X-ray Microtomography to Assess Determinants of In Vivo N-Butyl Cyanoacrylate Glubran®2 Polymerization: A Rabbit-Model Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Model and Procedure
2.2. Acquisition and Reconstruction Parameters for Micro-CT
2.3. Data Analyses and Outcomes
2.3.1. Objective Outcomes
2.3.2. Subjective Outcomes
2.3.3. Image-Quality Criteria
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Experiments
3.2. Cast Distribution Outcomes
3.2.1. Objective Outcomes
3.2.2. Subjective Outcomes
3.3. Multivariate Analyses
3.4. Image Quality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, J.; Albadawi, H.; Chong, B.W.; Deipolyi, A.R.; Sheth, R.A.; Khademhosseini, A.; Oklu, R. Advances in biomaterials and technologies for vascular embolization. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1901071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loffroy, R.; Guillen, K.; Salet, E.; Marcelin, C.; Comby, P.O.; Midulla, M.; Grenier, N.; Chevallier, O.; Petitpierre, F. Prostate artery embolization using N-butyl cyanoacrylate glue for urinary tract symptoms due to benign prostatic hyperplasia: A valid alternative to microparticles? J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szmygin, M.; Pyra, K.; Sojka, M.; Jargiełło, T. Successful endovascular treatment of intralobar pulmonary sequestration—An effective alternative to surgery. Pol. J. Radiol. 2021, 86, e112–e114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas, R.K.; Monsignore, L.M.; de Castro-Afonso, L.H.; Nakiri, G.S.; Elias-Junior, J.; Muglia, V.F.; Scarpelini, S.; Abud, D.G. Transarterial embolization with N-butyl cyanoacrylate for the treatment of active abdominopelvic bleeding in the polytraumatized patient. CVIR Endovasc. 2021, 4, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubarsky, M.; Ray, C.E.; Funaki, B. Embolization agents-Which one should be used when? Part 1: Large-vessel embolization. Semin. Intervent. Radiol. 2009, 26, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baro, V.; Gabrieli, J.D.; Cester, G.; D’Errico, I.; Landi, A.; Denaro, L.; Causin, F. Preoperative devascularization of choroid plexus tumors: Specific issues about anatomy and embolization technique. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loffroy, R.; Comby, P.O.; Guillen, K.; Salsac, A.V. N-butyl cyanoacrylate-lipiodol mixture for endovascular purpose: Polymerization kinetics differences between in vitro and in vivo experiments. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2020, 43, 1409–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comby, P.O.; Guillen, K.; Chevallier, O.; Lenfant, M.; Pellegrinelli, J.; Falvo, N.; Midulla, M.; Loffroy, R. Endovascular use of cyanoacrylate-lipiodol mixture for peripheral embolization: Properties, techniques, pitfalls, and applications. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brothers, M.F.; Kaufmann, J.C.; Fox, A.J.; Deveikis, J.P. N-butyl 2-cyanoacrylate-substitute for IBCA in interventional neuroradiology: Histopathologic and polymerization time studies. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1989, 10, 777–786. [Google Scholar]
- Takasawa, C.; Seiji, K.; Matsunaga, K.; Matsuhashi, T.; Ohta, M.; Shida, S.; Takase, K.; Takahashi, S. Properties of N-butyl cyanoacrylate-iodized oil mixtures for arterial embolization: In vitro and in vivo experiments. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2012, 23, 1215–1221.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubarsky, M.; Ray, C.; Funaki, B. Embolization agents-Which one should be used when? Part 2: Small-vessel embolization. Semin. Intervent. Radiol. 2010, 27, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oowaki, H.; Matsuda, S.; Sakai, N.; Ohta, T.; Iwata, H.; Sadato, A.; Taki, W.; Hashimoto, N.; Ikada, Y. Non-adhesive cyanoacrylate as an embolic material for endovascular neurosurgery. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mine, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Hayashi, T.; Tomita, K.; Masuda, K.; Kawashima, M.; Sakamaki, F.; Hasebe, T. A stepwise embolization strategy for a bronchial arterial aneurysm: Proximal coil and distal glue with the optional use of a microballoon occlusion system. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2018, 41, 1267–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handbook of cerebrovascular disease and neurointerventional technique. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 30, E135. [CrossRef]
- Guillen, K.; Comby, P.O.; Chevallier, O.; Salsac, A.V.; Loffroy, R. In vivo experimental endovascular uses of cyanoacrylate in non-modified arteries: A systematic review. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.J.; Barthès-Biesel, D.; Salsac, A.V. Polymerization kinetics of a mixture of lipiodol and Glubran 2 cyanoacrylate glue upon contact with a proteinaceous solution. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 74, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nico, L.; Magro, E.; Ognard, J.; Fahed, R.; Salazkin, I.; Gevry, G.; Darsaut, T.; Raymond, J.; Gentric, J.C. Comparing N-hexyl cyanoacrylate (Magic Glue) and N-butyl cyanoacrylate (NBCA) for neurovascular embolization using the pressure cooker technique: An experimental study in swine. J. Neuroradiol. 2021, 48, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.J.; Barthes-Biesel, D.; Salsac, A.V. Polymerization kinetics of N-butyl cyanoacrylate glues used for vascular embolization. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 69, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedvedova, M.; Kresalek, V.; Vaskova, H.; Provaznik, I. Studying the kinetics of N-butyl-cyanoacrylate tissue adhesive and its oily mixtures. J. Infrared. Millim. Terahertz Waves 2016, 37, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, N.; Sato, M.; Minamiguchi, H.; Ikoma, A.; Sanda, H.; Nakata, K.; Tanaka, F.; Nakai, M.; Sonomura, T. Basic study of a mixture of N-butyl cyanoacrylate, ethanol, and lipiodol as a new embolic material. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2012, 23, 1516–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hama, M.; Sonomura, T.; Ikoma, A.; Koike, M.; Kamisako, A.; Tanaka, R.; Koyama, T.; Sato, H.; Tanaka, F.; Ueda, S.; et al. Balloon-assisted embolization of wide-neck aneurysms using a mixture of N-butyl cyanoacrylate, lipiodol, and ethanol in swine: A comparison of four N-butyl cyanoacrylate concentrations. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2020, 43, 1540–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levrier, O.; Mekkaoui, C.; Rolland, P.H.; Murphy, K.; Cabrol, P.; Moulin, G.; Bartoli, J.M.; Raybaud, C. Efficacy and low vascular toxicity of embolization with radical versus anionic polymerization of N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate (NBCA). An experimental study in the swine. J. Neuroradiol. 2003, 30, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Judy, P.F.; Swensson, R.G.; Szulc, M. Lesion detection and signal-to-noise ratio in CT images. Med. Phys. 1981, 8, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Brown, J.L.; Treves, S.T.; Cao, X.; Fahey, F.H.; Sgouros, G.; Bolch, W.E.; Frey, E.C. DeepAMO: A multi-slice, multi-view anthropomorphic model observer for visual detection tasks performed on volume images. J. Med. Imaging 2021, 8, 041204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steuwe, A.; Rademacher, C.; Valentin, B.; Köhler, M.H.; Appel, E.; Keitel, V.; Timm, J.; Antoch, G.; Aissa, J. Dose-optimised