Molecules 2023, 28(2), 793; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020793 - 13 Jan 2023
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 3821
Abstract
Wedelia chinensis is a folk medicine used in many Asian countries to treat various ailments. Earlier investigations reported that the petroleum ether extract of the plant has potential biological activity, but the compounds responsible for activity are not yet completely known. Therefore, the
[...] Read more.
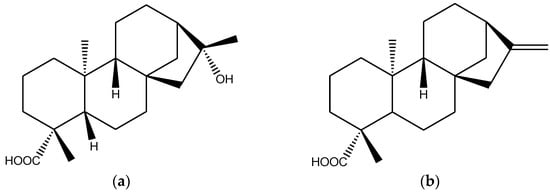
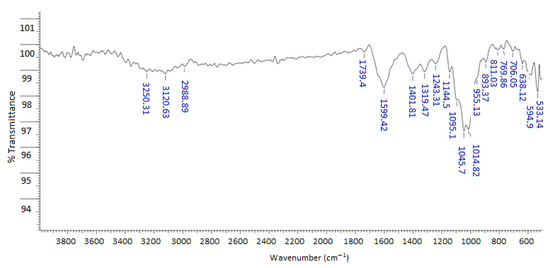
Wedelia chinensis is a folk medicine used in many Asian countries to treat various ailments. Earlier investigations reported that the petroleum ether extract of the plant has potential biological activity, but the compounds responsible for activity are not yet completely known. Therefore, the current work was designed to isolate and characterize the compounds from the petroleum ether extract and to study their bioactivities. Four compounds including two diterepenes (-) kaur-16α-hydroxy-19-oic acid (1) and (-) kaur-16-en-19-oic acid (2), and two steroids β-sitosterol (3), and cholesta-5,23-dien-3-ol (4) were isolated and characterized. Among the compounds, the diterpenes were found to have more biological activities than the steroidal compounds. Compound 1 showed the highest cytotoxicity with LC50 of 12.42 ± 0.87 μg/mL. Likewise, it possesses good antioxidant activity in terms of reducing power. On the contrary, compound 2 exerted the highest antiacetylcholinesterase and antibutyrylcholinesterase activity. Both the diterpenes showed almost similar antibacterial and antifungal activity. The identification of diterpenoid and steroid compounds with multifunctional activities suggests that W. chinensis may serve as an important source of bioactive compounds which should be further investigated in animal model for therapeutic potential in the treatment of different chronic diseases.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Natural Compounds for Treatment and Prevention of Inflammation, Oxidative Stress and Metabolic Disorders)
►
Show Figures