EEG Markers of Treatment Resistance in Idiopathic Generalized Epilepsy: From Standard EEG Findings to Advanced Signal Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. EEG Features of Idiopathic Generalized Epilepsy
3. EEG Features Associated with Treatment Resistance Observed during Routine EEG Recordings
3.1. Focal Abnormalities
3.2. Photoparoxysmal Response
3.3. EEG Slowing on Background Activity
3.4. Other EEG Findings
4. EEG Biomarkers Found with paEEG Recordings Associated with Poor Seizure Outcome
4.1. EEG Findings Selectively Occurring during Sleep
4.2. Generalized Discharge Duration Measured during 24-h EEG Recordings
5. The Emerging Role of Advanced EEG Analysis in the Identification of New Biomarkers of Medication Refractoriness
6. Future Perspectives and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Gesche, J.; Christensen, J.; Hjalgrim, H.; Rubboli, G.; Beier, C.P. Epidemiology and outcome of idiopathic generalized epilepsy in adults. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, E.; French, J.; Scheffer, I.E.; Bogacz, A.; Alsaadi, T.; Sperling, M.R.; Abdulla, F.; Zuberi, S.M.; Trinka, E.; Specchio, N.; et al. ILAE definition of the Idiopathic Generalized Epilepsy Syndromes: Position statement by the ILAE Task Force on Nosology and Definitions. Epilepsia 2022, 63, 1475–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irelli, E.C.; Morano, A.; Orlando, B.; Salamone, E.M.; Fanella, M.; Fattouch, J.; Manfredi, M.; Giallonardo, A.T.; Di Bonaventura, C. Seizure outcome trajectories in a well-defined cohort of newly diagnosed juvenile myoclonic epilepsy patients. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2022, 145, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josephson, C.B.; Patten, S.B.; Bulloch, A.; Williams, J.V.A.; Lavorato, D.; Fiest, K.M.; Secco, M.; Jette, N. The impact of seizures on epilepsy outcomes: A national, community-based survey. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szaflarski, J.P.; Can, E.E.G. predict outcomes in genetic generalized epilepsies? Clin. Neurophysiol. 2014, 125, 215–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneviratne, U.; Cook, M.J.; D’Souza, W.J. Electroencephalography in the Diagnosis of Genetic Generalized Epilepsy Syndromes. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneviratne, U.; Cook, M.; D’Souza, W. Brainwaves beyond diagnosis: Wider applications of electroencephalography in idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Epilepsia 2022, 63, 22–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneviratne, U.; Cook, M.; D’Souza, W. Epileptiform K-Complexes and Sleep Spindles: An Underreported Phenomenon in Genetic Generalized Epilepsy. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 33, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrachovy, R.A.; Frost, J.D., Jr. The EEG in selected generalized seizures. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2006, 23, 312–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneviratne, U.; Cook, M.; D’Souza, W. Focal abnormalities in idiopathic generalized epilepsy: A critical review of the literature. Epilepsia 2014, 55, 1157–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneviratne, U.; Hepworth, G.; Cook, M.; D’Souza, W. Atypical EEG abnormalities in genetic generalized epilepsies. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 127, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, P.; Goosses, R. Relation of photosensitivity to epileptic syndromes. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatr. 1986, 49, 1386–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shen, C.; Jin, L.; Chen, B.; Jiang, Z.; Tao, J.X.; Liu, Y. The electroclinical features of idiopathic generalized epilepsy patients presenting with fixation-off sensitivity. Epileptic Disord. 2018, 20, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Shakankiry, H.M.; Kader, A.A. Pattern sensitivity: A missed part of the diagnosis. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2012, 8, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Matsuoka, H.; Takahashi, T.; Sasaki, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Yoshida, S.; Numachi, Y.; Saito, H.; Ueno, T.; Sato, M. Neuropsychological EEG activation in patients with epilepsy. Brain 2000, 123, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, H. The seizure prognosis of juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. Jpn. J. Psychiatr. Neurol. 1992, 46, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedström, A.; Olsson, I. Epidemiology of absence epilepsy: EEG findings and their predictive value. Pediatr. Neurol. 1991, 7, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmail, E.H.; Nawito, A.M.; Labib, D.M.; Basheer, M.A. Focal interictal epileptiform discharges in idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 37, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szaflarski, J.P.; Lindsell, C.J.; Zakaria, T.; Banks, C.; Privitera, M.D. Seizure control in patients with idiopathic generalized epilepsies: EEG determinants of medication response. Epilepsy Behav. 2010, 17, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayalakshmi, S.S.; Srinivasa Rao, B.; Sailaja, S. Focal clinical and electroencephalographic features in patients with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2010, 122, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshinaga, H.; Ohtsuka, Y.; Tamai, K.; Tamura, I.; Ito, M.; Ohmori, I.; Oka, E. EEG in childhood absence epilepsy. Seizure 2004, 13, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolomei, F.; Roger, J.; Bureau, M.; Genton, P.; Dravet, C.; Viallat, D.; Gastaut, J.L. Prognostic factors for childhood and juvenile absence epilepsies. Eur. Neurol. 1997, 37, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irelli, E.C.; Morano, A.; Cocchi, E.; Casciato, S.; Fanella, M.; Albini, M.; Avorio, F.; Basili, L.M.; Fisco, G.; Barone, F.A.; et al. Doing without valproate in women of childbearing potential with idiopathic generalized epilepsy: Implications on seizure outcome. Epilepsia 2020, 61, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japaridze, G.; Kasradze, S.; Lomidze, G.; Zhizhiashvili, L.; Kvernadze, D.; Geladze, K.; Beniczky, S. Focal EEG features and therapeutic response in patients with juvenile absence and myoclonic epilepsy. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 127, 1182–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakis, I.; Pathmanathan, J.S.; Chang, R.; Cook, E.F.; Cash, S.S.; Cole, A.J. Prognostic value of EEG asymmetries for development of drug-resistance in drug-naïve patients with genetic generalized epilepsies. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2014, 125, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incecik, F.; Altunbasak, S.; Herguner, O.M. First-drug treatment failures in children with typical absence epilepsy. Brain Dev. 2015, 37, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covanis, A.; Skiadas, K.; Loli, N.; Lada, C.; Theodorou, V. Absence epilepsy: Early prognostic signs. Seizure 1992, 1, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadler, B.; Shevell, M.I. Childhood absence epilepsy requiring more than one medication for seizure control. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2008, 35, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callenbach, P.M.; Bouma, P.A.; Geerts, A.T.; Arts, W.F.M.; Stroink, H.; Peeters, E.A.J.; van Donselaar, C.A.; Peters, A.C.; Brouwer, O.F. Long-term outcome of childhood absence epilepsy: Dutch Study of Epilepsy in Childhood. Epilepsy Res. 2009, 83, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loiseau, P.; Panayiotopoulos, C.P.; Hirsch, E. Childhood absence epilepsy and related syndromes. In Epileptic Syndromes in Infancy, Childhood and Adolescence, 3rd ed.; Roger, J., Bureau, M., Dravet, C., Genton, P., Tassinari, C.A., Wolf, P., Eds.; John Libbey: Eastleigh, UK, 2002; pp. 285–303. [Google Scholar]
- Grosso, S.; Galimberti, D.; Vezzosi, P.; Farnetani, M.; Di Bartolo, R.M.; Bazzotti, S.; Morgese, G.; Balestri, P. Childhood absence epilepsy: Evolution and prognostic factors. Epilepsia 2005, 46, 1796–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentin, A.; Hindocha, N.; Osei-Lah, A.; Fisniku, L.; McCormick, D.; Asherson, P.; Moran, N.; Makoff, A.; Nashef, L. Idiopathic generalized epilepsy with absences: Syndrome classification. Epilepsia 2007, 48, 2187–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolson, A.; Appleton, R.E.; Chadwick, D.W.; Smith, D.F. The relationship between treatment with valproate, lamotrigine, and topiramate and the prognosis of the idiopathic generalised epilepsies. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatr. 2004, 75, 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Verrotti, A.; Fiori, F.; Coppola, G.; Franzoni, E.; Parisi, P.; Chiarelli, F. Idiopathic generalized tonic-clonic epilepsy and photosensitivity: A long-term follow-up study. Acta Paediatr. 2009, 98, 1999–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Podewils, F.; Lapp, S.; Wang, Z.I.; Hartmann, U.; Herzer, R.; Kessler, C.; Runge, U. Natural course and predictors of spontaneous seizure remission in idiopathic generalized epilepsy: 7-27 years of follow-up. Epilepsy Res. 2014, 108, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirrell, E.C.; Camfield, C.S.; Camfield, P.R.; Gordon, K.E.; Dooley, J.M. Long-term prognosis of typical childhood absence epilepsy: Remission or progression to juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. Neurology 1996, 47, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, A.T.; Shinnar, S.; Levy, S.R.; Testa, F.M.; Smith-Rapaport, S.; Beckerman, B.; Ebrahimi, N. Two-year remission and subsequent relapse in children with newly diagnosed epilepsy. Epilepsia 2001, 42, 1553–1562, reprinted in Epilepsia 2002, 43, 207–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loiseau, P.; Pestre, M.; Dartigues, J.F.; Commenges, D.; Barberger-Gateau, C.; Cohadon, S. Long-term prognosis in two forms of childhood epilepsy: Typical absence seizures and epilepsy with rolandic (centrotemporal) EEG foci. Ann. Neurol. 