Electronics 2022, 11(22), 3717; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11223717 - 13 Nov 2022
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 2124
Abstract
In the current IoT era, the key to sports intelligence is the effective collection and analysis of sports data. Sports data can accurately reflect an athlete’s athletic status and help coaches to develop competitive tactics and training programs. Wearable electronic devices used to
[...] Read more.
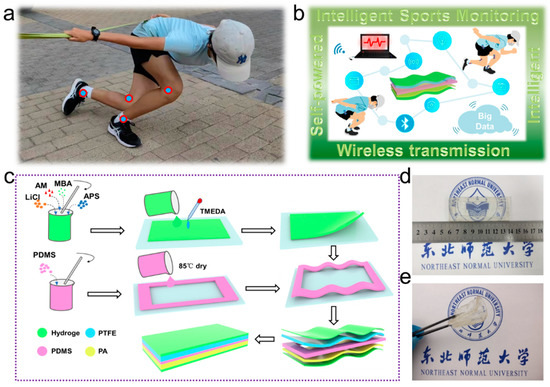
In the current IoT era, the key to sports intelligence is the effective collection and analysis of sports data. Sports data can accurately reflect an athlete’s athletic status and help coaches to develop competitive tactics and training programs. Wearable electronic devices used to collect sports data currently have several drawbacks, including their large size, heavy weight, complex wiring, high cost, and need for frequent power replacement. In this work, transparent polyamide-66 (PA-66) and transparent polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) films were used as friction layers, polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) was used as a support layer, and conductive hydrogels were used as electrodes, which were simply combined to create stable and durable triboelectric nanogenerators (SD-TENG) with good mechanical and triboelectric properties. In the test, the output power was 1mW under a load resistance of 10MΩ. In addition, the integrated intelligent speed skating land training assistance system monitors the changes in the joints and joint chains of skaters during land training in real time. The successful demonstration of the use of SD-TENG in speed skating land training will help to promote the development and application of TENG in the fields of intelligent sport monitoring, smart wearable devices, and big data analysis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Nanogenerators for Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Sensing)
►
Show Figures