Curcumin Hybrid Lipid Polymeric Nanoparticles: Antioxidant Activity, Immune Cellular Response, and Cytotoxicity Evaluation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of CUR Loaded Nanoparticles (CUR-NP)
2.3. Physicochemical Characterization of CUR-NP
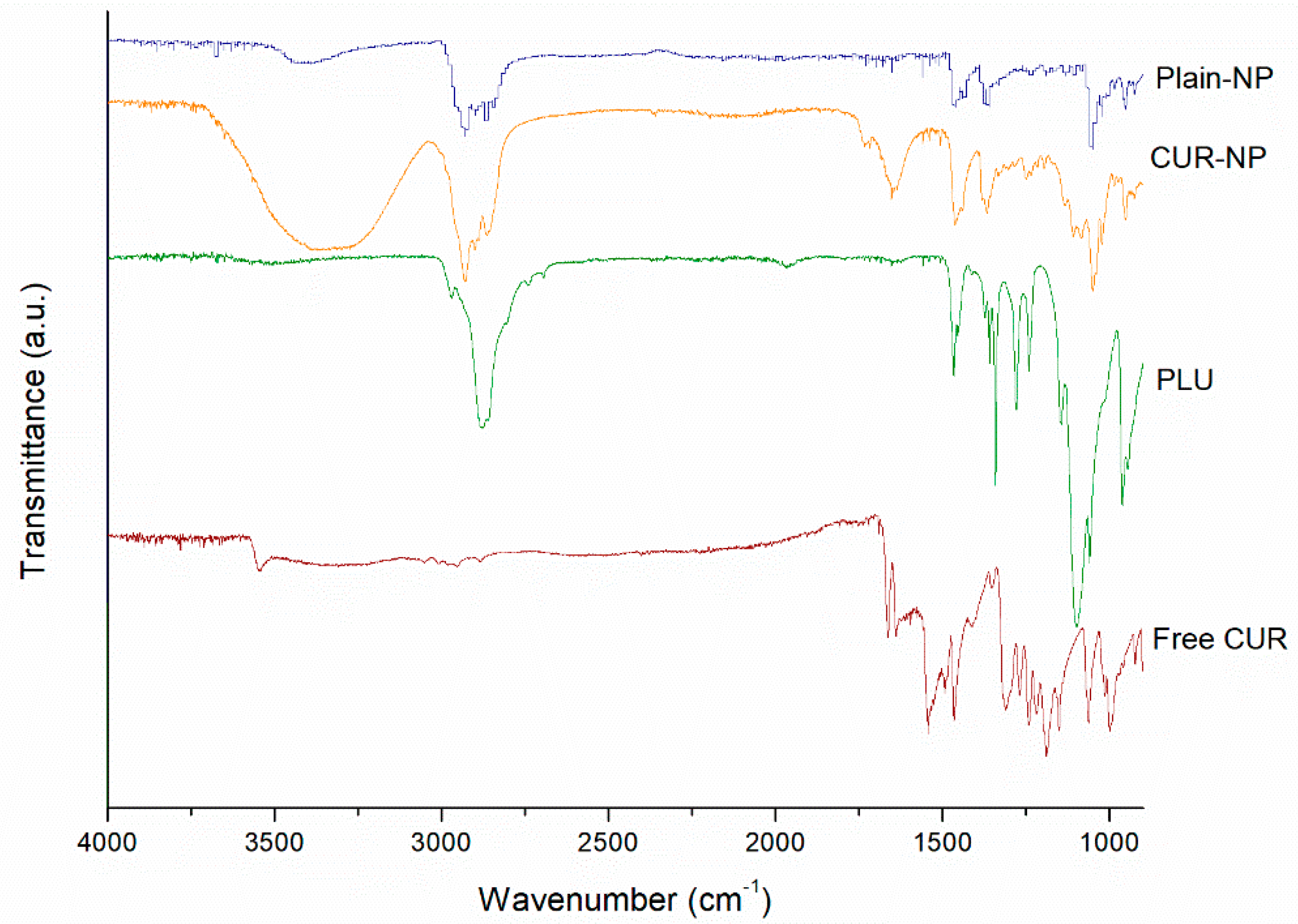
2.3.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
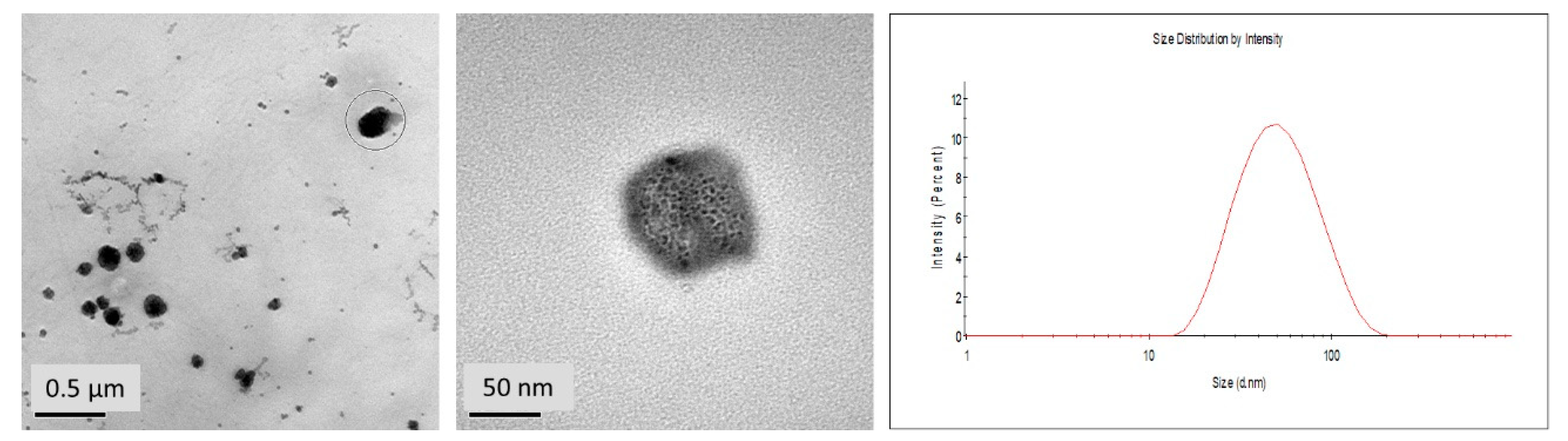
2.3.2. High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy (HR-TEM)
2.3.3. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
2.3.4. Encapsulation Efficiency (%EE)
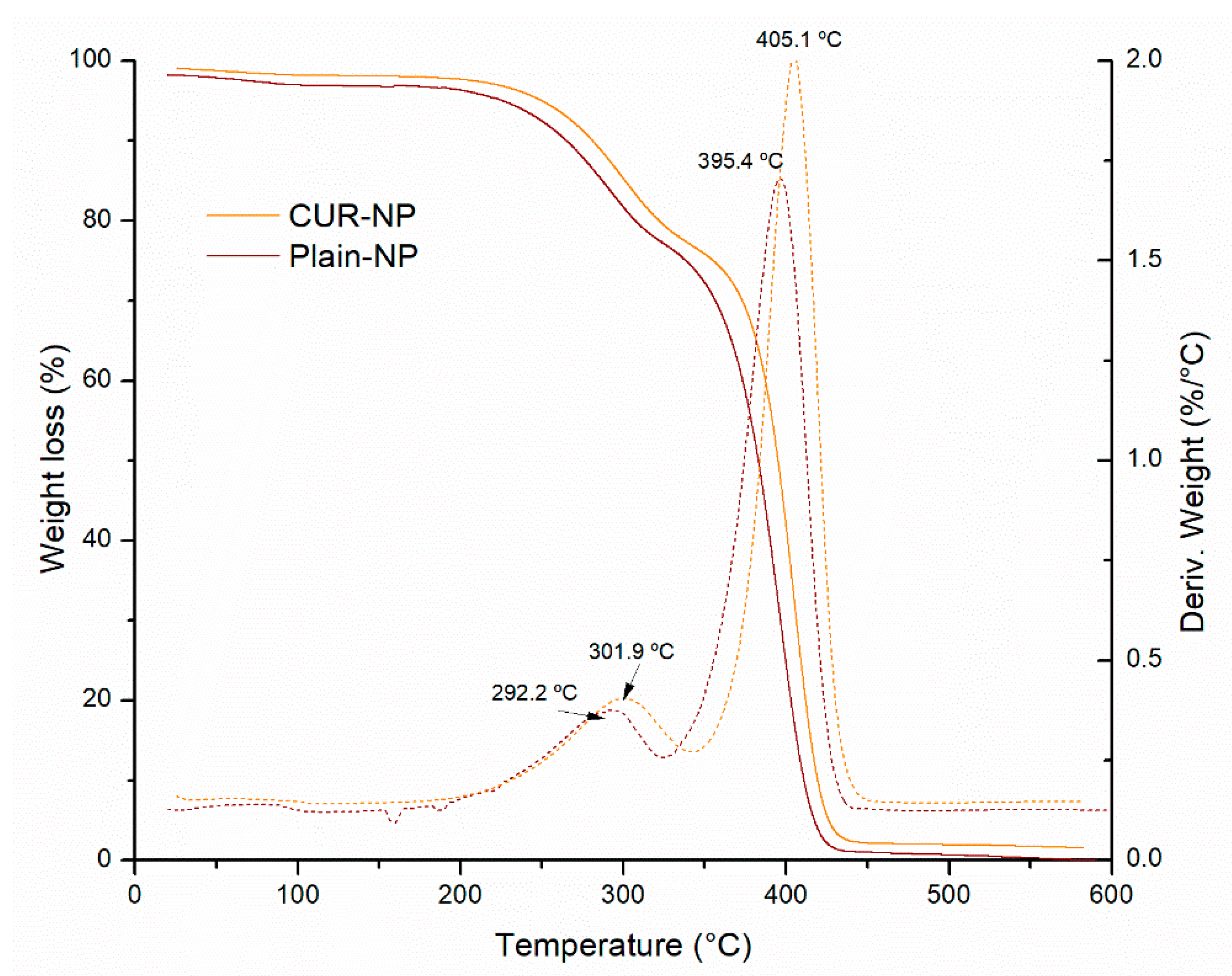
2.3.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.4. In Vitro Studies of CUR-NP
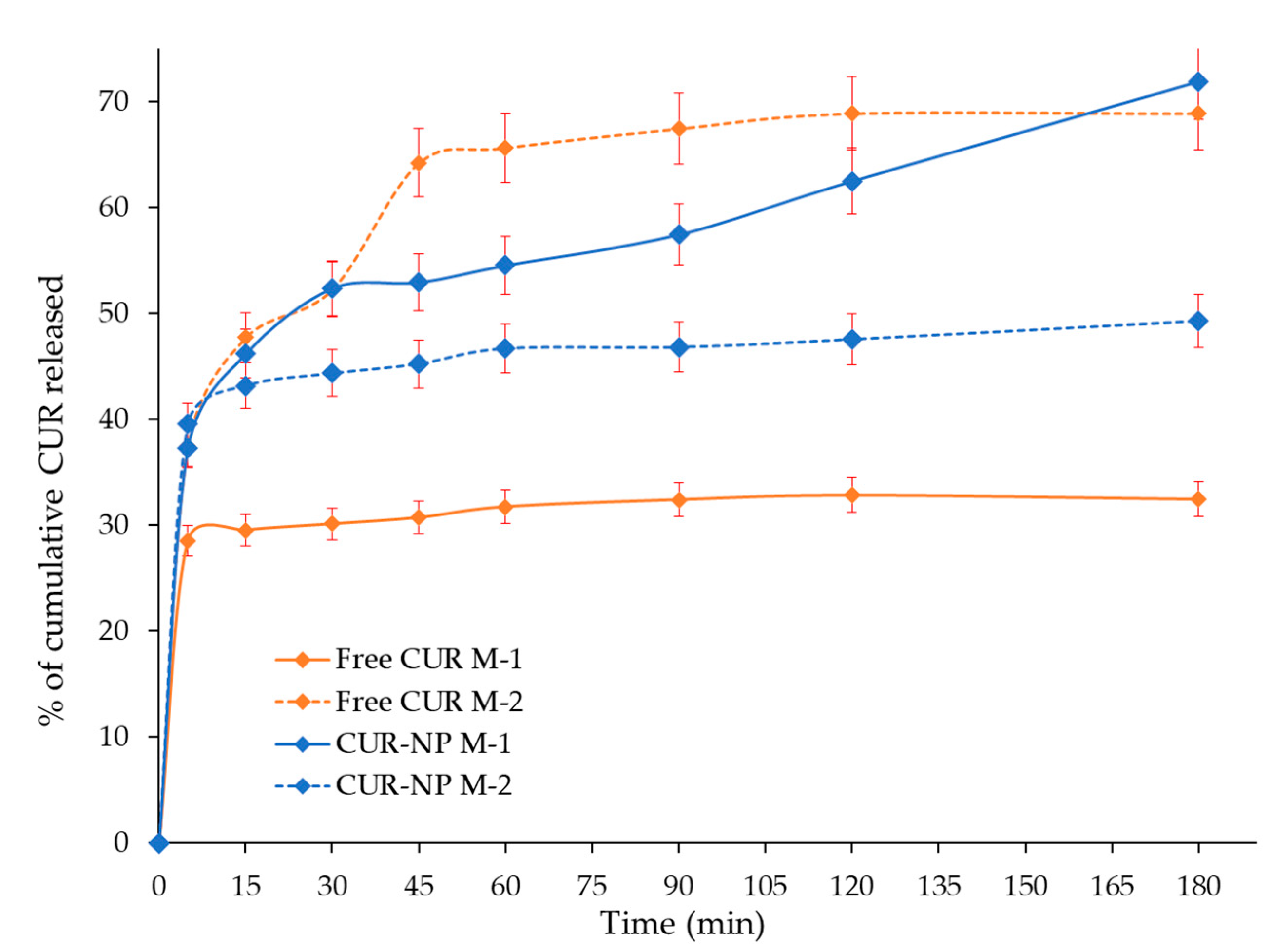
2.4.1. Release Profile of CUR-NP
2.4.2. DPPH Radical-Scavenging Activity
2.4.3. Evaluation of the Cellular Immune Response of Mice through DTH
2.4.4. Evaluation of Cytotoxicity on Tumoral Cells
Cell Culture
Assessment of Cytotoxicity by MTT Assay
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Encapsulation
3.2. Encapsulation Efficiency (%EE)
3.3. Particle Size and Morphology
3.4. Thermal Analysis
3.5. In Vitro Release Evaluation
3.6. Antioxidant Activity Evaluation of the Free CUR and CUR-NP
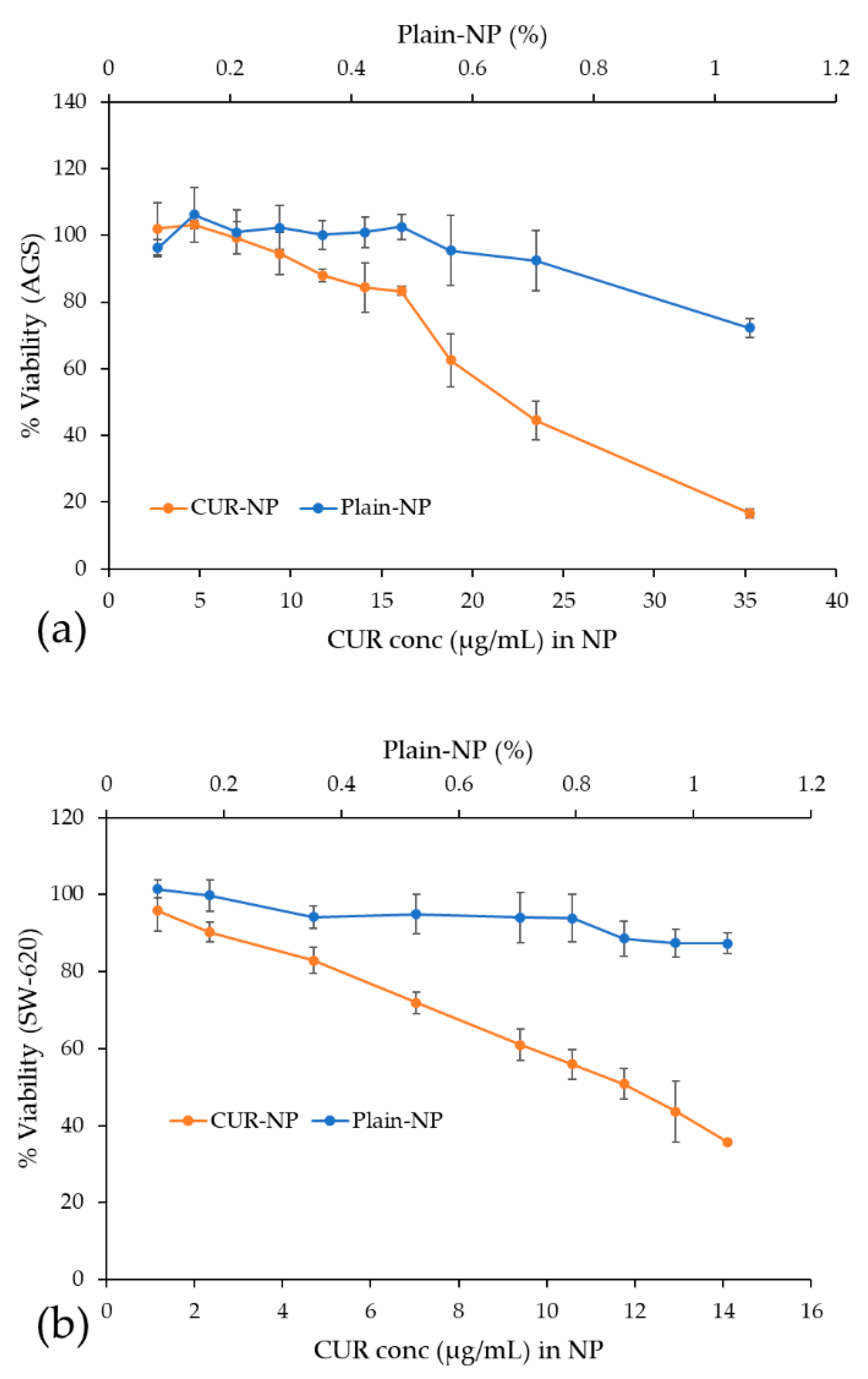
3.7. Cytotoxic Activity Evaluation of Free CUR and CUR-NP
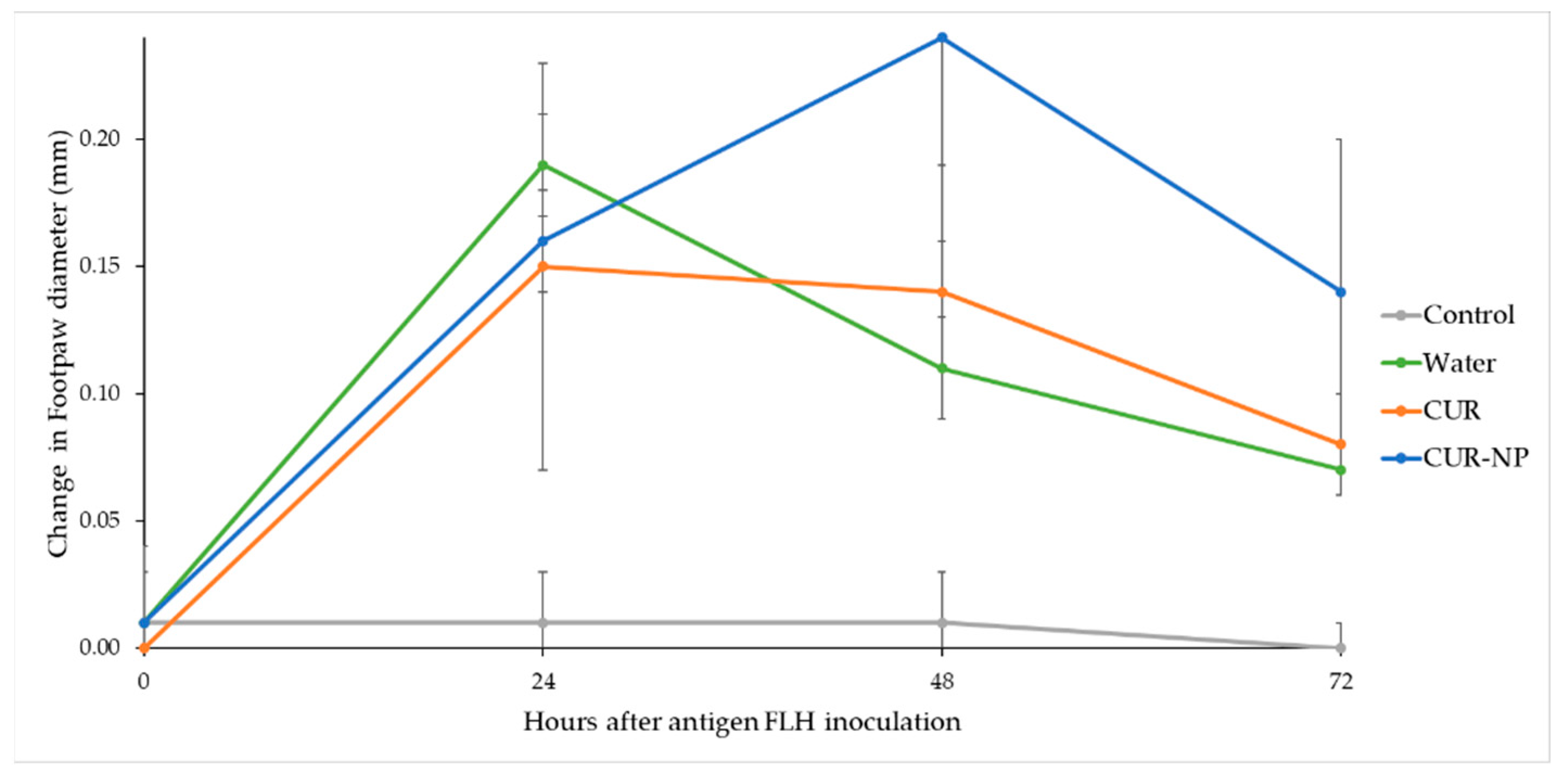
3.8. Evaluation of the Cellular Immune Response of Mice through DTH
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hsu, C.-H.; Cheng, A.-L. Clinical Studies with Curcumin. In The Molecular Targets and Therapeutic Uses of Curcumin in Health and Disease; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2007; pp. 471–480. [Google Scholar]
- Bhalekar, M.R.; Madgulkar, A.; Jagtap, T.V. Demonstration of Lymphatic Uptake of (6)-Gingerol Solid Lipid Nanoparticles. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2019, 9, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymusiak, M.; Hu, X.; Leon Plata, P.A.; Ciupinski, P.; Wang, Z.J.; Liu, Y. Bioavailability of Curcumin and Curcumin Glucuronide in the Central Nervous System of Mice after Oral Delivery of Nano-Curcumin. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 511, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-S.; Cho, D.-C.; Kim, C.H.; Han, I.; Gil, E.Y.; Kim, K.-T. Effect of Curcumin on the Inflammatory Reaction and Functional Recovery after Spinal Cord Injury in a Hyperglycemic Rat Model. Spine J. 2019, 19, 2025–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siviero, A.; Gallo, E.; Maggini, V.; Gori, L.; Mugelli, A.; Firenzuoli, F.; Vannacci, A. Curcumin, a Golden Spice with a Low Bioavailability. J. Herb. Med. 2015, 5, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadorozhna, M.; Tataranni, T.; Mangieri, D. Piperine: Role in Prevention and Progression of Cancer. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 5617–5629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, P.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Newman, R.A.; Aggarwal, B.B. Bioavailability of Curcumin: Problems and Promises. Mol. Pharm. 2007, 4, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, K.; Nangia, A. Curcumin: Pharmaceutical Solids as a Platform to Improve Solubility and Bioavailability. CrystEngComm 2018, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, K.W.; Quirós, M.I.; Huertas, F.V.; Vega-Baudrit, J.R.; Navarro-Hoyos, M.; Araya-Sibaja, A.M. Design of Hybrid Polymeric-Lipid Nanoparticles Using Curcumin as a Model: Preparation, Characterization, and In Vitro Evaluation of Demethoxycurcumin and Bisdemethoxycurcumin-Loaded Nanoparticles. Polymers 2021, 13, 4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapal, A.; Tiku, P.K. Complexation of Curcumin with Soy Protein Isolate and Its Implications on Solubility and Stability of Curcumin. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 960–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, L.N. Stability Testing of Nutraceuticals and Functional Foods; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; ISBN 9780429195570. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, G.H.; Kim, J.T. Observation of Chitosan Coated Lipid Nanoparticles with Different Lipid Compositions under Simulated in Vitro Digestion System. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 84, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saedi, A.; Rostamizadeh, K.; Parsa, M.; Dalali, N.; Ahmadi, N. Preparation and Characterization of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers as Drug Delivery System: Influence of Liquid Lipid Types on Loading and Cytotoxicity. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2018, 216, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotha, R.R.; Luthria, D.L. Curcumin: Biological, Pharmaceutical, Nutraceutical, and Analytical Aspects. Molecules 2019, 24, 2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Archivio, A.A.; Maggi, M.A. Investigation by Response Surface Methodology of the Combined Effect of PH and Composition of Water-Methanol Mixtures on the Stability of Curcuminoids. Food Chem. 2017, 219, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lateh, L.; Kaewnopparat, N.; Yuenyongsawad, S.; Panichayupakaranant, P. Enhancing the Water-Solubility of Curcuminoids-Rich Extract Using a Ternary Inclusion Complex System: Preparation, Characterization, and Anti-Cancer Activity. Food Chem. 2022, 368, 130827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocher, A.; Schiborr, C.; Behnam, D.; Frank, J. The Oral Bioavailability of Curcuminoids in Healthy Humans Is Markedly Enhanced by Micellar Solubilisation but Not Further Improved by Simultaneous Ingestion of Sesamin, Ferulic Acid, Naringenin and Xanthohumol. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 14, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, A.P.; Tiyaboonchai, W.; Patankar, S.; Madhusudhan, B.; Souto, E.B. Curcuminoids-Loaded Lipid Nanoparticles: Novel Approach towards Malaria Treatment. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 81, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Beevers, C.; Huang, S. The Targets of Curcumin. Curr. Drug Targets 2011, 12, 332–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, A.P.; Mukerjee, A.; Helson, L.; Gupta, R.; Vishwanatha, J.K. Efficacy of Liposomal Curcumin in a Human Pancreatic Tumor Xenograft Model: Inhibition of Tumor Growth and Angiogenesis. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 3603–3610. [Google Scholar]
- Mora Román, J.J.; Del Campo, M.; Villar, J.; Paolini, F.; Curzio, G.; Venuti, A.; Jara, L.; Ferreira, J.; Murgas, P.; Lladser, A.; et al. Immunotherapeutic Potential of Mollusk Hemocyanins in Combination with Human Vaccine Adjuvants in Murine Models of Oral Cancer. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 6942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quirós-Fallas, M.I.; Vargas-Huertas, F.; Quesada-Mora, S.; Azofeifa-Cordero, G.; Wilhelm-Romero, K.; Vásquez-Castro, F.; Alvarado-Corella, D.; Sánchez-Kopper, A.; Navarro-Hoyos, M. Polyphenolic HRMS Characterization, Contents and Antioxidant Activity of Curcuma Longa Rhizomes from Costa Rica. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi-Ghadi, Z.; Behjou, N.; Ebrahimnejad, P.; Mahkam, M.; Goli, H.R.; Lam, M.; Nokhodchi, A. Improving Antibacterial Efficiency of Curcumin in Magnetic Polymeric Nanocomposites. J. Pharm. Innov. 2022, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Sharma, S.; Wadhwa, J. Improved Uptake and Therapeutic Intervention of Curcumin via Designing Binary Lipid Nanoparticulate Formulation for Oral Delivery in Inflammatory Bowel Disorder. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, U.; Singh, V.; Kumar, V.; Khajuria, Y. Spectroscopic Studies of Cholesterol: Fourier Transform Infra-Red and Vibrational Frequency Analysis. Mater. Focus 2014, 3, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalan, K.; Jose, J. Development of Amphotericin b Based Organogels against Mucocutaneous Fungal Infections. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 56, e17509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumara, P.; Mohanb, C.; Uma Shankara, M.K.S.; Gulatia, M. Physiochemical Characterization and Release Rate Studies of SolidDispersions of Ketoconazole with Pluronic F127 and PVP K-30. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. IJPR 2011, 10, 685. [Google Scholar]
