Reculer Pour Mieux Sauter: A Review of Attachment and Other Developmental Processes Inherent in Identified Risk Factors for Juvenile Delinquency and Juvenile Offending
Abstract
:1. Introduction: Pathways to Delinquency and Offending
1.1. Attachment Quality
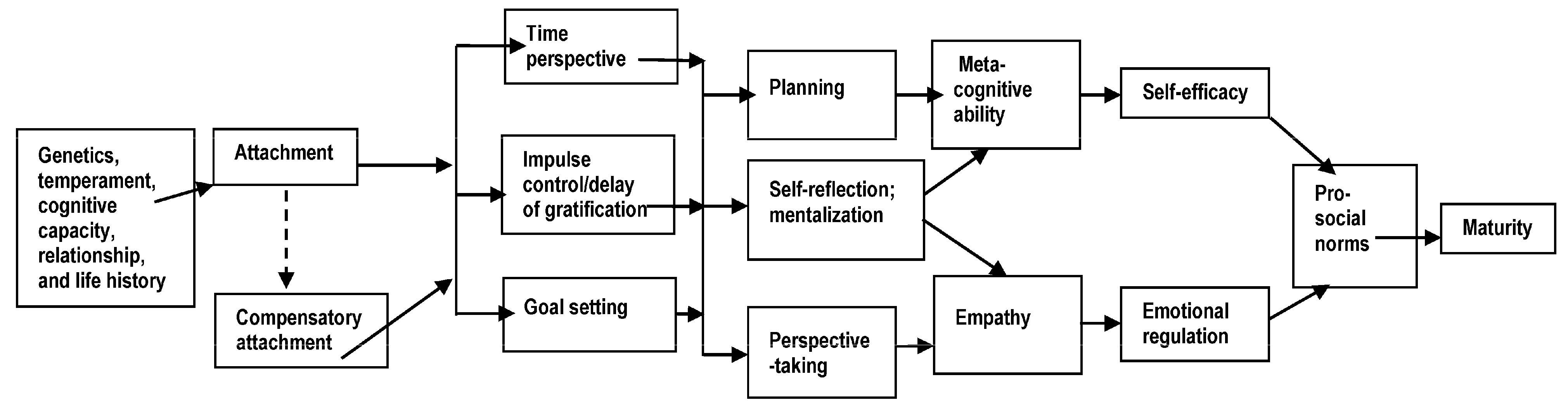
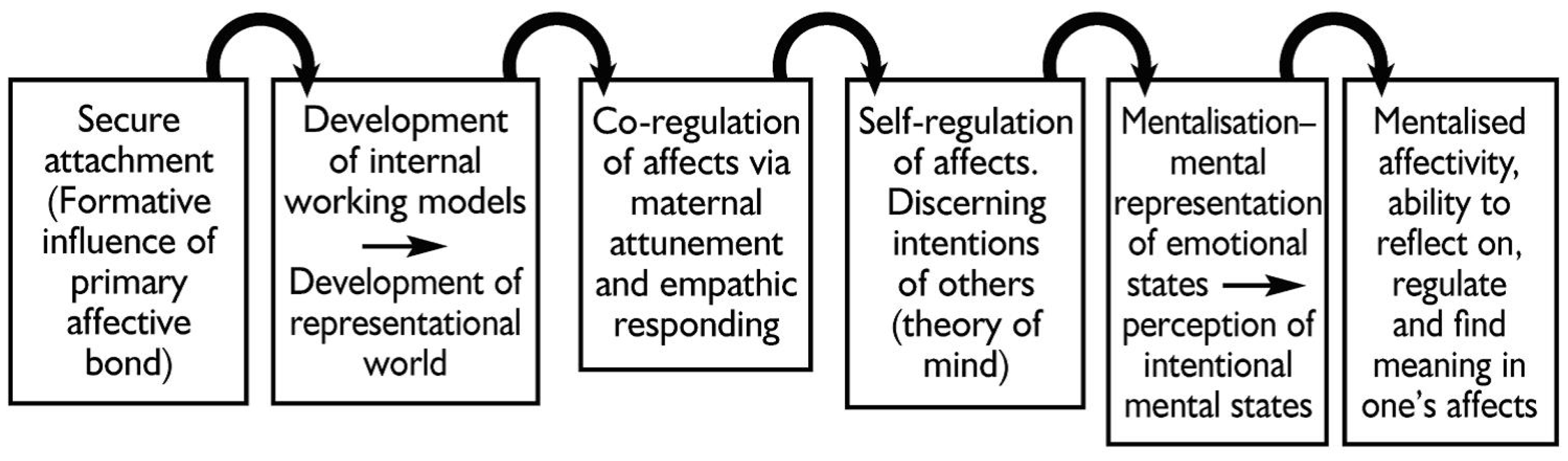
1.2. Maltreatment
1.3. Intervening Factors between Maltreatment, Delinquency and Offending
1.3.1. Homelessness
1.3.2. Mental Health Problems
1.3.3. Substance Abuse
1.3.4. Gang Membership
2. A Case Study: Lanh, 16 Years Old
2.1. Offence
2.2. Background
2.3. Family
2.4. Conditions of Release
2.5. Assessment
2.6. Case Formulation
2.7. Treatment Formulation
2.8. Treatment
2.9. Outcome
3. Implications for Policy, Programming and Practice
3.1. The Importance of Responsivity
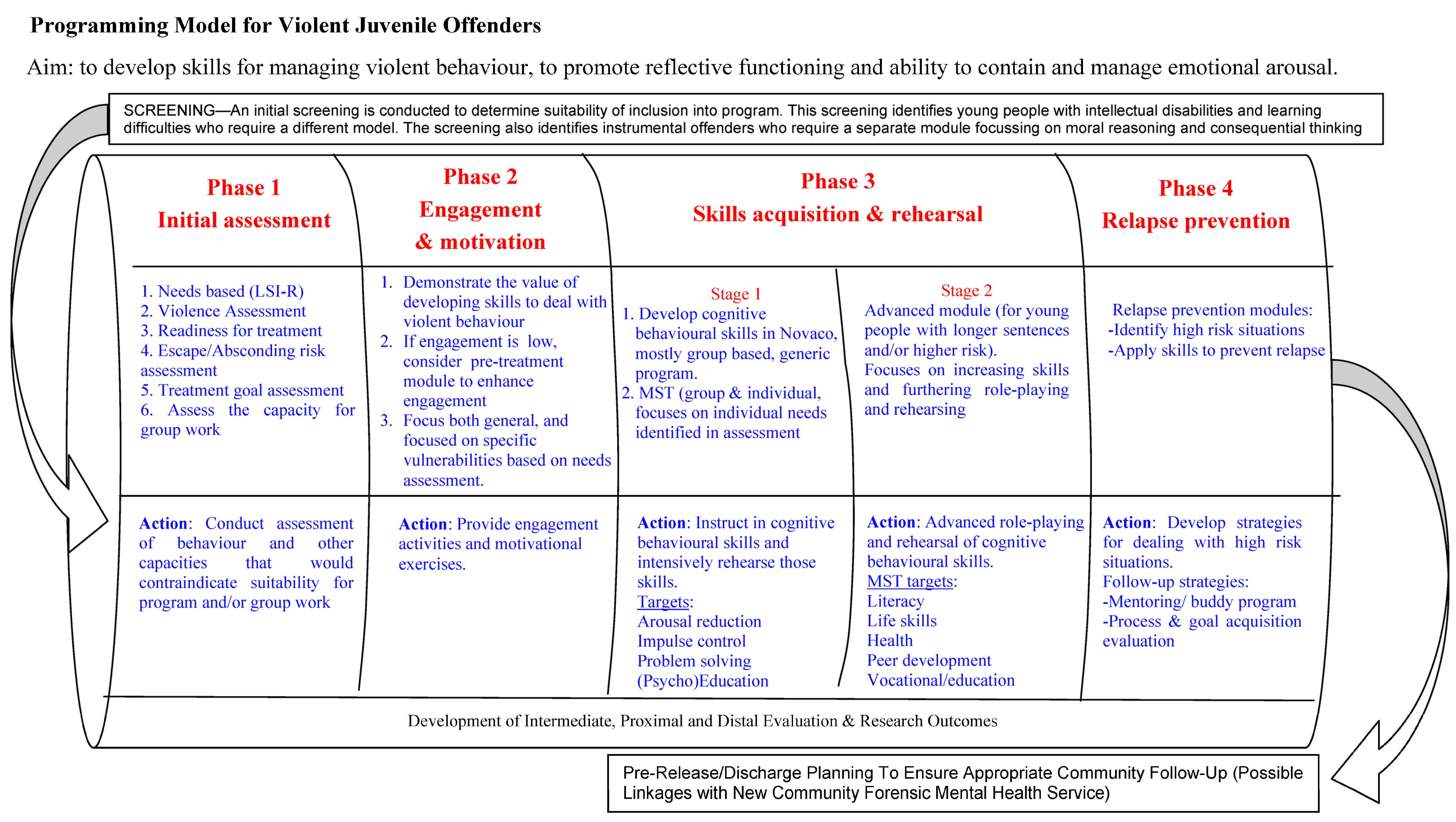
3.2. Intervention Programs for Troubled Youth
3.3. Early Intervention: Reculer Plus Loin
