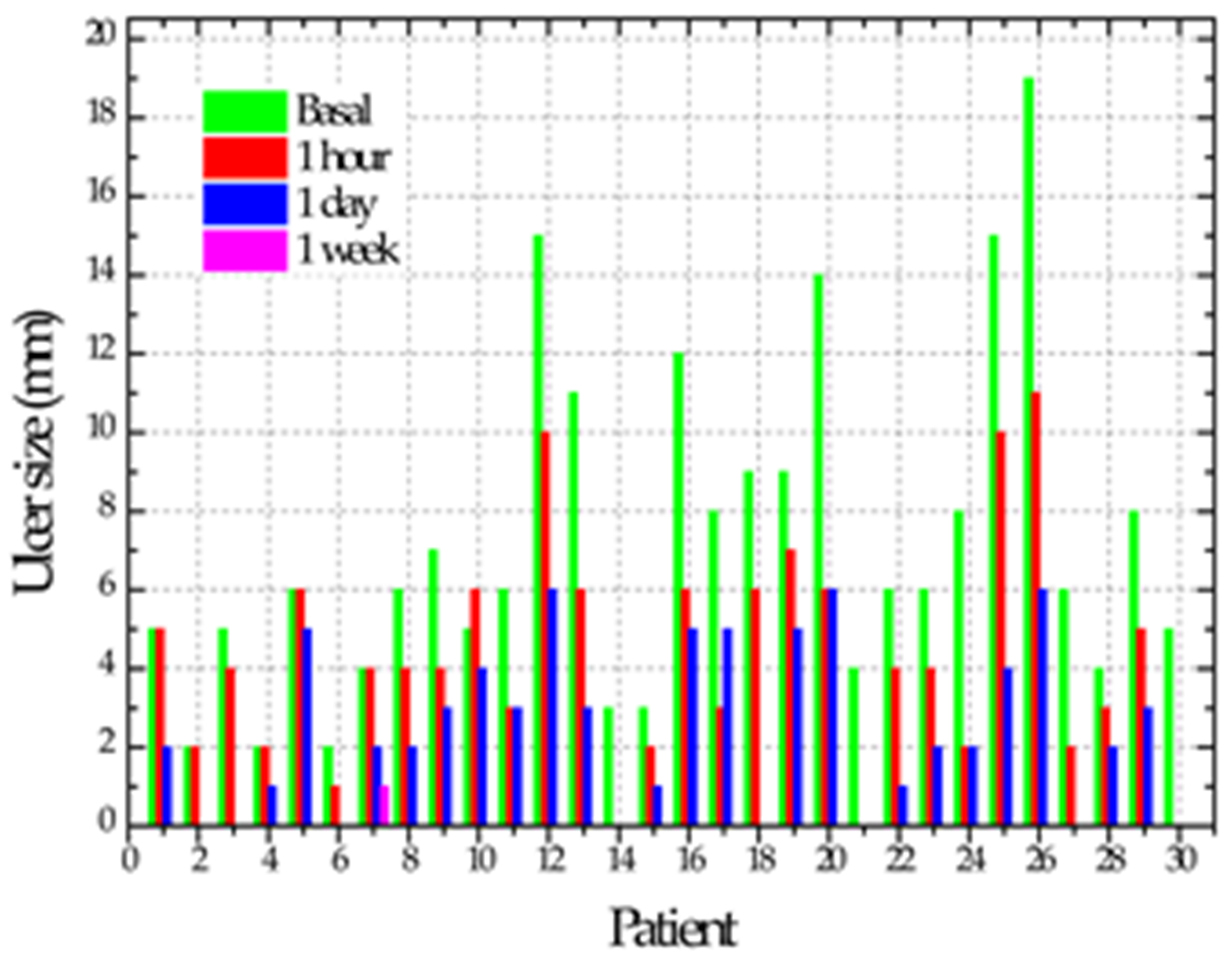 |
| One hour | 3.96 ± 3.1 B | |
| One day | 2 ± 2 BC | |
| One week | 0.03 ± 0.18 C | |
| p | <0.0001 | |
| Mean and Standard Deviation of Pain | ||
| Initial | 7.1 ± 2.5 A | 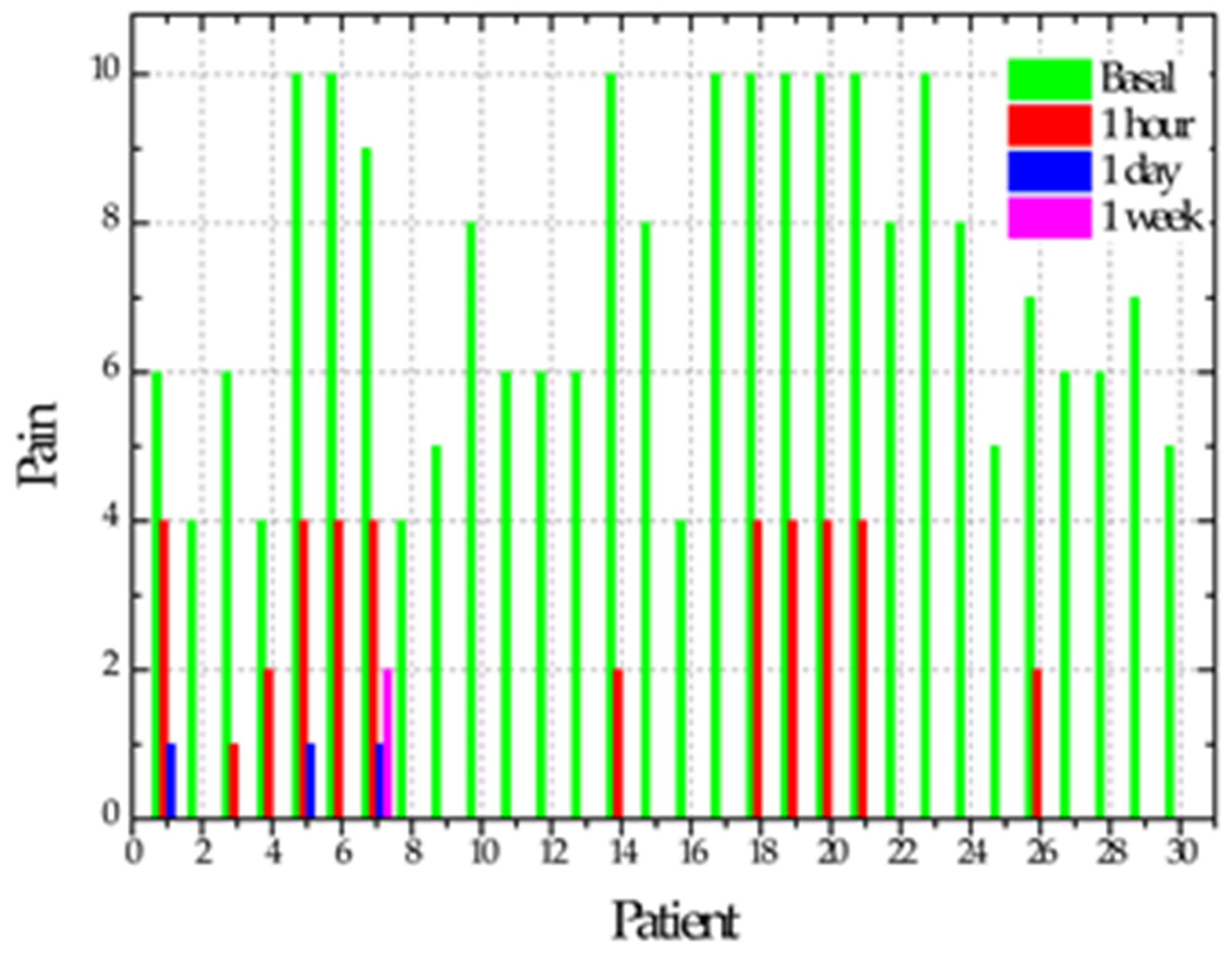 |
| One hour | 1.5 ± 2.3 B | |
| One day | 0.2 ± 0.7 C | |
| One week | 0.06 ± 0.3 C | |
| p | <0.0001 | |
| Mean and Standard Deviation of Erythema Size | ||
| Initial | 2.1 ± 1.1 A | 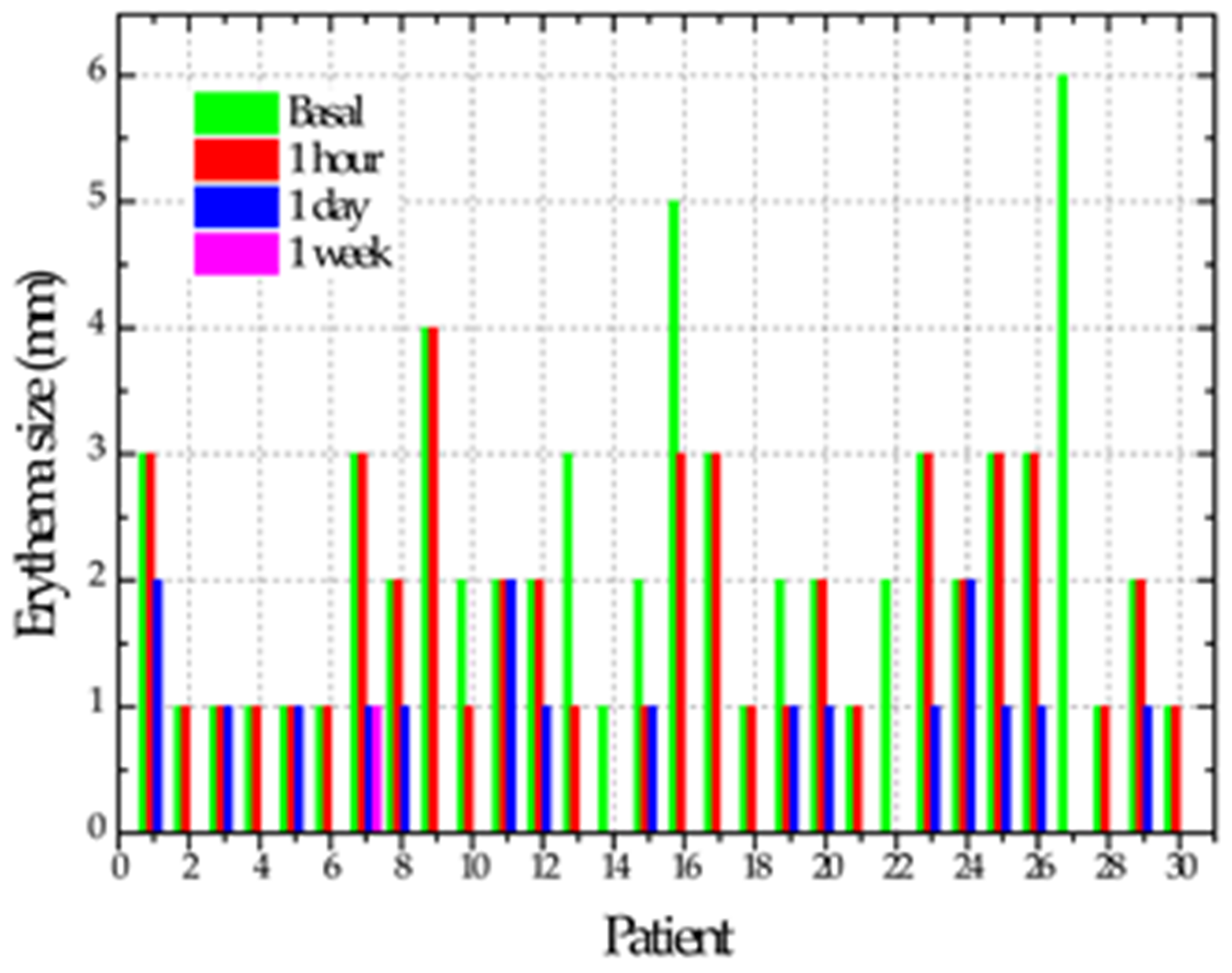 |
| One hour | 1.4 ± 1 B | |
| One day | 0.5 ± 0.6 C | |
| One week | 0.03 ± 0.18 C | |
| p | <0.0001 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ibáñez-Mancera, N.G.; López-Callejas, R.; Toral-Rizo, V.H.; Rodríguez-Méndez, B.G.; Lara-Carrillo, E.; Peña-Eguiluz, R.; do