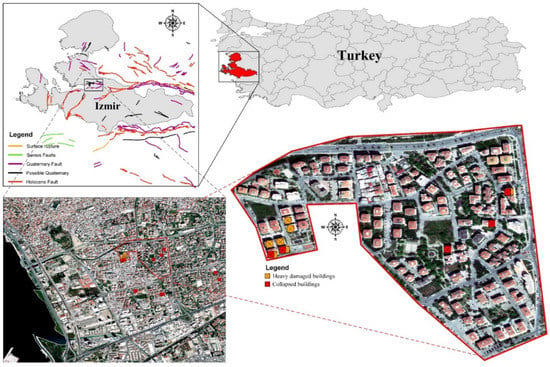
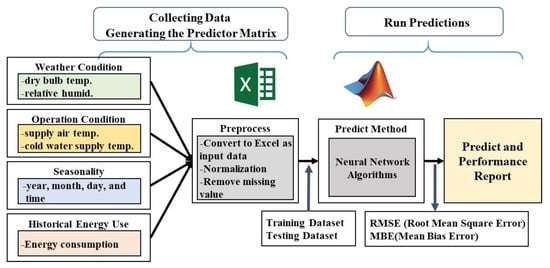
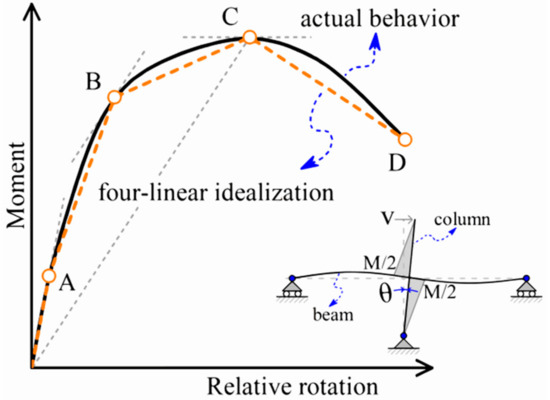
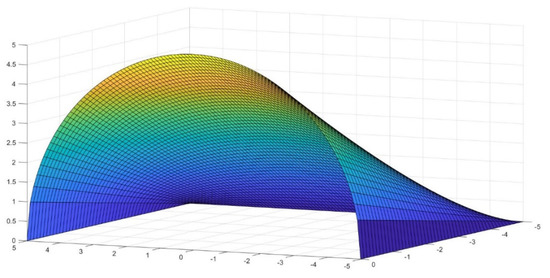
Buildings 2022, 12(1), 40; https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12010040 - 4 Jan 2022
Cited by 49 | Viewed by 11862
Abstract
Prefabricated house-building companies, as suppliers or supply chains, which use manufacturing as a business approach towards industrialization, struggle to implement principles and optimal practices driven from well-established and validated theories in operational research. Supply chain management has a mature body of knowledge that
[...] Read more.
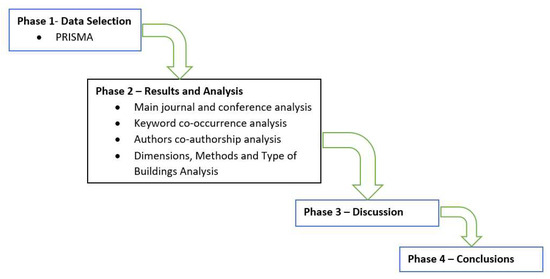
Prefabricated house-building companies, as suppliers or supply chains, which use manufacturing as a business approach towards industrialization, struggle to implement principles and optimal practices driven from well-established and validated theories in operational research. Supply chain management has a mature body of knowledge that has been widely adopted by research on offsite construction to improve its performance at an organisational level. However, there is no comprehensive review available in the literature for supply chain management theory within prefabricated house building research from the perspective of suppliers. In this study, a systematic review was conducted on the available literature on supply chain management within prefabricated house-building research. Initially, qualitative analysis was performed to identify the key themes. Later, quantitative analyses were applied to validate the overlapping themes and keywords. Further, key trends related to focus, methods and theories or frameworks were reported. The findings were discussed in the context of recent developments in all principal component bodies of supply chain management for future work. This study also provides a brief guide for potential future review studies to explore interdisciplinary intervention within the offsite stream.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Construction Management, and Computers & Digitization)
►
Show Figures