Assessing Agreement between miRNA Microarray Platforms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Samples
2.2. Sample Preparation and Hybridization
2.3. Data Pre-Processing
2.3.1. Affymetrix GeneChip© miRNA Array
2.3.2. Agilent Human miRNA Microarray (V1)
2.3.3. Illumina HumanMI_V2
2.3.4. miRNA Selection and Normalization
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.4.1. Intra-Platform Reliability
2.4.2. Between-Platform Agreement
- (a)
- No bias: ( = 0, = 1)
- (b)
- Fixed bias: (≠ 0, = 1)
- (c)
- Proportional bias: ( = 0, 1)
- (d)
- Fixed and Proportional bias: ( 0, 1)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Data Description

| Affymetrix | Agilent | Illumina | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Array | 25th | 50th | 75th | IQR | 25th | 50th | 75th | IQR | 25th | 50th | 75th | IQR |
| 1 | 4.907 | 5.044 | 5.592 | 0.685 | 3.415 | 3.911 | 5.804 | 2.389 | 6.821 | 8.830 | 10.772 | 3.951 | |
| hREF | 2 | 4.943 | 5.066 | 5.570 | 0.627 | 3.366 | 3.955 | 5.998 | 2.632 | 7.168 | 9.150 | 11.015 | 3.847 |
| 3 | 4.943 | 5.087 | 5.615 | 0.672 | 3.449 | 4.065 | 6.242 | 2.793 | 7.103 | 9.117 | 10.907 | 3.804 | |
| 1 | 5.160 | 5.285 | 5.508 | 0.348 | 3.139 | 3.432 | 4.065 | 0.926 | 5.492 | 6.863 | 8.782 | 3.290 | |
| A498 | 2 | 5.375 | 5.524 | 5.827 | 0.452 | 3.066 | 3.448 | 4.287 | 1.221 | 5.606 | 6.973 | 8.942 | 3.336 |
| 3 | 5.468 | 5.651 | 5.983 | 0.515 | 2.690 | 3.175 | 3.988 | 1.298 | 5.812 | 7.294 | 9.246 | 3.433 | |
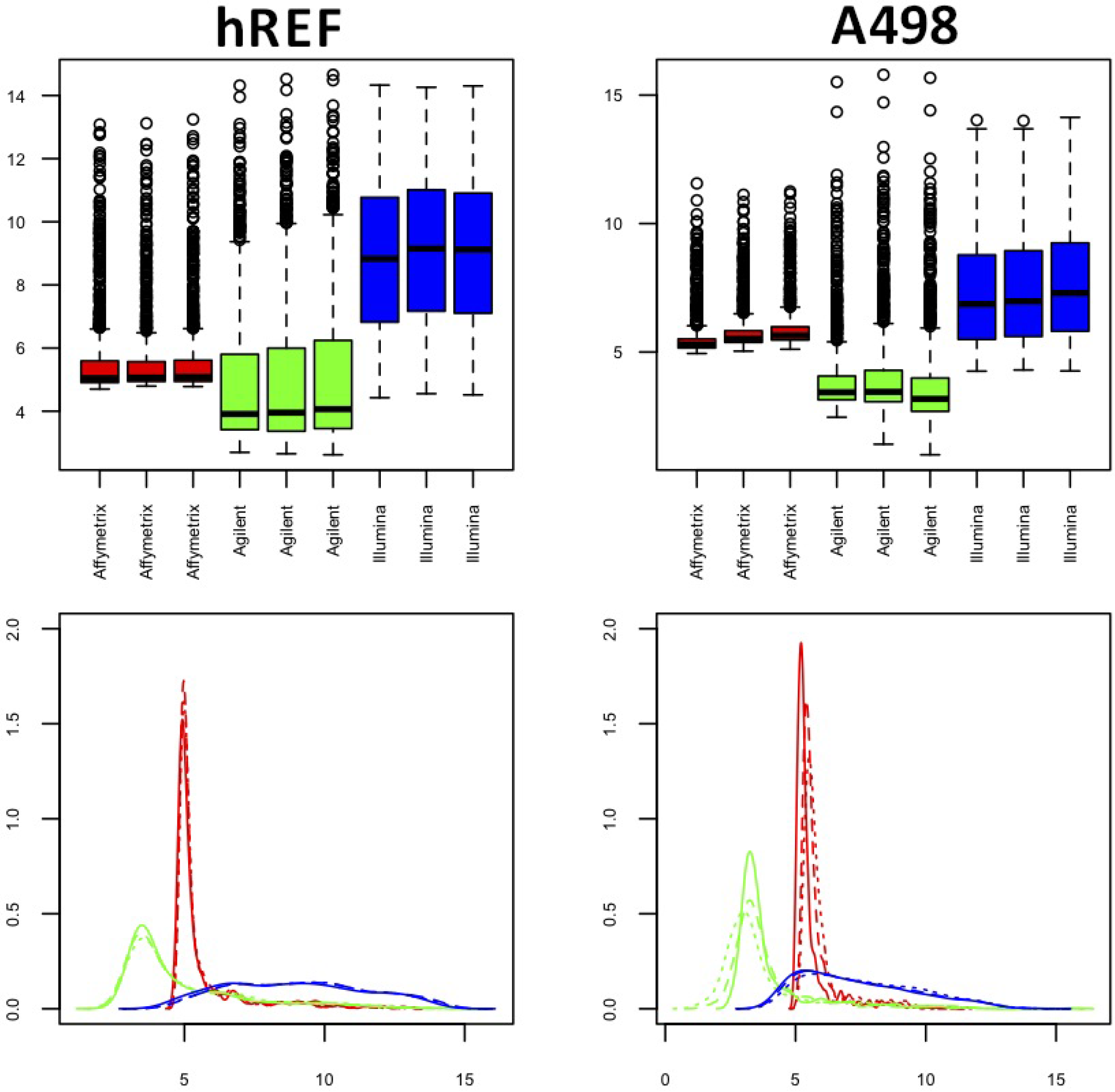
3.2. Intra-Platform Reliability
| Affymetrix | Agilent | Illumina | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Pair | CCC | OCCC | CI 95% | CCC | OCCC | CI 95% | CCC | OCCC | CI 95% |
| 1-2 | 0.988 | 0.997 | 0.991 | |||||||
