Foods 2022, 11(1), 74; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11010074 - 29 Dec 2021
Cited by 24 | Viewed by 3150
Abstract
Xinjiang is a major wine-making region in China, but its hot climate in summer and intense sun exposure negatively affect the aroma quality of Cabernet Sauvignon wine. The aim of this study was to characterize and differentiate the volatile composition of Cabernet Sauvignon
[...] Read more.
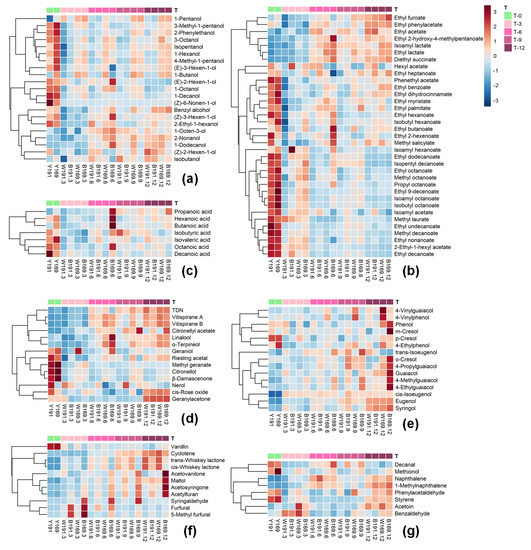
Xinjiang is a major wine-making region in China, but its hot climate in summer and intense sun exposure negatively affect the aroma quality of Cabernet Sauvignon wine. The aim of this study was to characterize and differentiate the volatile composition of Cabernet Sauvignon wines from two clones (169 and 191) in Xinjiang, and to study their aromatic profile evolution during 12-month oak barrel aging period. Results showed that before aging, clone 169 wine contained higher concentrations of several alcohols and ethyl esters, while acetate esters and furanic compounds were higher in clone 191 wine. After aging, levels of many terpenes, norisoprenoids, volatile phenols and phenolic aldehydes were significantly higher in clone 169 wine than 191 wine. Aroma series analysis revealed that clone 169 wine exhibited higher floral and roasty aromas after aging, while clone 191 wine had stronger chemical aroma. Principal component analysis indicated that aging process played a primary role in the alteration of volatile profile in these wines. Clone played a secondary role and oak barrel had a tertiary contribution to the variation. The present work indicates that clone 169 is a better choice for producing high-quality aged Cabernet Sauvignon wine with intense and elegant aroma in Xinjiang.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Wine Flavor Chemistry and Its Metabolic Mechanism)
►
Show Figures