1
Fundacion Tekniker, Polo Tecnológico de Eibar, Calle Iñaki Goenaga 5, 20600 Gipuzkoa, Spain
2
CENER (National Renewable Energy Centre of Spain), Ciudad de la Innovación 7, 31621 Navarra, Spain
Energies 2020, 13(7), 1816; https://doi.org/10.3390/en13071816 - 10 Apr 2020
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 6059
Abstract
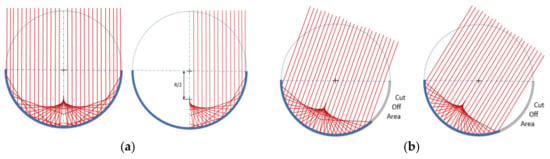
At any time of the day, a spherical mirror reflects the rays coming from the sun along a line that points to the sun through the center of the sphere. This makes it possible to build concentrated solar power(CSP) plants with fixed solar
[...] Read more.
At any time of the day, a spherical mirror reflects the rays coming from the sun along a line that points to the sun through the center of the sphere. This makes it possible to build concentrated solar power(CSP) plants with fixed solar fields and mobile receivers; that is, solar fields can be significantly cheaper and simpler, but challenging tracking systems for the mobile receiver need to be implemented. The cost-cutting possibilities for this technology have been under-researched. This article describes the MOSAIC concept, which aims to achieve low-cost solar energy by boosting the benefits of spherical reflectors while addressing their challenges. This new concept proposes to build large modular plants from semi-Fresnel solar bowls. One of these modules has been designed and is under construction in Spain. This article reports the main lessons learned during the design phase, describes the advantages and challenges of the concept, details the proposed routes to overcome them, and identifies the steps needed to develop a fully competitive industrial solution.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Research on Solar Collector)
▼
Show Figures