| hREF | 1-3 | 0.993 | 0.992 | (0.990–0.993) | 0.989 | 0.994 | (0.993–0.995) | 0.993 | 0.994 | (0.994–0.995) |
| 2-3 | 0.994 | 0.995 | 0.999 | |||||||
| 1-2 | 0.935 | 0.975 | 0.996 | |||||||
| A498 | 1-3 | 0.888 | 0.927 | (0.906–0.941) | 0.970 | 0.975 | (0.969–0.979) | 0.981 | 0.989 | (0.987–0.991) |
| 2-3 | 0.961 | 0.978 | 0.989 | |||||||
| Agilent | Illumina | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Pair | CCC | OCCC | CI 95% | CCC | OCCC | CI 95% |
| 1-2 | 0.996 | 0.988 | |||||
| hREF | 1-3 | 0.978 | 0.989 | (0.987–0.990) | 0.994 | 0.993 | (0.992–0.994) |
| 2-3 | 0.992 | 0.998 | |||||
| 1-2 | 0.974 | 0.997 | |||||
| A498 | 1-3 | 0.988 | 0.983 | (0.979–0.986) | 0.987 | 0.992 | (0.990–0.994) |
| 2-3 | 0.986 | 0.992 | |||||
3.3. Between-Platform Agreement
| Sample | Pair | Estimate | CI 95% | Estimate | CI 95% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
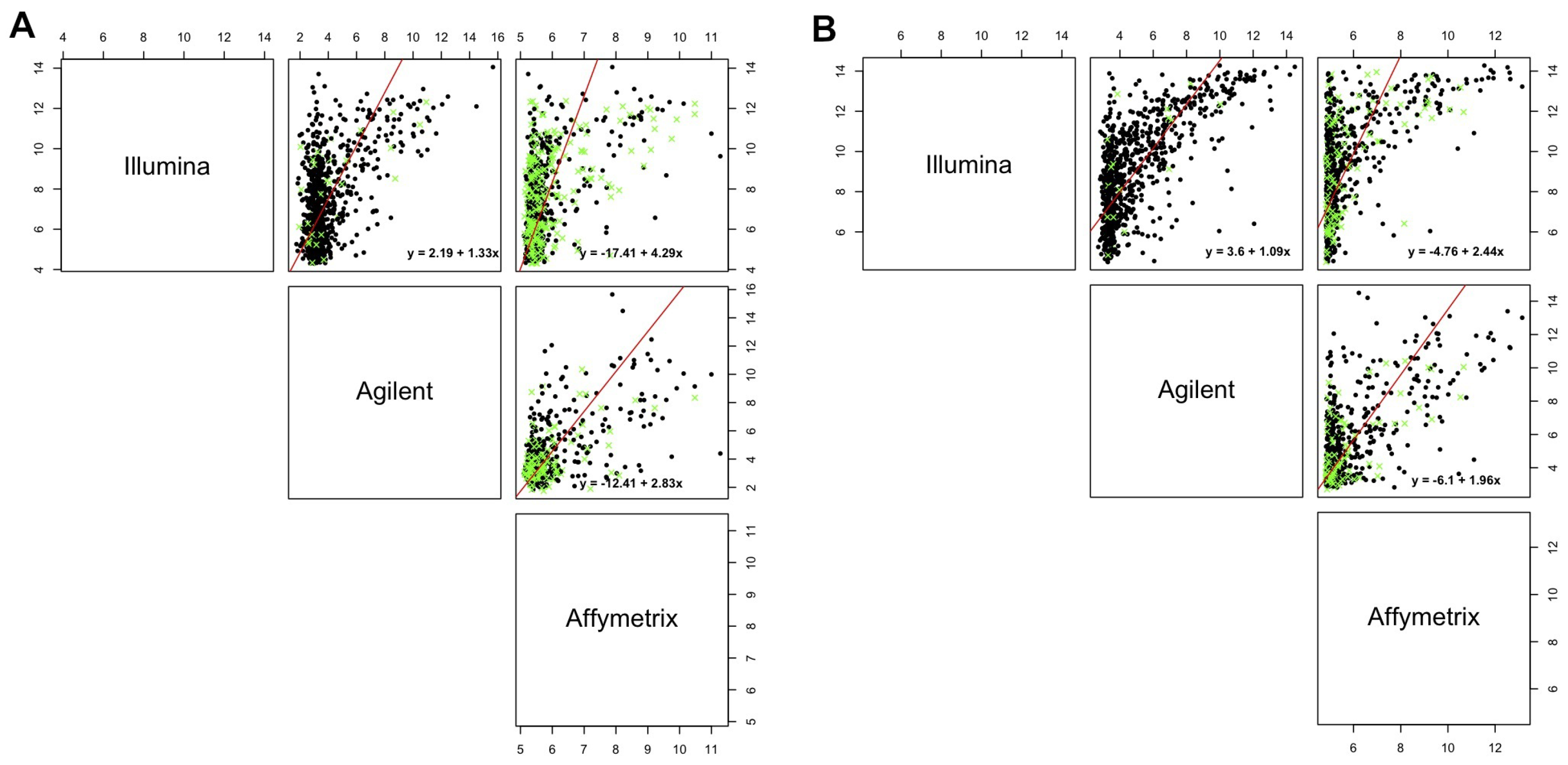
| Agilent vs. Affymetrix | −6.1037 | (−6.4471, −5.7603) | 1.9610 | (1.8964, 2.0255) | |
| hREF | Illumina vs. Affymetrix | −4.7630 | (−5.5006, −4.0254) | 2.4418 | (2.3472, 2.5363) |
| Illumina vs. Agilent | 3.6033 | (3.3791, 3.8274) | 1.0925 | (1.0371, 1.1479) | |
| Agilent vs. Affymetrix | −14.2358 | (−16.3792, −12.0923) | 3.1409 | (2.9815, 3.3004) | |
| A498 | Illumina vs. Affymetrix | −17.4064 | (−18.6406, −16.1722) | 4.2889 | (4.1679, 4.4098) |
| Illumina vs. Agilent | 2.1916 | (1.7773, 2.6058) | 1.3254 | (1.2407, 1.4100) | |
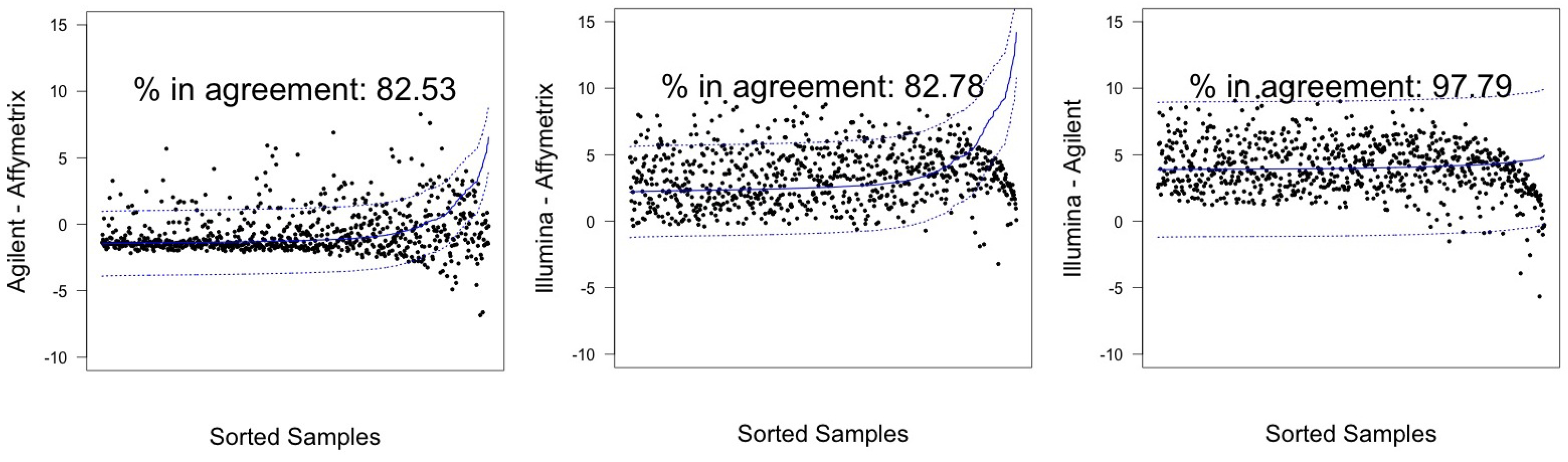
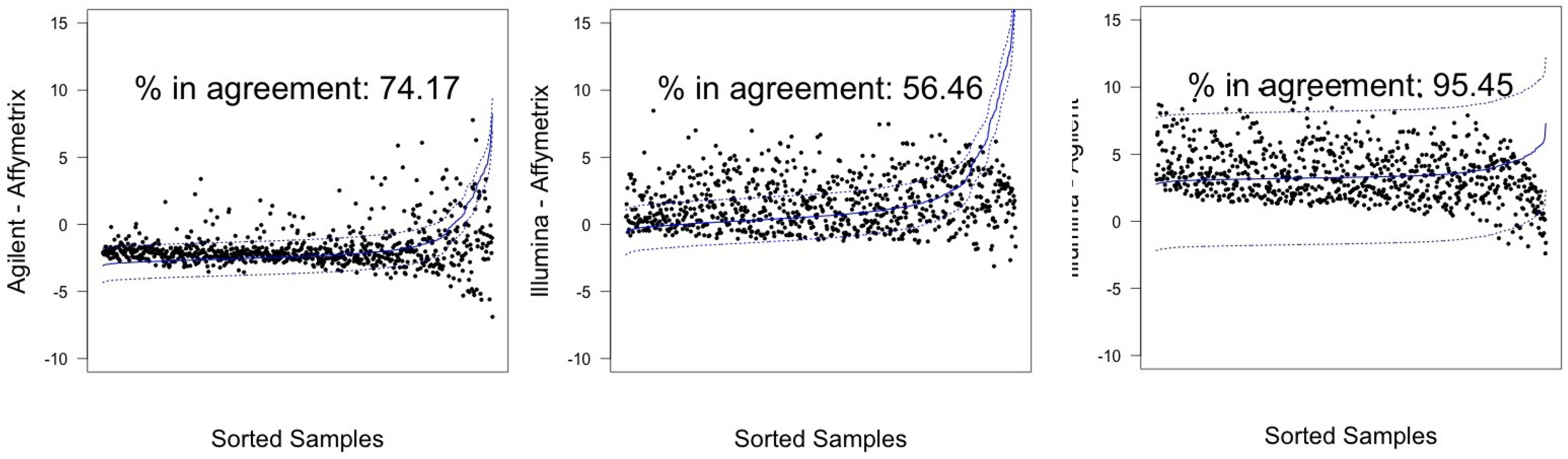
| Sample | Pair | λ | CI 95% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agilent-Affymetrix | 2.608 | 2.409–2.824 | |
| hREF | Illumina-Affymetrix | 2.935 | 2.711–3.178 |
| Illumina Agilent | 1.125 | 1.039–1.218 | |
| Agilent-Affymetrix | 4.125 | 3.810–4.466 | |
