Worsening Rhinosinusitis as a Prognostic Factor for Patients with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Characteristics
2.2. Radiation Therapy Protocol
2.3. Chemotherapy Protocol
2.4. Follow-Up
- Mucosal thickening of the sinus wall;
- Air–fluid level in the sinus cavity;
- Opacification at the ostiomeatal complex;
- Enhanced and thickened mucosa in the contrast-enhanced study.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient and Disease Characteristics
3.2. Factors Associated with the Prognosis of NPC Survival
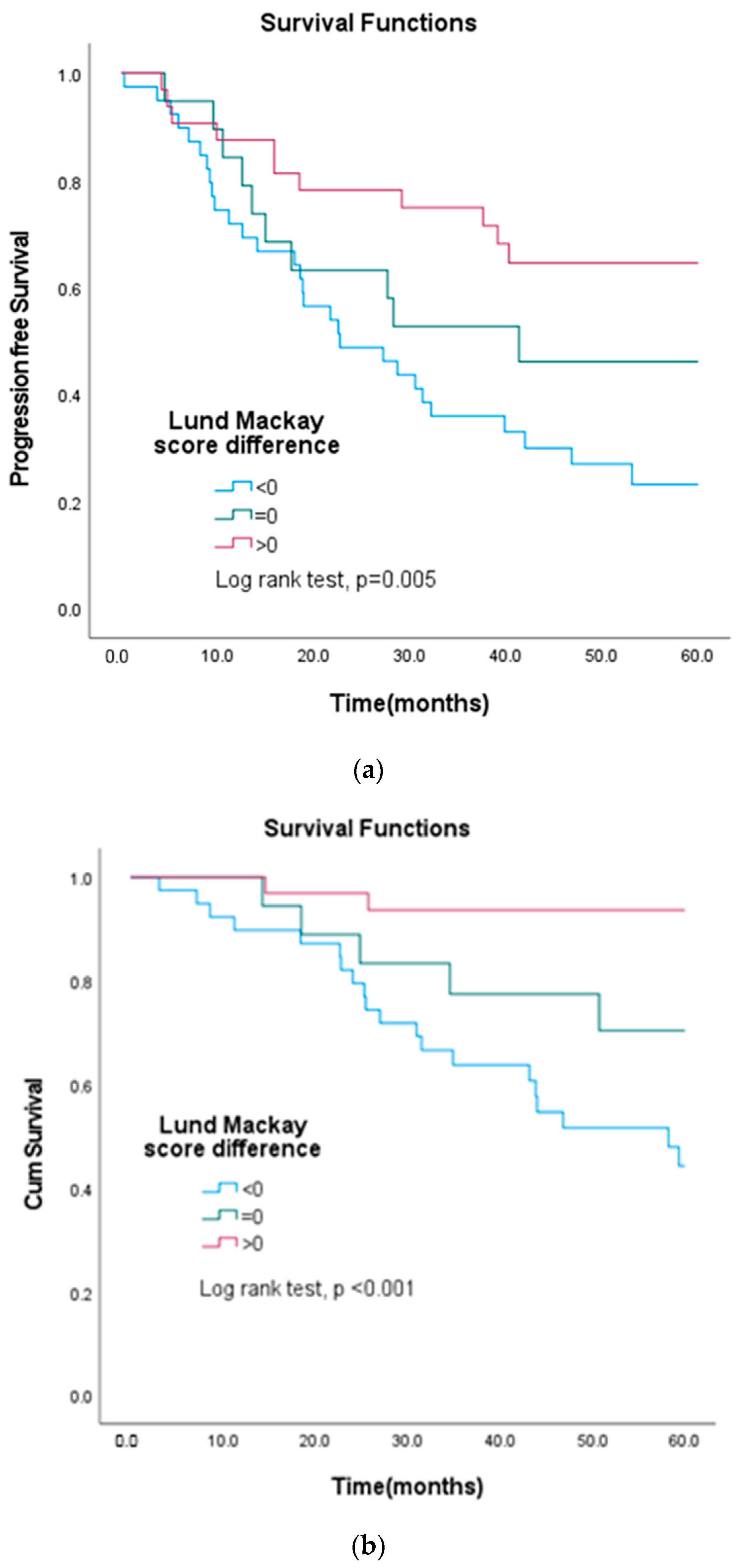
3.3. The Role of Rhinosinusitis before and after Treatment in the Overall Survival of Patients with NPC
4. Discussion
- Poor treatment response would lead to partial tumor regression.
