Regulatory Effects of Curcumin on Platelets: An Update and Future Directions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Functions of Platelets
2.1. Hemostasis
2.2. Platelet’s Role beyond Hemostasis
- a.
- Inflammation and immunity
- b.
- Cancer
- c.
- Wound healing
- d.
- Infection
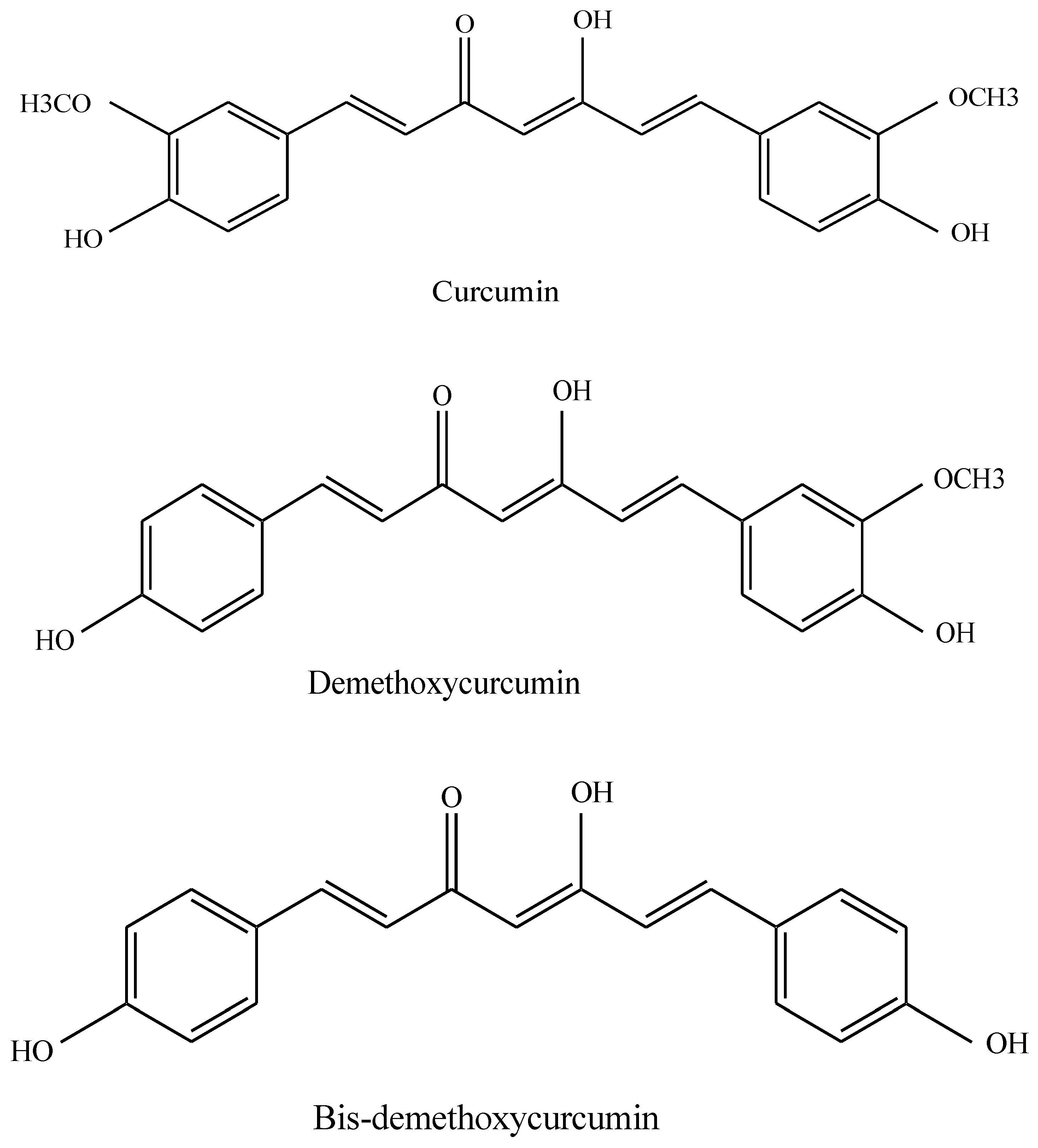
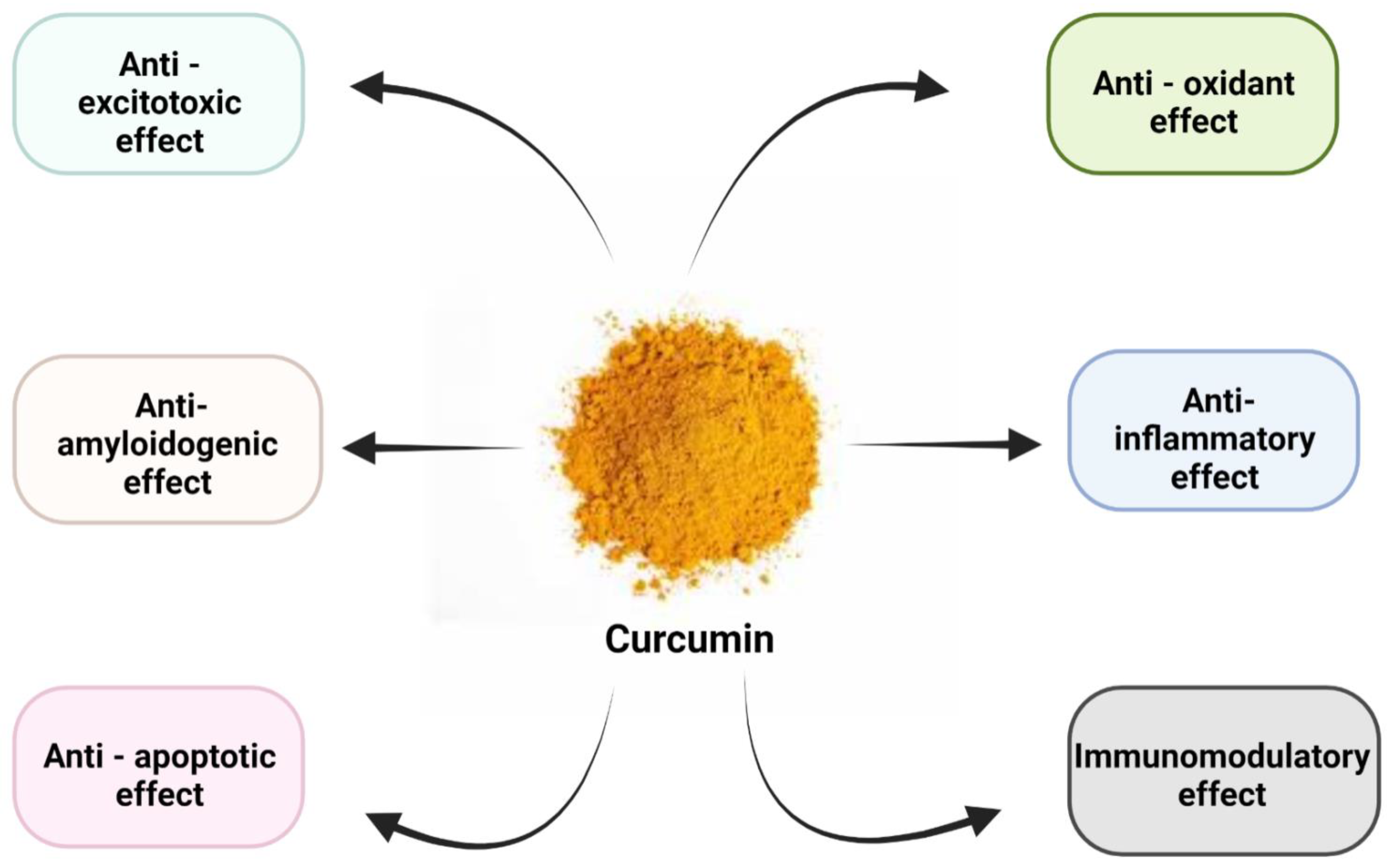
3. Pharmacological Effects of Curcumin
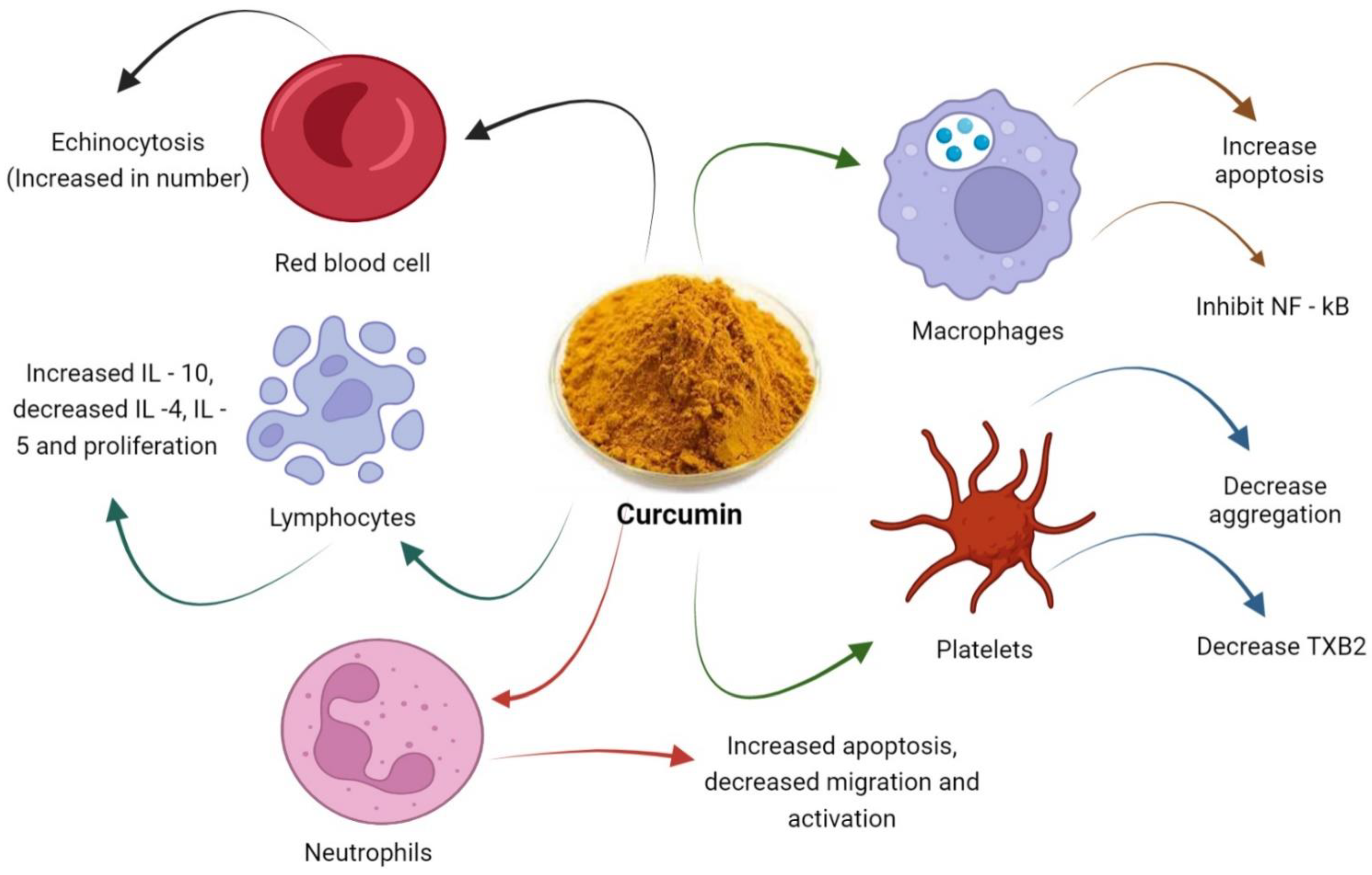
4. Effects of Curcumin on Platelets
4.1. Coagulation and Angiogenesis
| S.No. | Parameter | Effect/Mechanism | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Coagulation | Inhibit coagulation, ↓ TNF | [106] |
| 2 | Platelet aggregation | Inhibit platelet aggregation and platetlet plug formation, ↓ cell adhesion molecule 1, netrin G1, delta-like 1, and plasma cell endoplasmic reticulum protein-1 | [107] |
| 3 | Platelets activation | Inhibit activation of platelets to form thrombosis/embolism, ↓ P-selectin, E-selectin, and GP IIb/IIIa | [108] |
| 4 | Autophagy | inhibition of PKB, and activation of AMP kinase | [109] |
| 5 | Antioxidant effect | ↑ antioxidant enzymes, ↓ oxidative stress parameters, ↑ platelet factor-3-like activity | [110,111] |
| 6 | Platelet count | ↑ platelets level | [112] |
| 7 | PDGF | Ameliorated lung fibrosis, liver fibrosis, and cirrhosis, Inhibit PDGF | [113] |
| 8 | Platelet aggregation and hyperlipidemia | ↓ cholesterol, ↑ antioxidant activity | [114] |
| 9 | Atherosclerosis | Thromboxane inhibition, ↑ prostacyclin activity | [115] |
| 10 | Arachidonic acid-mediated platelet aggregation | Inhibition of TXA2 and mobilization of intracellular Ca2+ | [116] |
4.2. Activation of Platelets
4.3. Autophagy
4.4. Oxidative Status of Platelets
4.5. Platelets Count
4.6. Effect on Platelet Derived Growth Factor (PDGF)
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baldi, A.; De Luca, A.; Maiorano, P.; D’Angelo, C.; Giordano, A. Curcumin as an anticancer agent in malignant mesothelioma: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsamanesh, N.; Moossavi, M.; Bahrami, A.; Butler, A.E.; Sahebkar, A. Therapeutic potential of curcumin in diabetic complications. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 136, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hesari, A.; Azizian, M.; Sheikhi, A.; Nesaei, A.; Sanaei, S.; Mahinparvar, N.; Derakhshani, M.; Hedayt, P.; Ghasemi, F.; Mirzaei, H. Chemopreventive and therapeutic potential of curcumin in esophageal cancer: Current and future status. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Sundaram, C.; Malani, N.; Ichikawa, H. Curcumin: The Indian solid gold. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2007, 595, 1–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehanny, M.; Hathout, R.M.; Geneidi, A.S.; Mansour, S. Exploring the use of nanocarrier systems to deliver the magical molecule; Curcumin and its derivatives. J. Control Release 2016, 225, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Harikumar, K.B. Potential therapeutic effects of curcumin, the anti-inflammatory agent, against neurodegenerative, cardiovascular, pulmonary, metabolic, autoimmune and neoplastic diseases. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 41, 40–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unlu, A.; Nayir, E.; Dogukan Kalenderoglu, M.; Kirca, O.; Ozdogan, M. Curcumin (Turmeric) and cancer. J. Buon 2016, 21, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar]
- Funamoto, M.; Shimizu, K.; Sunagawa, Y.; Katanasaka, Y.; Miyazaki, Y.; Kakeya, H.; Yamakage, H.; Satoh-Asahara, N.; Wada, H.; Hasegawa, K.; et al. Effects of Highly Absorbable Curcumin in Patients with Impaired Glucose Tolerance and Non-Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. J. Diabetes Res. 2019, 2019, 8208237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Beevers, S.C.; Huang, S. The targets of curcumin. Curr. Drug Targets 2011, 12, 332–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Stojanović-Radić, Z.; Matejić, J.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Kumar, N.V.A.; Martins, N.; Sharifi-Rad, J. The therapeutic potential of curcumin: A review of clinical trials. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 163, 527–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radomska-Leśniewska, D.M.; Osiecka-Iwan, A.; Hyc, A.; Góźdź, A.; Dąbrowska, A.M.; Skopiński, P. Therapeutic potential of curcumin in eye diseases. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2019, 44, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moeini, A.; Pedram, P.; Makvandi, P.; Malinconico, M.; d’Ayala, G.G. Wound healing and antimicrobial effect of active secondary metabolites in chitosan-based wound dressings: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 233, 115839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.R.; Zhang, D.; Oswald, B.E.; Carrim, N.; Wang, X.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, Q.; LaValle, C.; McKeown, T.; Marshall, A.H.; et al. Platelets are versatile cells: New discoveries in hemostasis, thrombosis, immune responses, tumor metastasis and beyond. