Empagliflozin Reduces the Progression of Hepatic Fibrosis in a Mouse Model and Inhibits the Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells via the Hippo Signalling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Study
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Histopathological Staining
2.4. Western Blotting
2.5. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.6. Cell Viability Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Empagliflozin Attenuates Hepatic Fibrosis in CDAHFD-Induced Mice
3.2. Empagliflozin Decreased Fibrosis Markers and Proliferation in HSCs
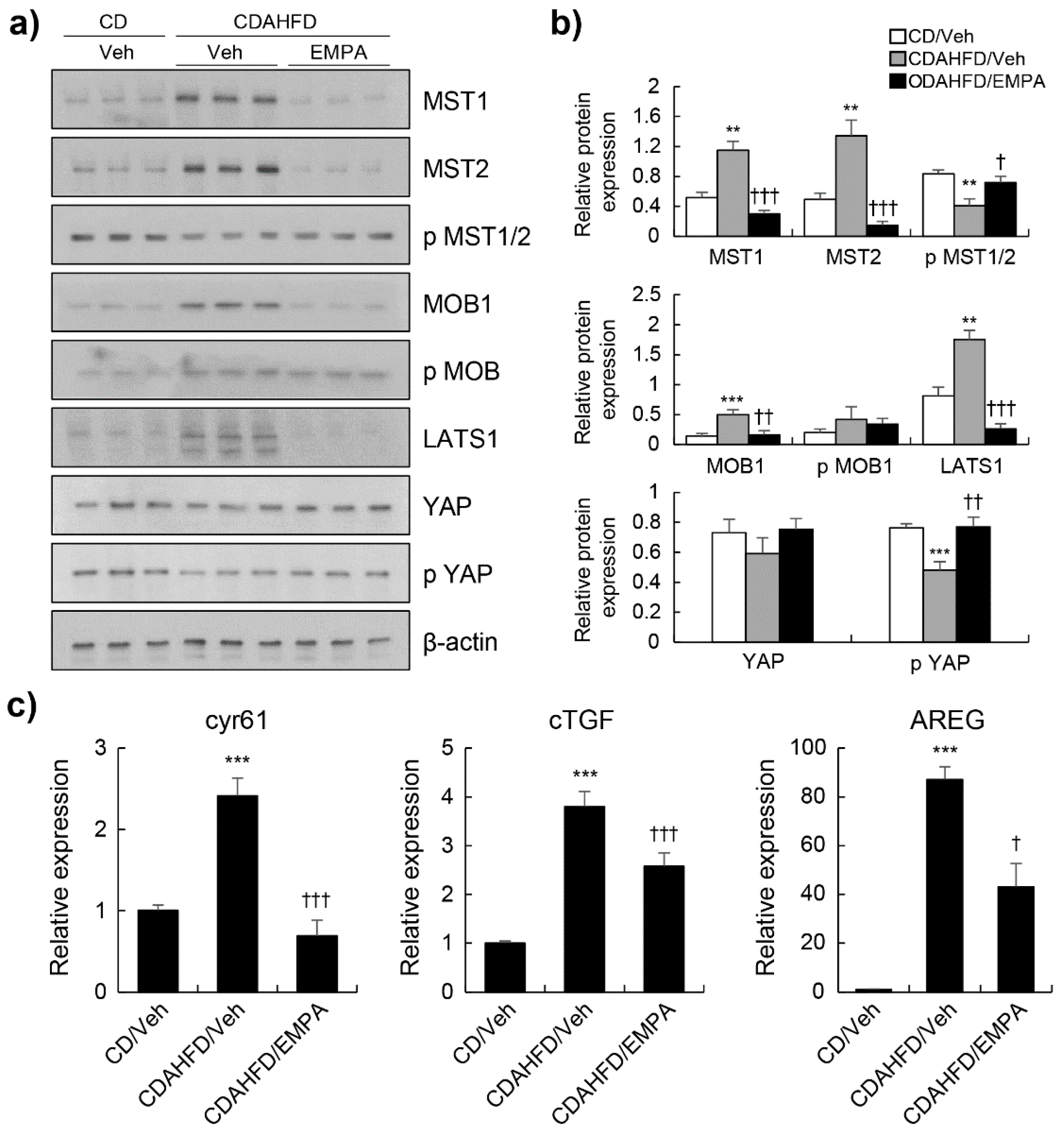
3.3. Empagliflozin Activated the Hippo Signalling Pathway in CDAHFD-Induced Mice
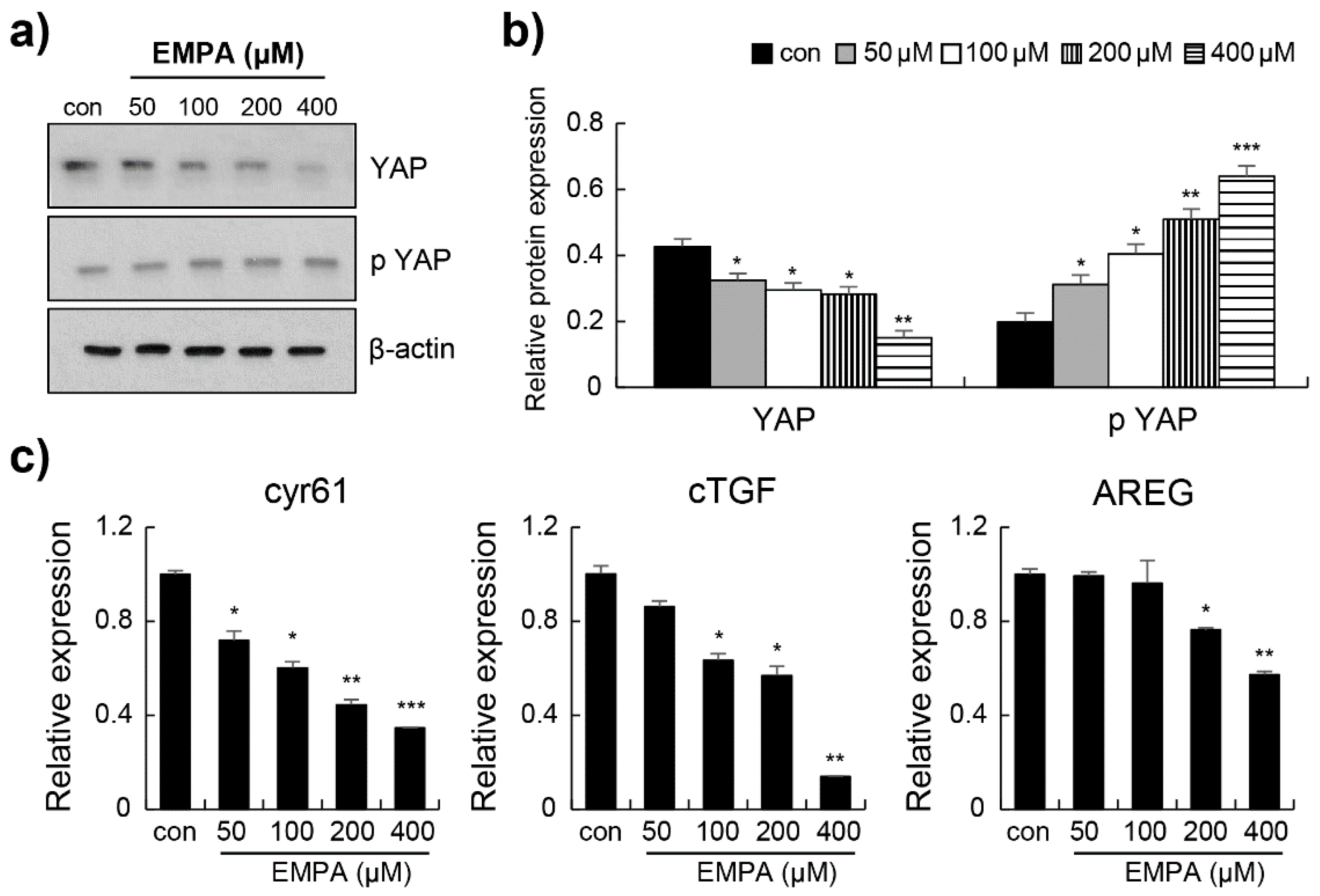
3.4. Empagliflozin Induced YAP Phosphorylation through the Hippo Signalling Pathway in LX-2 Cells
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Friedman, S.L. Evolving challenges in hepatic fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 7, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bataller, R.; Brenner, D.A. Liver fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, S.L. Molecular regulation of hepatic fibrosis, an integrated cellular response to tissue injury. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 2247–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Hui, A.Y.; Albanis, E.; Arthur, M.J.; O’Byrne, S.M.; Blaner, W.S.; Mukherjee, P.; Friedman, S.L.; Eng, F.J. Human hepatic stellate cell lines, LX-1 and LX-2: New tools for analysis of hepatic fibrosis. Gut 2005, 54, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Chang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Han, X.; Han, Y.; Yao, Q.; Hu, Z.; Cui, H.; Zheng, L.; Han, T.; et al. ω-3 PUFAs ameliorate liver fibrosis and inhibit hepatic stellate cells proliferation and activation by promoting YAP/TAZ degradation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, D. The hippo signaling pathway in development and cancer. Dev. Cell 2010, 19, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boopathy, G.T.K.; Hong, W. Role of hippo pathway-YAP/TAZ signaling in angiogenesis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Tian, J.; Zhou, D.; Chen, L. Mst1 and Mst2 kinases: Regulations and diseases. Cell Biosci. 2013, 3, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, T.; Moroishi, T. Hippo Pathway in Mammalian Adaptive Immune System. Cells 2019, 8, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Bai, H.; David, K.K.; Dong, J.; Zheng, Y.; Cai, J.; Giovannini, M.; Liu, P.; Anders, R.A.; Pan, D. The Merlin/NF2 tumor suppressor functions through the YAP oncoprotein to regulate tissue homeostasis in mammals. Dev. Cell 2010, 19, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.; Barry, E.; Yin, Y.; Lawrence, E.; Dawson, D.; Willis, J.E.; Markowitz, S.D.; Camargo, F.D.; et al. Mst1 and Mst2 protein kinases restrain intestinal stem cell proliferation and colonic tumorigenesis by inhibition of Yes-associated protein (Yap) overabundance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, E1312–E1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Li, L.; Lei, Q.; Guan, K.L. The Hippo-YAP pathway in organ size control and tumorigenesis: An updated version. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 862–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Q.Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, B.; Zha, Z.Y.; Bai, F.; Pei, X.H.; Zhao, S.; Xiong, Y.; Guan, K.L. TAZ promotes cell proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition and is inhibited by the hippo pathway. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 2426–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, L.; Tran, T.; Kavran, J.M. Structural insights into the regulation of hippo signaling. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017, 12, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.K.; Jang, J.W.; Bae, S.C. DNA binding partners of YAP/TAZ. BMB Rep. 2018, 51, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannaerts, I.; Leite, S.B.; Verhulst, S.; Claerhout, S.; Eysackers, N.; Thoen, L.F.; Hoorens, A.; Reynaert, H.; Halder, G.; van Grunsven, L.A. The Hippo pathway effector YAP controls mouse hepatic stellate cell activation. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, T.; Shimoda, M.; Nakashima, K.; Fushimi, Y.; Hirata, Y.; Tanabe, A.; Tatsumi, F.; Hirukawa, H.; Sanada, J.; Kohara, K.; et al. Comparison of the effects of three kinds of glucose-lowering drugs on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized, open-label, three-arm, active control study. J. Diabetes Investig. 2020, 11, 1612–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharaibeh, N.E.; Rahhal, M.N.; Rahimi, L.; Ismail-Beigi, F. SGLT-2 inhibitors as promising therapeutics for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Pathophysiology, clinical outcomes, and future directions. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2019, 12, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehrehgosha, H.; Sohrabi, M.R.; Ismail-Beigi, F.; Malek, M.; Reza Babaei, M.; Zamani, F.; Ajdarkosh, H.; Khoonsari, M.; Fallah, A.E.; Khamseh, M.E. Empagliflozin improves liver steatosis and fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Diabetes Ther. 2021, 12, 843–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Fang, T.; Xu, L.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Xue, M.; Yu, X.; Sun, B.; Chen, L. Empagliflozin Alleviates Hepatic Steatosis by Activating the AMPK-TET2-Autophagy Pathway in vivo and in vitro. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 622153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Heo, Y.J.; Choi, S.E.; Jeon, J.Y.; Han, S.J.; Kim, D.J.; Kang, Y.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, H.J. Anti-inflammatory effects of empagliflozin and gemigliptin on LPS-stimulated macrophage via the IKK/NF-κB, MKK7/JNK, and JAK2/STAT1 signalling pathways. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 9944880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.; Heo, Y.J.; Choi, S.E.; Jeon, J.Y.; Han, S.J.; Kim, D.J.; Kang, Y.