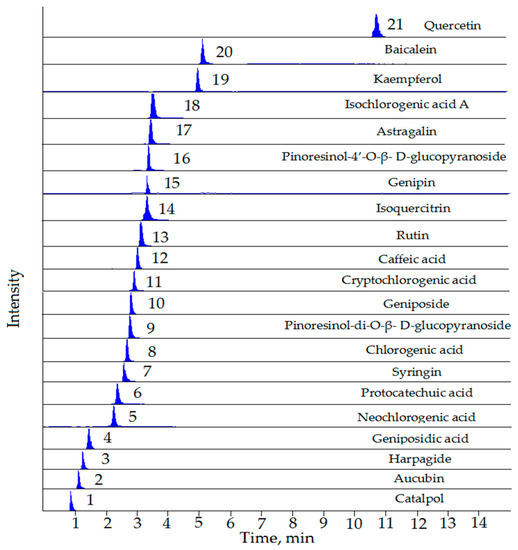
Molecules 2018, 23(3), 648; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23030648 - 13 Mar 2018
Cited by 38 | Viewed by 9038
Abstract
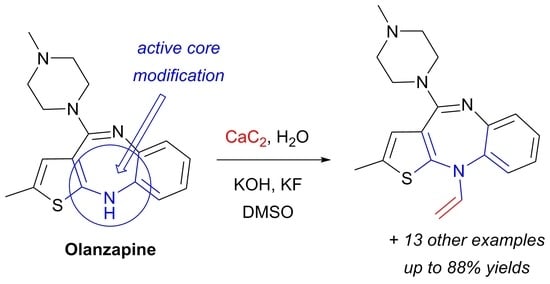
We developed a simple and efficient strategy to access N-vinyl secondary amines of various naturally occurring materials using readily available solid acetylene reagents (calcium carbide, KF, and KOH). Pyrrole, pyrazole, indoles, carbazoles, and diarylamines were successfully vinylated in good yields. Cross-linked and
[...] Read more.
We developed a simple and efficient strategy to access N-vinyl secondary amines of various naturally occurring materials using readily available solid acetylene reagents (calcium carbide, KF, and KOH). Pyrrole, pyrazole, indoles, carbazoles, and diarylamines were successfully vinylated in good yields. Cross-linked and linear polymers were synthesized from N-vinyl carbazoles through free radical and cationic polymerization. Post-modification of olanzapine (an antipsychotic drug substance) was successfully performed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Alkynes: From Reaction Design to Applications in Organic Synthesis)
►
Show Figures