chest computed tomography for diagnosis of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)—Evaluation of image quality and diagnostic impact. J. Radiol. Prot. 2020, 40, 877–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thieß, H.M.; Bressem, K.K.; Adams, L.; Böning, G.; Vahldiek, J.L.; Niehues, S.M. Do submillisievert-chest CT protocols impact diagnostic quality in suspected COVID-19 patients? Acta Radiol. Open 2022, 11, 20584601211073864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzitelli, S.; Holtzman, N.; Maleux, G.; De Baere, T.; Sun, F.; Comby, P.O.; Tal, M.; Bazin, G.; Montestruc, F.; Viel, T. Reduced nontarget embolization and increased targeted delivery with a reflux-control microcatheter in a swine model. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2021, 102, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, N.; Takeuchi, Y.; Miura, H.; Arima, Y.; Toda, M.; Okamoto, T.; Asai, S.; Sakai, K.; Hirota, T.; Yamada, K. Is the cessation of blood flow faster than the polymerization of an N-butyl cyanoacrylate-lipiodol mixture? An in vitro phantom study. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2019, 43, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, P.L.; An, Y.H. Animal models for therapeutic embolization. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2003, 26, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karges, H.E.; Funk, K.A.; Ronneberger, H. Activity of coagulation and fibrinolysis parameters in animals. Arzneimittelforschung 1994, 44, 793–797. [Google Scholar]
- Duffy, C.; Zetterlund, P.B.; Aldabbagh, F. Radical polymerization of alkyl 2-cyanoacrylates. Molecules 2018, 23, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xiao, L.; Wang, Z.; Chen, K.; Xue, C.; Yu, M.; Wang, Y.; Kong, F.; Liu, K.; Qin, K. Raman spectroscopic characterization of polymerization kinetics of cyanoacrylate embolic glues for vascular embolization. Polymers 2021, 13, 3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamaguchi, S.; Ogawa, Y.; Arai, Y.; Hashimoto, K.; Nakajima, Y. A case of pseudoaneurysm of the deep femoral artery successfully treated by NBCA embolization under occlusion. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2013, 31, 538–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petkewich, R. Liquid bandages. Chem. Eng. News Arch. 2008, 86, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandulache, M.C.; Paullier, P.; Bouzerar, R.; Yzet, T.; Balédent, O.; Salsac, A.V. Liquid injection in confined co-flow: Application to portal vein embolization by glue Injection. Phys. Fluids 2012, 24, 081902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, M.; Ikoma, A.; Loffroy, R.; Midulla, M.; Kamisako, A.; Higashino, N.; Fukuda, K.; Sonomura, T. Type II endoleak model creation and intraoperative aneurysmal sac embolization with N-butyl cyanoacrylate-lipiodol-ethanol mixture (NLE) in swine. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2018, 8, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loffroy, R.; Guillen, K.; Comby, P.O.; Chevallier, O. Adjunctive component to N-butyl cyanoacrylate-lipiodol mixture for best embolic profile in vivo: Ethanol or iopamidol? Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2021, 44, 1467–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, R.; Suzuki, Y. X-ray microtomography in biology. Micron 2012, 43, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehoon, O.; Kwon, H.J.; Cho, T.H.; Woo, S.H.; Rhee, Y.H.; Yang, H.M. Micro-computed tomography with contrast enhancement: An excellent technique for soft tissue examination in humans. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y.; Lee, J.M.; Sirlin, C.B. CT and MR imaging diagnosis and staging of hepatocellular carcinoma: Part II. Extracellular agents, hepatobiliary agents, and ancillary imaging features. Radiology 2014, 273, 30–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. The enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect: The significance of the concept and methods to enhance its application. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
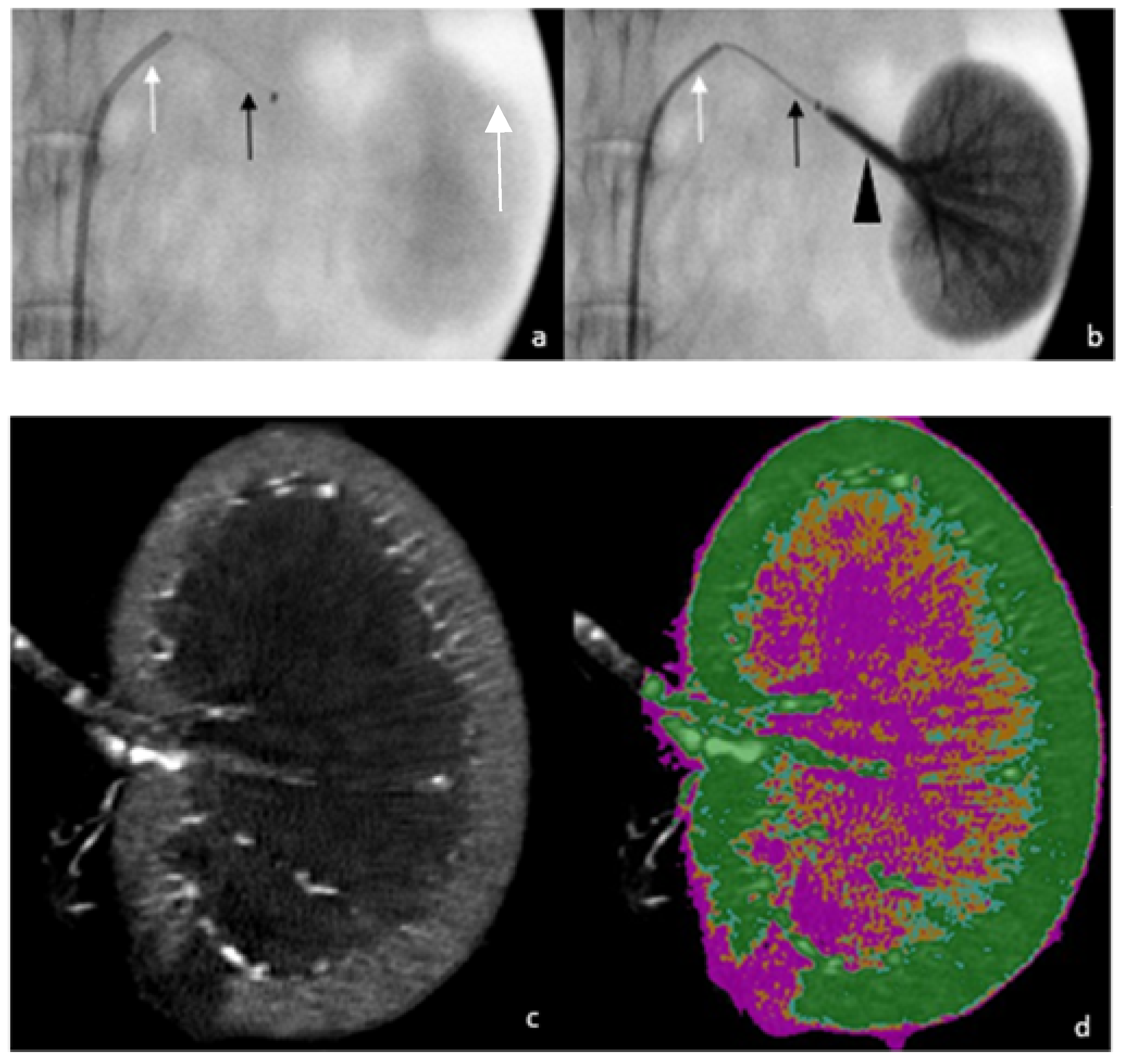
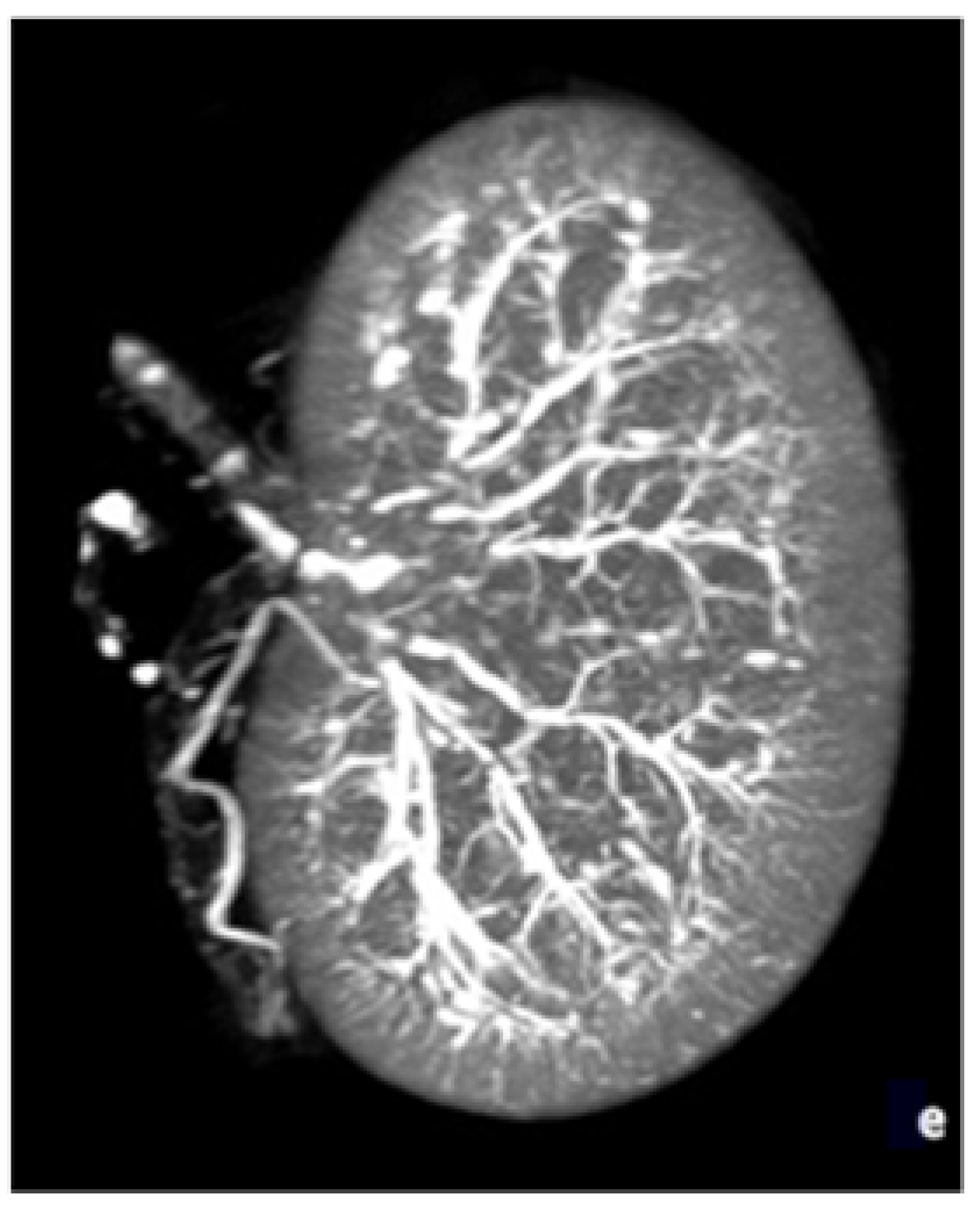
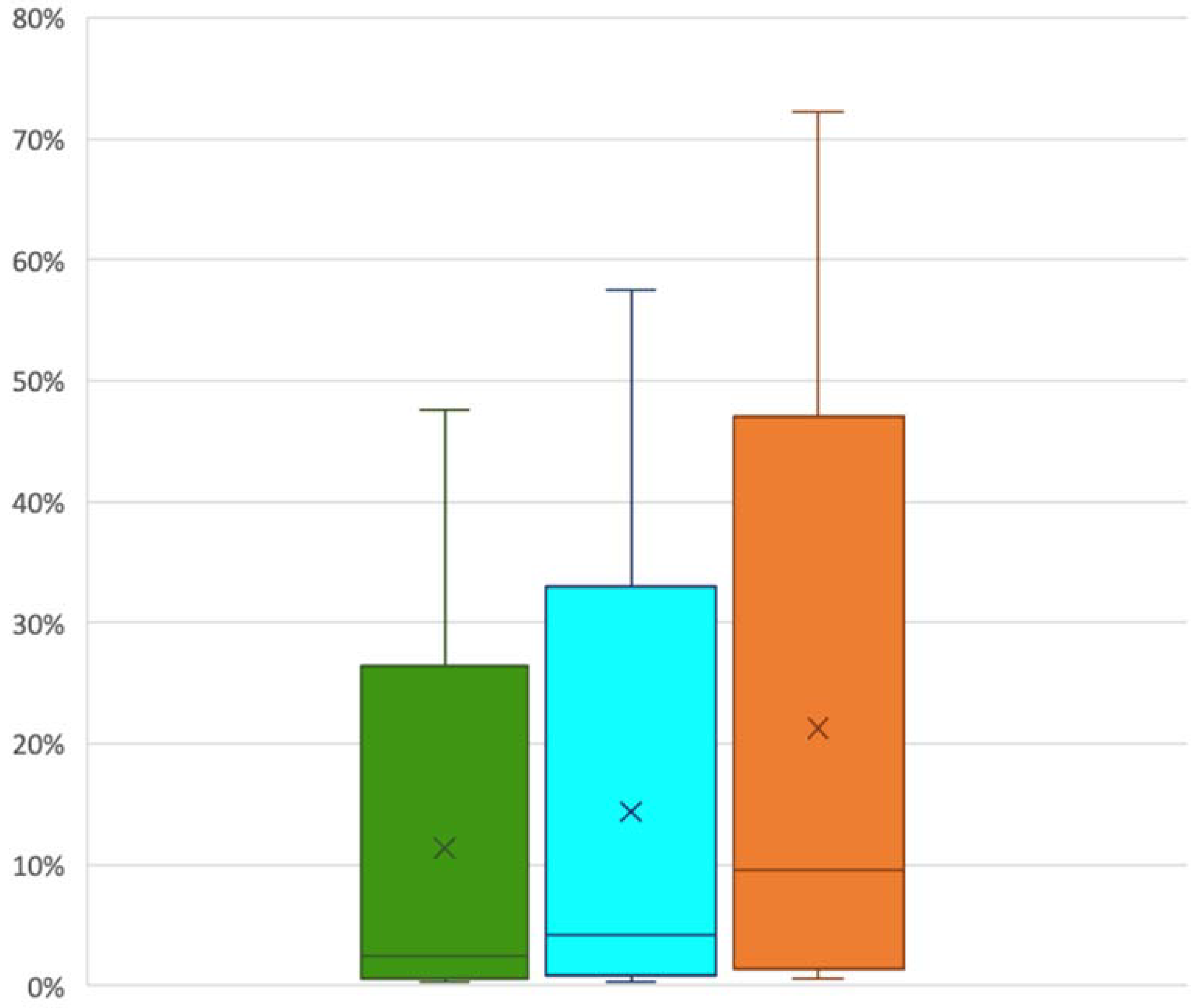

| Ratios a | BBF | Number of Procedures |
|---|---|---|
| 1:3 | No | 5 |
| 1:3 | Yes | 5 |
| 1:1 | No | 5 |
| 1:1 | Yes | 5 |
| 1:7 | No | 5 |
| 1:7 | Yes | 6 |
| 1:2:1 | No | 5 |
| 1:2:1 | Yes | 6 |
| Variables | n (%) or Mean ± SD |
|---|---|
| Rabbit weight, kg, mean ± SD | 3.18 ± 0.39 |
| Side, n (%) | |
| Right | 26 (61.90) |
| Left | 16 (38.10) |
| Injected glue-mixture volume (including dead space), mL, mean ± SD | 0.81 ± 0.25 |
| Injection time (including dead-space flushing), s, mean ± SD | 27.07 ± 9.00 |
| Blocked blood flow, n (%) | 22 (52.38) |
| Glubran®2 concentration, %, n (%) | |
| 12.5% | 12 (28.57) |
| 25% | 19 (45.24) |
| 50% | 11 (26.19) |
| Mixture containing 25% anhydrous ethanol, n (%) | 11 (26.19) |
| Injection termination criterion reached, n (%) | 41 (97.62) |
