Cerebrospinal Fluid in Classical Trigeminal Neuralgia: An Exploratory Study on Candidate Biomarkers
Abstract: Background
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Study Design
2.2. CSF Collection
2.3. Proximity Extension Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethics
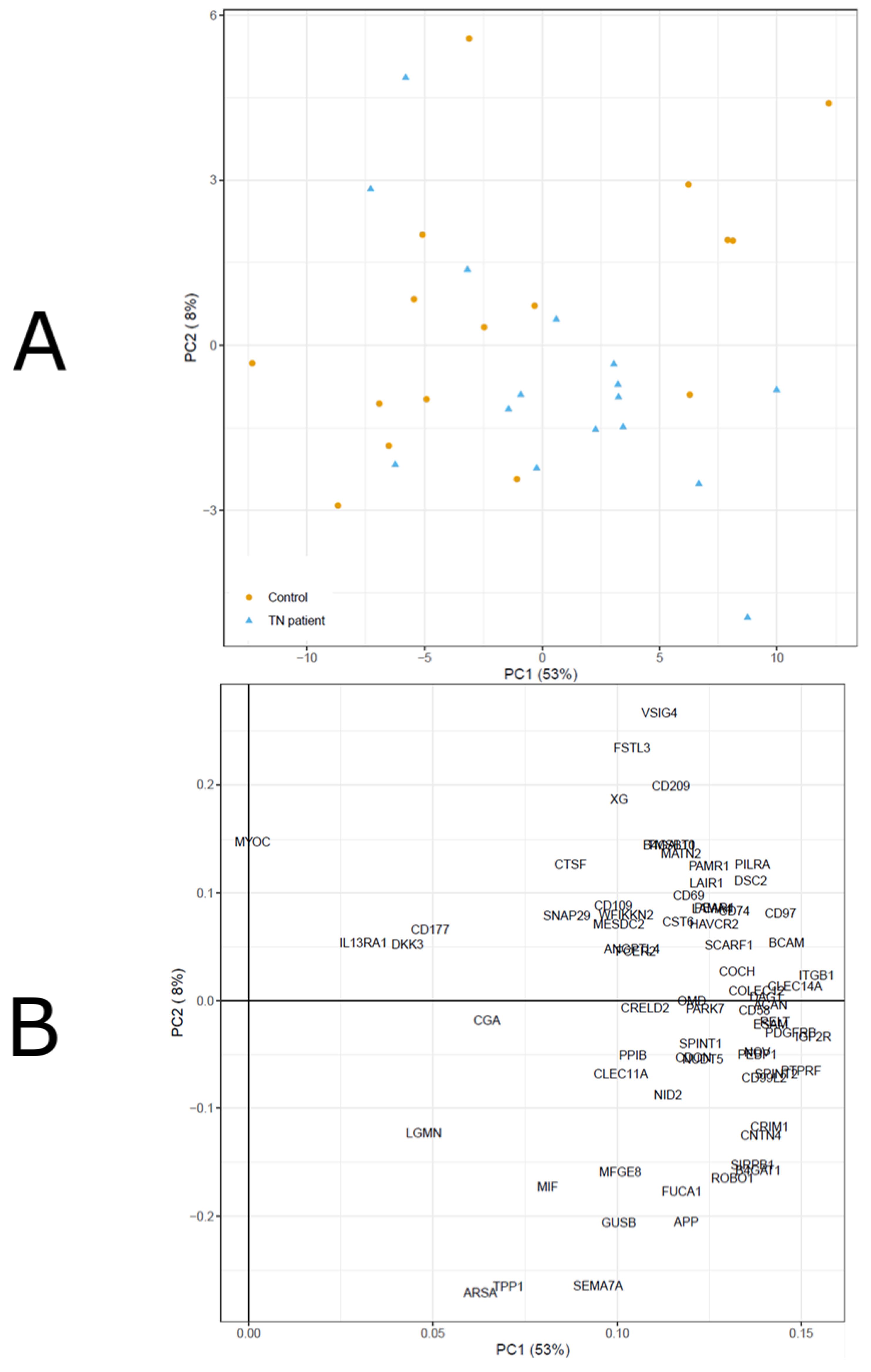
3. Results
Patients
4. Discussion
Methodological Considerations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bendtsen, L.; Zakrzewska, J.M.; Heinskou, T.B.; Hodaie, M.; Leal, P.R.L.; Nurmikko, T.; Obermann, M.; Cruccu, G.; Maarbjerg, S. Advances in diagnosis, classification, pathophysiology, and management of trigeminal neuralgia. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 784–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjaastad, O.; Bakketeig, L.S. The rare, unilateral headaches. Vågå study of headache epidemiology. J. Headache Pain 2007, 8, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mueller, D.; Obermann, M.; Yoon, M.S.; Poitz, F.; Hansen, N.; Slomke, M.A.; Dommes, P.; Gizewski, E.; Diener, H.C.; Katsarava, Z. Prevalence of trigeminal neuralgia and persistent idiopathic facial pain: A population-based study. Cephalalgia Int. J. Headache 2011, 31, 1542–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tölle, T.; Dukes, E.; Sadosky, A. Patient burden of trigeminal neuralgia: Results from a cross-sectional survey of health state impairment and treatment patterns in six European countries. Pain Pract. Off. J. World Inst. Pain 2006, 6, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, K.L.; Vilensky, J.A. The anatomy of vascular compression in trigeminal neuralgia. Clin. Anat. 2014, 27, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambeta, E.; Chichorro, J.G.; Zamponi, G.W. Trigeminal neuralgia: An overview from pathophysiology to pharmacological treatments. Mol. Pain 2020, 16, 1744806920901890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antonini, G.; Di Pasquale, A.; Cruccu, G.; Morino, S.; Romano, A.; Trasimeni, G.; Vanacore, N.; Bozzao, A. Magnetic resonance imaging contribution for diagnosing symptomatic neurovascular contact in classical trigeminal neuralgia: A blinded case-control study and meta-analysis. Pain 2014, 155, 1464–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maarbjerg, S.; Di Stefano, G.; Bendtsen, L.; Cruccu, G. Trigeminal neuralgia - diagnosis and treatment. Cephalalgia 2017, 37, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, P.R.; Barbier, C.; Hermier, M.; Souza, M.A.; Sindou, M. Atrophic changes in the trigeminal nerves of patients with trigeminal neuralgia due to neurovascular compression and their association with the severity of compression and clinical outcomes. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 120, 1484–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.A.; Paskhover, B.; Mammis, A. Molecular mechanisms of trigeminal neuralgia: A systematic review. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2021, 200, 106397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Hamdeh, S.; Khoonsari, P.E.; Shevchenko, G.; Gordh, T.; Ericson, H.; Kultima, K. Increased CSF Levels of Apolipoproteins and Complement Factors in Trigeminal Neuralgia Patients-In Depth Proteomic Analysis Using Mass Spectrometry. J. Pain 2020, 21, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ericson, H.; Abu Hamdeh, S.; Freyhult, E.; Stiger, F.; Bäckryd, E.; Svenningsson, A.; Gordh, T.; Kultima, K. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of inflammation in trigeminal neuralgia patients operated with microvascular decompression. Pain 2019, 160, 2603–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jannetta, P.J.; McLaughlin, M.R.; Casey, K.F. Technique of microvascular decompression. Technical note. Neurosurg. Focus 2005, 18, E5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition (beta version). Cephalalgia Int. J. Headache 2013, 33, 629–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Guo, J.; Zhang, L.; Kuek, V.; Xu, J.; Zou, J. Molecular structure, expression, and functional role of Clec11a in skeletal biology and cancers. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 6357–6365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonin, S.; Zanotta, N.; Sartori, A.; Bratina, A.; Manganotti, P.; Trevisan, G.; Comar, M. Cerebrospinal Fluid Cytokine Expression Profile in Multiple Sclerosis and Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy. Immunol. Investig. 2018, 47, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, A.; Panjwani, A.; Sison, C.; Rosen, L.; Chugh, R.; Metz, C.; Bank, M.; Bloom, O. Pilot study: Elevated circulating levels of the proinflammatory cytokine macrophage migration inhibitory factor in patients with chronic spinal cord injury. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 94, 1498–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall, E.; Brandstetter, H. Structure and function of legumain in health and disease. Biochimie 2016, 122, 126–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manoury, B.; Mazzeo, D.; Fugger, L.; Viner, N.; Ponsford, M.; Streeter, H.; Mazza, G.; Wraith, D.C.; Watts, C. Destructive processing by asparagine endopeptidase limits presentation of a dominant T cell epitope in MBP. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oveland, E.; Ahmad, I.; Lereim, R.R.; Kroksveen, A.C.; Barsnes, H.; Guldbrandsen, A.; Myhr, K.M.; Bø, L.; Berven, F.S.; Wergeland, S. Cuprizone and EAE mouse frontal cortex proteomics revealed proteins altered in multiple sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.Z.; Zhang, H.Y.; Pan, H.F.; Ye, D.Q. Identification of MFG-E8 as a novel therapeutic target for diseases. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2013, 17, 1275–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fricker, M.; Neher, J.J.; Zhao, J.W.; Théry, C.; Tolkovsky, A.M.; Brown, G.C. MFG-E8 mediates primary phagocytosis of viable neurons during neuroinflammation. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 2657–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krautler, N.J.; Kana, V.; Kranich, J.; Tian, Y.; Perera, D.; Lemm, D.; Schwarz, P.; Armulik, A.; Browning, J.L.; Tallquist, M.; et al. Follicular dendritic cells emerge from ubiquitous perivascular precursors. Cell 2012, 150, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheyuo, C.; Aziz, M.; Wang, P. Neurogenesis in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Role of MFG-E8. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, A.; Kamermans, A.; van Het Hof, B.; Castricum, K.; Aanhane, E.; van Horssen, J.; Thijssen, V.L.; Scheltens, P.; Teunissen, C.E.; Fontijn, R.D.; et al. Angiopoietin like-4 as a novel vascular mediator in capillary cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Brain J. Neurol. 2018, 141, 3377–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Li, S.Y.; Ji, F.Y.; Zhao, Y.F.; Zhong, Y.; Lv, X.J.; Wu, X.L.; Qian, G.S. Role of Angptl4 in vascular permeability and inflammation. Inflamm. Res. Off. J. Eur. Histamine Res. Soc. 2014, 63, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Song, Q.Y.; Niu, S.X.; Chen, H.J.; Petersen, R.B.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, K. Emerging roles of angiopoietin-like proteins in inflammation: Mechanisms and potential as pharmacological targets. J. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 237, 98–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, N.A.; Nawrocki, A.; Molnar, V.; Elkjaer, M.L.; Thygesen, E.K.; Palkovits, M.; Acs, P.; Sejbaek, T.; Nielsen, H.H.; Hegedus, Z.; et al. Orthologous proteins of experimental de- and remyelination are differentially regulated in the CSF proteome of multiple sclerosis subtypes. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamermans, A.; Rijnsburger, M.; Chakraborty, A.; van der Pol, S.; de Vries, H.E.; van Horssen, J. Reduced Angiopoietin-Like 4 Expression in Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Facilitates Lipid Uptake by Phagocytes via Modulation of Lipoprotein-Lipase Activity. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruce, K.D.; Gorkhali, S.; Given, K.; Coates, A.M.; Boyle, K.E.; Macklin, W.B.; Eckel, R.H. Lipoprotein Lipase Is a Feature of Alternatively-Activated Microglia and May Facilitate Lipid Uptake in the CNS During Demyelination. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montano, N.; Rapisarda, A.; Ioannoni, E.; Olivi, A. Microvascular decompression in patients with trigeminal neuralgia and multiple sclerosis: Results and analysis of possible prognostic factors. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2020, 120, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruccu, G.; Biasiotta, A.; Di Rezze, S.; Fiorelli, M.; Galeotti, F.; Innocenti, P.; Mameli, S.; Millefiorini, E.; Truini, A. Trigeminal neuralgia and pain related to multiple sclerosis. Pain 2009, 143, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strittmatter, M.; Grauer, M.; Isenberg, E.; Hamann, G.; Fischer, C.; Hoffmann, K.H.; Blaes, F.; Schimrigk, K. Cerebrospinal fluid neuropeptides and monoaminergic transmitters in patients with trigeminal neuralgia. Headache 1997, 37, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Z.L.; Yang, L.Q.; Li, N.; Yue, J.N.; Wu, B.S.; Tang, Y.Z.; Guo, Y.N.; Lai, G.H.; Ni, J.X. Clinical study of cerebrospinal fluid neuropeptides in patients with primary trigeminal neuralgia. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2016, 143, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Variables | TN | Controls | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients, n | 16 | 16 | |
