Foods 2021, 10(4), 846; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040846 - 13 Apr 2021
Cited by 39 | Viewed by 4083
Abstract
The plant resistance elicitor Benzo (1,2,3)-thiadiazole-7-carbothioic acid S-methyl ester (BTH) can enhance disease resistance of harvested fruit. Nonetheless, it is still unknown whether BTH plays a role in regulating fruit senescence. In this study, exogenous BTH treatment efficiently delayed the senescence of postharvest
[...] Read more.
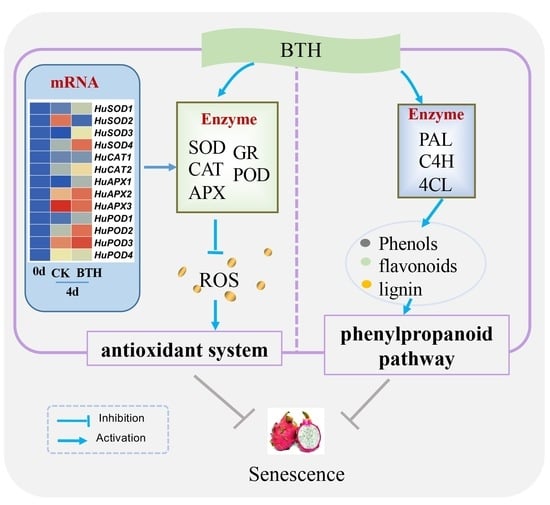
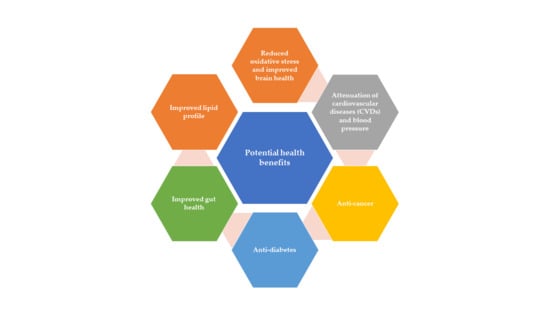
The plant resistance elicitor Benzo (1,2,3)-thiadiazole-7-carbothioic acid S-methyl ester (BTH) can enhance disease resistance of harvested fruit. Nonetheless, it is still unknown whether BTH plays a role in regulating fruit senescence. In this study, exogenous BTH treatment efficiently delayed the senescence of postharvest pitaya fruit with lower lipid peroxidation level. Furthermore, BTH-treated fruit exhibited lower hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) content, higher contents of reduced ascorbic acid (AsA) and reduced glutathione (GSH) levels and higher ratios of reduced to oxidized glutathione (GSH/GSSG) and ascorbic acid (AsA/DHA), as well as higher activities of ROS scavenging enzymes, including superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), ascorbate peroxidase (APX), peroxidase (POD) and glutathione reductase (GR) in comparison with control fruit. Moreover, BTH treatment enhanced the activities of phenylpropanoid pathway-related enzymes, including cinnamate-4-hydroxylase (C4H), phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) and 4-coumarate/coenzyme A ligase (4CL) and the levels of phenolics, flavonoids and lignin. In addition, BTH treatment upregulated the expression of HuSOD1/3/4, HuCAT2, HuAPX1/2 and HuPOD1/2/4 genes. These results suggested that application of BTH delayed the senescence of harvested pitaya fruit in relation to enhanced antioxidant system and phenylpropanoid pathway.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Effects of Preservation Technology on Quality and Safety of Food Products)
►
Show Figures