Continued Complexity of Mutations in Omicron Sublineages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
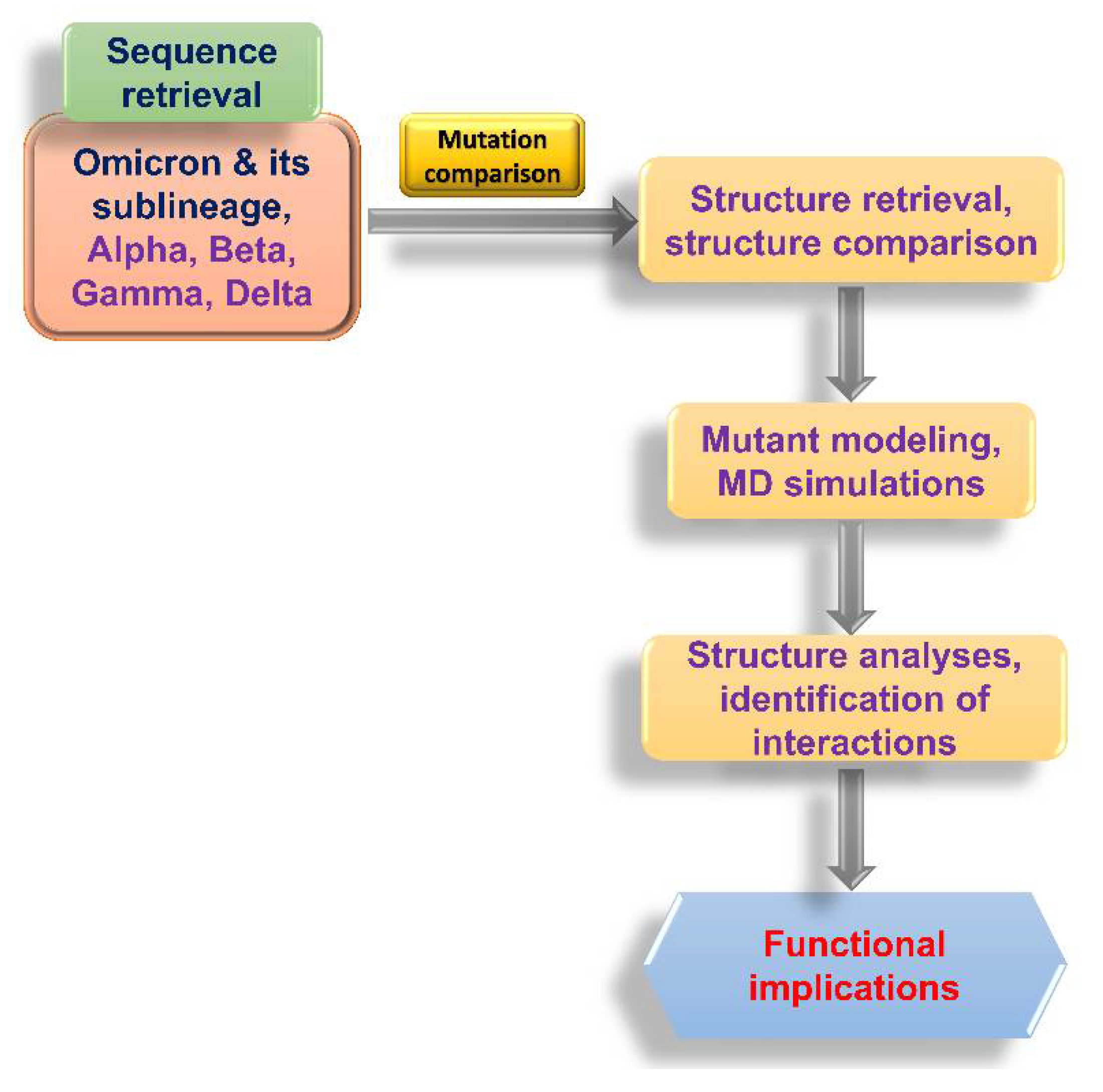
2.1. Flowchart of the Study
2.2. Sequence Acquisition and Analysis
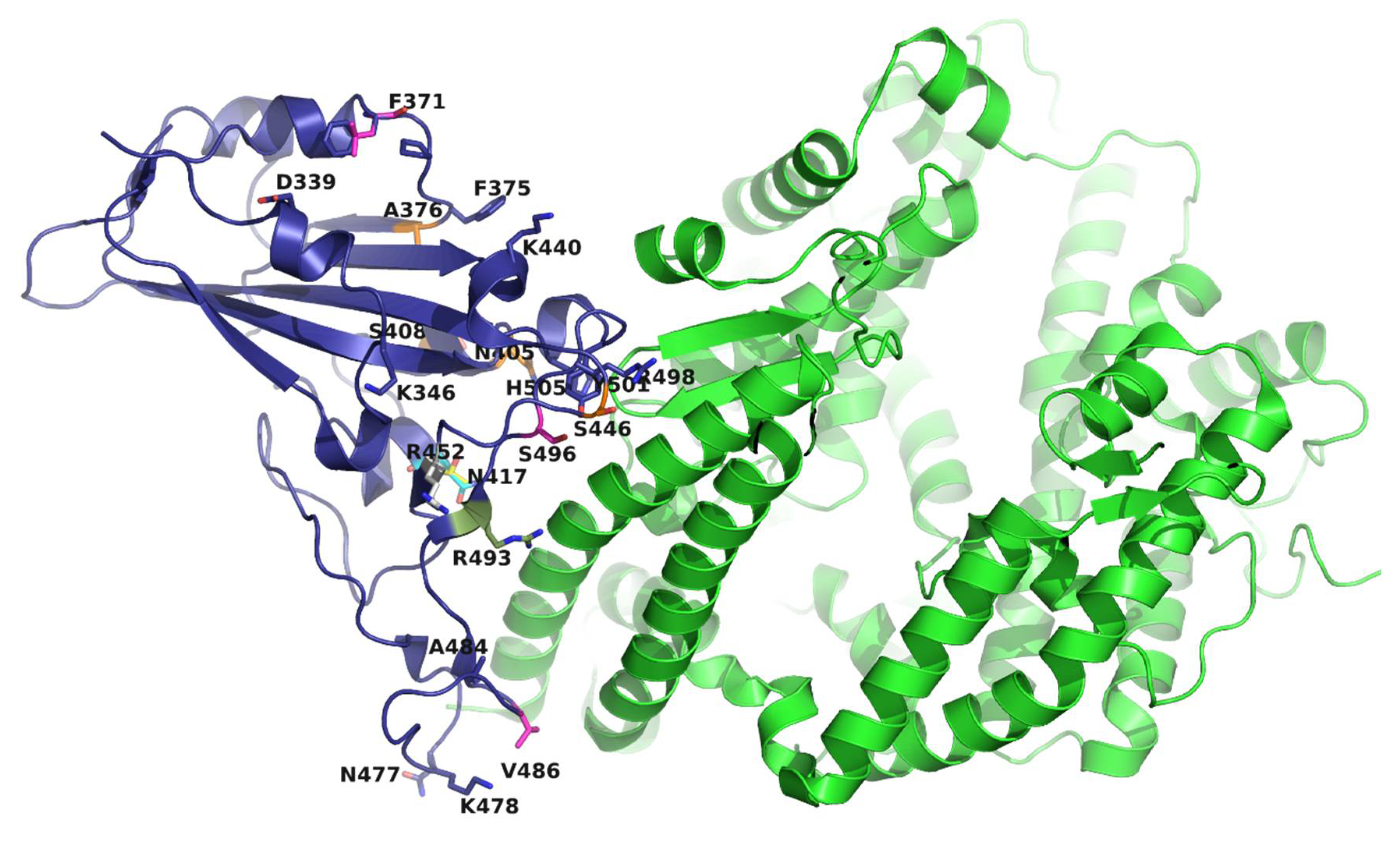
2.3. Structural Analysis
2.4. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulations
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tegally, H.; Wilkinson, E.; Giovanetti, M.; Iranzadeh, A.; Fonseca, V.; Giandhari, J.; Doolabh, D.; Pillay, S.; San, E.J.; Msomi, N.; et al. Detection of a SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern in South Africa. Nature 2021, 592, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennehy, J.J.; Gupta, R.K.; Hanage, W.P.; Johnson, M.C.; Peacock, T.P. Where is the next SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern? Lancet 2022, 399, 1938–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkhout, B.; Herrera-Carrillo, E. SARS-CoV-2 evolution: On the sudden appearance of the omicron variant. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0009022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, D.P.; Lytras, S.; Lucaci, A.G.; Maier, W.; Gruning, B.; Shank, S.D.; Weaver, S.; MacLean, O.A.; Orton, R.J.; Lemey, P.; et al. Selection analysis identifies clusters of unusual mutational changes in omicron lineage ba.1 that likely impact spike function. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2022, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, A.; Hill, V.; Pybus, O.G.; Watts, A.; Bogoch, I.I.; Khan, K.; Messina, J.P.; Tegally, H.; Lessells, R.R.; Giandhari, J.; et al. Tracking the international spread of SARS-CoV-2 lineages B. 1.1. 7 and B. 1.351/501Y-V2 with grinch. Wellcome Open Res. 2021, 6, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnleitner, S.T.; Prelog, M.; Sonnleitner, S.; Hinterbichler, E.; Halbfurter, H.; Kopecky, D.B.C.; Almanzar, G.; Koblmuller, S.; Sturmbauer, C.; Feist, L.; et al. Cumulative SARS-CoV-2 mutations and corresponding changes in immunity in an immunocompromised patient indicate viral evolution within the host. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, W.F.; Chorlton, S.; Tyson, J.; Al-Rawahi, G.N.; Jassem, A.N.; Prystajecky, N.; Masud, S.; Deans, G.D.; Chapman, M.G.; Mirzanejad, Y.; et al. COVID-19 in an immunocompromised host: Persistent shedding of viable SARS-CoV-2 and emergence of multiple mutations: A case report. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 114, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockett, R.; Basile, K.; Maddocks, S.; Fong, W.; Agius, J.E.; Johnson-Mackinnon, J.; Arnott, A.; Chandra, S.; Gall, M.; Draper, J.; et al. Resistance mutations in SARS-CoV-2 delta variant after sotrovimab use. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1477–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, W.T.; Carabelli, A.M.; Jackson, B.; Gupta, R.K.; Thomson, E.C.; Harrison, E.M.; Ludden, C.; Reeve, R.; Rambaut, A.; Consortium, C.-G.U.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Iketani, S.; Guo, Y.; Chan, J.F.; Wang, M.; Liu, L.; Luo, Y.; Chu, H.; Huang, Y.; Nair, M.S.; et al. Striking antibody evasion manifested by the omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2022, 602, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameroni, E.; Bowen, J.E.; Rosen, L.E.; Saliba, C.; Zepeda, S.K.; Culap, K.; Pinto, D.; VanBlargan, L.A.; De Marco, A.; di Iulio, J.; et al. Broadly neutralizing antibodies overcome SARS-CoV-2 omicron antigenic shift. Nature 2022, 602, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Jian, F.; Xiao, T.; Song, W.; Yisimayi, A.; Huang, W.; Li, Q.; Wang, P.; An, R.; et al. Omicron escapes the majority of existing SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies. Nature 2022, 602, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbe, S.; Buckland-Merrett, G. Data, disease and diplomacy: Gisaid’s innovative contribution to global health. Glob. Chall. 2017, 1, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangavarapu, K.; Latif, A.A.; Mullen, J.L.; Alkuzweny, M.; Hufbauer, E.; Tsueng, G.; Haag, E.; Zeller, M.; Aceves, C.M.; Zaiets, K.; et al. Outbreak.Info genomic reports: Scalable and dynamic surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 variants and mutations. medRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; Ge, J.; Yu, J.; Shan, S.; Zhou, H.; Fan, S.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; et al. Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor. Nature 2020, 581, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, B.J.; Rodrigues, A.P.; ElSawy, K.M.; McCammon, J.A.; Caves, L.S. Bio3d: An r package for the comparative analysis of protein structures. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2695–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Chandrasekhar, L.; Madura, J.D. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. Vmd: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, S.R.; Spratt, A.N.; Sharma, K.; Chand, H.S.; Byrareddy, S.N.; Singh, K. Omicron SARS-CoV-2 variant: Unique features and their impact on pre-existing antibodies. J. Autoimmun. 