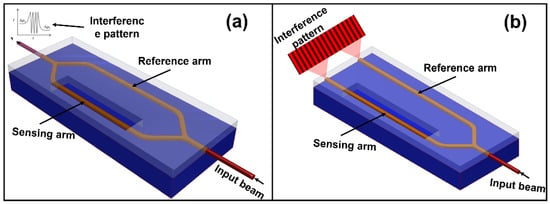
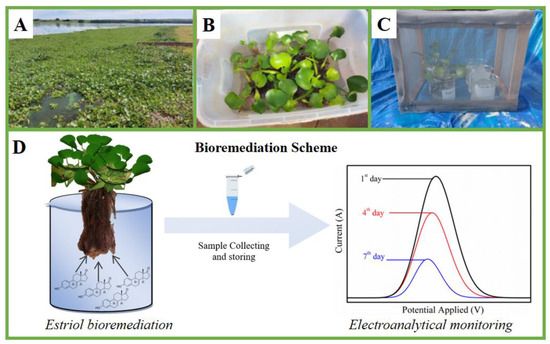
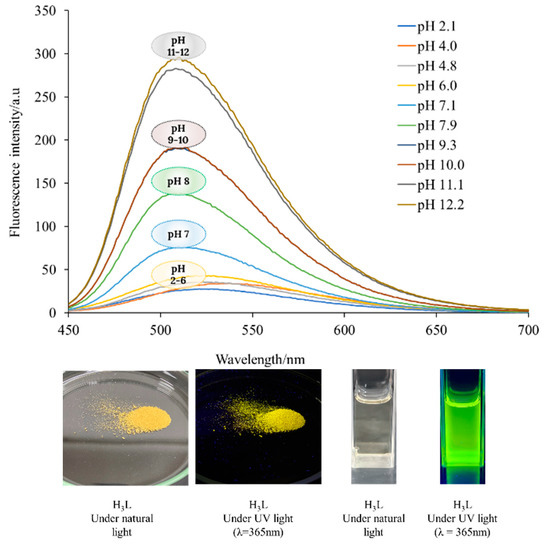
Chemosensors 2022, 10(10), 406; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10100406 - 10 Oct 2022
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 2440
Abstract
In this study, a surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) substrate based on high-refractive-index reflective glass beads (HRGBs) was prepared by a facile method and successfully applied to the detection of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). The HRGB-SERS substrate was prepared by depositing silver nanoparticles (Ag
[...] Read more.
In this study, a surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) substrate based on high-refractive-index reflective glass beads (HRGBs) was prepared by a facile method and successfully applied to the detection of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). The HRGB-SERS substrate was prepared by depositing silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) onto the surface of HRGBs. The preparation procedure of the substrate was simplified by accelerating the hydrolysis of (3-Aminopropyl) trimethoxysilane (APTMS) and increasing the concentration of Ag NPs. Compared with previous methods, the HRGB-SERS substrate prepared with one round of deposition has the same detection performance, a simpler preparation process, and lower cost. Additionally, halide ions were used to modify the substrate to increase the detection sensitivity of PAHs. Adding 10 mM KBr solution to the HRGB-SERS substrate was found to achieve the best modification effect. Under the optimal modification conditions, the detection sensitivity of pyrene was improved by 3 orders of magnitude (10−7 M). Due to the HRGB-SERS substrate’s excellent performance, the rapid identification and trace detection of spiked water samples mixed with anthracene, phenanthrene, and pyrene was realized using a Raman spectrometer with only a volume of 10 μL of the water samples.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Nanoparticles in Chemical and Biological Sensing)
►
Show Figures