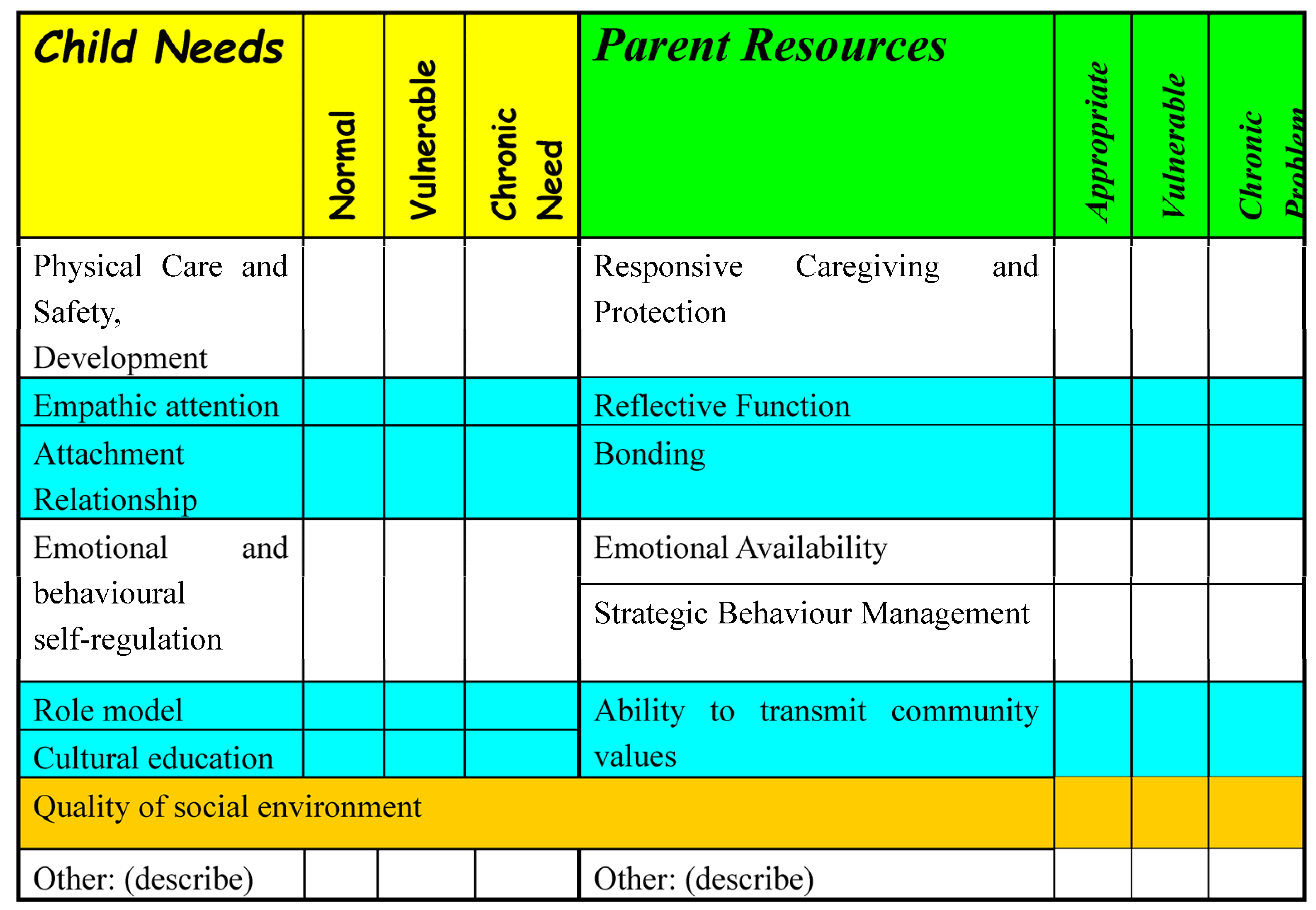
3.4. School Based Intervention—Head Start
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADD | Attention Deficit Disorder |
| ADHD | Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder |
| ASPD | Antisocial Personality Disorder |
| CD | Conduct Disorder |
| DJJ | Department of Juvenile Justice |
| ID | Intellectual disability |
| JO | Juvenile (Young) offender(s) |
| NSW | New South Wales, Australia |
| ODD | Oppositional Defiant Disorder |
| PRF | Parental reflective function |
| PTSD | Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder |
| RAD | reactive attachment disorders |
| RIGs | Representations of interactions that have generalized |
| SES | Socioeconomic status |
References
- Machteld Hoeve, Geert Jan J. Stams, Claudia E. Put, Judith Semon Dubas, Peter H. Laan, and Jan R. Gerris. “A Meta-Analysis of Attachment to Parents and Delinquency.” Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology 40 (2012): 771–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John Bowlby. A Secure Base. New York: Basic Books, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Urie Bronfenbrenner. The Ecology of Human Development. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Dianna T. Kenny. “Psychological Foundations of Stress and Coping: A Developmental Perspective.” In Stress and Health: Research and Clinical Applications. Edited by Dianna T. Kenny, Jac G. Carlson, F. Jospeh McGuigan and John L. Sheppard. Ryde, NSW: Gordon Breach Science/Harwood Academic, 2000, pp. 73–104. [Google Scholar]
- Andrew Day, and Michael Daffern. “Responding to Serious Antisocial Behaviour: The Psychological Assessment and Treatment of Aggression and Violence.” InPsych. June 2013, pp. 8–11. Available online: http://www.psychology.org.au/publications/inpsych/2013/june/day/ (accessed on 23 July 2014).