- Rafiee, Z.; Nejatian, M.; Daeihamed, M.; Jafari, S.M. Application of Different Nanocarriers for Encapsulation of Curcumin. Crit Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 59, 3468–3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.; Ramsey, J.D.; Kabanov, A.V. Polymeric Micelles for the Delivery of Poorly Soluble Drugs: From Nanoformulation to Clinical Approval. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 156, 80–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweers, M.L.T.; Grijpma, D.W.; Engbers, G.H.M.; Feijen, J. The Preparation of Monodisperse Biodegradable Polyester Nanoparticles with a Controlled Size. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2003, 66B, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinno, J.I.; Kamada, N.; Miyake, M.; Yamada, K.; Mukai, T.; Odomi, M.; Toguchi, H.; Liversidge, G.G.; Higaki, K.; Kimura, T. Effect of Particle Size Reduction on Dissolution and Oral Absorption of a Poorly Water-Soluble Drug, Cilostazol, in Beagle Dogs. J. Control. Release 2006, 111, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, M.P.; Vaz, A.F.M.; Correia, M.T.S.; Cerqueira, M.A.; Vicente, A.A.; Carneiro-da-Cunha, M.G. Quercetin-Loaded Lecithin/Chitosan Nanoparticles for Functional Food Applications. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2014, 7, 1149–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, M.S.; da Silva Júnior, M.F.; Xavier-Júnior, F.H.; de Oliveira Veras, B.; de Albuquerque, P.B.S.; de Oliveira Borba, E.F.; da Silva, T.G.; Xavier, V.L.; de Souza, M.P.; das Graças Carneiro-da-Cunha, M. Characterization of Curcumin-Loaded Lecithin-Chitosan Bioactive Nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2021, 2, 100119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, F.-L.; Wu, T.-H.; Lin, L.-T.; Cham, T.-M.; Lin, C.-C. Nanoparticles Formulation of Cuscuta Chinensis Prevents Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 1771–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhlaghi, S.; Rabbani, S.; Alavi, S.; Alinaghi, A.; Radfar, F.; Dadashzadeh, S.; Haeri, A. Green Formulation of Curcumin Loaded Lipid-Based Nanoparticles as a Novel Carrier for Inhibition of Post-Angioplasty Restenosis. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 105, 110037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Péret-Almeida, L.; Cherubino, A.P.F.; Alves, R.J.; Dufossé, L.; Glória, M.B.A. Separation and Determination of the Physico-Chemical Characteristics of Curcumin, Demethoxycurcumin and Bisdemethoxycurcumin. Food Res. Int. 2005, 38, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garti, N.; Karpuj, L.; Sarig, S. Correlation between Crystal Habit and the Composition of Solvated and Nonsolvated Cholesterol Crystals. J. Lipid Res. 1981, 22, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumbhar, D.D.; Pokharkar, V.B. Physicochemical Investigations on an Engineered Lipid–Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticle Containing a Model Hydrophilic Active, Zidovudine. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 436, 714–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Chaudhury, A. Recent Advances in Lipid Nanoparticle Formulations with Solid Matrix for Oral Drug Delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2011, 12, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehiabar, M.; Nosrati, H.; Javani, E.; Aliakbarzadeh, F.; Kheiri Manjili, H.; Davaran, S.; Danafar, H. Production of Biological Nanoparticles from Bovine Serum Albumin as Controlled Release Carrier for Curcumin Delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffernan, C.; Ukrainczyk, M.; Gamidi, R.K.; Hodnett, B.K.; Rasmuson, Å.C. Extraction and Purification of Curcuminoids from Crude Curcumin by a Combination of Crystallization and Chromatography. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2017, 21, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, N.; Ahmad, M.; Minhas, M.U.; Barkat, K.; Khalid, M.F. PH-Responsive Smart Gels of Block Copolymer [Pluronic F127-Co-Poly(Acrylic Acid)] for Controlled Delivery of Ivabradine Hydrochloride: Its Toxicological Evaluation. J. Polym. Res. 2019, 26, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouelmagd, S.A.; Sun, B.; Chang, A.C.; Ku, Y.J.; Yeo, Y. Release Kinetics Study of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs from Nanoparticles: Are We Doing It Right? Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baby, T.; Liu, Y.; Yang, G.; Chen, D.; Zhao, C.-X. Microfluidic Synthesis of Curcumin Loaded Polymer Nanoparticles with Tunable Drug Loading and PH-Triggered Release. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 594, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharat, M.; Du, Z.; Zhang, G.; McClements, D.J. Physical and Chemical Stability of Curcumin in Aqueous Solutions and Emulsions: Impact of PH, Temperature, and Molecular Environment. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 1525–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Tao, Q.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, F.; Guo, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Q.; Yu, S. PLGA Nanoparticles Improve the Oral Bioavailability of Curcumin in Rats: Characterizations and Mechanisms. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 9280–9289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajakta, D.; Ratnesh, J.; Chandan, K.; Suresh, S.; Grace, S.; Meera, V.; Vandana, P. Curcumin Loaded PH-Sensitive Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Colon Cancer. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2009, 5, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, T.; Singh, J.; Kaur, S.; Sandhu, S.; Singh, G.; Kaur, I.P. Enhancing Bioavailability and Stability of Curcumin Using Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (CLEN): A Covenant for Its Effectiveness. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X.Y.; Tam, K.C.; Gan, L.H. Release Kinetics of Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic Model Drugs from Pluronic F127/Poly(Lactic Acid) Nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2005, 103, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenhaute, M.; Snoeck, D.; Vanderleyden, E.; De Belie, N.; Van Vlierberghe, S.; Dubruel, P. Stability of Pluronic® F127 Bismethacrylate Hydrogels: Reality or Utopia? Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 146, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, D.Q. The Mechanisms of Drug Release from Solid Dispersions in Water-Soluble Polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 231, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Ming, J.; He, B.; Fan, Y.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, X. Preparation and Characterization of Novel Polymeric Micelles for 9-Nitro-20(S)-Camptothecin Delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 34, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PubChem Curcumin Water Solubility. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Curcumin#section=Solubility&fullscreen=true (accessed on 10 January 2021).
- Dos Santos, P.D.F.; Francisco, C.R.L.; Coqueiro, A.; Leimann, F.V.; Pinela, J.; Calhelha, R.C.; Porto Ineu, R.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Bona, E.; Gonçalves, O.H. The Nanoencapsulation of Curcuminoids Extracted from: Curcuma Longa L. and an Evaluation of Their Cytotoxic, Enzymatic, Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Li, W.; Wang, H.; Fan, Y.-Y.; Wang, H.; Gao, X.; Niu, B.; Gong, X. Preparation, Characterization, Release and Antioxidant Activity of Curcumin-Loaded Amorphous Calcium Phosphate Nanoparticles. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 2018, 500, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Huang, X.; Gong, Y.; Xiao, H.; McClements, D.J.; Hu, K. Enhancement of Curcumin Water Dispersibility and Antioxidant Activity Using Core-Shell Protein-Polysaccharide Nanoparticles. Food Res. Int. 2016, 87, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jyoti, K.; Bhatia, R.K.; Martis, E.A.F.; Coutinho, E.C.; Jain, U.K.; Chandra, R.; Madan, J. Soluble Curcumin Amalgamated Chitosan Microspheres Augmented Drug Delivery and Cytotoxicity in Colon Cancer Cells: In Vitro and in Vivo Study. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 148, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, T.-Y.; Wu, Y.-C.; Gong, P.-X.; Li, H.-J. Foxtail Millet Prolamin as an Effective Encapsulant Deliver Curcumin by Fabricating Caseinate Stabilized Composite Nanoparticles. Food Chem. 2022, 367, 130764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Nian, S.; Huang, Q. Assembly of Kafirin/Carboxymethyl Chitosan Nanoparticles to Enhance the Cellular Uptake of Curcumin. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 51, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, L.; Peng, H.; Li, Y.; Xiong, J.; Xu, Z. The Formulation and Delivery of Curcumin with Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for the Treatment of on Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer both in Vitro and in Vivo. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 4802–4808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, L.E.; Tan, L.T.-H.; Goh, B.-H.; Tey, B.T.; Ong, B.H.; Tang, S.Y. Magnetic Cellulose Nanocrystal Stabilized Pickering Emulsions for Enhanced Bioactive Release and Human Colon Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 127, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuah, L.H.; Roberts, C.J.; Billa, N.; Abdullah, S.; Rosli, R. Cellular Uptake and Anticancer Effects of Mucoadhesive Curcumin-Containing Chitosan Nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 116, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Geng, D.; Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Cao, J. Co-Delivery of Etoposide and Curcumin by Lipid Nanoparticulate Drug Delivery System for the Treatment of Gastric Tumors. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 3665–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, C.A. Delayed Type Hypersensitivity: Current Theories with a Historic Perspective. Dermatol. Online J. 1999, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.R. Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity Skin Testing. A Review. Arch. Dermatol. 1983, 119, 934–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Disis, M.L.; Schiffman, K.; Gooley, T.A.; McNeel, D.G.; Rinn, K.; Knutson, K.L. Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity Response Is a Predictor of Peripheral Blood T-Cell Immunity after HER-2/Neu Peptide Immunization—PubMed. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 1347–1350. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mollazadeh, H.; Cicero, A.F.G.; Blesso, C.N.; Pirro, M.; Majeed, M.; Sahebkar, A. Immune Modulation by Curcumin: The Role of Interleukin-10. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Goebeler, M. Nickel Allergies: Paying the Toll for Innate Immunity. J. Mol. Med. 2011, 89, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdi, A.S.; Ghoreschi, K.; Röcken, M. Inflammasome Activation in Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity Reactions. J. Invest Dermatol. 2007, 127, 1853–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afolayan, F.I.D.; Erinwusi, B.; Oyeyemi, O.T. Immunomodulatory Activity of Curcumin-Entrapped Poly d, l -Lactic- Co -Glycolic Acid Nanoparticles in Mice. Integr. Med. Res. 2018, 7, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuandani; Nugraha, S.; Laila, L.; Satria, D. Immunomodulatory Effects of Standardized Extract of Curcuma Mangga Val. on Cytokines, Antibody and Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity Response in Wistar Rats. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 16, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karchuli, M.; Pradhan, D. Curcuma Amada Roxb. Rhizome Extract Modulates Cellular and Humoral Immune System. Pharmacologyonline 2011, 3, 947–952. [Google Scholar]