- Impaired sinus drainage destroys the bony sinus wall, or tumor sinus mucosa invasion would make the sinusitis persist.
- NPC cells created a proinflammatory microenvironment, putting the nasal cavity and nasopharynx under inflammatory status. Sinus drainage pathway and sinus wall and mucosa restoration indicate substantial tumor volume shrinkage after radiation therapy.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.P.; Chan, A.T.C.; Le, Q.T.; Blanchard, P.; Sun, Y.; Ma, J. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet 2019, 394, 64–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Registry Report, 2019 Taiwan. 2019. Available online: https://www.hpa.gov.tw/File/Attach/14913/File_18302.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Luo, W. Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Ecology Theory: Cancer as Multidimensional Spatiotemporal “Unity of Ecology and Evolution” Pathological Ecosystem. Med. Pharmacol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.J.C.; Riaz, N.; Cheng, S.K.; Lu, J.J.; Lee, N.Y. Intensity-modulated radiation therapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A review. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2012, 1, 129–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanda, C.; Sarafoleanu, C. Advantages of VMAT-IMRT technique in nasopharyngeal cancer. Rom. J. Rhinol. 2016, 6, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Su, Y.X.; Liu, L.P.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Cao, X.J.; Dong, W.; Yang, X.H.; Xu, J.; Yu, S.; Hao, J.F. Factors influencing the incidence of sinusitis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients after intensity-modulated radiation therapy. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2014, 271, 3195–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennis, P.; Sherrill, B.; Fernandez, C.; Dolan, C. Cancer risk in asthmatic populations. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2005, 95, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekbom, A.; Helmick, C.; Zack, M.; Adami, H.O. Ulcerative colitis and colorectal cancer: A population-based study. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 323, 1228–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, C.A.; Marino, M.J.; Hawkey, N.; Lawlor, C.M.; McCoul, E.D. Sinonasal tract inflammation as a precursor to nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2016, 154, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, E.L.; Riley, C.A.; Hsieh, M.C.; Marino, M.J.; Wu, X.C.; McCoul, E.D. Chronic sinonasal tract inflammation as a precursor to nasopharyngeal carcinoma and sinonasal malignancy in the United States. Int. Forum. Allergy Rhinol. 2017, 7, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, S.H.; Chen, P.Y.; Lin, H.C.; Ting, J.; Chung, S.D. Association of rhinosinusitis with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A population-based study. Laryngoscope 2014, 124, 1515–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.J.; Huang, M.Y.; Shih, M.P.; Cheng, K.Y.; Lee, K.W.; Lu, T.Y.; Yuan, S.S.; Fang, P.T. Post-radiation sinusitis is associated with recurrence in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients treated with intensity-modulated radiation therapy. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 14, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.W.; Bhattacharyya, N. Diagnostic and staging accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging for the assessment of sinonasal disease. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2009, 23, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathor, A.; Bhattacharjee, A. Clinical-radiological correlation and role of computed tomography staging in chronic rhinosinusitis. World J. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2017, 3, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, V.J.; Kennedy, D.W. Staging for rhinosinusitis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1997, 117, S35–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, S.G.; Trope, M.; Blasetti, M.; Doghramji, L.; Parasher, A.; Glicksman, J.T.; Kennedy, D.W.; Thaler, E.R.; Cohen, N.A.; Palmer, J.N.; et al. Preoperative Lund-Mackay computed tomography score is associated with preoperative symptom severity and predicts quality-of-life outcome trajectories after sinus surgery. Int. Forum. Allergy Rhinol. 