BifA Triggers Phosphorylation of Ezrin to Benefit Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus Survival from Neutrophils Killing
Abstract
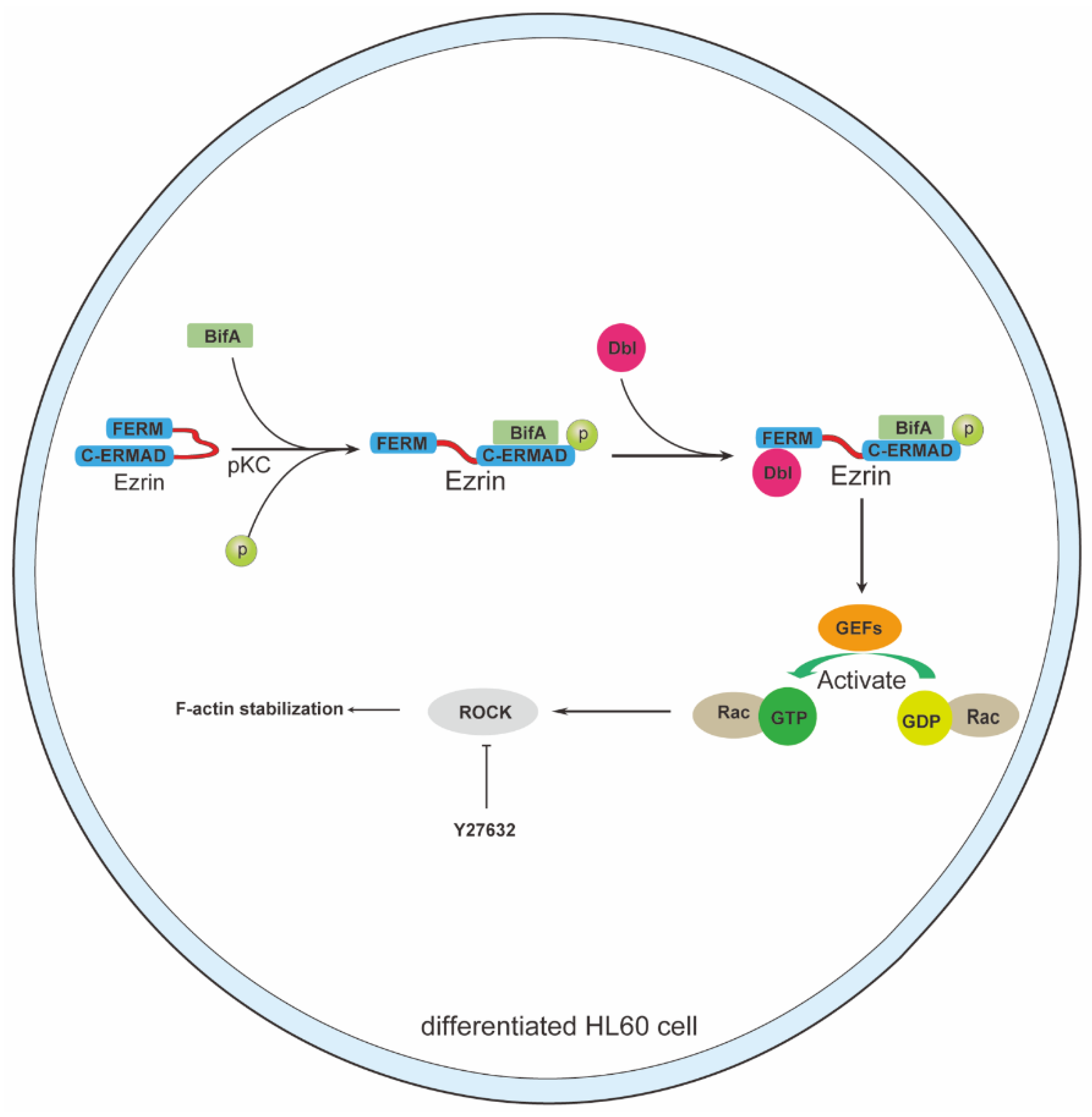
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacteria Strains, Growth Conditions, and Cell Culture
2.2. Ethics Statement and Animal Experiments
2.3. Protein Expression and Purification
2.4. Immunofluorescence and Confocal Microscopy
2.5. Co-Immunoprecipitation
2.6. Western Blot
2.7. Rac1 Activation Detection
2.8. dHL60 Cells and Primary Mouse Neutrophils Bactericidal Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
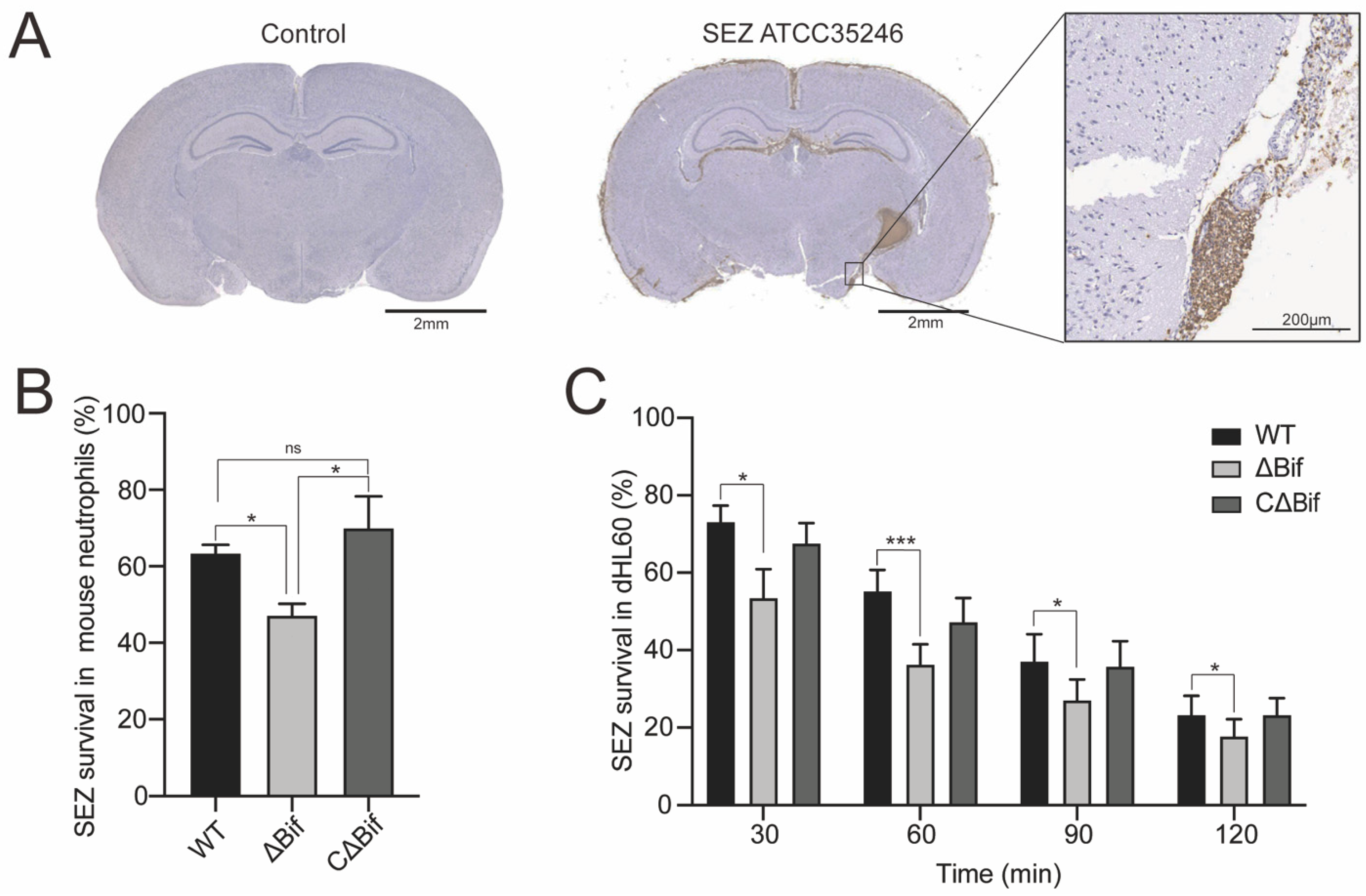
3.1. The bifA Gene Defective SEZ Has a Lower Tolerance to Neutrophils Killing In Vitro
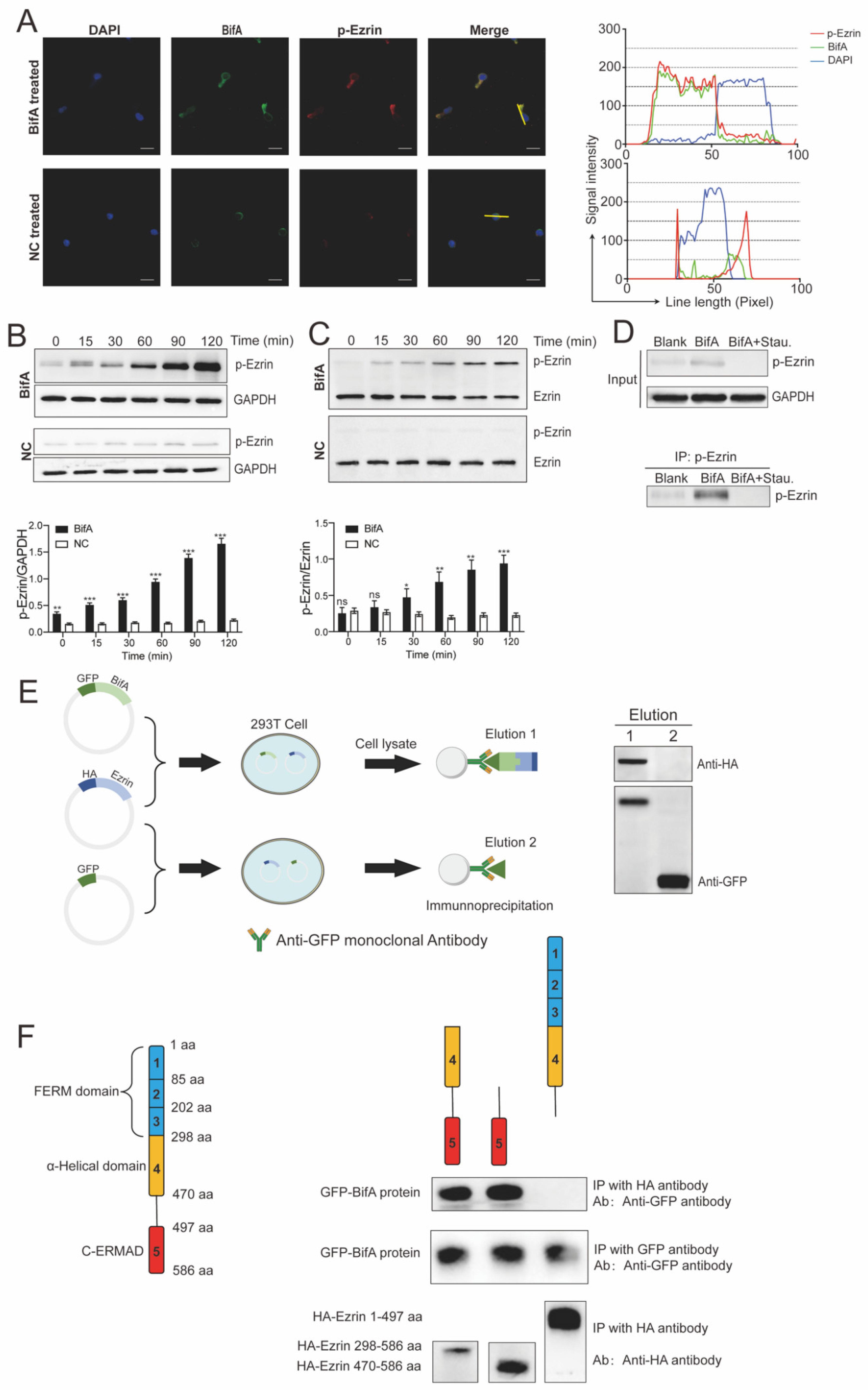
3.2. BifA Can Interact with Ezrin in Neutrophils and Elevate the p-Ezrin Level in PKC-Dependent Manner
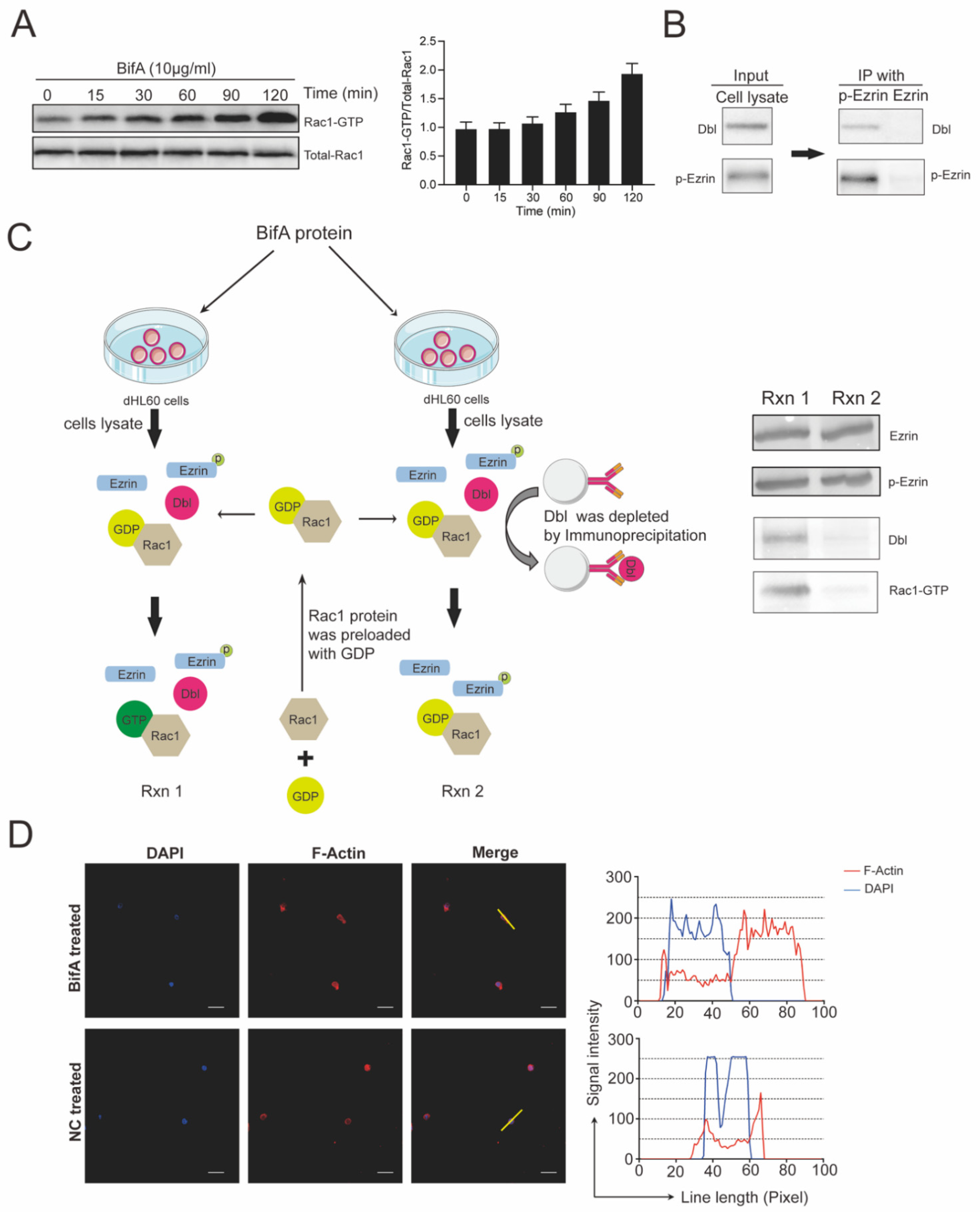
3.3. BifA Triggered p-Ezrin Elevation Recruited Dbl and Led to Rac1 Activation
3.4. Rho-ROCK Pathway Inhibitor Y27632 Restores Neutrophils Killing Capability Reduced by BifA
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Feng, Z.G.; Hu, J.S. Outbreak of swine streptococcosis in Sichuan province and identification of pathogen. Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. Lett. 1977, 2, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Resende-De-Macedo, N.; Sitthicharoenchai, P.; Sahin, O.; Burrough, E.; Clavijo, M.; Derscheid, R.; Schwartz, K.; Lantz, K.; Robbe-Austerman, S.; et al. Genetic characterization of Streptococcus equi subspecies zooepidemicus associated with high swine mortality in the United States. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 2797–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Geng, J.; Yi, L.; Xu, B.; Jia, R.; Li, Y.; Meng, Q.; Fan, H.; Hu, S. Insight into the specific virulence related genes and toxin-antitoxin virulent pathogenicity islands in swine streptococcosis pathogen Streptococcus equi ssp. zooepidemicus strain ATCC35246. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, Z.; Geng, J.; Zhang, H.; Yu, H.; Yi, L.; Lei, M.; Lu, C.P.; Fan, H.J.; Hu, S. Complete genome sequence of Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus strain ATCC 35246. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 5583–5584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Costa, M.O.; Lage, B. Streptococcus equi Subspecies zooepidemicus and Sudden Deaths in Swine, Canada. Emerg Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 2522–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, C.R.; Cherfils, J. Structure and function of Fic proteins. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Peng, J.; Yu, D.; Park, J.S.; Lin, H.; Xu, B.; Lu, C.; Fan, H.; Waldor, M.K. A streptococcal Fic domain-containing protein disrupts blood-brain barrier integrity by activating moesin in endothelial cells. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dewitt, S.; Hallett, M. Leukocyte membrane “expansion”: A central mechanism for leukocyte extravasation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007, 81, 1160–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, M.H.; Dupree, R.S.; Zhu, P.; Saotome, I.; Schmidt, R.F.; McClatchey, A.I.; Freedman, B.D.; Burkhardt, J.K. Ezrin and Moesin Function Together to Promote T Cell Activation. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fehon, R.G.; McClatchey, A.I.; Bretscher, A. Organizing the cell cortex: The role of ERM proteins. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoe, N.P.; Ireland, R.M.; DeLeo, F.R.; Gowen, B.B.; Dorward, D.W.; Voyich, J.M.; Liu, M.; Burns, E.H., Jr.; Culnan, D.M.; Bretscher, A.; et al. Insight into the molecular basis of pathogen abundance: Group A Streptococcus inhibitor of complement inhibits bacterial adherence and