1983, 13, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irelli, E.C.; Cocchi, E.; Ramantani, G.; Caraballo, R.H.; Giuliano, L.; Yilmaz, T.; Morano, A.; Panagiotakaki, E.; Operto, F.F.; Gonzalez Giraldez, B.; et al. Electroclinical Features and Long-term Seizure Outcome in Patients With Eyelid Myoclonia With Absences. Neurology 2022, 98, e1865–e1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevgi, E.B.; Saygi, S.; Ciger, A. Eye closure sensitivity and epileptic syndromes: A retrospective study of 26 adult cases. Seizure 2007, 16, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güveli, B.T.; Baykan, B.; Dörtcan, N.; Bebek, N.; Gürses, C.; Gökyiğit, A. Eye closure sensitivity in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy and its effect on prognosis. Seizure 2013, 22, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, C.G.P.; de Carvalho, K.C.; Guaranha, M.S.B.; Guilhoto, L.M.F.F.; de Araújo Filho, G.M.; Yacubian, E.M.T. Prognosis of Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy with eye-closure sensitivity. Seizure 2018, 62, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goossens, L.A.; Andermann, F.; Andermann, E.; Remillard, G.M. Reflex seizures induced by calculation, card or board games, and spatial tasks: A review of 25 patients and delineation of the epileptic syndrome. Neurology 1990, 40, 1171–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yacubian, E.M.; Wolf, P. Praxis induction. Definition, relation to epilepsy syndromes, nosological and prognostic significance. A focused review. Seizure 2014, 23, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinhoff, B.J.; Scholly, J.; Dentel, C.; Staack, A.M. Is routine electroencephalography (EEG) a useful biomarker for pharmacoresistant epilepsy? Epilepsia 2013, 54 (Suppl. 2), 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Ibañez, A.; McLachlan, R.S.; Mirsattari, S.M.; Diosy, D.C.; Burneo, J.G. Prognostic factors in patients with refractory idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2017, 130, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vierck, E.; Cauley, R.; Kugler, S.L.; Mandelbaum, D.E.; Pal, D.K.; Durner, M. Polyspike and waves do not predict generalized tonic-clonic seizures in childhood absence epilepsy. J. Child Neurol. 2010, 25, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irelli, E.C.; Cocchi, E.; Morano, A.; Casciato, S.; Fanella, M.; Albini, M.; Fisco, G.; Barone, F.A.; Orlando, B.; Mascia, A.; et al. Valproate impact and sex-dependent seizure remission in patients with idiopathic generalized epilepsy. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 415, 116940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataria, L.; Vaughn, B.V. Sleep and Epilepsy. Sleep Med. Clin. 2016, 11, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinopoulos, A.; Tsirouda, M.A.; Bonakis, A.; Pons, R.; Pavlopoulou, I.D.; Tsoumakas, K. Sleep architecture and epileptic characteristics of drug naïve patients in childhood absence epilepsy spectrum. A prospective study. Seizure 2018, 59, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelucci, R.; Rubboli, G.; Passarelli, D.; Riguzzi, P.; Volpi, L.; Parmeggiani, L.; Rizzi, R.; Gardella, E.; Tassinari, C.A. Electroclinical features of idiopathic generalised epilepsy with persisting absences in adult life. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatr. 1996, 61, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, R.P.; Atkinson, R. Generalized paroxysmal fast activity: Electroencephalographic and clinical features. Ann. Neurol. 