| Variables | n (%) or Mean ± SD |
|---|---|
| Cast distality a, n (%) | |
| Zone 3 | 7 (17) |
| Zone 4 | 7 (17) |
| Zone 5 | 28 (67) |
| Increased cortical blurring, n (%) | 19 (45) |
| Cast fragmentation, n (%) | |
| No | 19 (45) |
| Yes | 23 (55) |
| Cast heterogeneity score b | |
| Renal artery and first branches | 2.57 ± 1.09 |
| Interlobar artery | 2.60 ± 0.91 |
| Variables | p-Value | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|
| Subjective distality | ||
| NBCA concentration | 0.000 | −17.3 to 5.24 |
| Blood flow | 0.000 | −21.3 to 17.66 |
| Glue-mixture volume injected (including into dead space) | 0.263 | −5.45 to 19.97 |
| Rabbit weight | 0.093 | −2.76 to 0.21 |
| Cast fragmentation | ||
| NBCA concentration | 0.437 | −7.00 to 3.02 |
| Blood flow | 0.009 | 0.56 to 4.04 |
| Glue-mixture volume injected (including into dead space) | 0.250 | −19.60 to 5.11 |
| Increased cortical blurring | ||
| NBCA concentration | 0.068 | −18.81 to 0.66 |
| Blood flow | 0.014 | −4.55 to 0.51 |
| Glue-mixture volume injected (including into dead space) | 0.007 | 3.77 to 24.20 |
| Rabbit weight | 0.018 | −6.34 to 0.60 |
| Anhydrous ethanol in the mixture | 0.103 | −0.34 to 3.73 |
| Cast heterogeneity Zone 1 a | ||
| Blood flow | 0.077 | −2.54 to 0.13 |
| Glue-mixture volume injected (including into dead space) | 0.073 | −0.41 to 9.40 |
| Anhydrous ethanol in the mixture | 0.048 | −2.81 to 0.01 |
| Zone 2 b | ||
| NBCA concentration | 0.244 | −7.17 to 1.82 |
| Blood flow | 0.005 | −3.59 to 0.62 |
| Glue-mixture volume injected (including into dead space) | 0.066 | −0.27 to 8.29 |
| Rabbit weight | 0.202 | −0.50 to 2.38 |
| Cast-to-capsule distance (mean) | ||
| NBCA concentration | 0.127 | −0.69 to 5.22 |
| Blood flow | 0.002 | 0.49 to 1.92 |
| Glue-mixture volume injected (including into dead space) | 0.209 | −2.10 to 0.48 |
| Indexed cast ratio | ||
| Glue concentration | 0.023 | −0.25 to −0.02 |
| Blood flow | 0.339 | −0.05 to 0.02 |
| Glue-mixture volume injected (including into dead space) | 0.000 | 0.35 to 0.50 |
| Rabbit weight | 0.187 | −0.08 to 0.02 |
| Anhydrous ethanol in the mixture | 0.584 | −0.05 to 0.03 |
| Variables | n (%) or Mean ± SD |
|---|---|
| Likert scale rating, n (%) | |
| 2 | 5 (12) |
| 3 | 19 (45) |
| 4 | 17 (40) |
| 5 | 1 (2) |
| SNR, mean ± SD | |
| Background ROI | 74.65 ± 104.67 |
| Kidney ROI | 7.04 ± 2.23 |
| Segmented kidney parenchyma | 2.91 ± 0.67 |
| Variables | p-Value | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|