internalization into human cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 7646–7651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Doulet, N.; Donnadieu, E.; Laran-Chich, M.P.; Niedergang, F.; Nassif, X.; Couraud, P.O.; Bourdoulous, S. Neisseria meningitidis infection of human endothelial cells interferes with leukocyte transmigration by preventing the formation of endothelial docking structures. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 173, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolaczkowska, E.; Kubes, P. Neutrophil recruitment and function in health and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.; Guo, X.; Fan, H. Extracellular Nucleases of Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus Degrade Neutrophil Extracellular Traps and Impair Macrophage Activity of the Host. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e02468-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roberts, R.E.; Hallett, M.B. Neutrophil Cell Shape Change: Mechanism and Signalling during Cell Spreading and Phagocytosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roberts, R.E.; Elumalai, G.L.; Hallett, M.B. Phagocytosis and Motility in Human Neutrophils is Competent but Compromised by Pharmacological Inhibition of Ezrin Phosphorylation. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2018, 11, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieg, J.; Hunter, T. Identification of the two major epidermal growth factor-induced tyrosine phosphorylation sites in the microvillar core protein ezrin. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 19258–19265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shcherbina, A.; Bretscher, A.; Kenney, D.M.; Remold-O’Donnell, E. Moesin, the major ERM protein of lymphocytes and platelets, differs from ezrin in its insensitivity to calpain. FEBS Lett. 1999, 443, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.H.; Katakai, T.; Hara, T.; Gonda, H.; Sugai, M.; Shimizu, A. Roles of p-ERM and Rho-ROCK signaling in lymphocyte polarity and uropod formation. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 167, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonemura, S.; Matsui, T.; Tsukita, S.; Tsukita, S. Rho-dependent and -independent activation mechanisms of ezrin/radixin/moesin proteins: An essential role for polyphosphoinositides in vivo. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 2569–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvao, I.; Athayde, R.M.; Perez, D.A.; Reis, A.C.; Rezende, L.; de Oliveira, V.L.S.; Rezende, B.M.; Goncalves, W.A.; Sousa, L.P.; Teixeira, M.M.; et al. ROCK Inhibition Drives Resolution of Acute Inflammation by Enhancing Neutrophil Apoptosis. Cells 2019, 8, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Lyu, X.; Liao, J.; Werth, V.P.; Liu, M.-L. Rho Kinase regulates neutrophil NET formation that is involved in UVB-induced skin inflammation. Theranostics 2022, 12, 2133–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Gama, J.D.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Fan, H.; Morris, E.R.A.; Cohen, N.D.; Cywes-Bentley, C.; Pier, G.B.; Waldor, M.K. A Conserved Streptococcal Virulence Regulator Controls the Expression of a Distinct Class of M-Like Proteins. mBio 2019, 10, e02500-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilson, K.; Lewalle, A.; Fritzsche, M.; Thorogate, R.; Duke, T.; Charras, G. Mechanisms of leading edge protrusion in interstitial migration. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Swamydas, M.; Lionakis, M.S. Isolation, Purification and Labeling of Mouse Bone Marrow Neutrophils for Functional Studies and Adoptive Transfer Experiments. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 77, e50586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdes, K.M.; Sundar, G.S.; Vega, L.A.; Belew, A.T.; Islam, E.; Binet, R.; El-Sayed, N.M.; Le Breton, Y.; McIver, K.S. The fruRBA Operon Is Necessary for Group A Streptococcal Growth in Fructose and for Resistance to Neutrophil Killing during Growth in Whole Human Blood. Infect. Immun. 2016, 84, 1016–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.Y.; Kim, S.; Bae, D.J.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, G.Y.; Park, G.M.; Kim, I.S. Coordinated balance of Rac1 and RhoA plays key roles in determining phagocytic appetite. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizaki, T.; Uehata, M.; Tamechika, I.; Keel, J.; Nonomura, K.; Maekawa, M.; Narumiya, S. Pharmacological properties of Y-27632, a specific inhibitor of rho-associated kinases. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 57, 976–983. [Google Scholar]
- Brostjan, C.; Oehler, R. The role of neutrophil death in chronic inflammation and cancer. Cell Death Discov. 2020, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bretscher, A.; Chambers, D.; Nguyen, R.; Reczek, D. ERM-Merlin and EBP50 protein families in plasma membrane organization and function. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2000, 16, 113–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivetic, A.; Ridley, A.J. Ezrin/radixin/moesin proteins and Rho GTPase signalling in leucocytes. Immunology 2004, 112, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agbor, T.A.; Demma, Z.C.; Mumy, K.L.; Bien, J.D.; McCormick, B.A. The ERM protein, ezrin, regulates neutrophil transmigration by modulating the apical localization of MRP2 in response to the SipA effector protein during Salmonella Typhimurium infection. Cell Microbiol. 