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2016, 53, 409–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachowicz, B.; Morel, A.; Miller, E.; Saluk, J. The physiology of blood platelets and changes of their biological activities in multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2016, 76, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefrançais, E.; Ortiz-Muñoz, G.; Caudrillier, A.; Mallavia, B.; Liu, F.; Sayah, D.M.; Thornton, E.E.; Headley, M.B.; David, T.; Coughlin, S.R.; et al. The lung is a site of platelet biogenesis and a reservoir for haematopoietic progenitors. Nature 2017, 544, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegner, D.; Vaneeuwijk, J.M.M.; Angay, O.; Gorelashvili, M.G.; Semeniak, D.; Pinnecker, J.; Schmithausen, P.; Meyer, I.; Friedrich, M.; Dütting, S.; et al. Thrombopoiesis is spatially regulated by the bone marrow vasculature. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grozovsky, R.; Giannini, S.; Falet, H.; Hoffmeister, K.M. Regulating billions of blood platelets: Glycans and beyond. J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2015, 126, 1877–1884. [Google Scholar]
- Kaser, A.; Brandacher, G.; Steurer, W.; Kaser, S.; Offner, F.A.; Zoller, H.; Theurl, I.; Widder, W.; Molnar, C.; Ludwiczek, O. Interleukin-6 stimulates thrombopoiesis through thrombopoietin: Role in inflammatory thrombocytosis. J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2001, 98, 2720–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semeniak, D.; Kulawig, R.; Stegner, D.; Meyer, I.; Schwiebert, S.; Bösing, H.; Eckes, B.; Nieswandt, B.; Schulze, H. Proplatelet formation is selectively inhibited by collagen type I through Syk-independent GPVI signaling. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 3473–3484. [Google Scholar]
- Coppinger, J.A.; Cagney, G.; Toomey, S.; Kislinger, T.; Belton, O.; McRedmond, J.P.; Cahill, D.J.; Emili, A.; Fitzgerald, D.J.; Maguire, P.B. Characterization of the proteins released from activated platelets leads to localization of novel platelet proteins in human atherosclerotic lesions. Blood 2004, 103, 2096–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijten, P.; van Holten, T.; Woo, L.L.; Bleijerveld, O.B.; Roest, M.; Heck, A.J.; Scholten, A. High precision platelet releasate definition by quantitative reversed protein profiling—Brief report. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 1635–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, P.; Flaumenhaft, R. Platelet α-granules: Basic biology and clinical correlates. Blood Rev. 2009, 23, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Italiano, J.E., Jr.; Battinelli, E.M. Selective sorting of alpha-granule proteins. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 7, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrell, C.N.; Aggrey, A.A.; Chapman, L.M.; Modjeski, K.L.J.B. Emerging roles for platelets as immune and inflammatory cells. J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2014, 123, 2759–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, F.A.; Lea, C.R.; Oldfield, E.; Docampo, R.; Gande, R.; Gibson, K.J.C.; Brown, A.K.; Krumbach, K.; Dover, L.G.; Sahm, H.; et al. Human platelet dense granules contain polyphosphate and are similar to acidocalcisomes of bacteria and unicellular eukaryotes. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 44250–44257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijnen, H.; Van Der Sluijs, P.J. Platelet secretory behaviour: As diverse as the granules… or not? J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13, 2141–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thon, J.N.; Peters, C.G.; Machlus, K.R.; Aslam, R.; Rowley, J.; MacLeod, H.; Devine, M.T.; Fuchs, T.A.; Weyrich, A.S.; Semple, J.W.; et al. T granules in human platelets function in TLR9 organization and signaling. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 198, 561–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurden, A.T.; Nurden, P. The gray platelet syndrome: Clinical spectrum of the disease. Blood Rev. 2007, 21, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerrits, A.J.; Frelinger III, A.L.; Michelson, A.D. Whole blood analysis of leukocyte-platelet aggregates. Curr. Protoc. Cytom. 2016, 78, 6.15.1–6.15.10. [Google Scholar]
- Habets, K.L.; Huizinga, T.W.; Toes, R.E. Platelets and autoimmunity. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 43, 746–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenne, C.N.; Kubes, P. Platelets in inflammation and infection. Platelets 2015, 26, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapur, R.; Zufferey, A.; Boilard, E.; Semple, J.W. Nouvelle cuisine: Platelets served with inflammation. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 5579–5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salamanna, F.; Maglio, M.; Sartori, M.; Landini, M.P.; Fini, M. Vitamin D and platelets: A menacing duo in COVID-19 and potential relation to bone remodeling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrono, C.; Coller, B.; FitzGerald, G.A.; Hirsh, J.; Roth, G. Platelet-active drugs: The relationships among dose, effectiveness, and side effects: The Seventh ACCP Conference on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy. Comp. Study 2004, 126, 234S–264S. [Google Scholar]
