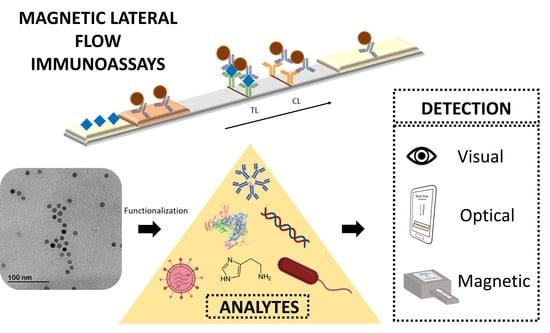
Diagnostics 2020, 10(5), 295; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10050295 - 11 May 2020
Cited by 20 | Viewed by 3737
Abstract
Aging of functional ovaries occurs many years before aging of other organs in the female body. In recent years, a greater number of women continue to postpone their pregnancies to later stages in their lives, raising concerns of the effect of ovarian aging.
[...] Read more.
Aging of functional ovaries occurs many years before aging of other organs in the female body. In recent years, a greater number of women continue to postpone their pregnancies to later stages in their lives, raising concerns of the effect of ovarian aging. Mitochondria play an important role in the connection between the aging granulosa cells and oocytes. However, the underlying mechanisms of mitochondrial dysfunction in these cells remain poorly understood. Therefore, we evaluated the molecular mechanism of the aging granulosa cells, including aspects such as accumulation of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species, reduction of mtDNA, imbalance of mitochondrial dynamics, and diminished cell proliferation. Here, we applied bioinformatics approaches, and integrated publicly available resources, to investigate the role of CREB1 gene expression in reproduction. Senescence hallmark enrichment and pathway analysis suggested that the downregulation of bioenergetic-related genes in CREB1. Gene expression analyses showed alterations in genes related to energy metabolism and ROS production in ovary tissue. We also demonstrate that the biogenesis of aging granulosa cells is subject to CREB1 binding to the PRKAA1 and PRKAA2 upstream promoters. In addition, cofactors that regulate biogenesis significantly increase the levels of SIRT1 and PPARGC1A mRNA in the aging granulosa cells. These findings demonstrate that CREB1 elevates an oxidative stress-induced senescence in granulosa cells by reducing the mitochondrial function.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pathology and Molecular Diagnostics)
►
Show Figures