A Novel Anti-CD73 Antibody That Selectively Inhibits Membrane CD73 Shows Antitumor Activity and Induces Tumor Immune Escape
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Culture Conditions
2.2. Transfection of 293T Cells
2.3. Isolation of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMCs)
2.4. Flow Cytometry
2.5. Cloning and Production of Fab-22E6
2.6. Western Blotting Analysis
2.7. Immunoprecipitation
2.8. Isolation of Tumor-Derived Extracellular Vesicles (TEVs)
2.9. Generation of the 22E6 Antibody
2.10. CD73 Activity Assay
2.11. Apoptosis Assay and Analysis of Mitochondrial Activity
2.12. In Vivo Treatment Trials
2.13. Statistics
3. Results
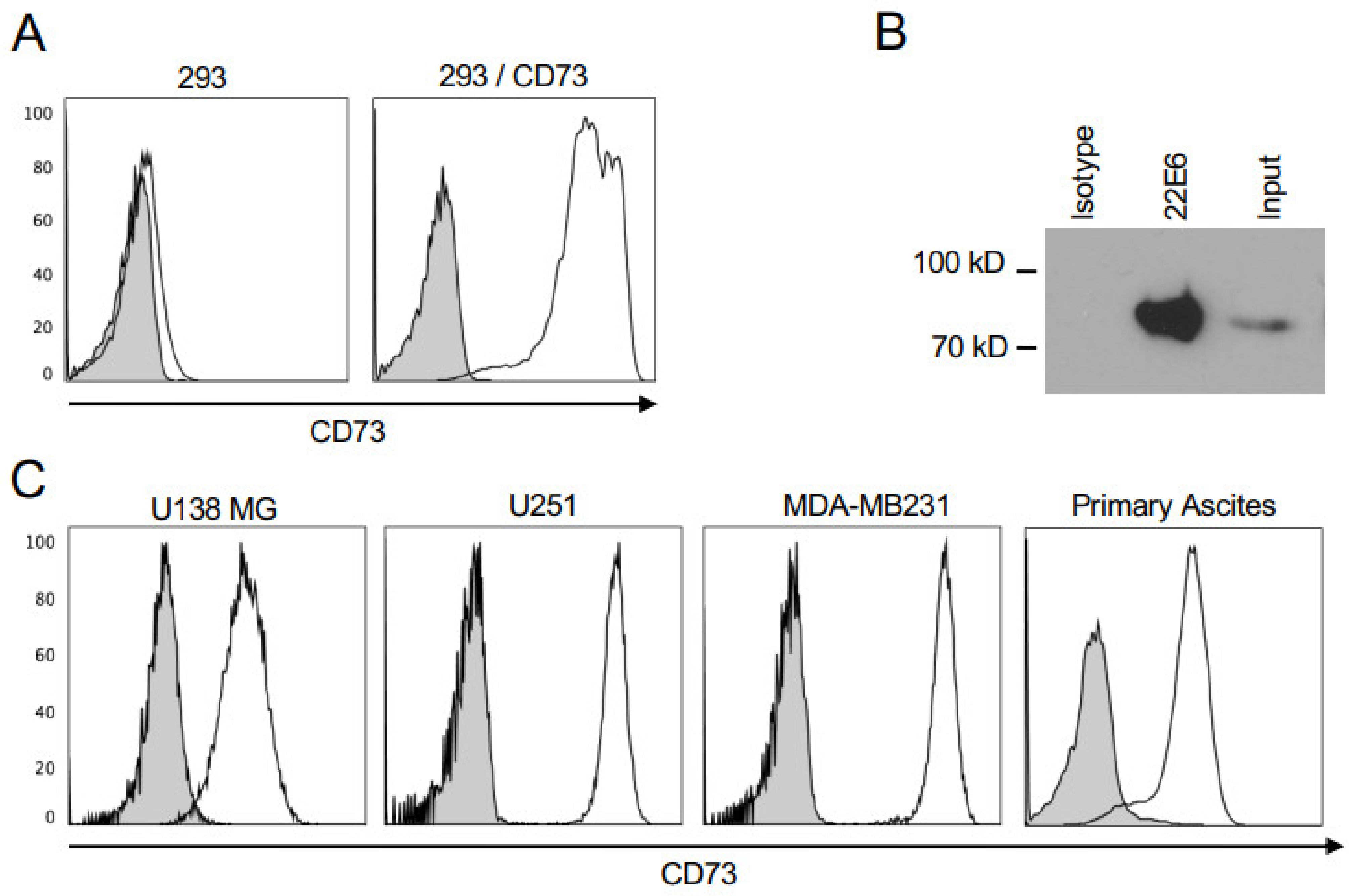
3.1. 22E6 Specifically Binds CD73 on Human Cancer Cell Lines
3.2. 22E6 Inhibits Membrane CD73 on Tumor Cell Lines
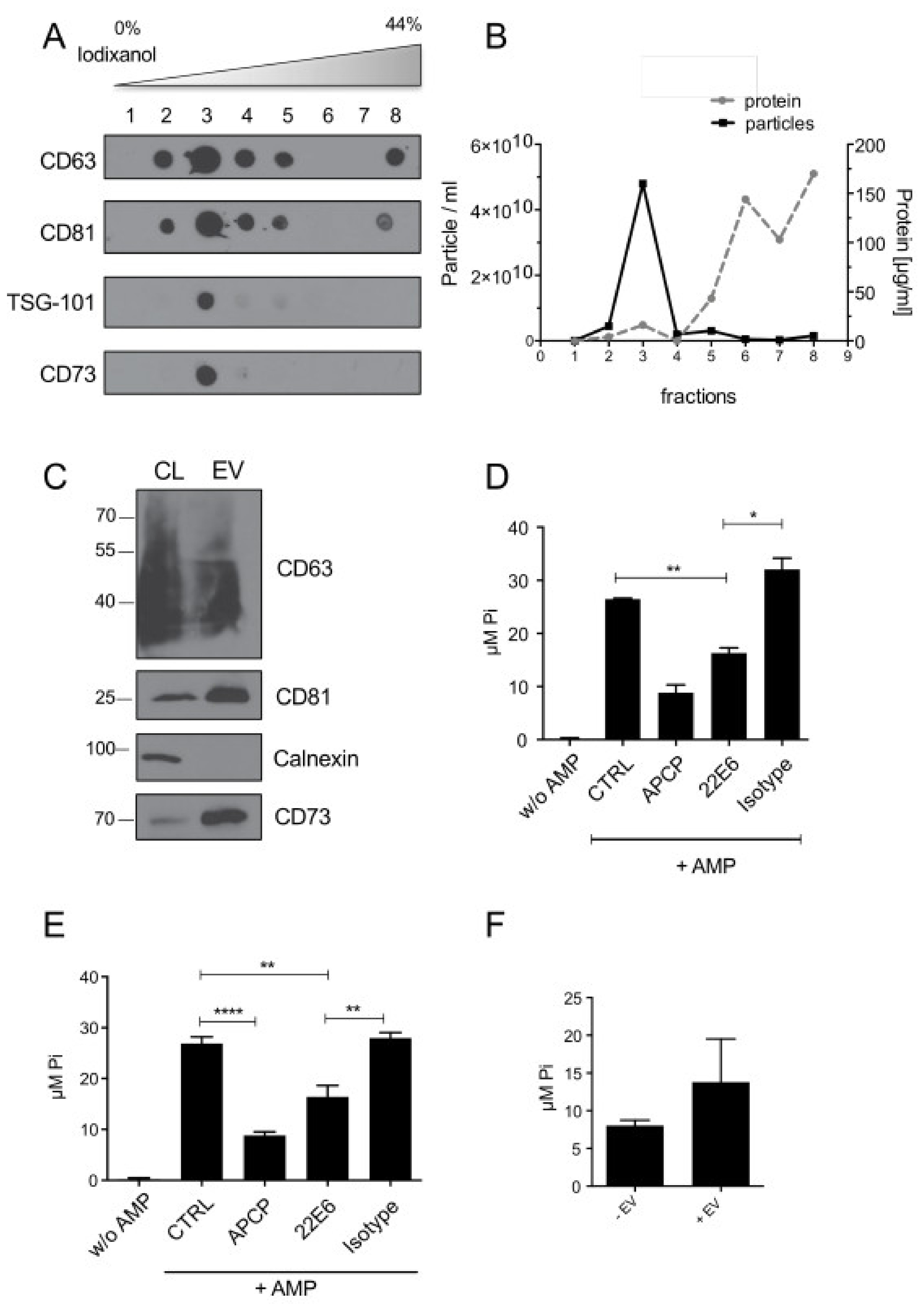
3.3. 22E6 Inhibits CD73 Enzymatic Activity on Tumor Derived Extracellular Vesicles
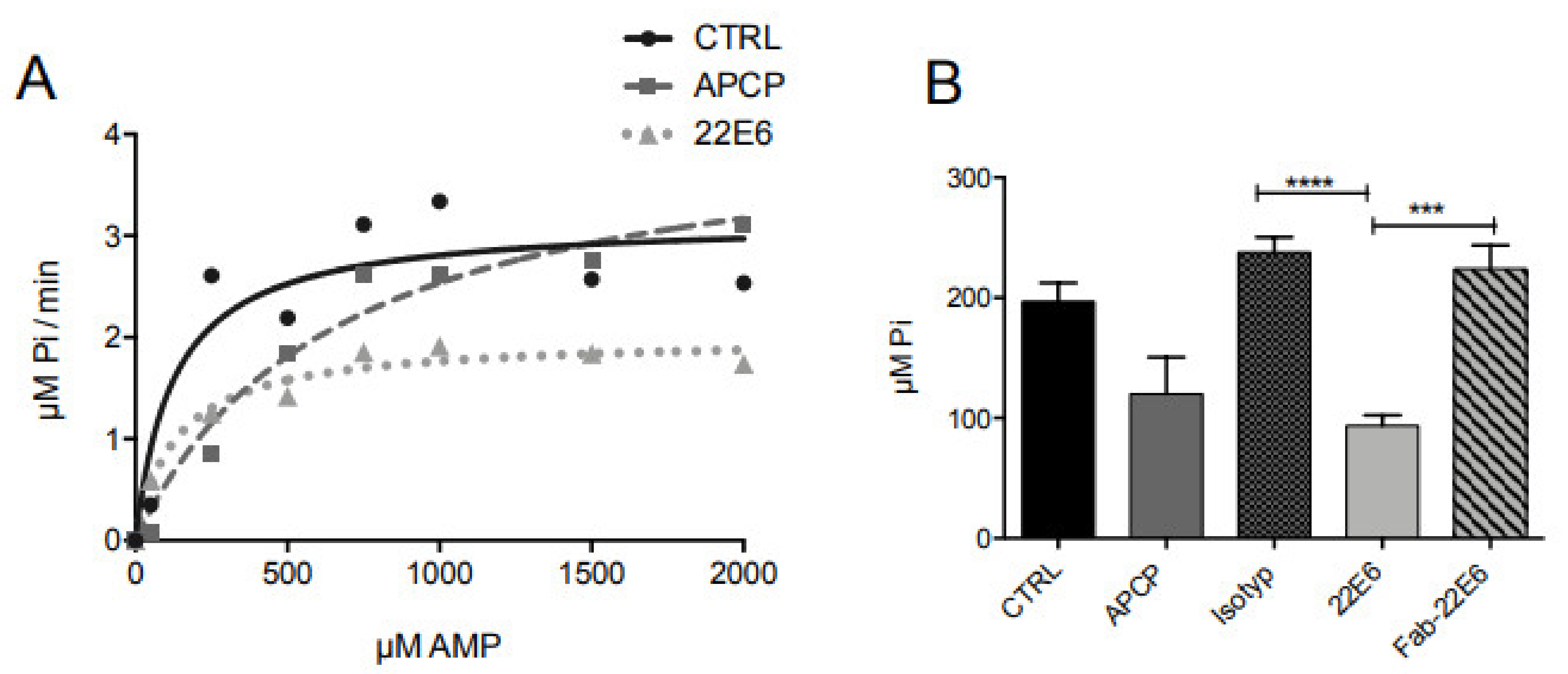
3.4. 22E6 Is a Non-Competitive CD73 Inhibitor
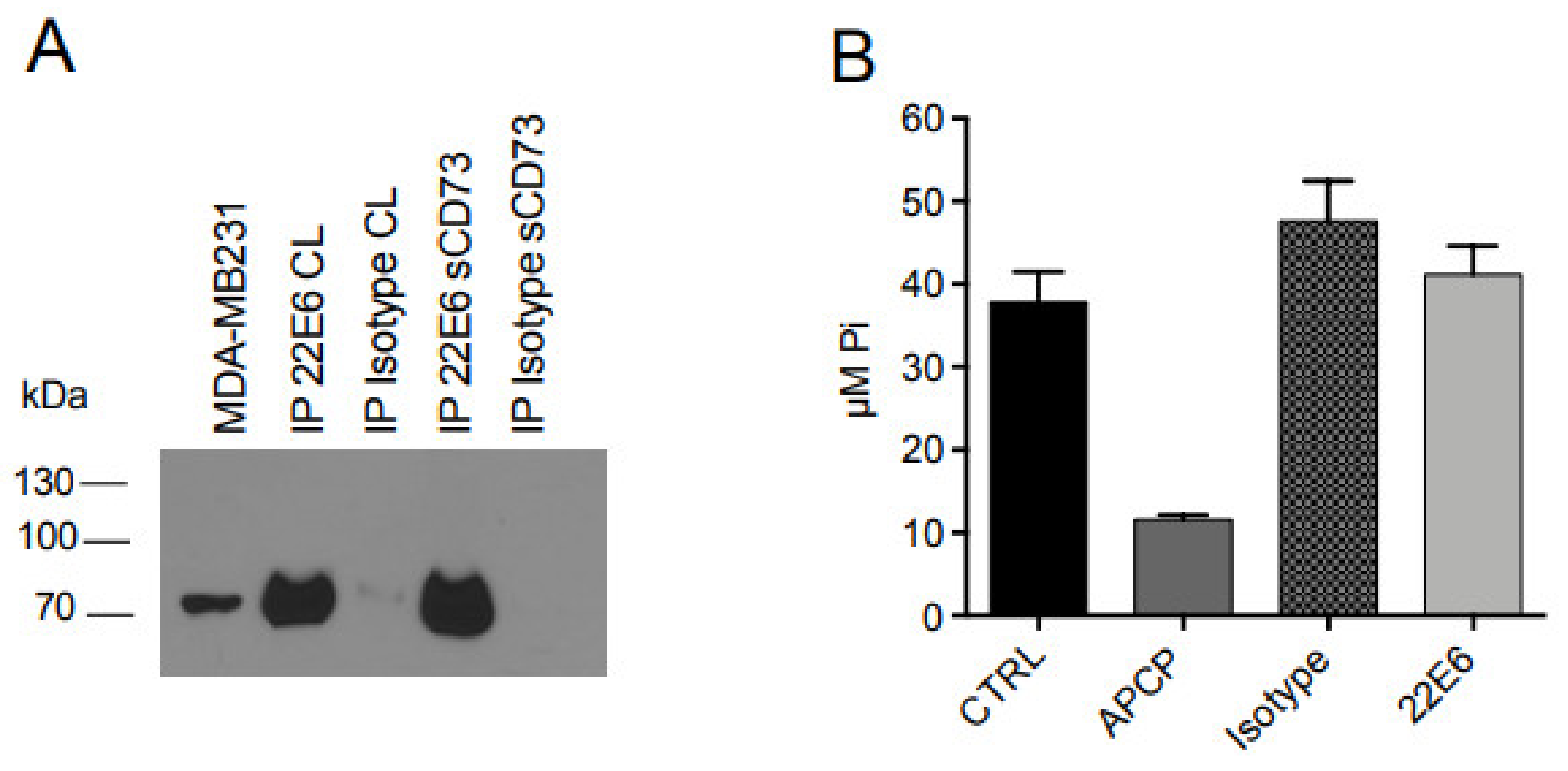
3.5. 22E6 Does Not Inhibit the Enzymatic Activity of Soluble CD73 (sCD73)
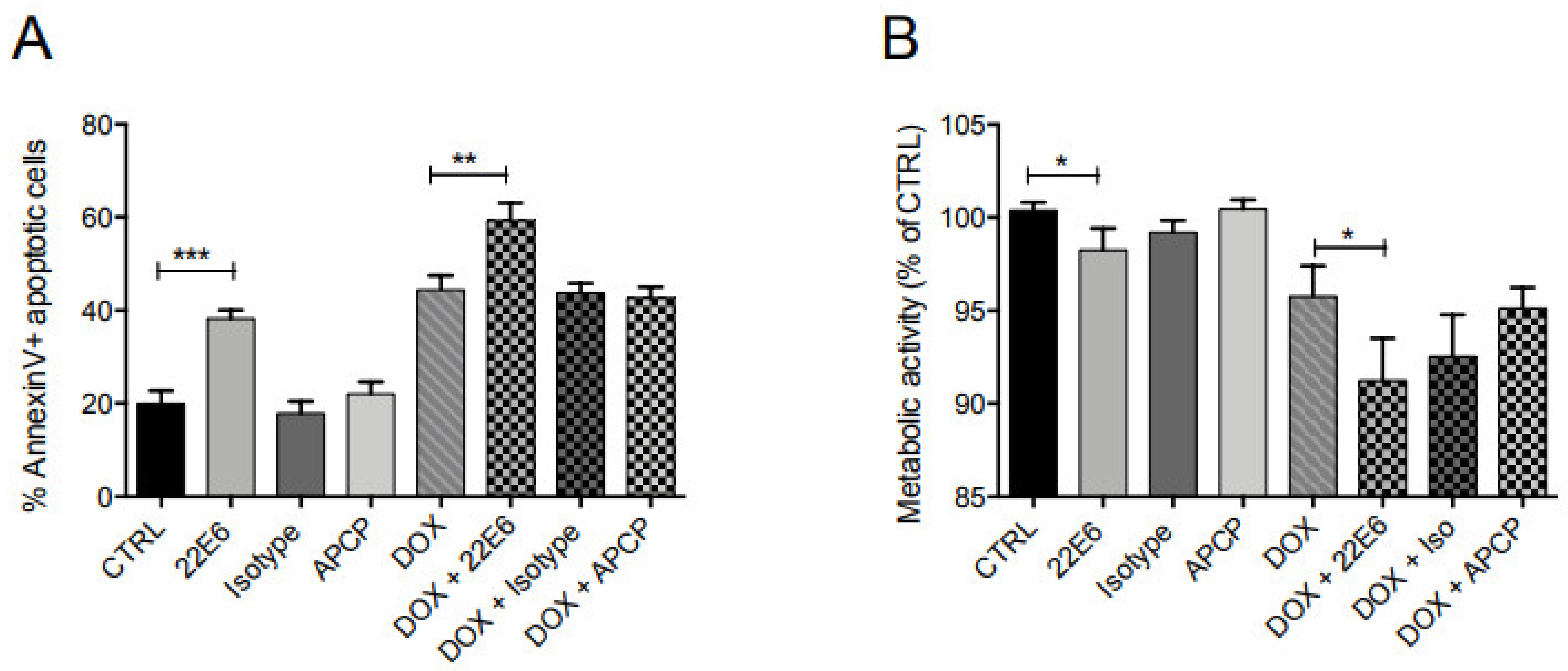
3.6. 22E6 Induces Apoptosis in TNBC
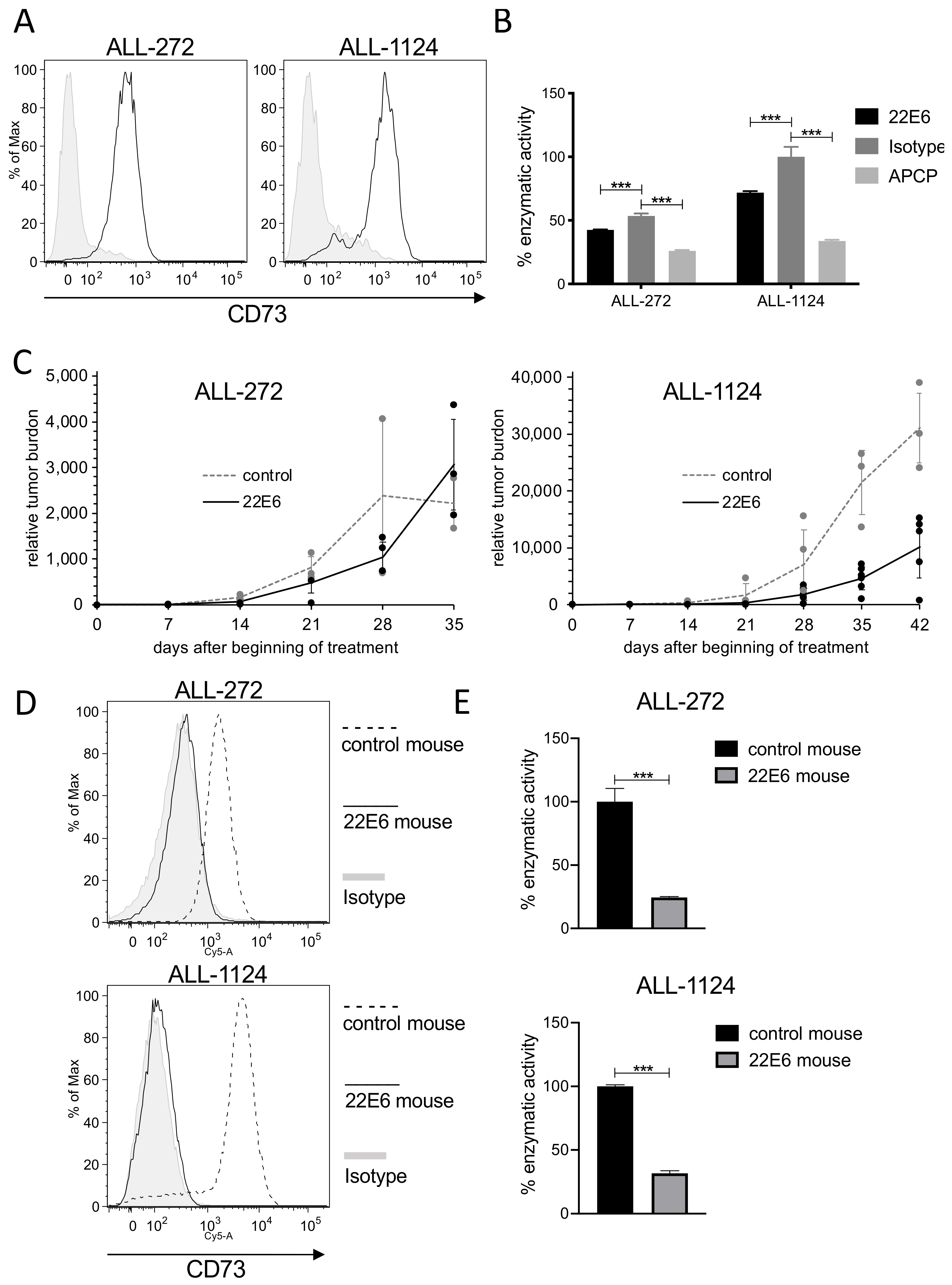
