Appl. Sci. 2022, 12(12), 6262; https://doi.org/10.3390/app12126262 - 20 Jun 2022
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 3848
Abstract
Intelligence capabilities will be the cornerstone in the development of next-generation cognitive networks. These capabilities allow them to observe network conditions, learn from them, and then, using prior knowledge gained, respond to its operating environment to optimize network performance. This study aims to
[...] Read more.
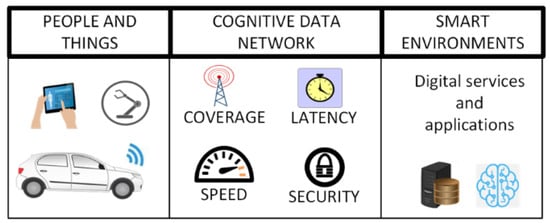
Intelligence capabilities will be the cornerstone in the development of next-generation cognitive networks. These capabilities allow them to observe network conditions, learn from them, and then, using prior knowledge gained, respond to its operating environment to optimize network performance. This study aims to offer an overview of the current state of the art related to the use of deep learning in applications for intelligent cognitive networks that can serve as a reference for future initiatives in this field. For this, a systematic literature review was carried out in three databases, and eligible articles were selected that focused on using deep learning to solve challenges presented by current cognitive networks. As a result, 14 articles were analyzed. The results showed that applying algorithms based on deep learning to optimize cognitive data networks has been approached from different perspectives in recent years and in an experimental way to test its technological feasibility. In addition, its implications for solving fundamental challenges in current wireless networks are discussed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Internet of Things, Artificial Intelligence, and Blockchain Infrastructure: Applications, Security, and Perspectives)
►
Show Figures