2018, 8, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, V.J.; Mackay, I.S. Staging in rhinosinusitis. Rhinology 1993, 31, 183–184. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, N.; Bhattacharyya, N. Determination of the “incidental” Lund score for the staging of chronic rhinosinusitis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2001, 125, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.C.; Huang, S.F.; Lee, T.J.; Ng, S.H.; Chang, J.T. Postirradiation sinus mucosa disease in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Laryngoscope 2007, 117, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsin, C.H.; Tseng, H.C.; Lin, H.P.; Chen, T.H. Sinus mucosa status in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated with intensity-modulated radiotherapy: A 5-year follow-up. Head Neck 2016, 38, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.; Guo, X.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Chen, P.; Liang, F.; Tang, H.; Deng, M.; Wu, M.; Ma, J.; et al. Analysis of the contribution of nasopharyngeal epithelial cancer cells to the induction of a local inflammatory response. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 138, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubizarreta, P.A.; D’Antonio, G.; Raslawski, E.; Gallo, G.; Preciado, M.V.; Casak, S.J.; Scopinaro, M.; Morales, G.; Sackmann-Muriel, F. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma in childhood and adolescence: A single-institution experience with combined therapy. Cancer 2000, 89, 690–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siala, W.; Mnejja, W.; Elloumi, F.; Ghorbel, A.; Mnif, J.; Frikha, M.; Daoud, J. Late toxicities after conventional radiotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Incidence and risk factors. J. Radiother. 2014, 2014, 268340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pow, E.H.; Kwong, D.L.; McMillan, A.S.; Wong, M.C.; Sham, J.S.; Leung, L.H.; Leung, W.K. Xerostomia and quality of life after intensity-modulated radiotherapy vs. conventional radiotherapy for early-stage nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Initial report on a randomized controlled clinical trial. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2006, 66, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Han, F.; Xiao, W.; Xiang, Y.; Lu, L.; Deng, X.; Cui, N.; Zhao, C. Analysis of late toxicity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients treated with intensity modulated radiation therapy. Radiat. Oncol. 2015, 10, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, G.D.; Holliday, E.B.; Kocak-Uzel, E.; Hernandez, M.; Garden, A.S.; Rosenthal, D.I.; Frank, S.J. Intensity-modulated proton therapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Decreased radiation dose to normal structures and encouraging clinical outcomes. Head Neck 2016, 38 (Suppl. 1), E1886–E1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.W.; Huang, C.C.; Lee, Y.S.; Chou, Y.C.; Fan, K.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Huang, B.S.; Yang, S.W.; Huang, C.C.; Chang, P.H.; et al. Post-irradiation sinus mucosa disease in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients treated with intensity-modulated proton therapy. Cancers 2022, 14, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsin, C.H.; Tseng, H.C.; Lin, H.P.; Chen, T.H. Post-irradiation otitis media, rhinosinusitis, and their interrelationship in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients treated by IMRT. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 273, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, F.A. Inflammation, carcinogenesis and cancer. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2001, 1, 1651–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lane, A.P. Chronic rhinosinusitis as a multifactorial inflammatory disorder. Curr. Infect Dis. Rep. 2011, 13, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Tsang, C.M.; Deng, W.; Yip, Y.L.; Lui, V.W.; Wong, S.C.; Cheung, A.L.; Hau, P.M.; Zeng, M.; Lung, M.L.; et al. Enhanced IL-6/IL-6R signaling promotes growth and malignant properties in EBV-infected premalignant and cancerous nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | NPC (N = 90) n (%) |
|---|---|
| Sex | |
| Female | 27 (30.0) |