3.7. 22E6 Selects for a CD73dim/neg Subpopulation of Patient Derived ALL Cells In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Colgan, S.P.; Eltzschig, H.K.; Eckle, T.; Thompson, L.F. Physiological roles for ecto-5′-nucleotidase (CD73). Purinergic Signal. 2006, 2, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schneider, E.; Rissiek, A.; Winzer, R.; Puig, B.; Rissiek, B.; Haag, F.; Mittrücker, H.-W.; Magnus, T.; Tolosa, E. Generation and Function of Non-cell-bound CD73 in Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Antonioli, L.; Blandizzi, C.; Pacher, P.; Haskó, G. Immunity, inflammation and cancer: A leading role for adenosine. Nat. Cancer 2013, 13, 842–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loi, S.; Pommey, S.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Beavis, P.A.; Darcy, P.K.; Smyth, M.J.; Stagg, J. CD73 promotes anthracycline resistance and poor prognosis in triple negative breast cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 11091–11096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blay, J.; White, T.D.; Hoskin, D.W. The extracellular fluid of solid carcinomas contains immunosuppressive concentrations of adenosine. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 2602–2605. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary, B.; Elkord, E. Regulatory T Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment and Cancer Progression: Role and Therapeutic Targeting. Vaccines 2016, 4, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quezada, C.; Garrido, W.; Oyarzún, C.; Fernández, K.; Segura, R.; Melo, R.; Casanello, P.; Sobrevia, L.; Martín, R.S. 5′-ectonucleotidase mediates multiple-drug resistance in glioblastoma multiforme cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2013, 228, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, S.; Horenstein, A.L.; Vaisitti, T.; Brusa, D.; Rossi, D.; Laurenti, L.; D’Arena, G.; Coscia, M.; Tripodo, C.; Inghirami, G.; et al. CD73-generated extracellular adenosine in chronic lymphocytic leukemia creates local conditions counteracting drug-induced cell death. Blood 2011, 118, 6141–6152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, T.; Ma, D.; Chen, S.; Zhi, X.; Yin, L.; Shao, Z.; Ou, Z.; Zhou, P. Ecto-5′-nucleotidase promotes invasion, migration and adhesion of human breast cancer cells. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 134, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B. CD73 promotes tumor growth and metastasis. OncoImmunology 2012, 1, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allard, B.; Turcotte, M.; Spring, K.; Pommey, S.; Royal, I.; Stagg, J. Anti-CD73 therapy impairs tumor angiogenesis. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 1466–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Gu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, B.; Fang, H.; Fei, Y.; Lv, K.