Materials 2021, 14(12), 3214; https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14123214 - 10 Jun 2021
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 3581
Abstract
Herein, we report the first synthesis of covalent triazine-based frameworks (CTFs) based on a hexanitrile monomer, namely the novel pseudo-octahedral hexanitrile 1,4-bis(tris(4′-cyano-phenyl)methyl)benzene 1 using both ionothermal reaction conditions with ZnCl2 at 400 °C and the milder reaction conditions with the strong Brønsted
[...] Read more.
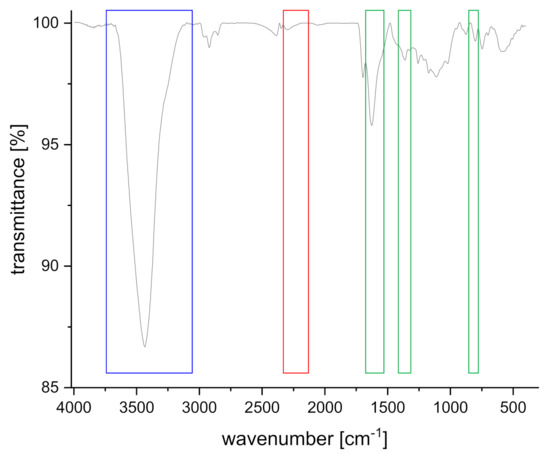
Herein, we report the first synthesis of covalent triazine-based frameworks (CTFs) based on a hexanitrile monomer, namely the novel pseudo-octahedral hexanitrile 1,4-bis(tris(4′-cyano-phenyl)methyl)benzene 1 using both ionothermal reaction conditions with ZnCl2 at 400 °C and the milder reaction conditions with the strong Brønsted acid trifluoromethanesulfonic acid (TFMS) at room temperature. Additionally, the hexanitrile was combined with different di-, tri-, and tetranitriles as a second linker based on recent work of mixed-linker CTFs, which showed enhanced carbon dioxide captures. The obtained framework structures were characterized via infrared (IR) spectroscopy, elemental analysis, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and gas sorption measurements. Nitrogen adsorption measurements were performed at 77 K to determine the Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) surface areas range from 493 m2/g to 1728 m2/g (p/p0 = 0.01–0.05). As expected, the framework CTF-hex6 synthesized from 1 with ZnCl2 possesses the highest surface area for nitrogen adsorption. On the other hand, the mixed framework structure CTF-hex4 formed from the hexanitrile 1 and 1,3,5 tricyanobenzene (4) shows the highest uptake of carbon dioxide and methane of 76.4 cm3/g and 26.6 cm3/g, respectively, at 273 K.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Microporous and Mesoporous Materials)
►
Show Figures