1982, 11, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guye, M.; Bartolomei, F.; Gastaut, J.L.; Chauvel, P.; Dravet, C. Absence epilepsy with fast rhythmic discharges during sleep: An intermediary form of generalized epilepsy? Epilepsia 2001, 42, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagi, V.; Kim, I.; Bhatt, A.B.; Sonmezturk, H.; Abou-Khalil, B.W.; Arain, A.M. Generalized paroxysmal fast activity in EEG: An unrecognized finding in genetic generalized epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2017, 76, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin-Özemir, Z.; Matur, Z.; Bebek, N.; Gürses, C.; Gökyiğit, A.; Baykan, B. Long-term follow-up of adult patients with genetic generalized epilepsy with typical absence seizures and generalized paroxysmal fast activity in their EEG. Seizure 2014, 23, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halász, P.; Janszky, J.; Barcs, G.; Szucs, A. Generalised paroxysmal fast activity (GPFA) is not always a sign of malignant epileptic encephalopathy. Seizure 2004, 13, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irelli, E.C.; Orlando, B.; Salamone, E.M.; Fisco, G.; Barone, F.A.; Morano, A.; Fanella, M.; Fattouch, J.; Manfredi, M.; Giallonardo, A.T.; et al. High rates of early remission pattern in adult-onset compared with earlier-onset idiopathic generalized epilepsy: A long-term follow-up study. Seizure 2022, 94, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Seneviratne, U.; Perucca, P.; Chen, Z.; Tan, M.K.; O’Brien, T.J.; D’Souza, W.; Kwan, P. Generalized polyspike train: An EEG biomarker of drug-resistant idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Neurology 2018, 91, e1822–e1830, reprinted in Neurology 2018, 91, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, E.C.; Chugh, N.; Ganguly, T.M.; Gugger, J.J.; Tizazu, E.F.; Shinohara, R.T.; Raghupathi, R.; Becker, D.A.; Gelfand, M.A.; Omole, A.T.; et al. Using Generalized Polyspike Train to Predict Drug-Resistant Idiopathic Generalized Epilepsy. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2020; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irelli, E.C.; Morano, A.; Barone, F.A.; Fisco, G.; Fanella, M.; Orlando, B.; Fattouch, J.; Manfredi, M.; Giallonardo, A.T.; Di Bonaventura, C. Persistent treatment resistance in genetic generalized epilepsy: A long-term outcome study in a tertiary epilepsy center. Epilepsia 2020, 61, 2452–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamitaki, B.K.; Janmohamed, M.; Kandula, P.; Elder, C.; Mani, R.; Wong, S.; Perucca, P.; O’Brien, T.; Lin, H.; Heiman, G.A.; et al. Clinical and EEG factors associated with antiseizure medication resistance in idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Epilepsia 2022, 63, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irelli, E.C.; Barone, F.A.; Mari, L.; Morano, A.; Orlando, B.; Salamone, E.M.; Marchi, A.; Fanella, M.; Fattouch, J.; Placidi, F.; et al. Generalized Fast Discharges Along the Genetic Generalized Epilepsy Spectrum: Clinical and Prognostic Significance. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 844674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, C.D.; Gesche, J.; Krøigård, T.; Beier, C.P. Prognostic Value of Generalized Polyspike Trains and Prolonged Epileptiform EEG Runs. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2021, 38, 208–212.7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seneviratne, U.; Boston, R.C.; Cook, M.; D’Souza, W. EEG correlates of seizure freedom in genetic generalized epilepsies. Neurol. Clin. Pract. 2017, 7, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turco, F.; Bonanni, E.; Milano, C.; Pizzanelli, C.; Steinwurzel, C.; Morganti, R.; Fornai, F.; Maestri, M.; Siciliano, G.; Giorgi, F.S. Prolonged epileptic discharges predict seizure recurrence in JME: Insights from prolonged ambulatory EEG. Epilepsia 2021, 62, 1184–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemens, B.; Szigeti, G.; Barta, Z. EEG frequency profiles of idiopathic generalised epilepsy syndromes. Epilepsy Res. 2000, 42, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glomb, K.; Cabral, J.; Cattani, A.; Mazzoni, A.; Raj, A.; Franceschiello, B. Computational Models in Electroencephalography. Brain Topogr. 