Processes 2019, 7(9), 578; https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7090578 - 1 Sep 2019
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 5615
Abstract
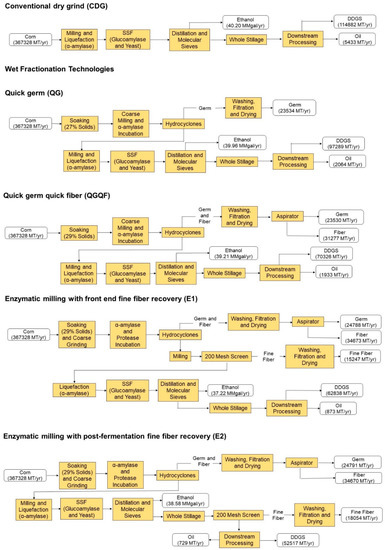
Use of corn fractionation techniques in dry grind process increases the number of coproducts, enhances their quality and value, generates feedstock for cellulosic ethanol production and potentially increases profitability of the dry grind process. The aim of this study is to develop process
[...] Read more.
Use of corn fractionation techniques in dry grind process increases the number of coproducts, enhances their quality and value, generates feedstock for cellulosic ethanol production and potentially increases profitability of the dry grind process. The aim of this study is to develop process simulation models for eight different wet and dry corn fractionation techniques recovering germ, pericarp fiber and/or endosperm fiber, and evaluate their techno-economic feasibility at the commercial scale. Ethanol yields for plants processing 1113.11 MT corn/day were 37.2 to 40 million gal for wet fractionation and 37.3 to 31.3 million gal for dry fractionation, compared to 40.2 million gal for conventional dry grind process. Capital costs were higher for wet fractionation processes ($92.85 to $97.38 million) in comparison to conventional ($83.95 million) and dry fractionation ($83.35 to $84.91 million) processes. Due to high value of coproducts, ethanol production costs in most fractionation processes ($1.29 to $1.35/gal) were lower than conventional ($1.36/gal) process. Internal rate of return for most of the wet (6.88 to 8.58%) and dry fractionation (6.45 to 7.04%) processes was higher than the conventional (6.39%) process. Wet fractionation process designed for germ and pericarp fiber recovery was most profitable among the processes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Process Simulation and Techno-Economic Analysis of Food and Bioproducts Processing Systems)
►
Show Figures