| A498 | Illumina-Affymetrix | 5.576 | 5.150–6.037 |
| Illumina-Agilent | 1.352 | 1.248–1.463 |
| Sample | Pair | Estimate | CI 95% | Estimate | CI 95% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agilent vs. Affymetrix | −7.3495 | (−8.1460, −6.5529) | 2.1806 | (2.0824, 2.2789) | |
| hREF | Illumina vs. Affymetrix | −7.0221 | (−9.3909, −4.6533) | 2.8402 | (2.6707, 3.0096) |
| Illumina vs. Agilent | 3.4477 | (3.2018, 3.6936) | 1.1235 | (1.0655, 1.1816) | |
| Agilent vs. Affymetrix | −12.4128 | (−12.9575, −11.8681) | 2.8265 | (2.7461, 2.9068) | |
| A498 | Illumina vs. Affymetrix | −20.3938 | (−29.7127, −11.0749) | 4.8042 | (4.4718, 5.1366) |
| Illumina vs. Agilent | 1.5756 | (0.9998, 2.1514) | 1.4804 | (1.3806, 1.5802) | |
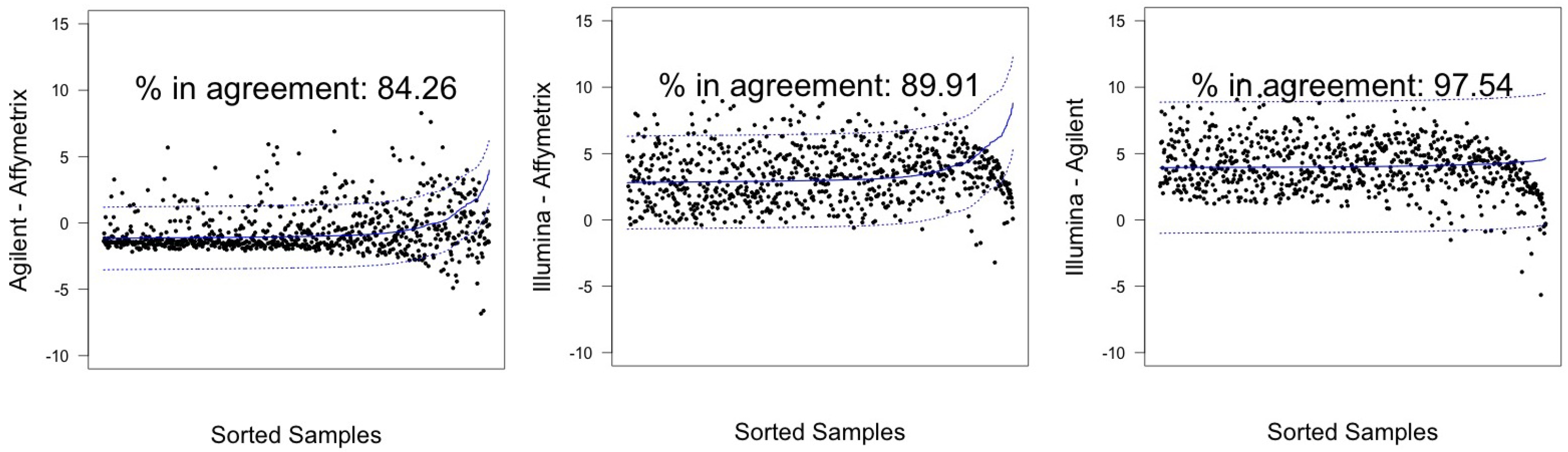
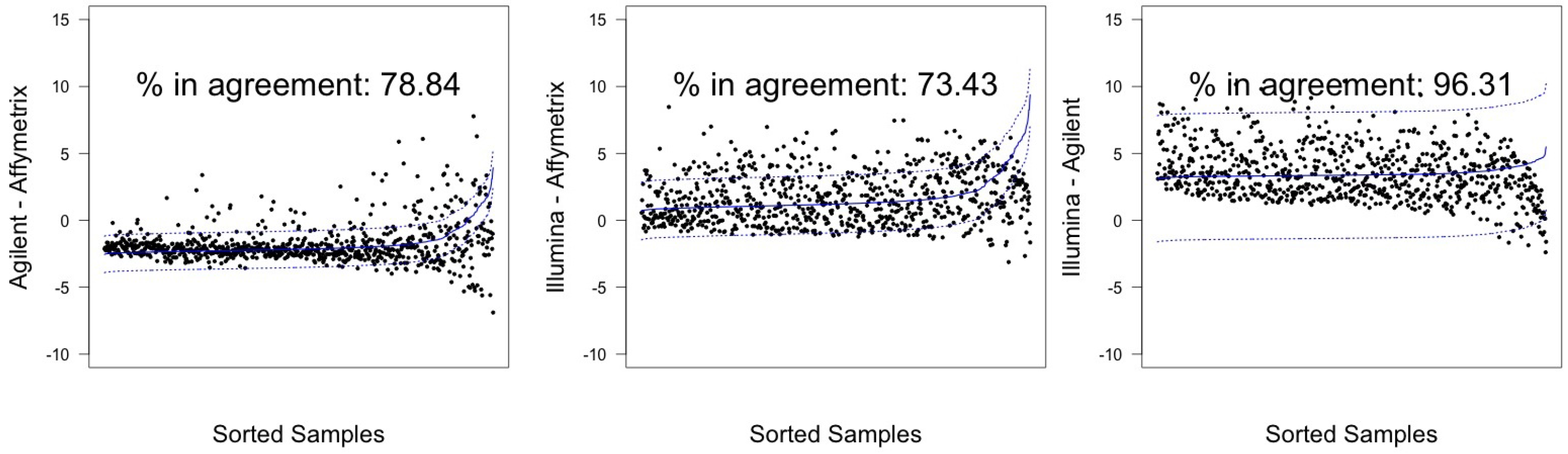
| λ Estimated | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Comparison | n | n | ||
| Agilent-Affymetrix | 82.53 (79.75–85.08) | 671 | 84.26 (81.57–86.70) | 685 | |
| hREF | Illumina–Affymetrix | 82.78 (80.01–85.31) | 673 | 89.91 (87.64–91.90) | 731 |
| Illumina-Agilent | 97.79 (96.52–98.68) † | 795 | 97.54(96.23–98.49) † | 793 | |
| Agilent-Affymetrix | 74.17 (71.02–77.15) | 603 | 78.84 (75.87–81.60) | 641 | |
| A498 | Illumina-Affymetrix | 56.46 (52.97–59.90) | 459 | 73.43 (70.25–76.44) | 597 |
| Illumina-Agilent | 95.45 (93.78–96.78) | 776 | 96.31 (94.77–97.50) | 783 | |
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Esquela-Kerscher, A.; Slack, F.J. Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Getz, G.; Miska, E.A.; Alvarez-Saavedra, E.; Lamb, J.; Peck, D.; Sweet-Cordero, A.; Ebert, B.L.; Mak, R.H.; Ferrando, A.A.; et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 2005, 435, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blower, P.E.; Verducci, J.S.; Lin, S.; Zhou, J.; Chung, J.; Dai, Z.; Liu, C.; Reinhold, W.; Lorenzi, P.L.; Kaldjian, E.P.; et al. MicroRNA expression profiles for the NCI-60 cancer cell panel. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 1483–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Søkilde, R.; Kaczkowski, B.; Podolska, A.; Cirera, S.; Gorodkin, J.; Møller, S.; Litman, T. Global microRNA analysis of the NCI-60 cancer cell panel. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, S.S.; Horre, K.; Nicolaï, S.; Bergmans, B.; Papadopoulou, A.S.; Delacourte, A.; De Strooper, B. MicroRNA regulation of Alzheimer’s Amyloid precursor protein expression. Neurobiol. Dis. 2009, 33, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehwah, M.A.; Huang, Q. MicroRNAs and Type 2 Diabetes/Obesity. J. Genet. Genomics 2012, 39, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paraboschi, E.M.; Soldà, G.; Gemmati, D.; Orioli, E.; Zeri, G.; Benedetti, M.D.; Salviati, A.; Barizzone, N.; Leone, M.; Duga, S.; et al. Genetic Association and Altered Gene Expression of Mir-155 in Multiple Sclerosis Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 8695–8712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasanaro, P.; Greco, S.; Ivan, M.; Capogrossi, M.C.; Martelli, F. microRNA: Emerging therapeutic targets in acute ischemic diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 125, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ach, R.A.; Wang, H.; Curry, B. Measuring microRNAs: Comparisons of microarray and quantitative PCR measurements, and of different total RNA prep methods. BMC Biotechnol. 