| Formulation | Size Average (nm) | Polydispersity Index (PDI) |
|---|---|---|
| CUR-NP | 49.5 ± 0.8 | 0.27 ± 0.03 |
| IC50 (µg/mL) 1,2,3,4 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ethanol | Water | |
| CUR | 9.60 a,& ± 0.12 | 2444.80 b,^ ± 19.68 |
| CUR-NP 5 | -- | 9.55 # ± 0.18 |
| Trolox | 7.77 a,≠ ± 0.10 | 7.82 a,# ± 0.34 |
| Formulation | 0 h (mm) | 24 h (mm) | 48 h (mm) | 72 h (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 0.01 ± 0.03 a | 0.01 ± 0.02 b | 0.01 ± 0.02 c | 0.00 ± 0.01 c |
| Water (FLH) | 0.01 ± 0.03 a | 0.19 ± 0.05 a | 0.14 ± 0.04 b | 0.07 ± 0.02 b |
| CUR | 0.00 ± 0.01 a | 0.15 ± 0.08 a | 0.14 ± 0.05 b | 0.08 ± 0.02 b |
| CUR-NP | 0.01 ± 0.02 a | 0.16 ± 0.02 a | 0.24 ± 0.10 a | 0.14 ± 0.06 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quirós-Fallas, M.I.; Wilhelm-Romero, K.; Quesada-Mora, S.; Azofeifa-Cordero, G.; Vargas-Huertas, L.F.; Alvarado-Corella, D.; Mora-Román, J.J.; Vega-Baudrit, J.R.; Navarro-Hoyos, M.; Araya-Sibaja, A.M. Curcumin Hybrid Lipid Polymeric Nanoparticles: Antioxidant Activity, Immune Cellular Response, and Cytotoxicity Evaluation. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2431. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102431
Quirós-Fallas MI, Wilhelm-Romero K, Quesada-Mora S, Azofeifa-Cordero G, Vargas-Huertas LF, Alvarado-Corella D, Mora-Román JJ, Vega-Baudrit JR, Navarro-Hoyos M, Araya-Sibaja AM. Curcumin Hybrid Lipid Polymeric Nanoparticles: Antioxidant Activity, Immune Cellular Response, and Cytotoxicity Evaluation. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(10):2431. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102431
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuirós-Fallas, María Isabel, Krissia Wilhelm-Romero, Silvia Quesada-Mora, Gabriela Azofeifa-Cordero, Luis Felipe Vargas-Huertas, Diego Alvarado-Corella, Juan José Mora-Román, José Roberto Vega-Baudrit, Mirtha Navarro-Hoyos, and Andrea Mariela Araya-Sibaja. 2022. "Curcumin Hybrid Lipid Polymeric Nanoparticles: Antioxidant Activity, Immune Cellular Response, and Cytotoxicity Evaluation" Biomedicines 10, no. 10: 2431. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102431
APA StyleQuirós-Fallas, M. I., Wilhelm-Romero, K., Quesada-Mora, S., Azofeifa-Cordero, G., Vargas-Huertas, L. F., Alvarado-Corella, D., Mora-Román, J. J., Vega-Baudrit, J. R., Navarro-Hoyos, M., & Araya-Sibaja, A. M. (2022). Curcumin Hybrid Lipid Polymeric Nanoparticles: Antioxidant Activity, Immune Cellular Response, and Cytotoxicity Evaluation. Biomedicines, 10(10), 2431. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102431