2022, 35, 142–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagarde, S.; Roehri, N.; Lambert, I.; Trebuchon, A.; McGonigal, A.; Carron, R.; Scavarda, D.; Milh, M.; Pizzo, F.; Colombet, B.; et al. Interictal stereotactic-EEG functional connectivity in refractory focal epilepsies. Brain 2018, 141, 2966–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abela, E.; Pawley, A.D.; Tangwiriyasakul, C.; Yaakub, S.N.; Chowdhury, F.A.; Elwes, R.D.C.; Brunnhuber, F.; Richardson, M.P. Slower alpha rhythm associates with poorer seizure control in epilepsy. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2018, 6, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegg, E.J.; Taylor, J.R.; Mohanraj, R. Spectral power of interictal EEG in the diagnosis and prognosis of idiopathic generalized epilepsies. Epilepsy Behav. 2020, 112, 107427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dömötör, J.; Clemens, B.; Puskás, S.; Fekete, I. Decrease of global current source density predicts successful treatment in absence and juvenile myoclonic epilepsies. Epilepsy Res. 2017, 133, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béla, C.; Mónika, B.; Márton, T.; István, K. Valproate selectively reduces EEG activity in anterior parts of the cortex in patients with idiopathic generalized epilepsy. A low resolution electromagnetic tomography (LORETA) study. Epilepsy Res. 2007, 75, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeom, J.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, J.H.; Jung, S.; Kwon, O.Y. Temporal current-source of spikes suggests initial treatment failure in childhood absence epilepsy. Seizure 2015, 31, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Szaflarski, J.P.; Kay, B.; Gotman, J.; Privitera, M.D.; Holland, S.K. The relationship between the localization of the generalized spike and wave discharge generators and the response to valproate. Epilepsia 2013, 54, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Diessen, E.; Numan, T.; van Dellen, E.; van der Kooi, A.W.; Boersma, M.; Hofman, D.; van Lutterveld, R.; van Dijk, B.W.; van Straaten, E.C.W.; Hillebrand, A.; et al. Opportunities and methodological challenges in EEG and MEG resting state functional brain network research. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 126, 1468–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossini, P.M.; Di Iorio, R.; Bentivoglio, M.; Bertini, G.; Ferreri, F.; Gerloff, C.; Ilmoniemi, R.J.; Miraglia, F.; Nitsche, M.A.; Pestilli, F.; et al. Methods for analysis of brain connectivity: An IFCN-sponsored review. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2019, 130, 1833–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccalá, L.A.; Sameshima, K. Partial directed coherence: A new concept in neural structure determination. Biol. Cybern. 2001, 84, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canafoglia, L.; Dettori, M.S.; Duran, D.; Ragona, F.; Freri, E.; Casellato, S.; Granata, T.; Franceschetti, S.; Panzica, F. Early clinical and EEG findings associated with the outcome in childhood absence epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2019, 98, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Cao, W.; Liao, X.; Chen, Z.; Yang, T.; Gong, Q.; Zhou, D.; Luo, C.; Yao, D. Altered resting state functional network connectivity in children absence epilepsy. J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 354, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Liu, R.; Luo, C.; Jiang, S.; Dong, L.; Peng, R.; Guo, F.; Wang, P. Altered Structural and Functional Connectivity of Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy: An fMRI Study. Neural. Plast. 