Agriculture 2023, 13(10), 1950; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13101950 - 6 Oct 2023
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 3137
Abstract
Based on the panel data of 31 provinces in China from 2005 to 2020, this paper analyzes the mechanism and spatial spillover effect of agricultural insurance on the urban–rural income gap using a fixed effect model, an intermediary effect model, and a two-stage
[...] Read more.
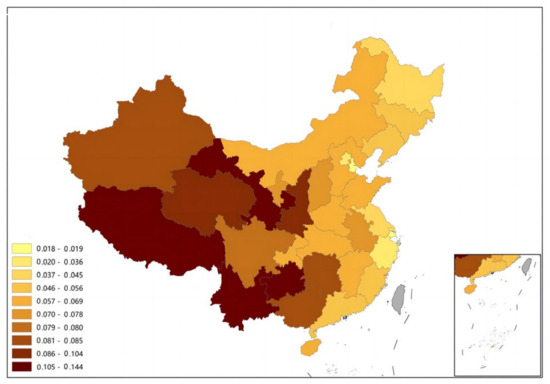
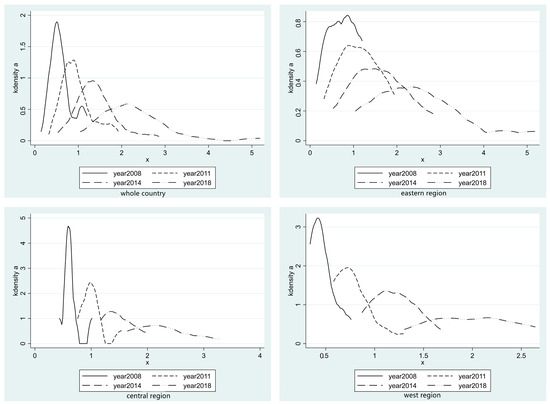
Based on the panel data of 31 provinces in China from 2005 to 2020, this paper analyzes the mechanism and spatial spillover effect of agricultural insurance on the urban–rural income gap using a fixed effect model, an intermediary effect model, and a two-stage least square method. The results show that agricultural insurance has a significant inhibitory effect on the income gap between urban and rural areas. This inhibitory effect is realized through the path of “improving the development level of agricultural insurance-improving agricultural total factor productivity-reducing the income gap between urban and rural areas”, in which the intermediary effect of agricultural total factor productivity accounts for 19.74% of the total effect. At the same time, the income gap between urban and rural areas in China exhibits typical spatial agglomeration characteristics. The western region has always been the region with the largest income gap between urban and rural areas, while the eastern region is the region with the smallest income gap between urban and rural areas. The development of agricultural insurance has had a spatial spillover effect on the income gap between urban and rural areas, and the development of agricultural insurance in neighboring areas expands the income gap between urban and rural areas in this region. In order to prevent the siphon effect, agricultural insurance investment should be increased in the neighboring regions. The results of this paper support the view of the resource flow model. Finally, we put forward some suggestions for the development of agricultural insurance, improvement in agricultural total factor productivity, and the narrowing of the income gap between urban and rural areas.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Agricultural Insurance, Risk Management and Sustainable Development-Series II)
►
Show Figures