2008, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miska, E.A.; Alvarez-Saavedra, E.; Townsend, M.; Yoshii, A.; Sestan, N.; Rakic, P.; Constantine-Paton, M.; Horvitz, H.R. Microarray analysis of microRNA expression in the developing mammalian brain. Genome Biol. 2004, 5, R68.1–R68.13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Git, A.; Dvinge, H.; Salmon-Divon, M.; Osborne, M.; Kutter, C.; Hadfield, J.; Bertone, P.; Caldas, C. Systematic comparison of microarray profiling, real-time PCR, and next-generation sequencing technologies for measuring differential microRNA expression. RNA 2010, 16, 991–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willenbrock, H.; Salomon, J.; Søkilde, R.; Barken, K.B.; Hansen, T.N.; Nielsen, F.C.; Møller, S.; Litman, T. Quantitative miRNA expression analysis: Comparing microarrays with next-generation sequencing. RNA 2009, 15, 2028–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin, R.D.; O’Connor, M.D.; Griffith, M.; Kuchenbauer, F.; Delaney, A.; Prabhu, A.; Zhao, Y.; McDonald, H.; Zeng, T.; Hirst, M.; et al. Application of massively parallel sequencing to microRNA profiling and discovery in human embryonic stem cells. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sah, S.; McCall, M.N.; Eveleigh, D.; Wilson, M.; Irizarry, R.A. Performance evaluation of commercial miRNA expression array platforms. BMC Res. Note 2010, 3, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, F.; Tsuchiya, S.; Terasawa, K.; Tsujimoto, G. Intra-Platform Repeatability and Inter-Platform Comparability of MicroRNA Microarray Technology. PLoS One 2009, 4, e5540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yauk, C.L.; Rowan-Carroll, A.; Stead, J.D.H.; Williams, A. Cross-platform analysis of global microRNA expression technologies. BMC Genomics 2010, 11, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.I. A concordance