Amaral, R.C.; Mercado-Cabrera, A.; Valencia-Alvarado, R. Healing of Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis by Non-Thermal Plasma: Pilot Study. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11010167
Ibáñez-Mancera NG, López-Callejas R, Toral-Rizo VH, Rodríguez-Méndez BG, Lara-Carrillo E, Peña-Eguiluz R, do Amaral RC, Mercado-Cabrera A, Valencia-Alvarado R. Healing of Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis by Non-Thermal Plasma: Pilot Study. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(1):167. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11010167
Chicago/Turabian StyleIbáñez-Mancera, Norma Guadalupe, Régulo López-Callejas, Víctor Hugo Toral-Rizo, Benjamín Gonzalo Rodríguez-Méndez, Edith Lara-Carrillo, Rosendo Peña-Eguiluz, Regiane Cristina do Amaral, Antonio Mercado-Cabrera, and Raúl Valencia-Alvarado. 2023. "Healing of Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis by Non-Thermal Plasma: Pilot Study" Biomedicines 11, no. 1: 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11010167
APA StyleIbáñez-Mancera, N. G., López-Callejas, R., Toral-Rizo, V. H., Rodríguez-Méndez, B. G., Lara-Carrillo, E., Peña-Eguiluz, R., do Amaral, R. C., Mercado-Cabrera, A., & Valencia-Alvarado, R. (2023). Healing of Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis by Non-Thermal Plasma: Pilot Study. Biomedicines, 11(1), 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11010167






