Foods 2023, 12(11), 2214; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12112214 - 31 May 2023
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 2510
Abstract
The recovery of valuable bioactive compounds from the main underutilised by-products of the food industry is one of the greatest challenges to be addressed in circular economy. Potato peels are the largest waste generated during potato processing. However, they could be a potential
[...] Read more.
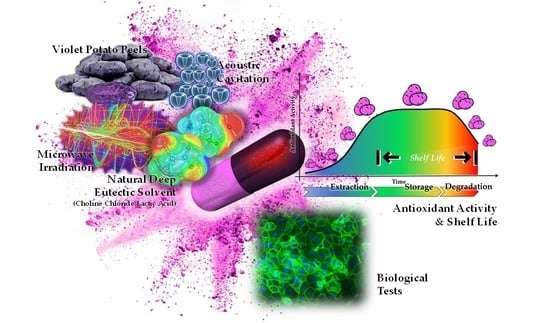
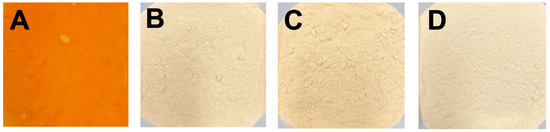
The recovery of valuable bioactive compounds from the main underutilised by-products of the food industry is one of the greatest challenges to be addressed in circular economy. Potato peels are the largest waste generated during potato processing. However, they could be a potential source of valuable bioactive compounds, such as polyphenols, that can be reused as natural antioxidants. Currently, environmentally benign enabling technologies and new types of non-toxic organic solvents for the extraction of bioactive compounds may dramatically improve the sustainability of these processes. This paper focuses on the potential inherent in the valorisation of violet potato peels (VPPs) by recovering antioxidants using natural deep eutectic solvents (NaDES) under ultrasound (US)- and microwave (MW)-assisted extraction. Both the enabling technologies provided performances that were superior to those of conventional extractions in terms of antioxidant activity determined by the DPPH· (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) assay. In particular, the most promising approach using NaDES is proven to be the acoustic cavitation with a Trolox eq. of 1874.0 mmolTE/gExtr (40 °C, 500 W, 30 min), vs. the 510.1 mmolTE/gExtr of hydroalcoholic extraction (80 °C, 4 h). The shelf-life of both hydroalcoholic and NaDES-VPPs extracts have been assessed over a period of 24 months, and found that NaDES granted a 5.6-fold shelf-life extension. Finally, the antiproliferative activity of both hydroalcoholic and NaDES-VPPs extracts was evaluated in vitro using the MTS assay on human tumour Caco-2 cells and normal human keratinocyte cells (HaCaT). In particular, NaDES-VPPs extracts exhibited a significantly more pronounced antiproliferative activity compared to the ethanolic extracts without a noteworthy difference between effects on the two cell lines.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Innovative Food Processing Technologies—2nd Volume)
►
Show Figures