2018, 2018, 7392187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, M.A.; Cash, S.S. Epilepsy as a disorder of cortical network organization. Neuroscientist 2012, 18, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegg, E.J.; Taylor, J.R.; Keller, S.S.; Mohanraj, R. Interictal structural and functional connectivity in idiopathic generalized epilepsy: A systematic review of graph theoretical studies. Epilepsy Behav. 2020, 106, 107013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farahani, F.V.; Karwowski, W.; Lighthall, N.R. Application of Graph Theory for Identifying Connectivity Patterns in Human Brain Networks: A Systematic Review. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pegg, E.J.; Taylor, J.R.; Laiou, P.; Richardson, M.; Mohanraj, R. Interictal electroencephalographic functional network topology in drug-resistant and well-controlled idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Epilepsia 2021, 62, 492–503, reprinted in Epilepsia 2021, 62, 2304–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Lee, W.G.; Park, S.; Park, K.M. Can we predict drug response by functional connectivity in patients with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy? Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2020, 198, 106119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, C.M.; Koenig, T. EEG microstates as a tool for studying the temporal dynamics of whole-brain neuronal networks: A review. Neuroimage 2018, 180, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, T.; Lehmann, D.; Merlo, M.C.; Kochi, K.; Hell, D.; Koukkou, M. A deviant EEG brain microstate in acute, neuroleptic-naive schizophrenics at rest. Eur. Arch. Psychiatr. Clin. Neurosci. 1999, 249, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britz, J.; Van De Ville, D.; Michel, C.M. BOLD correlates of EEG topography reveal rapid resting-state network dynamics. Neuroimage 2010, 52, 1162–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Zotev, V.; Phillips, R.; Drevets, W.C.; Bodurka, J. Spatiotemporal dynamics of the brain at rest--exploring EEG microstates as electrophysiological signatures of BOLD resting state networks. Neuroimage 2012, 60, 2062–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Xie, Y.; Dong, D.; Pei, H.; Jiang, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Q.; et al. Reconfiguration of dynamic large-scale brain network functional connectivity in generalized tonic-clonic seizures. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2020, 41, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Hu, Y.; Wang, K. Altered Resting-State Electroencephalography Microstates in Idiopathic Generalized Epilepsy: A Prospective Case-Control Study. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 710952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.C.; Ouyang, C.S.; Chiang, C.T.; Yang, R.C.; Wu, R.C.; Wu, H.C. Early prediction of medication refractoriness in children with idiopathic epilepsy based on scalp EEG analysis. Int. J. Neural. Syst. 2014, 24, 1450023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaba, P.; Latka, M.; Krause, M.J.; Kroczka, S.; Kurylo, M.; Kaczorowska-Frontczak, M.; Walas, W.; Jernajczyk, W.; Sebzda, T.; West, B.J. Absence Seizure Detection Algorithm for Portable EEG Devices. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 685814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omidvarnia, A.; Warren, A.E.L.; Dalic, L.J.; Pedersen, M.; Jackson, G. Automatic detection of generalized paroxysmal fast activity in interictal EEG using time-frequency analysis. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 133, 104287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