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Lin, C.; et al. Impact of intratumoural CD73 expression on prognosis and therapeutic response in patients with gastric cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 157, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Pu, N.; Yin, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, G.; Lou, W.; Wu, W. CD73 acts as a prognostic biomarker and promotes progression and immune escape in pancreatic cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 8674–8686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.-L.; Shen, M.-N.; Hu, B.; Wang, B.-L.; Yang, W.-J.; Lv, L.-H.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Jin, A.-L.; Sun, Y.-F.; et al. CD73 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression and metastasis via activating PI3K/AKT signaling by inducing Rap1-mediated membrane localization of P110β and predicts poor prognosis. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turcotte, M.; Spring, K.; Pommey, S.; Chouinard, G.; Cousineau, I.; George, J.; Chen, G.M.; Gendoo, D.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Karn, T.; et al. CD73 Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 4494–4503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gärtner, K.; Battke, C.; Dünzkofer, J.; Hüls, C.; Von Neubeck, B.; Kellner, M.-K.; Fiestas, E.; Fackler, S.; Lang, S.; Zeidler, R. Tumor-derived extracellular vesicles activate primary monocytes. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 2013–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebinger, S.; Özdemir, E.Z.; Ziegenhain, C.; Tiedt, S.; Alves, C.C.; Grunert, M.; Dworzak, M.; Lutz, C.; Turati, V.A.; Enver, T.; et al. Characterization of Rare, Dormant, and Therapy-Resistant Cells in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 849–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhattarai, S.; Freundlieb, M.; Pippel, J.; Meyer, A.; Abdelrahman, A.; Fiene, A.; Lee, S.Y.; Zimmermann, H.; Yegutkin, G.G.; Strater, N.; et al. alpha,beta-Methylene-ADP (AOPCP) Derivatives and Analogues: Development of Potent and Selective ecto-5′-Nucleotidase (CD73) Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 6248–6263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, A.; Al-Taei, S.; Webber, J.; Mason, M.D.; Tabi, Z. Cancer Exosomes Express CD39 and CD73, Which Suppress T Cells through Adenosine Production. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, K.; Zebisch, M.; Pippel, J.; El-Tayeb, A.; Müller, C.; Sträter, N. Crystal Structure of the Human Ecto-5′-Nucleotidase (CD73): Insights into the Regulation of Purinergic Signaling. Structure 2012, 20, 