2022, 126, 102779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, S.R.; Spratt, A.N.; Sharma, K.; Goyal, R.; Sonnerborg, A.; Apparsundaram, S.; Lorson, C.L.; Byrareddy, S.N.; Singh, K. Complex mutation pattern of omicron ba.2: Evading antibodies without losing receptor interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutalai, R.; Zhou, D.; Tuekprakhon, A.; Ginn, H.M.; Supasa, P.; Liu, C.; Huo, J.; Mentzer, A.J.; Duyvesteyn, H.M.E.; Dijokaite-Guraliuc, A.; et al. Potent cross-reactive antibodies following omicron breakthrough in vaccinees. Cell 2022, 185, 2116–2131.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lusvarghi, S.; Wang, W.; Herrup, R.; Neerukonda, S.N.; Vassell, R.; Bentley, L.; Eakin, A.E.; Erlandson, K.J.; Weiss, C.D. Key substitutions in the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 variants can predict resistance to monoclonal antibodies, but other substitutions can modify the effects. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0111021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCallum, M.; Czudnochowski, N.; Rosen, L.E.; Zepeda, S.K.; Bowen, J.E.; Walls, A.C.; Hauser, K.; Joshi, A.; Stewart, C.; Dillen, J.R.; et al. Structural basis of SARS-CoV-2 omicron immune evasion and receptor engagement. Science 2022, 375, 864–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Iketani, S.; Li, Z.; Mohri, H.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; Bowen, A.D.; Chang, J.Y.; Shah, J.G.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 omicron ba.2.12.1, ba.4, and ba.5 subvariants evolved to extend antibody evasion. BioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, B.; Kemp, S.A.; Papa, G.; Datir, R.; Ferreira, I.; Marelli, S.; Harvey, W.T.; Lytras, S.; Mohamed, A.; Gallo, G.; et al. Recurrent emergence of SARS-CoV-2 spike deletion h69/v70 and its role in the alpha variant b.1.1.7. Cell Rep. 2021, 35, 109292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motozono, C.; Toyoda, M.; Zahradnik, J.; Saito, A.; Nasser, H.; Tan, T.S.; Ngare, I.; Kimura, I.; Uriu, K.; Kosugi, Y.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 spike l452r variant evades cellular immunity and increases infectivity. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 1124–1136 e1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Fang, Y.; Liu, J.; Ye, Q.; Ding, L. SARS-CoV-2 spike l452r mutation increases omicron variant fusogenicity and infectivity as well as host glycolysis. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, Y.; Mandel, M.; Bar-On, Y.M.; Bodenheimer, O.; Freedman, L.S.; Ash, N.; Alroy-Preis, S.; Huppert, A.; Milo, R. Protection and waning of natural and hybrid immunity to SARS-CoV-2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 2201–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Mutation | Omicron Sublineage | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G339D | BA.1 | BA.1.1 | BA.2 | BA.2.11 | BA.3 | BA.4 | BA.4 |