2011, 13, 2007–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prag, S.; Parsons, M.; Keppler, M.D.; Ameer-Beg, S.M.; Barber, P.; Hunt, J.; Beavil, A.J.; Calvert, R.; Arpin, M.; Vojnovic, B.; et al. Activated ezrin promotes cell migration through recruitment of the GEF Dbl to lipid rafts and preferential downstream activation of Cdc42. Mol. Biol. Cell 2007, 18, 2935–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wiedemann, A.; Lim, J.; Caron, E. Small GTP Binding Proteins and the Control of Phagocytic Uptake. In Molecular Mechanisms of Phagocytosis; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, S.D.; Malachowa, N.; DeLeo, F.R. Neutrophils and Bacterial Immune Evasion. J. Innate Immun. 2018, 10, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai, Y.; Kaibuchi, K.; Sasaki, T.; Tanaka, K.; Shirataki, H.; Nakanishi, H. Rho small G protein and cytoskeletal control. Princess Takamatsu Symp. 1994, 24, 338–350. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, F.; Peng, J.; Yu, D.; Li, L.; Fan, H.; Ma, Z. BifA Triggers Phosphorylation of Ezrin to Benefit Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus Survival from Neutrophils Killing. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10050932
Pan F, Peng J, Yu D, Li L, Fan H, Ma Z. BifA Triggers Phosphorylation of Ezrin to Benefit Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus Survival from Neutrophils Killing. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(5):932. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10050932
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Fei, Jie Peng, Dandan Yu, Lianyue Li, Hongjie Fan, and Zhe Ma. 2022. "BifA Triggers Phosphorylation of Ezrin to Benefit Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus Survival from Neutrophils Killing" Biomedicines 10, no. 5: 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10050932
APA StylePan, F., Peng, J., Yu, D., Li, L., Fan, H., & Ma, Z. (2022). BifA Triggers Phosphorylation of Ezrin to Benefit Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus Survival from Neutrophils Killing. Biomedicines, 10(5), 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10050932