2161–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mikhailov, A.; Sokolovskaya, A.; Yegutkin, G.G.; Amdahl, H.; West, A.; Yagita, H.; Lahesmaa, R.; Thompson, L.F.; Jalkanen, S.; Blokhin, D.; et al. CD73 Participates in Cellular Multiresistance Program and Protects against TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, A.; Joachims, M.L.; Thompson, L.F.; Miller, A.D.; Canoll, P.D.; Bynoe, M.S. CD73 Promotes Glioblastoma Pathogenesis and Enhances Its Chemoresistance via A2B Adenosine Receptor Signaling. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 4387–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geoghegan, J.C.; Diedrich, G.; Lu, X.; Rosenthal, K.; Sachsenmeier, K.F.; Wu, H.; Dall’Acqua, W.F.; Damschroder, M.M. Inhibition of CD73 AMP hydrolysis by a therapeutic antibody with a dual, non-competitive mechanism of action. mAbs 2016, 8, 454–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Antonioli, L.; Yegutkin, G.; Pacher, P.; Blandizzi, C.; Haskó, G. Anti-CD73 in Cancer Immunotherapy: Awakening New Opportunities. Trends Cancer 2016, 2, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahimova, R.; Fontanel, S.; Lionne, C.; Jordheim, L.P.; Peyrottes, S.; Chaloin, L. Identification of allosteric inhibitors of the ecto-5′-nucleotidase (CD73) targeting the dimer interface. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, e1005943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckle, T.; Füllbier, L.; Wehrmann, M.; Khoury, J.; Mittelbronn, M.; Ibla, J.; Rosenberger, P.; Eltzschig, H.K. Identification of Ectonucleotidases CD39 and CD73 in Innate Protection during Acute Lung Injury. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 8127–8137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenz, A.; Zhang, H.; Eckle, T.; Mittelbronn, M.; Wehrmann, M.; Köhle, C.; Kloor, D.; Thompson, L.F.; Osswald, H.; Eltzschig, H.K. Protective Role of Ecto-5′-Nucleotidase (CD73) in Renal Ischemia. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hart, M.L.; Köhler, D.; Eckle, T.; Kloor, D.; Stahl, G.L.; Eltzschig, H.K. Direct Treatment of Mouse or Human Blood with Soluble 5′-Nucleotidase Inhibits Platelet Aggregation. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 1477–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thompson, L.F.; Eltzschig, H.K.; Ibla, J.C.; Van De Wiele, C.J.; Resta, R.; Morote-Garcia, J.C.; Colgan, S.P. Crucial Role for Ecto-5′-Nucleotidase (CD73) in Vascular Leakage during Hypoxia. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 200, 1395–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yu, J.; Jian, R.; Tang, S.; Yin, L.; Zhou, P. RNAi-mediated CD73 suppression induces apoptosis and cell-cycle arrest in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2010, 