| Male | 63 (70.0) |
| Mean age, y (±SD) | 55.3 ± 12.1 |
| Age group | |
| <45 | 15 (16.7) |
| 45–64 | 58 (64.4) |
| ≥65 | 17 (18.9) |
| Histology (WHO type) | |
| Type I | 1 (1.1) |
| Type II | 69 (76.7) |
| Type III | 20 (22.2) |
| AJCC staging | |
| I | 9 (10.0) |
| II | 17 (18.9) |
| III | 22 (24.4) |
| IVa | 29 (32.2) |
| IVb | 8 (8.9) |
| IVc | 5 (5.6) |
| Treatment | |
| RT | 12 (13.3) |
| CCRT | 66 (73.3) |
| NACCRT | 12 (13.3) |
| Treatment response | |
| CR | 71 (78.9) |
| PR | 12 (13.3) |
| Residual | 7 (7.8) |
| Recurrence | |
| None | 40 (44.4) |
| Local | 20 (22.2) |
| Regional | 10 (11.1) |
| Distant | 20 (22.2) |
| PRCRS | 31 (34.4) |
| L–M total score | 7.7 ± 4.9 |
| PSCRS | 33 (36.7) |
| L–M total score | 8.1 ± 4.7 |
| L–M score Txdifferent | |
| All | −0.5 ± 4.4 |
| PRCRS | 2.0 ± 4.7 |
| PSCRS | −2.8 ± 5.9 |
| Follow-up time (months) | 44.9 ± 16.8 |
| Total death | 27 (30.0) |
| Variable | Crude | Adjusted | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | (95% CI) | p-Value | HR | (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Sex (male vs. female) | 0.63 | 0.26–1.57 | 0.324 | |||
| Age (every one year) | 1.03 | 0.99–1.06 | 0.084 | |||
| AJCC staging | ||||||
| I | Ref. | |||||
| II | 1.47 | 0.15–14.11 | 0.740 | |||
| III | 2.88 | 0.35–23.99 | 0.327 | |||
| IV | 5.08 | 0.67–38.35 | 0.115 | |||
| Histology (WHO type) | ||||||
| Type I and II | Ref. | |||||
| Type III | 1.06 | 0.40–2.82 | 0.902 | |||
| Recurrence (yes vs. no) | 79.1 | 3.49–1795.82 | 0.006 | |||
| Tumor | ||||||
| 1 | Ref. | Ref. | ||||
| 2 | 1.70 | 0.49–5.86 | 0.403 | 1.05 | 0.30–3.72 | 0.943 |
| 3 | 1.29 | 0.31–5.41 | 0.728 | 0.96 | 0.23–4.07 | 0.953 |
| 4 | 3.13 | 1.12–8.74 | 0.029 | 2.47 | 0.85–7.16 | 0.097 |
| Node | ||||||
| 0 | Ref. | |||||
| 1 | 2.02 | 0.55–7.48 | 0.291 | |||
| 2 | 3.08 | 0.84–11.24 | 0.089 | |||
| 3 | 2.78 | 0.66–11.72 | 0.164 | |||
| Metastasis (yes vs. no) | 2.85 | 0.85–9.51 | 0.089 | |||
| PRRS (yes vs. no) | 0.98 | 0.44–2.18 | 0.955 | |||
| PSRS (yes vs. no) | 3.51 | 1.60–7.68 | 0.002 | 1.76 | 0.72–4.30 | 0.214 |
| L–M score Txdifferent group | ||||||
| Positive | Ref. | Ref. | ||||
| Zero | 4.68 | 0.91–24.13 | 0.065 | 5.09 | 0.98–26.35 | 0.053 |
| Negative | 10.09 | 2.36–43.18 | 0.002 | 8.41 | 1.86–38.14 | 0.006 |
| Adjusted: tumor and PSRS | ||||||
| Variables | Number of Patients | Lund–Mackay Score Difference Median (Q1, Q3) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor | 0.181 | ||
| 1 | 29 | 0 (−2.2) | |
| 2 | 16 | −1 (−4.0) | |
| 3 | 13 | 0 (−2.1) | |
| 4 | 32 | 0 (−3.2) | |
| Node | 0.714 | ||
| 0 | 18 | 0 (−2.0) | |
| 1 | 30 | 0 (−4.3) | |
| 2 | 27 | 0 (−2.1) | |
| 3 | 15 | 0 (−2.2) | |
| Metastasis | 0.210 * | ||
| 0 | 85 | 0 (−2.2) | |
| 1 | 5 | −5 (−6.0) | |
| AJCC staging | 0.531 | ||
| I | 9 | 0 (−2.0) | |
| II | 17 | 0 (−4.1) | |
| III | 22 | 0 (−2.3) | |
| IV | 42 | 0 (−3.2) | |
| Treatment | 0.641 | ||
| RT | 12 | 0 (−2.0) | |
| CCRT | 66 | 0 (−3.2) | |
| NACCRT | 12 | 1 (−2.2) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, W.-C.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Hsu, C.-J.; Wu, H.-P.; Hsu, Y.-J. Worsening Rhinosinusitis as a Prognostic Factor for Patients with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Retrospective Study. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3235. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123235
Lin W-C, Kuo Y-H, Hsu C-J, Wu H-P, Hsu Y-J. Worsening Rhinosinusitis as a Prognostic Factor for Patients with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Retrospective Study. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(12):3235. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123235
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Wei-Chieh, Yu-Hung Kuo, Chuan-Jen Hsu, Hung-Pin Wu, and Yuan-Jhen Hsu. 2022. "Worsening Rhinosinusitis as a Prognostic Factor for Patients with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Retrospective Study" Biomedicines 10, no. 12: 3235. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123235
APA StyleLin, W.-C., Kuo, Y.-H., Hsu, C.-J., Wu, H.-P., & Hsu, Y.-J. (2022). Worsening Rhinosinusitis as a Prognostic Factor for Patients with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Retrospective Study. Biomedicines, 10(12), 3235. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123235