- Peter Fonagy, Gyorgy Gergely, Elliot Jurist, and Mary Target. Affect Regulation, Mentalization and the Development of the Self. London: Karnac, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Brian S. Stafford, and Charles H. Zeanah. “Attachment Disorders.” In Attachment Handbook of Preschool Mental Health. Edited by Joan L. Luby. New York: Guilford, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Dianna T. Kenny. Bringing up Baby: The Psychoanalytic Infant Comes of Age. London: Karnac, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Arthur N. Schore. Affect Dysregulation and Disorders of the Self. New York: Norton, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lisa A. Serbin, and Jennifer Karp. “The Intergenerational Transfer of Psychosocial Risk: Mediators of Vulnerability and Resilience.” Annual Review of Psychology 55 (2004): 333–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesar J. Rebellon, and Karen Van Gundy. “Can Control Theory Explain the Link Between Parental Physical Abuse and Delinquency? A Longitudinal Analysis.” Journal of Research in Crime and Delinquency 3 (2005): 247–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasco Fearon, Marian J. Bakermans-Kranenburg, Marinus H. van Ijzendoorn, Anne-Marie Lapsley, and Glenn I. Roisman. “The Significance of Insecure Attachment and Disorganization in the Development of Children with Externalizing Behavior: A Meta-Analytic Study.” Child Development 81 (2010): 435–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinus H. Van Ijzendoorn, Carlo Schuengel, and Marian J. Bakermans-Kranenburg. “Disorganized Attachment in Early Childhood: Meta-Analysis of Precursors, Concomitants, and Sequelae.” Development and Psychopathology 11 (1999): 225–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovanni Liotti. “Trauma, Dissociation and Disorganized Attachment: Three Strands of a Single Braid.” Psychotherapy: Theory, Research, Practice, Training 41 (2004): 472–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathleen Boykin McElhaney, Annalies Immele, Felicia D. Smith, and Joseph P. Allen. “Attachment organization as a moderator of the link between friendship quality and adolescent delinquency.” Attachment & Human Development 1 (2006): 33–46. [Google Scholar]
- Mark Warr. “The tangled web: Delinquency, deception, and parental attachment.” Journal of Youth and Adolescence 5 (2007): 607–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall T. Salekin, Richard Rogers, and Karen L. Ustad. “Juvenile waiver to adult criminal courts: Prototypes for dangerousness, sophistication-maturity, and amenability to treatment.” Psychology, Public Policy, and Law 2 (2001): 381–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- William Revelle. “Personality processes.” Annual Review of Psychology 63 (1995): 295–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen W. Baron. “Self-Control, Social Consequences, and Criminal Behavior: Street Youth And The General Theory Of Crime.” Journal of Research in Crime and Delinquency 4 (2003): 403–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter Fonagy, Miriam Steele, Howard Steele, Anna Higgitt, and Mary Target. “The Emanuel Miller Memorial Lecture 1992: The Theory and Practice of Resilience.” Child Psychology & Psychiatry & Allied Disciplines 35 (1994): 231–57. [Google Scholar]
- Cindy Hazan, and Phillip R. Shaver. “Attachment as an organizational framework for research on close relationships.” Psychological Inquiry 5 (1994): 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefer Bembenutty, and Stuart A. Karabenick. “Inherent Association Between Academic Delay of Gratification, Future Time Perspective, and Self-Regulated Learning.” Educational Psychology Review 1 (2004): 35–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark H. Davis. “Measuring individual differences in empathy: Evidence for a multidimensional approach.” Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 1 (1983): 113–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter Fonagy, and Mary Target. “Attachment and Reflective Function: Their Role in Self-Organization.” Development and Psychopathology 9 (1997): 679–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaus Boers, Jost Reinecke, Daniel Seddig, and Luca Mariotti. “Explaining the Development of Adolescent Violent Delinquency.” European Journal of Criminology 7 (2010): 499–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katharine L. Bowen, Joanne E. Morgan, Simon C. Moore, and Stephanie H. van Goozen. “Young Offenders’ Emotion Recognition Dysfunction across Emotion Intensities: Explaining Variation Using Psychopathic Traits, Conduct Disorder and Offense Severity.” Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment 36 (2014): 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clara Moller, Fredrik Falkenstrom, Mattias Holmqvist Larsson, and Rolf Holmqvist. “Mentalizing in Young Offenders.” Psychoanalytic Psychology 31 (2014): 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark W. Lipsey, and James H. Derzon. “Predictors of Violent or Serious Delinquency in Adolescence and Early Adulthood: A Synthesis of Longitudinal Research.” In Serious & Violent Juvenile Offenders: Risk Factors and Successful Interventions. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 1998, pp. 86–105. [Google Scholar]