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, H.J. Hepatoprotective effects of gemigliptin and empagliflozin in a murine model of diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 588, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kern, M.; Klöting, N.; Mark, M.; Mayoux, E.; Klein, T.; Blüher, M. The SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin improves insulin sensitivity in db/db mice both as monotherapy and in combination with linagliptin. Metabolism 2016, 65, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Marsh, S.; Hu, J.; Feng, W.; Wu, C. The Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Interplay between Diet, Gut Microbiota, and Genetic Background. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2016, 2016, 2862173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, C.; Djerir, N.E.H.; Danckaert, A.; Fernandes, J.; Roux, P.; Charrueau, C.; Lachagès, A.M.; Charlotte, F.; Brocheriou, I.; Clément, K.; et al. Hepatic Stellate Cell Hypertrophy Is Associated with Metabolic Liver Fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokugawa, T.; Konishi, H.; Ito, M.; Iimori, H.; Nagai, R.; Shimosegawa, E.; Hatazawa, J.; Abe, K. Evaluation of Hepatic Integrin Avβ3 Expression in Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) Model Mouse by 18F-FPP-RGD2 PET. EJNMMI Res. 2018, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikawa-Yoshida, A.; Matsuo, S.; Kato, A.; Ohmori, Y.; Higashida, A.; Kaneko, E.; Matsumoto, M. Hepatocellular Carcinoma in a Mouse Model Fed a Choline-Deficient, L-Amino Acid-Defined, High-Fat Diet. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2017, 98, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooring, M.; Fowl, B.H.; Lum, S.Z.C.; Liu, Y.; Yao, K.; Softic, S.; Kirchner, R.; Bernstein, A.; Singhi, A.D.; Jay, D.G.; et al. Hepatocyte stress increases expression of yes-associated protein and transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif in hepatocytes to promote parenchymal inflammation and fibrosis. Hepatology 2020, 1, 1813–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salloum, S.; Jeyarajan, A.J.; Kruger, A.J.; Holmes, J.A.; Shao, T.; Sojoodi, M.; Kim, M.H.; Zhuo, Z.; Shroff, S.G.; Kassa, A.; et al. Fatty acids activate the transcriptional coactivator YAP1 to promote liver fibrosis via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 12, 1297–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuypers, J.; Mathieu, C.; Benhalima, K. SGLT2-inhibitors: A novel class for the treatment of type 2 diabetes introduction of SGLT2-inhibitors in clinical practice. Acta Clin. Belg. 2013, 68, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsia, D.S.; Grove, O.; Cefalu, W.T. An update on sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors for the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2017, 24, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwinata, M.; Putera, D.D.; Hasan, I.; Raharjo, M. SGLT2 inhibitors for improving hepatic fibrosis and steatosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease complicated with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2020, 6, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.W.; Lee, Y.J.; You, Y.H.; Moon, M.K.; Yoon, K.H.; Ahn, Y.B.; Ko, S.H. Effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor, empagliflozin, and α-glucosidase inhibitor, voglibose, on hepatic steatosis in an animal model of type 2 diabetes. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 12, 8534–8546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zheng, Z.; Caviglia, J.M.; Corey, K.E.; Herfel, T.M.; Cai, B.; Masia, R.; Chung, R.T.; Lefkowitch, J.H.; Schwabe, R.F.; et al. Hepatocyte TAZ/WWTR1 promotes inflammation and fibrosis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 848–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; He, Q.; Feng, X.; Zhu, J.; Xu, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, F.; Li, X.; Dong, J. Differences in Yes-associated protein and mRNA levels in regenerating liver and hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 5, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Zhou, L.; Ling, L.; Meng, X.; Chu, F.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, F. The Crosstalk Between Hippo-YAP Pathway and Innate Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Yamamoto, G.; Fuji, H.; Kisseleva, T. Interleukin-17 in Liver Disease Pathogenesis. Semin Liver Dis. 2021, 41, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantino, G.; Costantini, S.; Finelli, C.; Capone, F.; Guerriero, E.; La Sala, N.; Gioia, S.; Castello, G. Is serum Interleukin-17 associated with early atherosclerosis in obese patients? J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, S.L. Hepatic stellate cells: Protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 125–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooqi, H.M.U.; Kang, B.; Khalid, M.A.U.; Salih, A.R.C.; Hyun, K.; Park, S.H.; Huh, D.; Choi, K.H. Real-time monitoring of liver fibrosis through embedded sensors in a microphysiological system. Nano Converg. 2021, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heo, Y.-J.; Lee, N.; Choi, S.-E.; Jeon, J.-Y.; Han, S.-J.; Kim, D.-J.; Kang, Y.; Lee, K.-W.; Kim, H.-J. Empagliflozin Reduces the Progression of Hepatic Fibrosis in a Mouse Model and Inhibits the Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells via the Hippo Signalling Pathway. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10051032
Heo Y-J, Lee N, Choi S-E, Jeon J-Y, Han S-J, Kim D-J, Kang Y, Lee K-W, Kim H-J. Empagliflozin Reduces the Progression of Hepatic Fibrosis in a Mouse Model and Inhibits the Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells via the Hippo Signalling Pathway. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(5):1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10051032
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeo, Yu-Jung, Nami Lee, Sung-E Choi, Ja-Young Jeon, Seung-Jin Han, Dae-Jung Kim, Yup Kang, Kwan-Woo Lee, and Hae-Jin Kim. 2022. "Empagliflozin Reduces the Progression of Hepatic Fibrosis in a Mouse Model and Inhibits the Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells via the Hippo Signalling Pathway" Biomedicines 10, no. 5: 1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10051032
APA StyleHeo, Y.-J., Lee, N., Choi, S.-E., Jeon, J.-Y., Han, S.-J., Kim, D.-J., Kang, Y., Lee, K.-W., & Kim, H.-J. (2022). Empagliflozin Reduces the Progression of Hepatic Fibrosis in a Mouse Model and Inhibits the Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells via the Hippo Signalling Pathway. Biomedicines, 10(5), 1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10051032