| R346K | BA.1.1 | ||||||
| S371L | BA.1 | BA.1.1 | |||||
| S371F | BA.2 | BA.2.11 | BA.3 | BA.4 | BA.4 | ||
| S373P | BA.1 | BA.1.1 | BA.2 | BA.2.11 | BA.3 | BA.4 | BA.4 |
| S375F | BA.1 | BA.1.1 | BA.2 | BA.2.11 | BA.3 | BA.4 | BA.4 |
| T376A | BA.2 | BA.2.11 | BA.4 | BA.4 | |||
| D405N | BA.2 | BA.2.11 | BA.3 | BA.4 | BA.4 | ||
| R408S | BA.2 | BA.2.11 | BA.4 | BA.4 | |||
| K417N | BA.1 | BA.1.1 | BA.2 | BA.2.11 | BA.3 | BA.4 | BA.4 |
| N440K | BA.1 | BA.1.1 | BA.2 | BA.2.11 | BA.3 | BA.4 | BA.4 |
| G446S | BA.1 | BA.1.1 | BA.3 | ||||
| L452R | BA.2.11 | BA.4 | BA.4 | ||||
| S477N | BA.1 | BA.1.1 | BA.2 | BA.2.11 | BA.3 | BA.4 | BA.4 |
| T478K | BA.1 | BA.1.1 | BA.2 | BA.2.11 | BA.3 | BA.4 | BA.4 |
| E484A | BA.1 | BA.1.1 | BA.2 | BA.2.11 | BA.3 | BA.4 | BA.4 |
| F486V | BA.4 | BA.4 | |||||
| Q493R | BA.1 | BA.1.1 | BA.2 | BA.2.11 | BA.3 | ||
| G496S | BA.1 | BA.1.1 | |||||
| Q498R | BA.1 | BA.1.1 | BA.2 | BA.2.11 | BA.3 | BA.4 | BA.4 |
| N501Y | BA.1 | BA.1.1 | BA.2 | BA.2.11 | BA.3 | BA.4 | BA.4 |
| Y505H | BA.1 | BA.1.1 | BA.2 | BA.2.11 | BA.3 | BA.4 | BA.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spratt, A.N.; Kannan, S.R.; Sharma, K.; Sachdev, S.; Kandasamy, S.L.; Sönnerborg, A.; Lorson, C.L.; Singh, K. Continued Complexity of Mutations in Omicron Sublineages. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2593. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102593
Spratt AN, Kannan SR, Sharma K, Sachdev S, Kandasamy SL, Sönnerborg A, Lorson CL, Singh K. Continued Complexity of Mutations in Omicron Sublineages. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(10):2593. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102593
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpratt, Austin N., Saathvik R. Kannan, Kalicharan Sharma, Shrikesh Sachdev, Shree L. Kandasamy, Anders Sönnerborg, Christian L. Lorson, and Kamal Singh. 2022. "Continued Complexity of Mutations in Omicron Sublineages" Biomedicines 10, no. 10: 2593. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102593
APA StyleSpratt, A. N., Kannan, S. R., Sharma, K., Sachdev, S., Kandasamy, S. L., Sönnerborg, A., Lorson, C. L., & Singh, K. (2022). Continued Complexity of Mutations in Omicron Sublineages. Biomedicines, 10(10), 2593. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102593