- Gunilla Bohlin, Lilianne Eninger, Karin Brocki, and Lisa Thorell. “Disorganized Attachment and Inhibitory Capacity: Predicting Externalizing Problem Behavior.” Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology 40 (2012): 449–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geoff Goodman, Robert C. Bartlett, and Martha Stroh. “Mothers’ Borderline Features and Children’s Disorganized Attachment Representations as Predictors of Children’s Externalizing Behavior.” Psychoanalytic Psychology 30 (2013): 16–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt F. Steele, and Carl B. Pollock. “A Psychiatric Study of Parents Who Abuse Infants and Small Children.” In The Battered Child. Edited by Mary Edna Helfer, Ruth S. Kempe and Richard D. Krugman. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1974, pp. 80–133. [Google Scholar]
- H. Martin. The Abused Child. Boston: Ballinger, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Patricia M. Crittenden. “Dangerous Behavior and Dangerous Contexts: A Thirty-Five Year Perspective on Research on the Developmental Effects of Child Physical Abuse.” In Violence to Children. Edited by Penelope Trickett. Washington, D.C.: American Psychological Association, 1998, pp. 11–38. [Google Scholar]
- Michael Rutter, Julia Kim-Cohen, and Barbara Maughan. “Continuities and Discontinuities in Psychopathology between Childhood and Adult Life.” Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry 47 (2006): 276–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael G. Maxfield, and Cathy Spatz Widom. “The Cycle of Violence. Revisited 6 Years Later.” Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 150 (1996): 390–95. [Google Scholar]
- Sara R. Jaffee, Avshalom Caspi, Terrie E. Moffitt, Monica Polo-Tomas, and Alan Taylor. “A Individual, Family, and Neighborhood Factors Distinguish Resilient from Non-Resilient Maltreated Children: A Cumulative Stressors Model.” Child Abuse & Neglect 31 (2007): 231–33. [Google Scholar]
- Janet Currie, and Erdal Tekin. “Understanding the Cycle: Childhood Maltreatment and Future Crime.” The Journal of Human Resources 47 (2011): 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John Bowlby. “Forty-Four Juvenile Thieves: Their Character and Home-Life.” International Journal of Psychoanalysis 25 (1944): 19–52. [Google Scholar]
- Michael Follan, and Helen Minnis. “Forty-Four Juvenile Thieves Revisited: From Bowlby to Reactive Attachment Disorder.” Child: Care, Health and Development 36 (2010): 639–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimberly Bender. “Why Do Some Maltreated Youth Become Juvenile Offenders?: A Call for Further Investigation and Adaptation of Youth Services.” Children and Youth Services Review 32 (2010): 466–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marvin D. Krohn, Nicole M. Schmidt, Alan J. Lizotte, and Julie M. Baldwin. “The impact of multiple marginality on gang membership and delinquent behavior for Hispanic, African American, and White male adolescents.” Journal of Contemporary Criminal Justice 1 (2011): 18–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toi B. Harris, Sara Elkins, Ashley Butler, Matthew Shelton, Barbara Robles, Stephanie Kwok, Sherri Simpson, Dennis W. Young, Amy Mayhew, Ayanna Brown, and et al. “Youth Gang Members: Psychiatric Disorders and Substance Use.” Laws 2 (2013): 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joanne Belknap, and Kristi Holsinger. “The Gendered Nature of Risk Factors for Delinquency.” Feminist Criminology 1 (2006): 48–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustine Brannigan. “Self-control, social control and evolutionary psychology: Towards an integrated perspective on crime.” Canadian Journal of Criminology 39 (1997): 403–31. [Google Scholar]
- Kimberly Bender, Sanna J. Thompson, Holly McManus, Janet Lantry, and Patrick M. Flynn. “Capacity for Survival: Exploring Strengths of Homeless Street Youth.” Child & Youth Care Forum 36 (2007): 25–42. [Google Scholar]
- Josh M. Cisler, Angela M. Begle, Ananda B. Amstadter, Heidi S. Resnick, Carla Kmett Danielson, Benjamin E. Saunders, and Dean G. Kilpatrick. “Exposure to interpersonal violence and risk for PTSD, depression, delinquency, and binge drinking among adolescents: Data from the NSA-R.” Journal of Traumatic Stress 1 (2012): 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elizabeth Moore, Claire Gaskin, and Devon Indig. “Childhood maltreatment and post-traumatic stress disorder among incarcerated young offenders.” Child Abuse & Neglect 10 (2013): 861–70. [Google Scholar]
- Dianna T. Kenny, Christopher Lennings, and Olivia A. Munn. “Risk Factors for Self-Harm and Suicide in Incarcerated Young Offenders: Implications for Policy and Practice.” Journal of Forensic Psychology Practice 8 (2008): 358–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dianna T. Kenny, and Paul K. Nelson. Young Offenders on Community Orders: Health, Welfare and Criminogenic Needs. Sydney: Sydney University Press, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Dean G. Kilpatrick, Kenneth J. Ruggiero, Ron Acierno, Benjamin E. Saunders, Heidi S. Resnick, and Connie L. Best. “Violence and Risk of PTSD, Major Depression, Substance Abuse/Dependence, and Comorbidity: Results from the National Survey of Adolescents.” Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 71 (2003): 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John Petraitis, Brian R. Flay, and Todd Q. Miller. “Reviewing Theories of Adolescent Substance Use: Organizing Pieces in the Puzzle.” Psychological Bulletin 117 (1995): 67–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dianna T. Kenny, and Istvan Schreiner. “Predictors of High-Risk Alcohol Consumption in Young Offenders on Community Orders: Policy and Treatment Implications.” Psychology, Public Policy, and Law 15 (2009): 54–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David M. Fergusson, Michael T. Lynskey, and John Horwood. “Alcohol Misuse and Juvenile Offending in Adolescence.” Addiction 91 (1996): 483–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- José Leon-Carrion, and Fagundes Ramos. “Blows to the Head During Development Can Predispose to Violent Criminal Behavior: Rehabilitation of Consequences of Head Injury Is a Measure of Crime Prevention.” Brain Injury 17 (2003): 207–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dianna T. Kenny, and Christopher Lennings. “Relationship between Head Injury and Violent Offending in Young Offenders.” Crime and Justice Bulletin 107 (2007): 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Adrian Raine, Monte Buchsbaum, and Jill Stanley. “Selective Reductions in Prefrontal Glucose Metabolism in Murderers.” Biological Psychiatry 36 (1994): 365–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher Lennings, Dianna T. Kenny, and Paul K. Nelson. “Substance Use and Treatment Seeking in Young Offenders on Community Orders.” Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment 31 (2006): 425–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dianna T. Kenny. From Id to Intersubjectivity: Talking About the Talking Cure with Master Clinicians. London: Karnac, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- David Polizzi. “Agnew’s General Strain Theory Reconsidered: A Phenomenological Perspective.” International Journal of Offender Therapy and Comparative Criminology 55 (2011): 1051–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerryn E. Bell. “Gangs and Gender: A Quantitative Comparison.” Crime & Delinquency 55 (2009): 363–87. [Google Scholar]
- Jon Gunnar Bernburg, Marvin D. Krohn, and Craig J. Rivera. “Official Labeling, Criminal Embeddedness, and Subsequent Delinquency: A Longitudinal Test of Labeling Theory.” Journal of Research in Crime and Delinquency 43 (2006): 67–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesar J. Rebellon. “Do Adolescents Engage in Delinquency to Attract the Social Attention of Peers? An Extension and Longitudinal Test of the Social Reinforcement Hypothesis.” Journal of Research in Crime and Delinquency 43 (2006): 387–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronald Akers. Juvenile Delinquency: Causes and Control. Los Angeles: Roxbury, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Laurence Steinberg, Ilana Blatt-Eisengart, and Elizabeth Cauffman. “Patterns of Competence and Adjustment Among Adolescents from Authoritative, Authoritarian, Indulgent, and Neglectful Homes: A Replication in a Sample of Serious Juvenile Offenders.” Journal of Research on Adolescence 16 (2006): 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James McGuire, ed. What Works: Reducing Reoffending: Guidelines from Research and Practice. West Sussex: Wiley-Blackwell, 1995.
- Katy Holloway, Trevor Bennett, and David Farrington. “The Effectiveness of Criminal Justice and Treatment Programs in Reducing Drug-Related Crime: A Systematic Review.” Available online: http://www.floridatac.com/files/document/rdsolr2605.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2014).
- Don A. Andrews, and James Bonta. The Psychology of Criminal Conduct, 5th ed. New Jersey: Matthew Bender, 2010, vol. 672. [Google Scholar]
- James R. Ogloff. “Offender Rehabilitation: From ‘Nothing Works’ to What Next? ” Australian Psychologist 37 (2002): 245–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie D. Leve, Patricia Chamberlain, and John B. Reid. “Intervention Outcomes for Girls Referred from Juvenile Justice: Effects on Delinquency.” Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 73 (2005): 1181–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvin M. Langton. “Introduction to the Special Issue: Treatment Considerations for Aggressive Adolescents in Secure Settings.” Criminal Justice and Behavior 39 (2012): 685–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry Krisberg, and Angela M. Wolf. “Juvenile Offending.” In Juvenile Delinquency: Prevention, Assessment, and Intervention. Edited by Kirk Heilbrun. New York: Oxford University Press, 2005, pp. 67–84. [Google Scholar]
- Julia C. Torquati, and Alexander T. Vazsonyi. “Attachment as an Organizational Construct for Affect, Appraisals, and Coping of Late Adolescent Females.” Journal of youth and Adolescence 28 (2004): 545–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elizabeth Cauffman, and Laurence Steinberg. “(Im)maturity of judgment in adolescence: Why adolescents may be less culpable than adults.” Behavioral Sciences & the Law 6 (2000): 741–60. [Google Scholar]
- Australian Institute of Criminology (AIC). Australian Crime: Facts and Figures; Canberra: Australian Institute of Criminology, 2013. Available online: http://www.aic.gov.au/media_library/publications/facts/2012/facts12.pdf (accessed on 4 April 2014).