correlation coefficient to evaluate reproducibility. Biometrics 1989, 45, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giard, D.J.; Aaronson, S.A.; Todaro, G.J.; Kersey, J.H.; Dosik, H.; Parks, W.P. In vitro cultivation of human tumors: Establishment of cell lines derived from a series of solid tumors. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1973, 51, 1417–1423. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Affymetrix. Affymetrix© miRNA QC Tool Guide; Affymetrix: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- López-Romero, P.; González, M.A.; Callejas, S.; Dopazo, A.; Irizarry, R.A. Processing of Agilent microRNA array data. BMC Res. Note 2010, 3, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Foundation for Statistical Computing. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- López-Romero, P. Pre-processing and differential expression analysis of Agilent microRNA arrays using the AgiMicroRna Bioconductor library. BMC Genomics 2011, 12, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentleman, R.C.; Carey, V.J.; Bates, D.M.; Bolstad, B.; Dettling, M.; Dudoit, S.; Ellis, B.; Gautier, L.; Ge, Y.; Gentry, J.; et al. Bioconductor: Open software development for computational biology and bioinformatics. Genome Biol. 2004, 5, R80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; He, X.; Band, M.; Wilson, C.; Liu, L. A study of inter-lab and inter-platform agreement of DNA microarray data. BMC Genomics 2005, 6, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, Y.J.; Tu, K.; Tang, Z.Y.; Li, Y.X.; Xiao, H.S. Comparison of normalization methods with microRNA microarray. Genomics 2008, 92, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, Y.; Lee, Y.; Jarjoura, D. A Comparison of Normalization Techniques