101, 2561–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kellner, M.; von Neubeck, B.; Czogalla, B.; Feederle, R.; Vick, B.; Jeremias, I.; Zeidler, R. A Novel Anti-CD73 Antibody That Selectively Inhibits Membrane CD73 Shows Antitumor Activity and Induces Tumor Immune Escape. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10040825
Kellner M, von Neubeck B, Czogalla B, Feederle R, Vick B, Jeremias I, Zeidler R. A Novel Anti-CD73 Antibody That Selectively Inhibits Membrane CD73 Shows Antitumor Activity and Induces Tumor Immune Escape. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(4):825. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10040825
Chicago/Turabian StyleKellner, Markus, Bettina von Neubeck, Bastian Czogalla, Regina Feederle, Binje Vick, Irmela Jeremias, and Reinhard Zeidler. 2022. "A Novel Anti-CD73 Antibody That Selectively Inhibits Membrane CD73 Shows Antitumor Activity and Induces Tumor Immune Escape" Biomedicines 10, no. 4: 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10040825
APA StyleKellner, M., von Neubeck, B., Czogalla, B., Feederle, R., Vick, B., Jeremias, I., & Zeidler, R. (2022). A Novel Anti-CD73 Antibody That Selectively Inhibits Membrane CD73 Shows Antitumor Activity and Induces Tumor Immune Escape. Biomedicines, 10(4), 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10040825