- Simon Duff, and Peter Kinderman. “An interacting cognitive subsystems approach to personality disorder.” Clinical Psychology & Psychotherapy 13 (2006): 233–45. [Google Scholar]
- Dianna T. Kenny, and Matthew Frize. “Intellectual disability, Aboriginal status and risk of re-offending in young offenders on community orders.” Indigenous Law Bulletin 18 (2010): 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Jon Bright. Turning the Tide: Crime, Community and Prevention. London: Demos, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Scott W. Henggeler, and Sonja K. Schoenwald. “Boot camps for juvenile offenders: Just say no.” Journal of Child and Family Studies 3 (1994): 243–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darrick Jolliffe, David P. Farrington, and Philip Howard. “How long did it last? A 10-year reconviction follow-up study of high intensity training for young offenders.” Journal of Experimental Criminology 4 (2013): 515–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert J. Botvin, and Kenneth W. Griffin. “Prevention Science, Drug Abuse Prevention, and Life Skills Training: Comments on the State of the Science.” Journal of Experimental Criminology 1 (2005): 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherie L. Barnes. “Outreach intervention reduces recidivism in juvenile delinquents.” In Compelling Counseling Interventions: Celebrating VISTAS’ Fifth Anniversary. Edited by Garry Richard Walz, Jeanne C. Bleuer and Richard K. Yep. Alexandria: Counseling Outfitters, LLC, 2008, pp. 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- MENTOR. “Mentoring in America 2005: A Snapshot of the Current State of Mentoring.” Available online: http://www.mentoring.org/downloads/mentoring_523.pdf (accessed on 25 March 2014).
- Ania Wilczynski, Clare Culvenor, Chris Cuneen, John Schwartzkoff, and Kerry Reed-Gilbert. Early Intervention: Youth Mentoring Programs: An Overview of Mentoring Programs for Young People at Risk of Offending. Edited by Australian Government Attorney-General’s Department. Canberra: Commonwealth of Australia, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- David L. DuBois, Nelson Portillo, Jean E. Rhodes, Naida Silverthorn, and Jeffrey Valentine. “How Effective Are Mentoring Programs for Youth? A Systematic Assessment of the Evidence.” Psycholgocial Science in the Public Interest 12 (2011): 57–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jean E. Rhodes. Stand by Me: The Risks and Rewards of Mentoring Today’s Youth. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Matthew A. Diemer, Adam M. Voight, and Cyndi Mark. “Youth Development in Traditional and Transformational Service-Learning Programs.” In Problematizing Service-Learning: Critical Reflections for Development and Action. Edited by Trae Stewart. Charlotte: Information Age Publishing (IAP), 2011, pp. 155–73. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph A. Durlak, and Christine I. Celio. “Service-Learning: Learning by Doing for Others.” In A Blueprint for Promoting Academic and Social Competence in After-School Programs. Edited by Thomas P. Gullotta, Martin Bloom, Christianne F. Gullotta and Jennifer C. Messina. New York: Springer US, 2009, pp. 101–18. [Google Scholar]
- Trae Stewart, and Nicole Webster. Problematizing Service-Learning: Critical Reflections for Development and Action. Charlotte: Information Age Publishing (IAP), 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Peter Fonagy. “Towards a developmental understanding of violence.” The British Journal of Psychiatry 3 (2003): 190–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travis Hirschi. Causes of Delinquency. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Heinzen Hanna, Denis Koehler, Tom Smeets, Tibor Hoffer, and Christian Huchzermeier. “Emotion Regulation in Incarcerated Young Offenders with Psychopathic Traits.” The Journal of Forensic Psychiatry & Psychology 22 (2011): 809–33. [Google Scholar]
- Marlene M. Moretti, Roy Holland, and Sherri Peterson. “Long term outcome of an attachment-based program for conduct disorder.” Canadian Journal of Psychiatry 6 (1994): 360–70. [Google Scholar]
- Gary M. Diamond. “Attachment-based family therapy Intervention.” Psychotherapy 1 (2014): 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaspar Burger. “How does early childhood care and education affect cognitive development? An international review of the effects of early interventions for children from different social backgrounds.” Early Childhood Research Quarterly 2 (2010): 140–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- “U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS). ” Available online: http://homvee.acf.hhs.gov/document.aspx?rid=4&sid=19&mid=6 (accessed on 15 June 2014).
- David L. Olds, John Eckenrode, Charles R. Henderson Jr., Harriet Kitzman, Jane Powers, Robert Cole, Kimberly Sidora, Pamela Morris, Lisa M. Pettitt, and Dennis Luckey. “Long-term effects of home visitation on maternal life course and child abuse and neglect. Fifteen-year follow-up of a randomized trial.” Journal of the American Medical Association 8 (1997): 637–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis W. Luckey, David L. Olds, Weiming Zhang, Charles Henderson, Michael Knudtson, John Eckenrode, Harriet Kitzman, Robert Cole, and Lisa Pettitt. “Revised Analysis of 15-Year Outcomes in the Elmira Trial of the Nurse-Family Partnership.” Available online: http://evidencebasedprograms.org/1366-2/nurse-family-partnership (accessed on 15 July 2014).