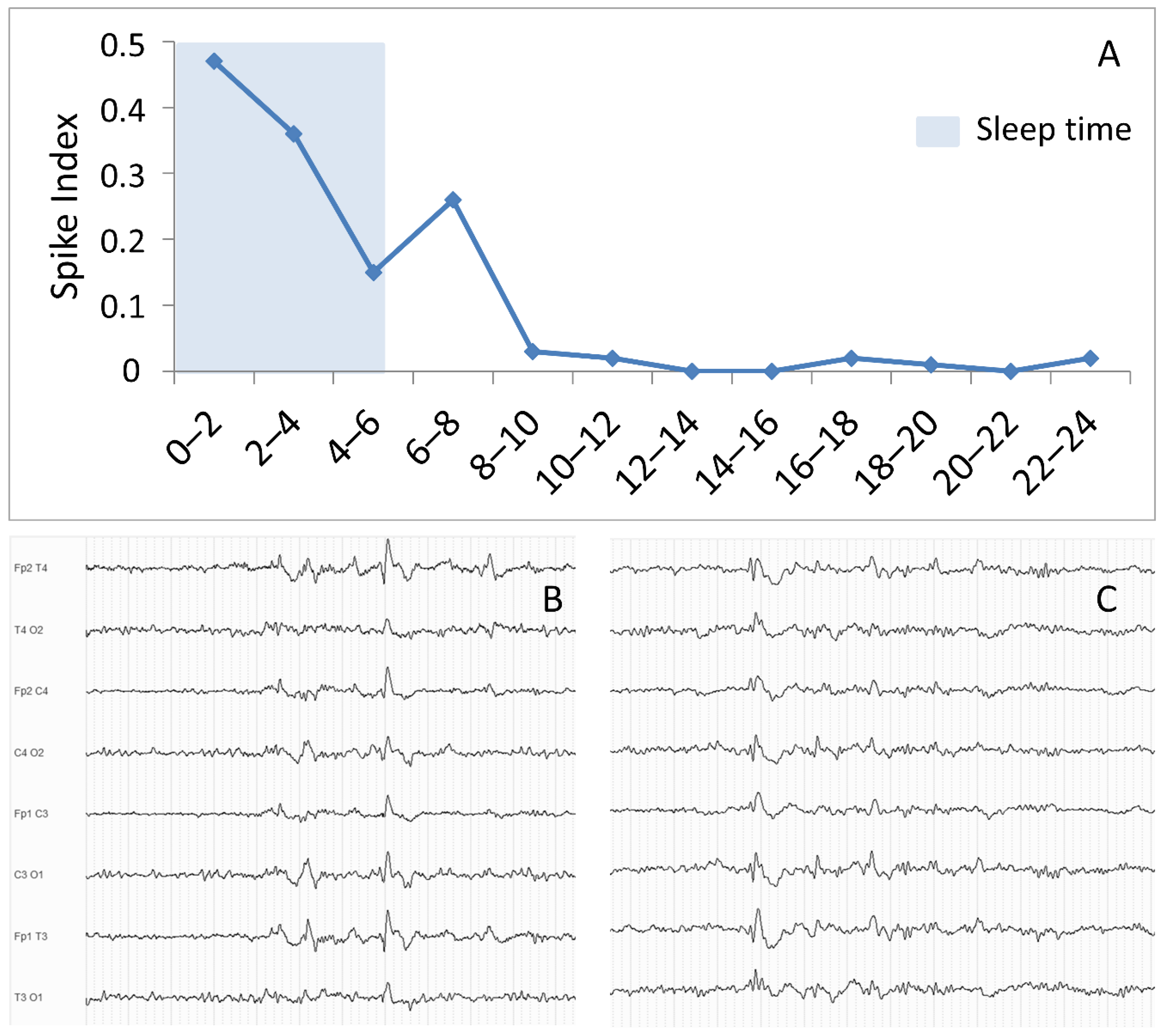

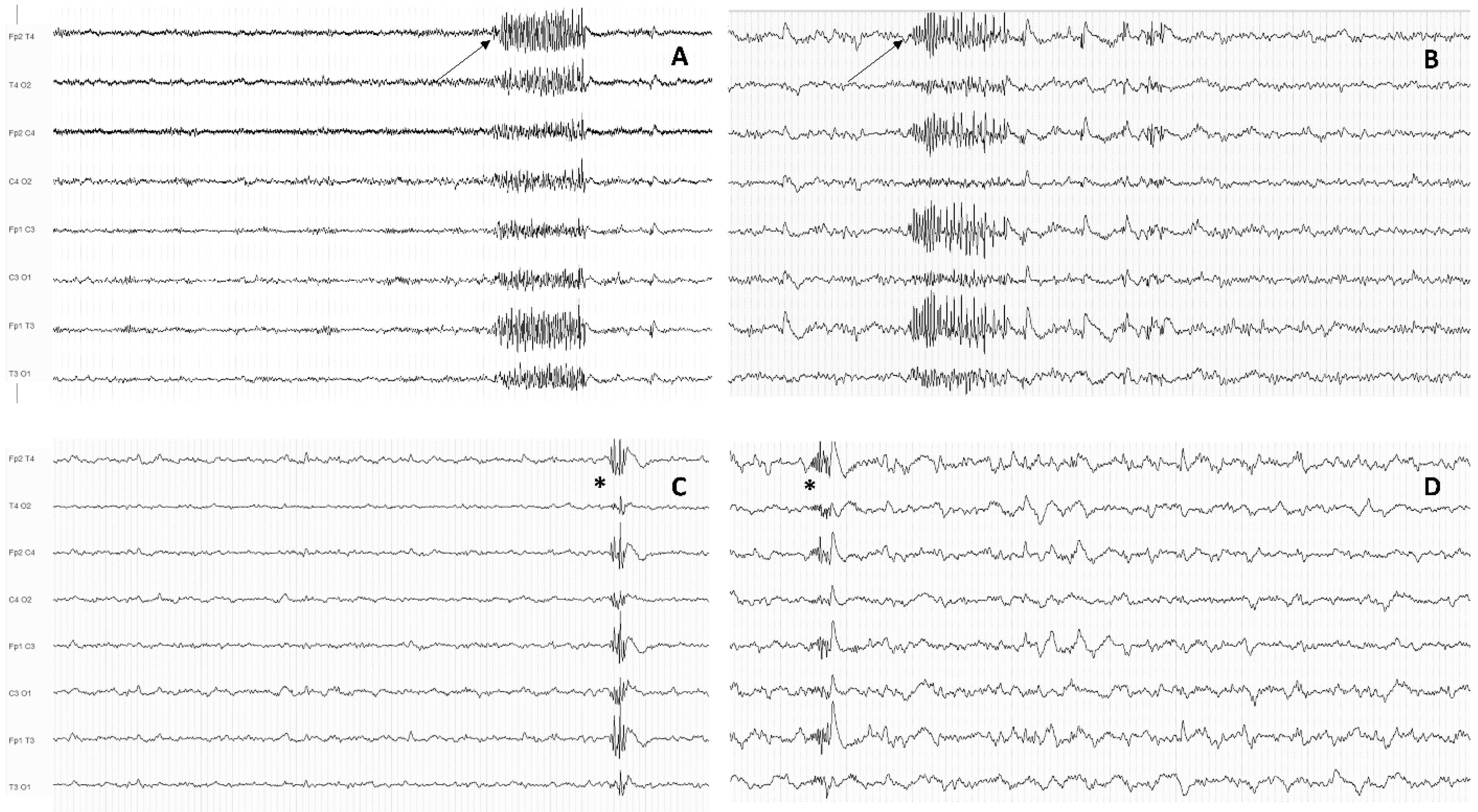
| EEG Marker | Subjects | Methodology | Association with Treatment Resistance | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Focal abnormalities | IGE, JME, JAE | Visual assessment of standard EEG—retrospective and prospective | Not associated | [16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25] |
| Photoparoxysmal response | IGE, CAE | Visual assessment of standard EEG—retrospective and prospective | Association in CAE, not useful in IGE in general | [23,26,27,28,29,33,34,35] |
| Eye closure sensitivity | JME | Visual assessment of standard EEG—retrospective | Not associated | [41,42] |
| Praxis-induction | JME | Visual assessment of standard EEG with neuropsychological activation—retrospective | Controversial | [43,44] |
| Generalized spike-wave and polyspike-wave discharge duration | IGE | 24-h EEG recordings, sleep EEG recordings -retrospective | Yes, except in one study | [63,64,65] |
| Generalized paroxysmal fast activity and generalized polyspike train | IGE | 24-h EEG recordings, sleep EEG recordings—retrospective | Yes, except in one study | [58,59,60,61,62,63] |
| Background slowing | IGE, CAE | Visual assessment of standard EEG, Quantitative analysis resting-state EEG—retrospective | Not associated, except in CAE | [36,37,69,70] |
| Frontal lobe connectivity | CAE | Partial directed coherence in resting state EEG—retrospective | Yes | [78] |
| Graph-theory based functional connectivity | JME | Coherence and phase locking value on resting state EEG—retrospective | Yes | [85] |
| Microstates analysis | IGE | Microstate analysis on resting-state EEG—retrospective | Yes | [91] |
| Machine-learning on quantitative EEG features | IGE | Support-vector-machine model on resting-state EEG quantitative features—retrospective | Yes | [92] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cerulli Irelli, E.; Leodori, G.; Morano, A.; Di Bonaventura, C. EEG Markers of Treatment Resistance in Idiopathic Generalized Epilepsy: From Standard EEG Findings to Advanced Signal Analysis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2428. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102428
Cerulli Irelli E, Leodori G, Morano A, Di Bonaventura C. EEG Markers of Treatment Resistance in Idiopathic Generalized Epilepsy: From Standard EEG Findings to Advanced Signal Analysis. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(10):2428. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102428
Chicago/Turabian StyleCerulli Irelli, Emanuele, Giorgio Leodori, Alessandra Morano, and Carlo Di Bonaventura. 2022. "EEG Markers of Treatment Resistance in Idiopathic Generalized Epilepsy: From Standard EEG Findings to Advanced Signal Analysis" Biomedicines 10, no. 10: 2428. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102428
APA StyleCerulli Irelli, E., Leodori, G., Morano, A., & Di Bonaventura, C. (2022). EEG Markers of Treatment Resistance in Idiopathic Generalized Epilepsy: From Standard EEG Findings to Advanced Signal Analysis. Biomedicines, 10(10), 2428. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102428