for MicroRNA Microarray Data. Stat. Appl. Mol. Genet. Biol. 2008, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradervand, S.; Weber, J.; Thomas, J.; Bueno, M.; Wirapati, P.A.; Lefort, K.; Dotto, G.P.; Harshman, K. Impact of normalization on miRNA microarray expression profiling. RNA 2009, 15, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Wang, X.F.; Howell, P.; Qian, X.; Huang, K.; Riker, A.I.; Ju, J.; Xi, Y. A personalized microRNA microarray normalization method using a logistic regression model. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suo, C.; Salim, A.; Chia, K.S.; Pawitan, Y.; Calza, S. Modified least-variant set normalization for miRNA microarray. RNA 2010, 16, 2293–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miron, M.; Woody, O.Z.; Marcil, A.; Murie, C.; Sladek, R.; Nadon, R. A methodology for global validation of microarray experiments. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnhart, H.X.; Haber, M.; Song, J. Overall Concordance Correlation Coefficient for Evaluating Agreement Among Multiple Observers. Biometrics 2002, 58, 1020–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efron, B.; Tibshirani, R.J. An Introduction to the Bootstrap; Chapman & Hall/CRC: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, C.T.; Lin, C.Y.; Liu, J.P. Noninferiority Tests Based on Concordance Correlation Coefficient for Assessment of the Agreement for Gene Expression Data from Microarray Experiments. J. Biopharm. Stat. 2007, 17, 309–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Measurement error and correlation coefficients. BMJ 1996, 313, 41–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.J.Z.; Robert, C. An Improved Bland–Altman Method for Concordance Assessment. Int. J. Biostat. 