| Age (years), median (IQR) | 66 (55–69) | 67 (52–72) | 1.00 |
| Sex (female/male), n (%) | 7/9 (44/56%) | 6/10 (38/63%) | 0.72 |
| BMI, median (IQR) | 28 (24–31) | 28 (24–31) | 0.93 |
| Tobacco use, n (%) | 4 (25%) | 8 (50%) | 0.14 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 8 (50%) | 9 (56%) | 0.72 |
| Cardiovascular morbidity, n (%) | 2 (13%) | 5 (31%) | 0.22 |
| Ischemic heart disease, n (%) | 1 (6%) | 3 (19%) | |
| Stroke, n (%) | 1 (6%) | 1 (6%) | |
| Peripheral, n (%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (6%) | |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (19%) | 0.07 |
| Pain other than TN, n (%) | 4 (25%) | 5 (31%) | 0.69 |
| Fibromyalgia, n (%) | 1 (6%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Osteoarthtritis, n (%) | 2 (13%) | 2 (13%) | |
| Lower back pain, n (%) | 1 (6%) | 2 (13%) | |
| Rheumatoid arthritis, n (%) | 1 (6%) | 1 (6%) | |
| ASA grade | 0.83 | ||
| 1, n (%) | 2 (13%) | 2 (13%) | |
| 2, n (%) | 13 (81%) | 12 (75%) | |
| 3, n (%) | 1 (6%) | 2 (13%) |
| Biomarker | Coefficient | p (lm) | q (lm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clec11a | 0.85 | 5.46 × 10−5 | 0.0037 |
| LGMN | 0.59 | 0.00015 | 0.0037 |
| MFG-E8 | 0.79 | 0.00016 | 0.0037 |
| ANGPTL-4 | 0.60 | 0.00097 | 0.017 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Svedung Wettervik, T.; Folkvaljon, D.; Gordh, T.; Freyhult, E.; Kultima, K.; Ericson, H.; Abu Hamdeh, S. Cerebrospinal Fluid in Classical Trigeminal Neuralgia: An Exploratory Study on Candidate Biomarkers. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 998. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10050998
Svedung Wettervik T, Folkvaljon D, Gordh T, Freyhult E, Kultima K, Ericson H, Abu Hamdeh S. Cerebrospinal Fluid in Classical Trigeminal Neuralgia: An Exploratory Study on Candidate Biomarkers. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(5):998. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10050998
Chicago/Turabian StyleSvedung Wettervik, Teodor, Dick Folkvaljon, Torsten Gordh, Eva Freyhult, Kim Kultima, Hans Ericson, and Sami Abu Hamdeh. 2022. "Cerebrospinal Fluid in Classical Trigeminal Neuralgia: An Exploratory Study on Candidate Biomarkers" Biomedicines 10, no. 5: 998. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10050998
APA StyleSvedung Wettervik, T., Folkvaljon, D., Gordh, T., Freyhult, E., Kultima, K., Ericson, H., & Abu Hamdeh, S. (2022). Cerebrospinal Fluid in Classical Trigeminal Neuralgia: An Exploratory Study on Candidate Biomarkers. Biomedicines, 10(5), 998. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10050998