| Likert scale rating | ||
| Glue-mixture volume injected (including into dead space) | 0.015 | −6.31 to 0.69 |
| Rabbit weight | 0.153 | −0.51 to 3.26 |
| SNR in background ROI | ||
| Blood flow | 0.666 | −56.19 to 86.41 |
| Rabbit weight | 0.054 | −129.99 to 1.10 |
| Anhydrous ethanol in the mixture | 0.272 | −113.66 to 33.39 |
| SNR in renal ROI | ||
| NBCA concentration | 0.401 | −1.90 to 4.60 |
| Blood flow | 0.004 | 0.97 to 4.51 |
| Glue-mixture volume injected (including into dead space) | 0.094 | −0.31 to 3.69 |
| Rabbit weight | 0.032 | −4.36 to 0.21 |
| Anhydrous ethanol in the mixture | 0.059 | −0.06 to 2.77 |
| SNR in segmented parenchyma | ||
| Blood flow | 0.281 | −0.20 to 0.67 |
| Glue-mixture volume injected (including into dead space) | 0.000 | −1.68 to 0.60 |
| Anhydrous ethanol in the mixture | 0.193 | −0.14 to 0.64 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guillen, K.; Comby, P.-O.; Salsac, A.-V.; Falvo, N.; Lenfant, M.; Oudot, A.; Sikner, H.; Dencausse, A.; Laveissiere, E.; Aho-Glele, S.L.; et al. X-ray Microtomography to Assess Determinants of In Vivo N-Butyl Cyanoacrylate Glubran®2 Polymerization: A Rabbit-Model Study. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2625. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102625
Guillen K, Comby P-O, Salsac A-V, Falvo N, Lenfant M, Oudot A, Sikner H, Dencausse A, Laveissiere E, Aho-Glele SL, et al. X-ray Microtomography to Assess Determinants of In Vivo N-Butyl Cyanoacrylate Glubran®2 Polymerization: A Rabbit-Model Study. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(10):2625. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102625
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuillen, Kévin, Pierre-Olivier Comby, Anne-Virginie Salsac, Nicolas Falvo, Marc Lenfant, Alexandra Oudot, Hugo Sikner, Anne Dencausse, Emilie Laveissiere, Serge Ludwig Aho-Glele, and et al. 2022. "X-ray Microtomography to Assess Determinants of In Vivo N-Butyl Cyanoacrylate Glubran®2 Polymerization: A Rabbit-Model Study" Biomedicines 10, no. 10: 2625. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102625
APA StyleGuillen, K., Comby, P.-O., Salsac, A.-V., Falvo, N., Lenfant, M., Oudot, A., Sikner, H., Dencausse, A., Laveissiere, E., Aho-Glele, S. L., & Loffroy, R. (2022). X-ray Microtomography to Assess Determinants of In Vivo N-Butyl Cyanoacrylate Glubran®2 Polymerization: A Rabbit-Model Study. Biomedicines, 10(10), 2625. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102625