- Cammisotto, V.; Baratta, F.; Simeone, P.G.; Barale, C.; Lupia, E.; Galardo, G.; Santilli, F.; Russo, I.; Pignatelli, P. Proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin type 9 (PCSK9) beyond lipids: The role in oxidative stress and thrombosis. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, G.M.; da Silva, M.C.; Nascimento, D.V.G.; Lima Silva, E.M.; Gouvêa, F.F.F.; de França Lopes, L.G.; Araújo, A.V.; Ferraz Pereira, K.N.; de Queiroz, T.M. Nitric oxide as a central molecule in hypertension: Focus on the vasorelaxant activity of new nitric oxide donors. Biology 2021, 10, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheswaraiah, A.; Jaganmohan Rao, L.; Naidu, K.A. Anti-platelet activity of water dispersible curcuminoids in rat platelets. Phytother. Res. 2015, 29, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heemskerk, J.; Sage, S. Calcium signalling in platelets and other cells. Platelets 1994, 5, 295–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukoyatkina, N.; Shpakova, V.; Sudnitsyna, J.; Panteleev, M.; Makhoul, S.; Gambaryan, S.; Jurk, K. Curcumin at Low Doses Potentiates and at High Doses Inhibits ABT-737-Induced Platelet Apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, Y. Hypocholesterolemic effects of curcumin via up-regulation of cholesterol 7a-hydroxylase in rats fed a high fat diet. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2010, 4, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, A.J. Continuing education course# 2: Current understanding of hemostasis. Toxicol Pathol. 2011, 39, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clemetson, K.J. Platelets and primary haemostasis. Thromb. Res. 2012, 129, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herter, J.M.; Rossaint, J.; Zarbock, A. Platelets in inflammation and immunity. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 12, 1764–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrör, K.; Huber, K. Platelets, inflammation and anti-inflammatory drugs in ACS and CAD. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 114, 446–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cognasse, F.; Nguyen, K.A.; Damien, P.; McNicol, A.; Pozzetto, B.; Hamzeh-Cognasse, H.; Garraud, O. The inflammatory role of platelets via their TLRs and Siglec receptors. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patzelt, J.; Verschoor, A.; Langer, H.F. Platelets and the complement cascade in atherosclerosis. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nording, H.; Langer, H.F. Complement links platelets to innate immunity. Semin. Immunol. 2018, 37, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, H.F.; Verschoor, A. Crosstalk between platelets and the complement system in immune protection and disease. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 110, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Conde, I.; Crúz, M.A.; Zhang, H.; López, J.A.; Afshar-Kharghan, V. Platelet activation leads to activation and propagation of the complement system. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boilard, E.; Nigrovic, P.A.; Larabee, K.; Watts, G.F.M.; Coblyn, J.S.; Weinblatt, M.E.; Massarotti, E.M.; Remold-O’Donnell, E.; Farndale, R.W.; Ware, J.; et al. Platelets Amplify Inflammation in Arthritis via Collagen-Dependent Microparticle Production. Science 2010, 327, 580–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pate, K.A.M.; Lyons, C.; Dorsey, J.L.; Queen, S.E.; Adams, R.J.; Morrell, C.N.; Mankowski, J.L. TGFβ-Mediated Downregulation of Thrombopoietin Is Associated with Platelet Decline in Asymptomatic SIV Infection. JAIDS J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2014, 65, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guclu, E.; Durmaz, Y.; Karabay, O. Effect of severe sepsis on platelet count and their indices. Afr. Health Sci. 2013, 13, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labelle, M.; Begum, S.; Hynes, R.O. Direct signaling between platelets and cancer cells induces an epithelial-mesenchymal-like transition and promotes metastasis. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 576–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, N.M.; Spillane, C.D.; Sheils, O.; O’Leary, J.; Kenny, D. Aspirin and P2Y12 inhibition attenuate platelet-induced ovarian cancer cell invasion. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erpenbeck, L.; Schön, M.P. Deadly allies: The fatal interplay between platelets and metastasizing cancer cells. J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2010, 115, 3427–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, H.N.; Hardman, M.J. Wound healing: Cellular mechanisms and pathological outcomes. Open Biol. 2020, 10, 200223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, M.; Kosaric, N.; Bonham, C.A.; Gurtner, G.C. Wound Healing: A Cellular Perspective. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 665–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, R.; Toyoda, E.; Maehara, M.; Wasai, S.; Omura, H.; Watanabe, M.; Sato, M. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on M1/M2 macrophage polarization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho-Tin-Noé, B.; Demers, M.; Wagner, D.D. How platelets safeguard vascular integrity. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 9, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EEisinger, F.; Patzelt, J.; Langer, H.F. The Platelet Response to Tissue Injury. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, G.; Arora, S. Platelet-rich plasma—Where do we stand today? A critical narrative review and analysis. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e14343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semple, J.W.; Italiano, J.E.; Freedman, J. Platelets and the immune continuum. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krijgsveld, J.; Zaat, S.A.J.; Meeldijk, J.; van Veelen, P.A.; Fang, G.; Poolman, B.; Brandt, E.; Ehlert, J.E.; Kuijpers, A.J.; Engbers, G.H.M.; et al. Thrombocidins, Microbicidal Proteins from Human Blood Platelets, Are C-terminal Deletion Products of CXC Chemokines. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 20374–20381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwakman, P.H.; Krijgsveld, J.; de Boer, L.; Nguyen, L.T.; Boszhard, L.; Vreede, J.; Dekker, H.L.; Speijer, D.; Drijfhout, J.W.; Velde, A.A.T.; et al. Native Thrombocidin-1 and Unfolded Thrombocidin-1 Exert Antimicrobial Activity via Distinct Structural Elements. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 43506–43514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, S.R.; Ma, A.C.; Tavener, S.A.; McDonald, B.; Goodarzi, Z.; Kelly, M.M.; Patel, K.D.; Chakrabarti, S.; McAvoy, E.; Sinclair, G.D.; et al. Platelet TLR4 activates neutrophil extracellular traps to ensnare bacteria in septic blood. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinod, K.; Wagner, D.D. Thrombosis: Tangled up in NETs. J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2014, 123, 2768–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkmann, V.; Zychlinsky, A. Beneficial suicide: Why neutrophils die to make NETs. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 5, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, B.F.; Campbell, R.A.; Schwertz, H.; Cody, M.J.; Franks, Z.; Tolley, N.D.; Kahr, W.H.A.; Lindemann, S.; Seizer, P.; Yost, C.C.; et al. Novel Anti-bacterial Activities of β-defensin 1 in Human Platelets: Suppression of Pathogen Growth and Signaling of Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation. PLOS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etulain, J.; Martinod, K.; Wong, S.L.; Cifuni, S.M.; Schattner, M.; Wagner, D.D. P-selectin promotes neutrophil extracellular trap formation in mice. J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2015, 126, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haselmayer, P.; Grosse-Hovest, L.; von Landenberg, P.; Schild, H.; Radsak, M.P. TREM-1 ligand expression on platelets enhances neutrophil activation. J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2007, 110, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannacone, M.; Sitia, G.; Isogawa, M.; Marchese, P.; Castro, M.G.; Lowenstein, P.R.; Chisari, F.; Ruggeri, Z.M.; Guidotti, L.G. Platelets mediate cytotoxic T lymphocyte–induced liver damage. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 1167–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elzey, B.D.; Tian, J.; Jensen, R.J.; Swanson, A.K.; Lees, J.; Lentz, S.; Stein, C.S.; Nieswandt, B.; Wang, Y.; Davidson, B.L.; et al. Platelet-Mediated Modulation of Adaptive Immunity: A Communication Link between Innate and Adaptive Immune Compartments. Immunity 2003, 19, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elzey, B.D.; Schmidt, N.W.; Crist, S.A.; Kresowik, T.P.; Harty, J.T.; Nieswandt, B.; Ratliff, T.L. Platelet-derived CD154 enables T-cell priming and protection against Listeria monocytogenes challenge. Blood 2008, 111, 3684–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, P.A.; Contaldo, C.; Georgiev, P.; El-Badry, A.M.; Recher, M.; Kurrer, M.; Cervantes-Barragan, L.; Ludewig, B.; Calzascia, T.; Bolinger, B.; et al. Aggravation of viral hepatitis by platelet-derived serotonin. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 756–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- León-Ponte, M.; Ahern, G.P.; O’Connell, P.J. Serotonin provides an accessory signal to enhance T-cell activation by signaling through the 5-HT7 receptor. Blood 2007, 109, 3139–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, A.; Angelosanto, J.M.; Nadwodny, K.L.; Blackburn, S.D.; Wherry, E.J. A role for the chemokine RANTES in regulating CD8 T cell responses during chronic viral infection. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Desoky, G.E.; Wabaidur, S.M.; AlOthman, Z.A.; Habila, M.A. Regulatory Role of Nano-Curcumin against Tartrazine-Induced Oxidative Stress, Apoptosis-Related Genes Expression, and Genotoxicity in Rats. Molecules 2020, 25, 5801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.-T.; Yang, Z.-H.; Yu, L.-Y.; Ren, Y.-Y.; Huang, Q.-X.; Liu, Q.; Ma, X.-Y.; Chen, Z.-K.; Wang, Z.-B.; Zheng, X. Synthesis and antioxidant activity of curcumin analogs. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 19, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubczyk, K.; Drużga, A.; Katarzyna, J.; Skonieczna-Żydecka, K. Antioxidant potential of curcumin—A Meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, R.; Wu, Z.; Xie, Q.-T.; Cheng, J.