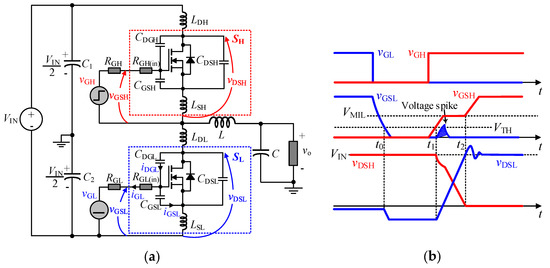
1
Electrical Engineering Department, Istanbul Technical University, Istanbul 34467, Turkey
2
Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department, Istanbul Okan University, Istanbul 34959, Turkey
3
ABB UK Engineering Centre, Leicestershire LE67 4JP, UK
†
These authors contributed equally to this work.
‡
Current address: Akfirat, Istanbul 34959, Turkey.
Energies 2018, 11(11), 3119; https://doi.org/10.3390/en11113119 - 12 Nov 2018
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 6241
Abstract
This paper comprises the design, analysis, experimental verification and field weakening performance study of a brushless direct current (BLDC) motor for a light electric vehicle. The main objective is to design a BLDC motor having a higher value d-axis inductance, which implies
[...] Read more.
This paper comprises the design, analysis, experimental verification and field weakening performance study of a brushless direct current (BLDC) motor for a light electric vehicle. The main objective is to design a BLDC motor having a higher value d-axis inductance, which implies an improved performance of field weakening and a higher constant power speed ratio (CPSR) operation. Field weakening operation of surface-mounted permanent magnet (SMPM) BLDC motors requires a large d-axis inductance, which is characteristically low for those motors due to large air gap and PM features. The design phases of the sub-fractional slot-concentrated winding structure with unequal tooth widths include the motivation and the computer aided study which is based on Finite Element Analysis using ANSYS Maxwell. A 24/20 slot–pole SMPM BLDC motor is chosen for prototyping. The designed motor is manufactured and performed at different phase-advanced currents in the field weakening region controlled by a TMS320F28335 digital signal processor. As a result of the experimental work, the feasibility and effectiveness of field weakening for BLDC motors are discussed thoroughly and the contribution of higher winding inductance is verified.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines)
▼
Show Figures