2011, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, D.G.; Bland, J.M. Measurement in medicine: The analysis of method comparison studies. Statistician 1983, 32, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1986, 327, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolstad, B.M.; Irizarry, R.A.; Astrand, M.; Speed, T.P. A Comparison of Normalization Methods for High Density Oligonucleotide Array Data Based on variance and bias. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clopper, C.; Pearson, E.S. The use of confidence or fiducial limits illustrated in the case of the binomial. Biometrika 1934, 26, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Accuracy (Trueness and Precision) of Measurement Methods and Results—Parts 1–6, ISO9725; International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Consortium, T.M. The MicroArray Quality Control (MAQC) project shows inter- and intraplatform reproducibility of gene expression measurements. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bassani, N.P.; Ambrogi, F.; Biganzoli, E.M. Assessing Agreement between miRNA Microarray Platforms. Microarrays 2014, 3, 302-321. https://doi.org/10.3390/microarrays3040302
Bassani NP, Ambrogi F, Biganzoli EM. Assessing Agreement between miRNA Microarray Platforms. Microarrays. 2014; 3(4):302-321. https://doi.org/10.3390/microarrays3040302
Chicago/Turabian StyleBassani, Niccolò P., Federico Ambrogi, and Elia M. Biganzoli. 2014. "Assessing Agreement between miRNA Microarray Platforms" Microarrays 3, no. 4: 302-321. https://doi.org/10.3390/microarrays3040302
APA StyleBassani, N. P., Ambrogi, F., & Biganzoli, E. M. (2014). Assessing Agreement between miRNA Microarray Platforms. Microarrays, 3(4), 302-321. https://doi.org/10.3390/microarrays3040302




