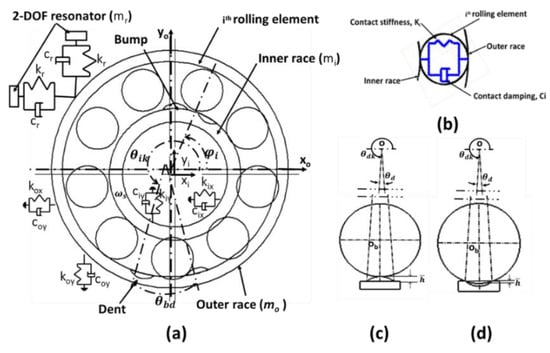
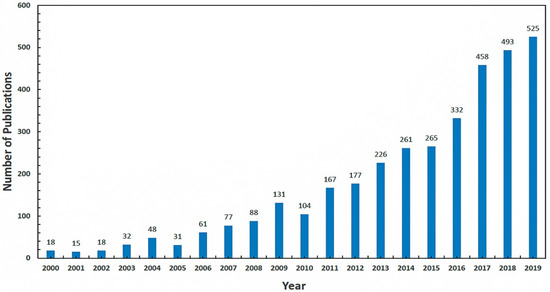
Machines 2022, 10(11), 1075; https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10111075 - 15 Nov 2022
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2731
Abstract
The subway sliding plug door system is crucial for ensuring normal operation. Due to the differences in the structure and motor control procedures of different sliding plug door systems, the rotational speed monitoring data curves show great differences. It is a challenging problem
[...] Read more.
The subway sliding plug door system is crucial for ensuring normal operation. Due to the differences in the structure and motor control procedures of different sliding plug door systems, the rotational speed monitoring data curves show great differences. It is a challenging problem to recognize the intervals of complex data curves, which fundamentally affect the sensitivity of feature extraction and the prediction of an assessment model. Aiming at the problem, a subway sliding plug door system health state adaptive assessment method is proposed based on interval intelligent recognition of rotational speed operation data curve. In the proposed method, firstly, the rotational speed operation data curve is adaptively divided by a long short-term memory (LSTM) neural network into four intervals, according to the motion characteristics of the door system. Secondly, the sensitive features of the door system are screened out by the random forest (RF) algorithm. Finally, the health state of the door system is assessed using the adaptive boosting (AdaBoost) classifier. The proposed method is comprehensively verified by the benchmark experiment data set. The results show that the average diagnostic accuracy of the method on multiple bench doors can reach 98.15%. The wider application scope and the higher state classification accuracy indicate that the proposed method has important engineering value and theoretical significance for the health management of subway sliding plug door systems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Extraction and Condition Monitoring in Physics and Mechanics)
►
Show Figures