Animals 2019, 9(11), 925; https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9110925 - 5 Nov 2019
Cited by 86 | Viewed by 6602
Abstract
Heat stress negatively impacts the health and milk production of dairy cows, and ruminal microbial populations play an important role in dairy cattle’s milk production. Currently there are no available studies that investigate heat stress-associated changes in the rumen microbiome of lactating dairy
[...] Read more.
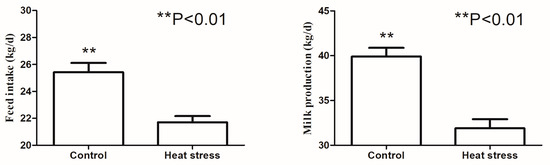
Heat stress negatively impacts the health and milk production of dairy cows, and ruminal microbial populations play an important role in dairy cattle’s milk production. Currently there are no available studies that investigate heat stress-associated changes in the rumen microbiome of lactating dairy cattle. Improved understanding of the link between heat stress and the ruminal microbiome may be beneficial in developing strategies for relieving the influence of heat stress on ruminants by manipulating ruminal microbial composition. In this study, we investigated the ruminal bacterial composition and metabolites in heat stressed and non-heat stressed dairy cows. Eighteen lactating dairy cows were divided into two treatment groups, one with heat stress and one without heat stress. Dry matter intake was measured and rumen fluid from all cows in both groups was collected. The bacterial 16S rRNA genes in the ruminal fluid were sequenced, and the rumen pH and the lactate and acetate of the bacterial metabolites were quantified. Heat stress was associated with significantly decreased dry matter intake and milk production. Rumen pH and rumen acetate concentrations were significantly decreased in the heat stressed group, while ruminal lactate concentration increased. The influence of heat stress on the microbial bacterial community structure was minor. However, heat stress was associated with an increase in lactate producing bacteria (e.g., Streptococcus and unclassified Enterobacteriaceae), and with an increase in Ruminobacter, Treponema, and unclassified Bacteroidaceae, all of which utilize soluble carbohydrates as an energy source. The relative abundance of acetate-producing bacterium Acetobacter decreased during heat stress. We concluded that heat stress is associated with changes in ruminal bacterial composition and metabolites, with more lactate and less acetate-producing species in the population, which potentially negatively affects milk production.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Effects of Environment on Behaviour, Productivity and Welfare of Farm Animals)
►
Show Figures