Cancers 2023, 15(4), 1090; https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041090 - 8 Feb 2023
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 4303
Abstract
Accurate risk stratification is key to reducing cancer morbidity through targeted screening and preventative interventions. Multiple breast cancer risk prediction models are used in clinical practice, and often provide a range of different predictions for the same patient. Integrating information from different models
[...] Read more.
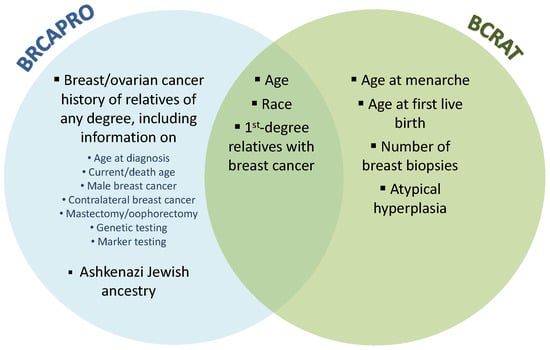
Accurate risk stratification is key to reducing cancer morbidity through targeted screening and preventative interventions. Multiple breast cancer risk prediction models are used in clinical practice, and often provide a range of different predictions for the same patient. Integrating information from different models may improve the accuracy of predictions, which would be valuable for both clinicians and patients. BRCAPRO is a widely used model that predicts breast cancer risk based on detailed family history information. A major limitation of this model is that it does not consider non-genetic risk factors. To address this limitation, we expand BRCAPRO by combining it with another popular existing model, BCRAT (i.e., Gail), which uses a largely complementary set of risk factors, most of them non-genetic. We consider two approaches for combining BRCAPRO and BCRAT: (1) modifying the penetrance (age-specific probability of developing cancer given genotype) functions in BRCAPRO using relative hazard estimates from BCRAT, and (2) training an ensemble model that takes BRCAPRO and BCRAT predictions as input. Using both simulated data and data from Newton-Wellesley Hospital and the Cancer Genetics Network, we show that the combination models are able to achieve performance gains over both BRCAPRO and BCRAT. In the Cancer Genetics Network cohort, we show that the proposed BRCAPRO + BCRAT penetrance modification model performs comparably to IBIS, an existing model that combines detailed family history with non-genetic risk factors.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Hereditary Breast Cancer in Men and Women: Genetic Mutations, Cancer Risk and Treatment)
►
Show Figures