- Harriet Kitzman, David L. Olds, Kimberly Sidora, Charles R. Henderson Jr., Carole Hanks, Robert Cole, Dennis W. Luckey, Jessica Bondy, Kimberly Cole, and Judith Glazner. “Enduring effects of nurse home visitation on maternal life course: A 3-year follow-up of a randomized trial.” Journal of the American Medical Association 15 (2000): 1983–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harriet J. Kitzman, David. L. Olds, Robert E. Cole, Carole A. Hanks, Elizabeth A. Anson, Kimberly J. Arcoleo, Dennis W. Luckey, Michael D. Knudtson, Charles R. Henderson Jr., and John R. Holmberg. “Enduring effects of prenatal and infancy home visiting by nurses on children: Follow-up of a randomized trial among children at age 12 years.” Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 5 (2010): 412–18. [Google Scholar]
- John Eckenrode, David Zielinski, Elliott Smith, Lyscha A. Marcynyszyn, Charles R. Henderson Jr., Harriet Kitzman, Robert Cole, Jane Powers, and David L. Olds. “Child maltreatment and the early onset of problem behaviors: Can a program of nurse home visitation break the link? ” Development & Psychopathology 4 (2001): 873–90. [Google Scholar]
- John Mary Campa Eckenrode, Dennis W. Luckey, Charles R. Henderson Jr., Robert Cole, Harriet Kitzman, Elizabeth Anson, Kimberly Sidora-Arcoleo, Jane Powers, and David Olds. “Long-term effects of prenatal and infancy nurse home visitation on the life course of youths: 19-year follow-up of a randomized trial.” Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 164 (2010): 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kimberly A. Dumont, Susan Mitchell-Herzfeld, Rose Greene, Eunju Lee, Ann Lowenfels, and Monica Rodriguez. “Healthy Families New York (HFNY).” In Randomized Trial: Impacts on Parenting after the First Two Years. New York: Office of Children and Family Service, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Anne Duggan, Loretta Fuddy, Lori Burrell, Susan M. Higman, Elizabeth McFarlane, Amy Windham, and Calvin Sia. “Randomized trial of a statewide home visiting program to prevent child abuse: Impact in reducing parental risk factors.” Child Abuse & Neglect 6 (2004): 623–43. [Google Scholar]
- Mary Dozier, Oliver Lindhiem, and John P. Ackerman. “Attachment and Biobehavioral Catch-Up: An Intervention Targeting Empirically Identified Needs of Foster Infants.” In Enhancing Early Attachments: Theory, Research, Intervention, and Policy. New York: Guilford Press, 2005, pp. 178–94. [Google Scholar]
- Johanna Bick, Kristin Bernard, and Mary Dozier. “Attachment and biobehavioral catch-up: An attachment-based intervention for substance using mothers and their infants.” In Parenting and Substance Abuse: Developmental Approaches to Intervention. New York: Oxford University Press, 2013, pp. 303–20. [Google Scholar]
- David L. Olds, JoAnn Robinson, Lisa Pettitt, Dennis W. Luckey, John Holmberg, Rossanna K. Ng, Kathy Isacks, Karen Sheff, and Charles R. Henderson Jr. “Effects of Home Visits by Paraprofessionals and by Nurses: Age 4 Follow-Up Results of a Randomized Trial.” Pediatrics 114 (2004): 1560–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariska Klein Velderman, Marian J. Bakermans-Kranenburg, Femmie Juffer, Marinus H. Van Ijzendoorn, Sarah C. Mangelsdorf, and Jolien Zevalkink. “Preventing preschool externalizing behavior problems through video-feedback intervention in infancy.” Infant Mental Health Journal 5 (2006): 466–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantien Van Zeijl, Judi Mesman, Marinus H. Van Ijzendoorn, Marian J. Bakermans-Kranenburg, Femmie Juffer, Mirjam N. Stolk, Hans M. Koot, and Lenneke R. Alink. “Attachment-based intervention for enhancing sensitive discipline in mothers of 1- to 3-year-old children at risk for externalizing behavior problems: A randomized controlled trial.” Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 6 (2006): 994–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Kenny, D.T.; Blacker, S.; Allerton, M. Reculer Pour Mieux Sauter: A Review of Attachment and Other Developmental Processes Inherent in Identified Risk Factors for Juvenile Delinquency and Juvenile Offending. Laws 2014, 3, 439-468. https://doi.org/10.3390/laws3030439
Kenny DT, Blacker S, Allerton M. Reculer Pour Mieux Sauter: A Review of Attachment and Other Developmental Processes Inherent in Identified Risk Factors for Juvenile Delinquency and Juvenile Offending. Laws. 2014; 3(3):439-468. https://doi.org/10.3390/laws3030439
Chicago/Turabian StyleKenny, Dianna T., Susan Blacker, and Mark Allerton. 2014. "Reculer Pour Mieux Sauter: A Review of Attachment and Other Developmental Processes Inherent in Identified Risk Factors for Juvenile Delinquency and Juvenile Offending" Laws 3, no. 3: 439-468. https://doi.org/10.3390/laws3030439
APA StyleKenny, D. T., Blacker, S., & Allerton, M. (2014). Reculer Pour Mieux Sauter: A Review of Attachment and Other Developmental Processes Inherent in Identified Risk Factors for Juvenile Delinquency and Juvenile Offending. Laws, 3(3), 439-468. https://doi.org/10.3390/laws3030439