-S.; Zhang, B. Preparation and characterization of zein/carboxymethyl dextrin nanoparticles to encapsulate curcumin: Physicochemical stability, antioxidant activity and controlled release properties. Food Chem. 2021, 340, 127893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadian, M.; Salami, M.; Momen, S.; Alavi, F.; Emam-Djomeh, Z. Fabrication of curcumin-loaded whey protein microgels: Structural properties, antioxidant activity, and in vitro release behavior. LWT 2019, 103, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, H.; Shahzad, M.; Shabbir, A.; Saghir, G. Immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory potential of curcumin for the treatment of allergic asthma: Effects on expression levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and aquaporins. Inflammation 2019, 42, 2037–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plavcová, Z.; Šalamúnová, P.; Saloň, I.; Štěpánek, F.; Hanuš, J.; Hošek, J. Curcumin encapsulation in yeast glucan particles promotes its anti-inflammatory potential in vitro. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 568, 118532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauridsen, C. From oxidative stress to inflammation: Redox balance and immune system. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 4240–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristofori, F.; Dargenio, V.N.; Dargenio, C.; Miniello, V.L.; Barone, M.; Francavilla, R. Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of probiotics in gut inflammation: A door to the body. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginwala, R.; Bhavsar, R.; Chigbu, D.G.I.; Jain, P.; Khan, Z.K. Potential role of flavonoids in treating chronic inflammatory diseases with a special focus on the anti-inflammatory activity of apigenin. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimi, K.; Hassanzadeh, K.; Khanbabaei, H.; Haftcheshmeh, S.M.; Ahmadi, A.; Izadpanah, E.; Mohammadi, A.; Sahebkar, A. Curcumin: A dietary phytochemical for targeting the phenotype and function of dendritic cells. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 1549–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.-S.; Chen, T.-H.; Weng, L.; Huang, L.; Lai, D.; Weng, C.-F. Pharmacological properties and underlying mechanisms of curcumin and prospects in medicinal potential. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 141, 111888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamani, S.; Moossavi, M.; Naghizadeh, A.; Abbasifard, M.; Majeed, M.; Johnston, T.P.; Sahebkar, A. Immunomodulatory effects of curcumin in systemic autoimmune diseases. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 1616–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forouzanfar, F.; Majeed, M.; Jamialahmadi, T.; Sahebkar, A. Curcumin: A Review of Its Effects on Epilepsy. Stud. Biomark. New Targets Aging Res. Iran 2021, 1291, 363–373. [Google Scholar]
- Momtazi-Borojeni, A.A.; Haftcheshmeh, S.M.; Esmaeili, S.-A.; Johnston, T.P.; Abdollahi, E.; Sahebkar, A. Curcumin: A natural modulator of immune cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoque, A.; Williamson, N.A.; Ameen, S.S.; Ciccotosto, G.D.; Hossain, M.I.; Oakhill, J.S.; Ng, D.C.; Ang, C.-S.; Cheng, H.-C. Quantitative proteomic analyses of dynamic signalling events in cortical neurons undergoing excitotoxic cell death. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.H.; Park, J.Y.; Kang, K.S.; Hwang, G.S. Neuroprotective effect of gallocatechin gallate on glutamate-induced oxidative stress in hippocampal ht22 cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olloquequi, J.; Cornejo-Córdova, E.; Verdaguer, E.; Soriano, F.X.; Binvignat, O.; Auladell, C.; Camins, A. Excitotoxicity in the pathogenesis of neurological and psychiatric disorders: Therapeutic implications. J. Psychopharmacol. 2018, 32, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, J. Curcumin in antidepressant treatments: An overview of potential mechanisms, pre-clinical/clinical trials and ongoing challenges. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2020, 127, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooqui, T.; Farooqui, A.A. Curcumin: Historical background, chemistry, pharmacological action, and potential therapeutic value. In Curcumin for Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 23–44. [Google Scholar]
- Numakawa, T.; Odaka, H.; Adachi, N. Actions of brain-derived neurotrophin factor in the neurogenesis and neuronal function, and its involvement in the pathophysiology of brain diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Xu, D.; Zhao, L.; Yuan, M.; Cui, Y.-L.; Li, Y. Therapeutic role of curcumin in adult neurogenesis for management of psychiatric and neurological disorders: A scientometric study to an in-depth review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.P.; Salehi, B.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Pezzani, R.; Kobarfard, F.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Nigam, M. Programmed cell death, from a cancer perspective: An overview. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2018, 22, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Kasinathan, A.; Ganesan, R.; Balasubramanian, A.; Bhaskaran, J.; Suresh, S.; Srinivasan, R.; Aravind, K.; Sivalingam, N. Curcumin induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest via the activation of reactive oxygen species–independent mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in Smad4 and p53 mutated colon adenocarcinoma HT29 cells. Nutr. Res. 2018, 51, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, B.; Jia, J. Curcumin alleviates β amyloid-induced neurotoxicity in HT22 cells via upregulating SOD2. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 67, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubauer, K.; Zieger, B. Endothelial cells and coagulation. Cell Tissue Res. 2021, 387, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoiber, D.; Assinger, A. Platelet-leukocyte interplay in cancer development and progression. Cells 2020, 9, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplanski, G.; Farnarier, C.; Porat, R.; Shapiro, L.; Bongrand, P.; Dinarello, C. Interleukin-1 induces interleukin-8 secretion from endothelial cells by a juxtacrine mechanism. Blood 1994, 84, 4242–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunjungputri, R.N.; Li, Y.; de Groot, P.G.; Dinarello, C.A.; Smeekens, S.P.; Jaeger, M.; Doppenberg-Oosting, M.; Cruijsen, M.; Lemmers, H.; Toenhake-Dijkstra, H. The inter-relationship of platelets with interleukin-1β-mediated inflammation in humans. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 118, 2112–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-W.; Kuo, H.-T.; Chai, C.-Y.; Ou, J.-L.; Yang, R.-C. Pretreatment of curcumin attenuates coagulopathy and renal injury in LPS-induced endotoxemia. J. Endotoxin Res. 2007, 13, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlstetter, M.; Lippe, E.; Walczak, Y.; Moehle, C.; Aslanidis, A.; Mirza, M.; Langmann, T. Curcumin is a potent modulator of microglial gene expression and migration. J. Neuroinflamm. 2011, 8, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Gu, Z.L.; Qin, Z.h.; Liang, Z.Q. Effect of curcumin on the adhesion of platelets to brain microvascular endothelial cells in vitro. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2008, 29, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourbagher-Shahri, A.M.; Farkhondeh, T.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Talebi, M.; Samargahndian, S. Curcumin and cardiovascular diseases: Focus on cellular targets and cascades. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 136, 111214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammon, H.; Safayhi, H.; Mack, T.; Sabieraj, J. Mechanism of antiinflammatory actions of curcumine and boswellic acids. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1993, 38, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weeraphan, C.; Srisomsap, C.; Chokchaichamnankit, D.; Subhasitanont, P.; Hatairaktham, S.; Charoensakdi, R.; Panichkul, N.; Siritanaratkul, N.; Fucharoen, S.; Svasti, J.; et al. Role of curcuminoids in ameliorating oxidative modification in β-thalassemia/Hb E plasma proteome. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.K.; Roy, A.K. Research. Role of curcumin and cumin on hematological parameters of profenofos exposed mice-Mus Musculus. Int. J. Curr. Pharm. Rev. Res. 2014, 4, 120–127. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; Kong, D.; Zhang, X.; Lu, C.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, S. Curcumin attenuates angiogenesis in liver fibrosis and inhibits angiogenic properties of hepatic stellate cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2014, 18, 1392–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y. Curcumin: An Ingredient that Reduces Platelet Aggregation and Hyperlipidemia, and Enhances Antioxidant and Immune Functions; ACS Publications: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Olszanecki, R.; Jawień, J.; Gajda, M.; Mateuszuk, L.; Gebska, A.; Korabiowska, M.; Chłopicki, S.; Korbut, R. Effect of curcumin on atherosclerosis in apoE/LDLR-double knockout mice. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. Off. J. Pol. Physiol. Soc. 2005, 56, 627–635. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, B.H.; Nawaz, Z.; Pertani, S.A.; Roomi, A.; Mahmood, H.; Saeed, S.A.; Gilani, A.H. Inhibitory effect of curcumin, a food spice from turmeric, on platelet-activating factor-and arachidonic acid-mediated platelet aggregation through inhibition of thromboxane formation and Ca2+ signaling. Biol. Chem. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1999, 58, 1167–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.-H.; Sim, E.-H.; Goh, R.-Y.; Park, J.-I.; Han, J.-Y. Platelet Activation: The Mechanisms and Potential Biomarkers. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 9060143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swieringa, F.; Spronk, H.M.; Heemskerk, J.W.; van der Meijden, P.E. Integrating platelet and coagulation activation in fibrin clot formation. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 2, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayanglambam, A.; Dangelmaier, C.A.; Thomas, D.; Reddy, C.D.; Daniel, J.L.; Kunapuli, S.P. Curcumin inhibits GPVI-mediated platelet activation by interfering with the kinase activity of Syk and the subsequent activation of PLCγ2. Platelets 2010, 21, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiaju, T.; Jin, W.; Changjiang, P.; Yajun, W.; Nan, H. Anticoagulation and drug release behavior of Curcumin-Loaded PLGA films. Key Eng. Mater. 2007, 342, 343. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, K.; Bordia, A.; Verma, S. Curcumin, a major component of food spice turmeric (Curcuma longa) inhibits aggregation and alters eicosanoid metabolism in human blood platelets. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 1995, 52, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allijn, I.E.; Vaessen, S.F.; Quarles van Ufford, L.C.; Beukelman, K.J.; De Winther, M.P.; Storm, G.; Schiffelers, R.M. Head-to-head comparison of anti-inflammatory performance of known natural products in vitro. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Chen, A. Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ by curcumin blocks the signaling pathways for PDGF and EGF in hepatic stellate cells. Lab. Investig. 2008, 88, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaques, J.A.D.S.; Ruchel, J.B.; Schlemmer, K.B.; Pimentel, V.C.; Bagatini, M.; Souza, V.D.C.G.; Moretto, M.B.; Morsch, V.M.; Schetinger, M.R.C.; Leal, D.B.R. Effects of curcumin on the activities of the enzymes that hydrolyse adenine nucleotides in platelets from cigarette smoke-exposed rats. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2011, 29, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiuri, M.C.; Zalckvar, E.; Kimchi, A.; Kroemer, G. Self-eating and self-killing: Crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, A. Autophagy and cell death: No longer at odds. Cell 2007, 131, 1032–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouseph, M.M.; Huang, Y.; Banerjee, M.; Joshi, S.; MacDonald, L.; Zhong, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; Xiang, B.; Zhang, G.J.B. Autophagy is induced upon platelet activation and is essential for hemostasis and thrombosis. J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2015, 126, 1224–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.; Chang, C.; Luo, D.; Su, H.; Yu, S.; Hua, W.; Chen, Z.; Hu, H.; Liu, W. Dissection of autophagy in human platelets. Autophagy 2014, 10, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Ma, S.; Bi, S.-J.; Su, L.; Huang, S.-Y.; Miao, J.-Y.; Ma, C.-H.; Gao, C.-J.; Hou, M.; Peng, J. Enhancing autophagy protects platelets in immune thrombocytopenia patients. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Du, J.; Stitham, J.; Atteya, G.; Lee, S.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, D.; Jin, Y.; Leslie, K.L.; Spollett, G.; et al. Inducing mitophagy in diabetic platelets protects against severe oxidative stress. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016, 8, 779–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santilli, F.; Guagnano, M.; Vazzana, N.; Barba, S.; Davi, G. Oxidative Stress Drivers and Modulators in Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease: From Biomarkers to Therapeutic Approach. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 582–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodziejczyk-Czepas, J.; Olas, B.; Saluk-Juszczak, J.; Wachowicz, B. Antioxidative properties of curcumin in the protection of blood platelets against oxidative stress in vitro. Platelets 2011, 22, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megid, A.-E.; Osman, E.; Khamis, T.; Arisha, A. Curcumin Effect on Rats Hepato-Renal Functions, Hematological Parameters, and Inflammatory Markers in Comparison with Celecoxib and Prednisolone. Zagazig Vet. J. 2021, 49, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Habibi, E.; El-Wakf, A.; Mogall, A. Efficacy of curcumin in reducing risk of cardiovascular disease in high fat diet-fed rats. J. Bioanal. Biomed. 2013, 5, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi Farsani, S.S.; Sadeghizadeh, M.; Gholampour, M.A.; Safari, Z.; Najafi, F. Nanocurcumin as a novel stimulator of megakaryopoiesis that ameliorates chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia in mice. Life Sci. 2020, 256, 117840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heldin, C.-H.; Westermark, B. Mechanism of action and in vivo role of platelet-derived growth factor. Physiol. Rev. 1999, 79, 1283–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: A perspective for the 1990s. Nature 1993, 362, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryckaert, M.; Rendu, F.; Tobelem, G.; Wasteson, Å. Collagen-induced binding to human platelets of platelet-derived growth factor leading to inhibition of P43 and P20 phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 4336–4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.C.; Patchva, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Therapeutic Roles of Curcumin: Lessons Learned from Clinical Trials. AAPS J. 2013, 15, 195–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basnet, P.; Skalko-Basnet, N. Curcumin: An anti-inflammatory molecule from a curry spice on the path to cancer treatment. Molecules 2011, 16, 4567–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chainani-Wu, N. Safety and anti-inflammatory activity of curcumin: A component of tumeric (Curcuma longa). J. Altern Complement Med. 2003, 9, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, N.-J.; Hu, J.-Y.; Wu, C.-S.; Kong, Z.-L. Curcumin represses the activity of inhibitor-κB kinase in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis by S-nitrosylation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 38, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.-H.; Chen, J.-W.; Kong, Z.-L.; Wu, J.-C.; Ho, C.-T.; Lai, C.-S. Attenuation by Tetrahydrocurcumin of Adiposity and Hepatic Steatosis in Mice with High-Fat-Diet-Induced Obesity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 12685–12695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatcher, H.; Planalp, R.; Cho, J.; Torti, F.; Torti, S. Curcumin: From ancient medicine to current clinical trials. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 1631–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soudamini, K.; Kuttan, R. Inhibition of chemical carcinogenesis by curcumin. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1989, 27, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurup, V.P.; Barrios, C.S. Immunomodulatory effects of curcumin in allergy. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2008, 52, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-M.; Jan, W.-C.; Chien, C.-F.; Lee, W.-C.; Lin, L.-C.; Tsai, T.-H. Optimised nano-formulation on the bioavailability of hydrophobic polyphenol, curcumin, in freely-moving rats. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabeshpour, J.; Hashemzaei, M.; Sahebkar, A. The regulatory role of curcumin on platelet functions. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 8713–8722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukoyatkina, N.; Shpakova, V.; Bogoutdinova, A.; Kharazova, A.; Mindukshev, I.; Gambaryan, S. Curcumin by activation of adenosine A2A receptor stimulates protein kinase a and potentiates inhibitory effect of cangrelor on platelets. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 586, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.-L.; Cai, H.-Y.; Chen, J.-P.; Li, R.; Zhong, S.-Y.; Jia, X.-J.; Liu, X.-F.; Song, B.-B. Chitosan/Alginate Nanoparticles for the Enhanced Oral Antithrombotic Activity of Clam Heparinoid from the Clam Coelomactra antiquata. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukoyatkina, N.; Butt, E.; Subramanian, H.; Nikolaev, V.O.; Mindukshev, I.; Walter, U.; Gambaryan, S.; Benz, P.M. Protein kinase A activation by the anti-cancer drugs ABT-737 and thymoquinone is caspase-3-dependent and correlates with platelet inhibition and apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogler, M.; Hamali, H.A.; Sun, X.-M.; Bampton, E.T.; Dinsdale, D.; Snowden, R.T.; Dyer, M.J.; Goodall, A.H.; Cohen, G.M. BCL2/BCL-XL inhibition induces apoptosis, disrupts cellular calcium homeostasis, and prevents platelet activation. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2011, 117, 7145–7154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladenović, M.; Mihailović, M.; Bogojević, D.; Vuković, N.; Sukdolak, S.; Matić, S.; Nićiforović, N.; Mihailović, V.; Mašković, P.; Vrvić, M.M. Biochemical and pharmacological evaluation of 4-hydroxychromen-2-ones bearing polar C-3 substituents as anticoagulants. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 54, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becattini, C.; Agnelli, G. Aspirin for prevention and treatment of venous thromboembolism. Blood Rev. 2014, 28, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collaboration, A.T. Collaborative meta-analysis of randomised trials of antiplatelet therapy for prevention of death, myocardial infarction, and stroke in high risk patients. BMJ 2002, 324, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, N.; Holbrook, L.; Jones, S.; Kaiser, W.; Moraes, L.; Rana, R.; Sage, T.; Stanley, R.; Tucker, K.; Wright, B. Future innovations in anti-platelet therapies. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 154, 918–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, E.; Palomo, I. Antiplatelet effects of natural bioactive compounds by multiple targets: Food and drug interactions. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 6, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, L.; Guo, L.; Xu, X. Effect of Kang Naoxueshuan tablet on protecting ischemic brain injury in rats. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi Zhongguo Zhongxiyi Jiehe Zazhi = Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. 2006, 26, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda, T.; Takasawa, A.; Nakazawa, T.; Ueda, J.; Ohsawa, K. Inhibitory effects of urinary metabolites on platelet aggregation after orally administering Shimotsu-To, a traditional Chinese medicine, to rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2003, 55, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hussain, Y.; Abdullah; Khan, F.; Alsharif, K.F.; Alzahrani, K.J.; Saso, L.; Khan, H. Regulatory Effects of Curcumin on Platelets: An Update and Future Directions. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3180. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123180
Hussain Y, Abdullah, Khan F, Alsharif KF, Alzahrani KJ, Saso L, Khan H. Regulatory Effects of Curcumin on Platelets: An Update and Future Directions. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(12):3180. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123180
Chicago/Turabian StyleHussain, Yaseen, Abdullah, Fazlullah Khan, Khalaf F. Alsharif, Khalid J. Alzahrani, Luciano Saso, and Haroon Khan. 2022. "Regulatory Effects of Curcumin on Platelets: An Update and Future Directions" Biomedicines 10, no. 12: 3180. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123180
APA StyleHussain, Y., Abdullah, Khan, F., Alsharif, K. F., Alzahrani, K. J., Saso, L., & Khan, H. (2022). Regulatory Effects of Curcumin on Platelets: An Update and Future Directions. Biomedicines, 10(12), 3180. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123180










